Abstract
In the present studies, the effect of ampicillin (40 mg intramuscularly twice a day) in combination with water diuresis, produced by the ingestion of 5% dextrose in water, was determined on renal titers of enterococci after intravenous inoculation of 4 × 108-2 × 109 enterococci into rats.
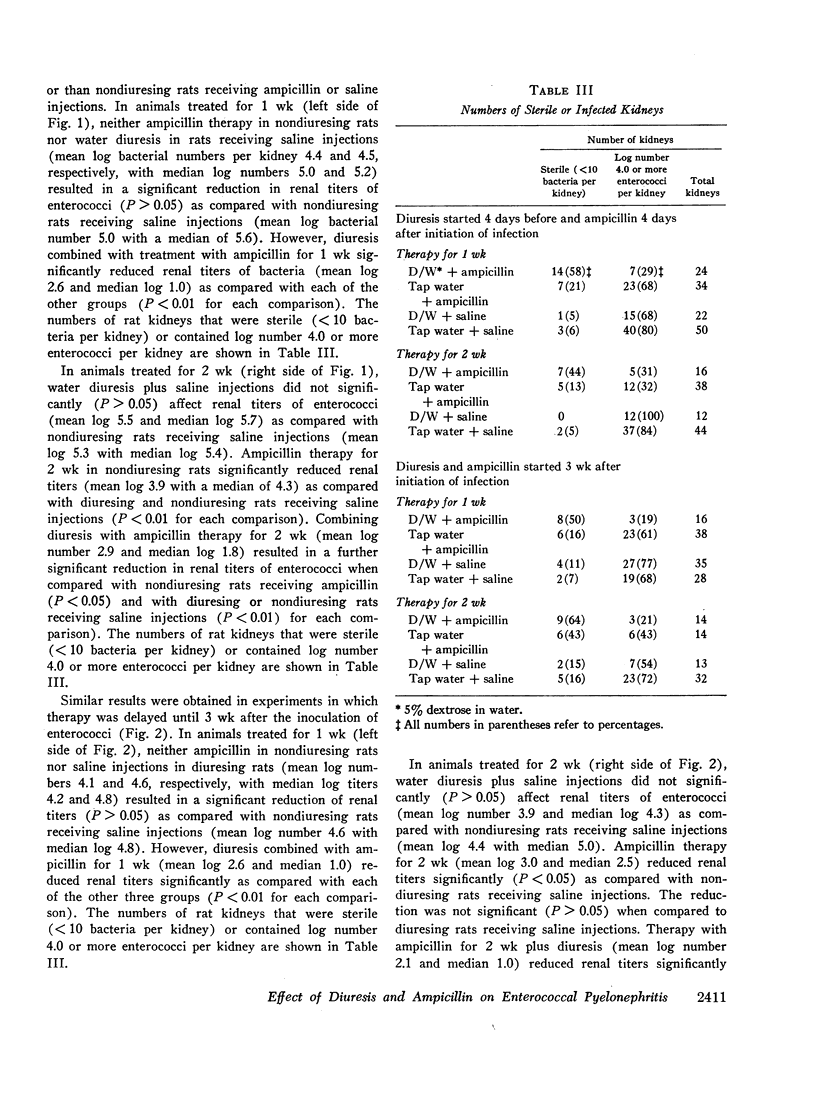
Ampicillin injections with or without diuresis were started 4 or 21 days after initiation of infection and continued for 7 or 14 days. In comparison to controls (saline injections in rats drinking tap water), diuresis plus saline injections did not lower renal titers of enterococci. Injection of ampicillin in nondiuresing rats had little effect on renal titers of enterococci after 7 days of treatment started 4 or 21 days after initiation of infection. However, 2 wk of ampicillin therapy resulted in a significant decrease in renal titers. The addition of water diuresis to ampicillin treatment markedly potentiated the effect of ampicillin alone in decreasing renal titers of enterococci after 1 or 2 wk of therapy.
These studies demonstrate that diuresis resulting from administration of dextrose in water plus ampicillin starting 4 or 21 days after intravenous injection of enterococci reduces renal titers more than ampicillin or diuresis alone.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRIOLE V. T., EPSTEIN F. H. PREVENTION OF PYELONEPHRITIS BY WATER DIURESIS: EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF MEDULLARY HYPERTONICITY IN PROMOTING RENAL INFECTION. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jan;44:73–79. doi: 10.1172/JCI105128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acquatella H., Little P. J., de Wardener H. E., Coleman J. C. The effect of urine osmolality and pH on the bactericidal activity of plasma. Clin Sci. 1967 Dec;33(3):471–480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andriole V. T. Acceleration of the inflammatory response of the renal medulla by water diuresis. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jun;45(6):847–854. doi: 10.1172/JCI105400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andriole V. T. Effect of water diuresis on chronic pyelonephritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jul;72(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulger R. J. Inhibition of human serum bactericidal action by a chemical environment simulating the hydropenic renal medulla. J Infect Dis. 1967 Dec;117(5):429–432. doi: 10.1093/infdis/117.5.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHERNEW I., BRAUDE A. I. Depression of phagocytosis by solutes in concentrations found in the kidney and urine. J Clin Invest. 1962 Oct;41:1945–1953. doi: 10.1172/JCI104652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A. Determinants of infection in the peritoneal cavity. III. The action of selected inhibitors on the fate of Staphylococcus aureus in the mouse. Yale J Biol Med. 1962 Aug;35:48–61. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUZE L. B., GOLDNER B. H., KALMANSON G. M. Pyelonephritis. I. Observations on the course of chronic non-obstructed enterococcal infection in the kidnev of the rat. Yale J Biol Med. 1961 Apr;33:372–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUZE L. B., HUBERT E. G., KALMANSON G. M. Pyelonephritis. II. Observations on the treatment of enterococcal infection in the nonobstructed kidney of the rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1963 Jul;62:90–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUZE L. B., KALMANSON G. M. PERSISTENCE OF BACTERIA IN "PROTOPLAST" FORM AFTER APPARENT CURE OF PYELONEPHRITIS IN RATS. Science. 1964 Mar 20;143(3612):1340–1341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D., Rocha H. Urinary concentrating ability in early experimental pyelonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1970 Jul;49(7):1427–1437. doi: 10.1172/JCI106360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye D. The effect of water diuresis on spread of bacteria through the urinary tract. J Infect Dis. 1971 Sep;124(3):297–305. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.3.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROCHA H., FEKETY F. R., Jr ACUTE INFLAMMATION IN THE RENAL CORTEX AND MEDULLA FOLLOWING THERMAL INJURY. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:131–138. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutsky E. A., Clapp J. R., Robinson R. R. Determinants of susceptibility to experimental enterococcal pyelonephritis. Nephron. 1971;8(2):109–124. doi: 10.1159/000179913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


