Abstract
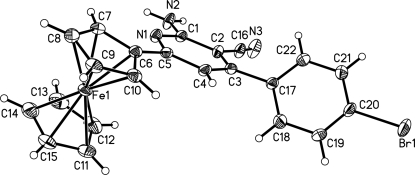
The title compound, [Fe(C5H5)(C17H11BrN3)], was synthesized by the reaction of 4-bromobenzaldehyde, acetylferrocene and ammonium acetate in an aqueous medium. The crystal packing is stabilized by intermolecular N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds. The dihedral angles between the phenyl ring and the pyridine and cyclopentadienyl rings are 51.67 (13) and 12.12 (21)°, respectively.
Related literature
For related literature, see: Alyoubi (2000 ▶); Desai & Shah (2003 ▶); Dombrowski et al. (1986 ▶); Murata et al. (2004 ▶).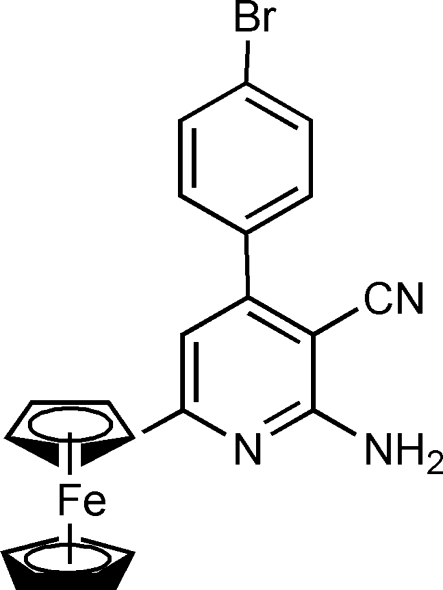
Experimental
Crystal data
[Fe(C5H5)(C17H11BrN3)]
M r = 458.14
Monoclinic,
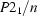
a = 12.250 (2) Å
b = 7.4511 (12) Å
c = 20.698 (3) Å
β = 97.729 (3)°
V = 1872.2 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.95 mm−1
T = 298 (2) K
0.16 × 0.11 × 0.07 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1998 ▶) T min = 0.650, T max = 0.820
9276 measured reflections
3290 independent reflections
2327 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.042
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.094
S = 1.02
3290 reflections
244 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.50 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1999 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 1997 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Bruker, 1999 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680705489X/bq2041sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680705489X/bq2041Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2B⋯N3i | 0.86 | 2.29 | 3.050 (5) | 148 |
Symmetry code: (i) 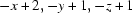 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No. 20672090) and the Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Province (grant No. BK2006033) for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Metallocenes are known to exhibit a wide range of biological activity. Among them, ferrocene has attracted special attention since it is neutral, chemically stable, non-toxic and able to cross cell membranes (Dombrowski et al., 1986). In fact, it is now well established that the incorporation of ferrocene units in organic molecules introduces significant and new properties in these materials. In addition, it has been demonstrated that molecules containing cyanopyridine moiety may be able to work as ligands towards transition-metal ions (Alyoubi, 2000), new drugs (Murata et al., 2004 and Desai et al., 2003), and significant intermediates for the synthesis of important vitamins such as nicotinic acids and nicotinamides. For these reasons, the synthesis of new compounds containing cyanopyridine derivatives is strongly desired. In this paper we report the crystal structure of the title compound (I).
In the crystal structure, the dihedral angle between the C1/C2/C3/C4/C5/N1 plane and the C17—C22 benzene ring is 51.65 (13)°.The dihedral angle between the C1/C2/C3/C4/C5/N1 plane and the C11—C16 ring is 12.21 (14)°. The molecules are connected via N—H···N hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional network (Fig. 2).
Experimental
Compound (I) was prepared by the reaction of 4-bromobenzaldehyde (2 mmol), malononitrile (2 mmol), acetylferrocene (2 mmol) and ammonium acetate (4 mmol) in water (2 ml). Single crystals of (I) suitable for X-ray diffraction were obtained by slow evaporation of a 95% aqueous ethanol solution (yield 94%; m.p. >573 K). IR (cm-1): 3457, 3354, 2211; 1H NMR (DMSO-d6): 4.10 (5H, s, ferrocenyl), 4.50 (2H, s, ferrocenyl), 5.04 (2H, s, ferrocenyl), 6.83 (2H, brs, NH2), 6.94 (1H, s, ArH), 7.60 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, ArH), 7.77 (2H, d, J = 8.0 Hz, ArH).7.87 (2H, brs, NH2), 7.88–8.01 (4H, m, ArH), 11.85 (1H, s, NH).
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically and treated as riding, with N—H = 0.86 Å and C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of title compound, showing 30% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Crystal data
| [Fe(C5H5)(C17H11BrN3)] | F(000) = 920 |
| Mr = 458.14 | Dx = 1.625 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Melting point > 573 K |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 12.250 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 9276 reflections |
| b = 7.4511 (12) Å | θ = 1.8–25.0° |
| c = 20.698 (3) Å | µ = 2.95 mm−1 |
| β = 97.729 (3)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 1872.2 (5) Å3 | Block, red |
| Z = 4 | 0.16 × 0.11 × 0.07 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3290 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2327 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.042 |
| phi and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 1.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 1998) | h = −14→12 |
| Tmin = 0.650, Tmax = 0.820 | k = −8→8 |
| 9276 measured reflections | l = −21→24 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.094 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0439P)2 + 0.873P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3290 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 244 parameters | Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.50 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Fe1 | 0.88176 (4) | 0.56744 (7) | 0.10748 (3) | 0.03294 (17) | |
| Br1 | 1.31762 (4) | −0.46355 (6) | 0.38737 (3) | 0.06095 (19) | |
| N1 | 0.8559 (2) | 0.4500 (4) | 0.27746 (15) | 0.0335 (7) | |
| N2 | 0.8621 (3) | 0.5510 (4) | 0.38201 (16) | 0.0441 (9) | |
| H2A | 0.8136 | 0.6301 | 0.3678 | 0.053* | |
| H2B | 0.8871 | 0.5466 | 0.4228 | 0.053* | |
| N3 | 1.0484 (3) | 0.3011 (5) | 0.48388 (19) | 0.0596 (11) | |
| C1 | 0.8991 (3) | 0.4337 (5) | 0.34017 (18) | 0.0319 (9) | |
| C2 | 0.9785 (3) | 0.3014 (5) | 0.36174 (18) | 0.0302 (8) | |
| C3 | 1.0146 (3) | 0.1847 (5) | 0.31590 (18) | 0.0302 (9) | |
| C4 | 0.9720 (3) | 0.2070 (5) | 0.25112 (18) | 0.0313 (9) | |
| H4 | 0.9956 | 0.1339 | 0.2193 | 0.038* | |
| C5 | 0.8928 (3) | 0.3408 (5) | 0.23362 (17) | 0.0274 (8) | |
| C6 | 0.8419 (3) | 0.3651 (5) | 0.16587 (17) | 0.0295 (8) | |
| C7 | 0.7494 (3) | 0.4767 (5) | 0.14559 (18) | 0.0328 (9) | |
| H7 | 0.7103 | 0.5424 | 0.1731 | 0.039* | |
| C8 | 0.7267 (3) | 0.4714 (5) | 0.0769 (2) | 0.0404 (10) | |
| H8 | 0.6696 | 0.5310 | 0.0514 | 0.048* | |
| C9 | 0.8063 (3) | 0.3594 (5) | 0.05372 (19) | 0.0384 (9) | |
| H9 | 0.8107 | 0.3334 | 0.0102 | 0.046* | |
| C10 | 0.8781 (3) | 0.2935 (5) | 0.10802 (18) | 0.0343 (9) | |
| H10 | 0.9379 | 0.2175 | 0.1064 | 0.041* | |
| C11 | 1.0377 (4) | 0.6526 (6) | 0.1005 (2) | 0.0542 (12) | |
| H11 | 1.0979 | 0.5798 | 0.0960 | 0.065* | |
| C12 | 1.0040 (4) | 0.7097 (6) | 0.1601 (3) | 0.0596 (13) | |
| H12 | 1.0381 | 0.6819 | 0.2018 | 0.072* | |
| C13 | 0.9095 (4) | 0.8163 (6) | 0.1444 (3) | 0.0597 (13) | |
| H13 | 0.8697 | 0.8711 | 0.1741 | 0.072* | |
| C14 | 0.8852 (4) | 0.8261 (6) | 0.0762 (3) | 0.0586 (13) | |
| H14 | 0.8269 | 0.8885 | 0.0530 | 0.070* | |
| C15 | 0.9639 (4) | 0.7257 (6) | 0.0495 (2) | 0.0533 (12) | |
| H15 | 0.9671 | 0.7098 | 0.0053 | 0.064* | |
| C16 | 1.0201 (3) | 0.2954 (5) | 0.4291 (2) | 0.0395 (10) | |
| C17 | 1.0911 (3) | 0.0326 (5) | 0.33629 (17) | 0.0306 (8) | |
| C18 | 1.1829 (3) | 0.0036 (5) | 0.3047 (2) | 0.0439 (10) | |
| H18 | 1.1986 | 0.0831 | 0.2725 | 0.053* | |
| C19 | 1.2509 (3) | −0.1418 (6) | 0.3206 (2) | 0.0461 (11) | |
| H19 | 1.3125 | −0.1601 | 0.2996 | 0.055* | |
| C20 | 1.2267 (3) | −0.2594 (5) | 0.3678 (2) | 0.0389 (10) | |
| C21 | 1.1376 (3) | −0.2323 (5) | 0.3997 (2) | 0.0484 (11) | |
| H21 | 1.1226 | −0.3120 | 0.4320 | 0.058* | |
| C22 | 1.0702 (3) | −0.0868 (5) | 0.3841 (2) | 0.0455 (11) | |
| H22 | 1.0097 | −0.0686 | 0.4060 | 0.055* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Fe1 | 0.0303 (3) | 0.0277 (3) | 0.0417 (3) | −0.0076 (2) | 0.0078 (2) | 0.0011 (2) |
| Br1 | 0.0584 (3) | 0.0489 (3) | 0.0780 (4) | 0.0306 (2) | 0.0181 (3) | 0.0102 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0335 (18) | 0.0312 (17) | 0.0363 (18) | 0.0084 (14) | 0.0065 (14) | −0.0016 (15) |
| N2 | 0.048 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.0387 (19) | 0.0278 (17) | 0.0043 (16) | −0.0063 (16) |
| N3 | 0.070 (3) | 0.065 (3) | 0.041 (2) | 0.031 (2) | −0.002 (2) | −0.005 (2) |
| C1 | 0.028 (2) | 0.030 (2) | 0.038 (2) | 0.0045 (16) | 0.0073 (17) | −0.0006 (18) |
| C2 | 0.030 (2) | 0.0270 (19) | 0.033 (2) | 0.0053 (16) | 0.0019 (16) | −0.0024 (16) |
| C3 | 0.027 (2) | 0.0275 (19) | 0.037 (2) | −0.0008 (16) | 0.0081 (17) | 0.0005 (17) |
| C4 | 0.027 (2) | 0.0300 (19) | 0.039 (2) | 0.0041 (16) | 0.0100 (17) | −0.0031 (17) |
| C5 | 0.026 (2) | 0.0267 (19) | 0.031 (2) | −0.0012 (15) | 0.0091 (16) | −0.0010 (16) |
| C6 | 0.028 (2) | 0.0263 (18) | 0.035 (2) | −0.0034 (16) | 0.0058 (16) | −0.0018 (17) |
| C7 | 0.029 (2) | 0.035 (2) | 0.036 (2) | −0.0065 (17) | 0.0084 (16) | −0.0015 (17) |
| C8 | 0.033 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.048 (3) | −0.0059 (18) | 0.0007 (18) | 0.005 (2) |
| C9 | 0.041 (2) | 0.041 (2) | 0.034 (2) | −0.013 (2) | 0.0084 (18) | −0.0028 (19) |
| C10 | 0.037 (2) | 0.0253 (19) | 0.042 (2) | −0.0050 (17) | 0.0114 (18) | −0.0030 (18) |
| C11 | 0.036 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.075 (4) | −0.018 (2) | 0.012 (2) | 0.008 (3) |
| C12 | 0.060 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.064 (3) | −0.035 (3) | −0.005 (3) | 0.003 (2) |
| C13 | 0.067 (4) | 0.035 (2) | 0.080 (4) | −0.021 (2) | 0.023 (3) | −0.012 (3) |
| C14 | 0.055 (3) | 0.035 (2) | 0.088 (4) | −0.006 (2) | 0.020 (3) | 0.011 (3) |
| C15 | 0.053 (3) | 0.050 (3) | 0.059 (3) | −0.017 (2) | 0.020 (2) | 0.011 (2) |
| C16 | 0.042 (3) | 0.037 (2) | 0.039 (3) | 0.0170 (19) | 0.006 (2) | −0.0008 (19) |
| C17 | 0.028 (2) | 0.0270 (19) | 0.037 (2) | 0.0028 (16) | 0.0087 (16) | −0.0027 (17) |
| C18 | 0.048 (3) | 0.038 (2) | 0.049 (3) | 0.0091 (19) | 0.018 (2) | 0.006 (2) |
| C19 | 0.038 (2) | 0.047 (2) | 0.058 (3) | 0.011 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.003 (2) |
| C20 | 0.033 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.052 (3) | 0.0118 (17) | 0.0080 (19) | −0.003 (2) |
| C21 | 0.050 (3) | 0.039 (2) | 0.061 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.023 (2) | 0.013 (2) |
| C22 | 0.040 (2) | 0.042 (2) | 0.059 (3) | 0.012 (2) | 0.024 (2) | 0.007 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Fe1—C7 | 2.013 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.412 (5) |
| Fe1—C13 | 2.017 (4) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| Fe1—C12 | 2.028 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.416 (5) |
| Fe1—C6 | 2.033 (4) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| Fe1—C14 | 2.035 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.419 (5) |
| Fe1—C11 | 2.037 (4) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| Fe1—C15 | 2.041 (4) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| Fe1—C10 | 2.042 (4) | C11—C15 | 1.404 (6) |
| Fe1—C8 | 2.049 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.417 (6) |
| Fe1—C9 | 2.054 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| Br1—C20 | 1.897 (4) | C12—C13 | 1.406 (6) |
| N1—C1 | 1.340 (5) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C5 | 1.342 (4) | C13—C14 | 1.404 (7) |
| N2—C1 | 1.351 (4) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N2—H2A | 0.8600 | C14—C15 | 1.392 (6) |
| N2—H2B | 0.8600 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C16 | 1.140 (5) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.415 (5) | C17—C22 | 1.380 (5) |
| C2—C3 | 1.402 (5) | C17—C18 | 1.392 (5) |
| C2—C16 | 1.420 (6) | C18—C19 | 1.379 (5) |
| C3—C4 | 1.382 (5) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C17 | 1.495 (5) | C19—C20 | 1.374 (5) |
| C4—C5 | 1.404 (5) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C20—C21 | 1.365 (5) |
| C5—C6 | 1.468 (5) | C21—C22 | 1.375 (5) |
| C6—C7 | 1.423 (5) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C10 | 1.435 (5) | C22—H22 | 0.9300 |
| C7—Fe1—C13 | 105.30 (18) | C6—C7—Fe1 | 70.1 (2) |
| C7—Fe1—C12 | 122.73 (18) | C8—C7—H7 | 125.6 |
| C13—Fe1—C12 | 40.67 (19) | C6—C7—H7 | 125.6 |
| C7—Fe1—C6 | 41.17 (14) | Fe1—C7—H7 | 124.8 |
| C13—Fe1—C6 | 119.91 (18) | C7—C8—C9 | 107.8 (3) |
| C12—Fe1—C6 | 106.72 (17) | C7—C8—Fe1 | 68.3 (2) |
| C7—Fe1—C14 | 119.64 (17) | C9—C8—Fe1 | 70.0 (2) |
| C13—Fe1—C14 | 40.54 (18) | C7—C8—H8 | 126.1 |
| C12—Fe1—C14 | 68.3 (2) | C9—C8—H8 | 126.1 |
| C6—Fe1—C14 | 155.28 (18) | Fe1—C8—H8 | 127.2 |
| C7—Fe1—C11 | 160.93 (17) | C8—C9—C10 | 108.5 (3) |
| C13—Fe1—C11 | 68.2 (2) | C8—C9—Fe1 | 69.6 (2) |
| C12—Fe1—C11 | 40.81 (18) | C10—C9—Fe1 | 69.3 (2) |
| C6—Fe1—C11 | 125.17 (17) | C8—C9—H9 | 125.7 |
| C14—Fe1—C11 | 67.84 (19) | C10—C9—H9 | 125.7 |
| C7—Fe1—C15 | 155.64 (17) | Fe1—C9—H9 | 127.0 |
| C13—Fe1—C15 | 67.7 (2) | C9—C10—C6 | 107.7 (3) |
| C12—Fe1—C15 | 68.07 (19) | C9—C10—Fe1 | 70.2 (2) |
| C6—Fe1—C15 | 162.71 (17) | C6—C10—Fe1 | 69.1 (2) |
| C14—Fe1—C15 | 39.94 (17) | C9—C10—H10 | 126.1 |
| C11—Fe1—C15 | 40.27 (17) | C6—C10—H10 | 126.1 |
| C7—Fe1—C10 | 69.07 (15) | Fe1—C10—H10 | 126.2 |
| C13—Fe1—C10 | 156.9 (2) | C15—C11—C12 | 107.7 (5) |
| C12—Fe1—C10 | 122.33 (18) | C15—C11—Fe1 | 70.1 (2) |
| C6—Fe1—C10 | 41.23 (14) | C12—C11—Fe1 | 69.3 (2) |
| C14—Fe1—C10 | 161.78 (19) | C15—C11—H11 | 126.2 |
| C11—Fe1—C10 | 109.48 (18) | C12—C11—H11 | 126.2 |
| C15—Fe1—C10 | 126.43 (17) | Fe1—C11—H11 | 126.1 |
| C7—Fe1—C8 | 40.67 (15) | C13—C12—C11 | 107.2 (4) |
| C13—Fe1—C8 | 122.68 (19) | C13—C12—Fe1 | 69.2 (2) |
| C12—Fe1—C8 | 159.3 (2) | C11—C12—Fe1 | 69.9 (2) |
| C6—Fe1—C8 | 68.75 (15) | C13—C12—H12 | 126.4 |
| C14—Fe1—C8 | 106.87 (18) | C11—C12—H12 | 126.4 |
| C11—Fe1—C8 | 157.92 (18) | Fe1—C12—H12 | 126.0 |
| C15—Fe1—C8 | 122.02 (18) | C14—C13—C12 | 108.6 (5) |
| C10—Fe1—C8 | 68.44 (16) | C14—C13—Fe1 | 70.4 (3) |
| C7—Fe1—C9 | 68.36 (15) | C12—C13—Fe1 | 70.1 (2) |
| C13—Fe1—C9 | 160.0 (2) | C14—C13—H13 | 125.7 |
| C12—Fe1—C9 | 158.7 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 125.7 |
| C6—Fe1—C9 | 68.62 (15) | Fe1—C13—H13 | 125.3 |
| C14—Fe1—C9 | 124.71 (19) | C15—C14—C13 | 107.8 (5) |
| C11—Fe1—C9 | 123.72 (18) | C15—C14—Fe1 | 70.3 (2) |
| C15—Fe1—C9 | 109.84 (17) | C13—C14—Fe1 | 69.0 (3) |
| C10—Fe1—C9 | 40.53 (14) | C15—C14—H14 | 126.1 |
| C8—Fe1—C9 | 40.36 (15) | C13—C14—H14 | 126.1 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 118.3 (3) | Fe1—C14—H14 | 126.2 |
| C1—N2—H2A | 120.0 | C14—C15—C11 | 108.7 (4) |
| C1—N2—H2B | 120.0 | C14—C15—Fe1 | 69.8 (2) |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 120.0 | C11—C15—Fe1 | 69.7 (2) |
| N1—C1—N2 | 116.1 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 125.6 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 122.3 (3) | C11—C15—H15 | 125.6 |
| N2—C1—C2 | 121.6 (3) | Fe1—C15—H15 | 126.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.0 (3) | N3—C16—C2 | 174.9 (4) |
| C3—C2—C16 | 122.8 (3) | C22—C17—C18 | 118.5 (3) |
| C1—C2—C16 | 118.2 (3) | C22—C17—C3 | 121.4 (3) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.0 (3) | C18—C17—C3 | 120.0 (3) |
| C4—C3—C17 | 120.4 (3) | C19—C18—C17 | 120.7 (4) |
| C2—C3—C17 | 121.5 (3) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.7 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.6 (3) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.7 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.2 | C20—C19—C18 | 119.3 (4) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.2 | C20—C19—H19 | 120.4 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 122.7 (3) | C18—C19—H19 | 120.4 |
| N1—C5—C6 | 115.6 (3) | C21—C20—C19 | 120.9 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.6 (3) | C21—C20—Br1 | 120.0 (3) |
| C7—C6—C10 | 107.1 (3) | C19—C20—Br1 | 119.1 (3) |
| C7—C6—C5 | 125.0 (3) | C20—C21—C22 | 119.8 (4) |
| C10—C6—C5 | 127.7 (3) | C20—C21—H21 | 120.1 |
| C7—C6—Fe1 | 68.7 (2) | C22—C21—H21 | 120.1 |
| C10—C6—Fe1 | 69.7 (2) | C21—C22—C17 | 120.9 (4) |
| C5—C6—Fe1 | 123.7 (2) | C21—C22—H22 | 119.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 108.8 (3) | C17—C22—H22 | 119.5 |
| C8—C7—Fe1 | 71.0 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2B···N3i | 0.86 | 2.29 | 3.050 (5) | 148 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BQ2041).
References
- Alyoubi, A. O. (2000). Spectrochim. Acta Part A, 56, 2397–2404. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (1998). SMART and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (1999). SAINT and SHELXTL Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Desai, J. M. & Shah, V. H. (2003). Indian J. Chem. Sect. B, 42, 382–385.
- Dombrowski, K. E., Baldwin, W. & Sheats, J. E. (1986). J. Organomet. Chem.302, 281–306.
- Murata, T., Shimada, M., Sakakibara, S., Yoshino, T., Masuda, T., Shintani, T., Sato, H., Koriyama, Y., Fukushima, K., Nunami, N., Yamauchi, M., Fuchikami, K., Komura, H., Watanabe, A., Ziegelbauer, K. B., Bacon, K. B. & Lowinger, T. B. (2004). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.14, 4019–4022. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1997). SHELXS97 and SHELXL97 University of Göttingen, Germany.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680705489X/bq2041sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680705489X/bq2041Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report