Abstract
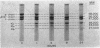
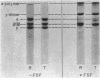
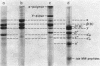
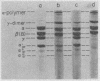
Fibrin formed in response to ancrod, reptilase, or thrombin was reduced by β-mercaptoethanol and examined by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. It was found that ancrod progressively and totally digested the α-chains of fibrin monomers at sites different than plasmin; however, further digestion of fibrin monomers by either reptilase or thrombin was not observed. Highly purified ancrod did not activate fibrin-stabilizing factor (FSF); however, the reptilase preparation used in these experiments, like thrombin, activated FSF and thereby promoted cross-link formation. Fibrin, formed by clotting purified human fibrinogen with ancrod, reptilase, or thrombin for increasing periods of time in the presence of plasminogen, was incubated with urokinase and observed for complete lysis. Fibrin formed by ancrod was strikingly more vulnerable to plasmin digestion than was fibrin formed by reptilase or thrombin. The lysis times for fibrin formed for 2 hr by ancrod, reptilase, or thrombin were 18, 89, and 120 min, respectively. Evidence was also obtained that neither ancrod nor reptilase activated human plasminogen. These results indicate that fibrin formed by ancrod is not cross-linked and has significantly degraded α-chains: as expected, ancrod-formed fibrin is markedly susceptible to digestion by plasmin.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashford A., Ross J. W., Southgate P. Pharmacology and toxicology of a defibrinating substance from Malayan pit viper venom. Lancet. 1968 Mar 9;1(7541):486–489. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91464-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOMBACK B., BLOMBACK M., NILSSON I. M. Coagulation studies on reptilase, an extract of the venom from Bothrops jararaca. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1958 Apr 15;1(1):76–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow G. H., Holleman W. H., Lorand L. The action of Arvin on Fibrin Stabilizing Factor (factor 13). Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1970 Jan;1(1):39–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow G. H., Summaria L., Robbins K. C. Molecular weight studies on human plasminogen and plasmin at the microgram level. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1138–1141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell W. R., Bolton G., Pitney W. R. The effect of arvin on blood coagulation factors. Br J Haematol. 1968 Dec;15(6):589–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1968.tb01581.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell W. R., Pitney W. R., Goodwin J. F. Therapeutic defibrination in the treatment of thrombotic disease. Lancet. 1968 Mar 9;1(7541):490–493. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91465-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAN K. E., REID H. A. FIBRINOLYSIS AND THE DEFIBRINATION SYNDROME OF MALAYAN VIPER BITE. Lancet. 1964 Feb 29;1(7331):461–463. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90795-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. E., Rizza C. R., Henderson M. P. A study of the coagulant properties of Malayan pit-viper venom. Br J Haematol. 1965 Nov;11(6):646–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb00113.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch D. G., Mertz E. T. Plasminogen: purification from human plasma by affinity chromatography. Science. 1970 Dec 4;170(3962):1095–1096. doi: 10.1126/science.170.3962.1095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunker A. K., Rueckert R. R. Observations on molecular weight determinations on polyacrylamide gel. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):5074–5080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvilansky A., Britten A. F., Loewy A. G. Factor XIII assay by an isotope method. I. Factor XIII (transamidase) in plasma, serum, leucocytes, erythrocytes and platelets and evaluation of screening tests of clot solubility. Br J Haematol. 1970 Apr;18(4):399–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01453.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvilansky A., Britten A. F., Loewy A. G. Factor XIII assay by an isotope method. II. Heparin inhibition of factor XIII activation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1970 Oct 31;24(1):256–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esnouf M. P., Tunnah G. W. The isolation and properties of the thrombin-like activity from Ancistrodon rhodostoma venom. Br J Haematol. 1967 Jul;13(4):581–590. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb00765.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewart M. R., Hatton M. W., Basford J. M., Dodgson K. S. The proteolytic action of Arvin on human fibrinogen. Biochem J. 1970 Jul;118(4):603–609. doi: 10.1042/bj1180603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORMSEN J., SIVERTSEN U. THE EFFECT OF SULFHYDRYLINHIBITORS AND GLYCINE DERIVATIVES ON FIBRIN POLYMERIZATION AND THE PHYSICAL STRENGTH OF FIBRIN IN PLASMA. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Jul 31;11:454–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holleman W. H., Coen L. J. Characterization of peptides released from human fibrinogen by Arvin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 31;200(3):587–589. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakkar V. V., Flanc C., Howe C. T., O'Shea M., Flute P. T. Treatment of deep vein thrombosis. A trial of heparin, streptokinase, and arvin. Br Med J. 1969 Mar 29;1(5647):806–810. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5647.806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopeć M., Latallo Z. S., Stahl M., Wegrzynowicz Z. The effect of proteolytic enzymes on fibrin stabilizing factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jul 1;181(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(69)90277-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L., Prose P. H., Cohen M. H. The role of the reticuloendothelial system in diffuse, low grade intravascular coagulation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1966;20:87–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Shulman N. R. High molecular weight derivatives of human fibrinogen produced by plasmin. II. Mechanism of their anticoagulant activity. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2120–2124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattock P., Esnouf M. P. Differences in the subunit structure of human fibrin formed by the action of arvin, reptilase and thrombin. Nat New Biol. 1971 Oct 27;233(43):277–279. doi: 10.1038/newbio233277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee P. A., Mattock P., Hill R. L. Subunit structure of human fibrinogen, soluble fibrin, and cross-linked insoluble fibrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):738–744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLSON R. E. Obesity as a nutritional disorder. Fed Proc. 1959 Jul;18(2 Pt 2):58–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen E. G., Pitney W. R. The effect of arvin on experimental pulmonary embolism in the rabbit. Br J Haematol. 1969 Nov;17(5):425–429. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb01390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Finlayson J. S., Peyton M. P., Nagai Y. Epsilon-(gamma glutamyl) lysine in fibrin: lack of crosslink formation in Factor 13 deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):770–772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitney W. R., Bell W. R., Bolton G. Blood fibrinolytic activity during arvin therapy. Br J Haematol. 1969 Jan-Feb;16(1):165–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb00389.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitney W. R., Oakley C. M., Goodwin J. F. Therapeutic defibrination with arvin. Am Heart J. 1970 Jul;80(1):144–146. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(70)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzo S. V., Schwartz M. L., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The effect of plasmin on the subunit structure of human fibrinogen. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):636–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REID H. A., CHAN K. E., THEAN P. C. Prolonged coagulation defect (defibrination syndrome) in Malayan viper bite. Lancet. 1963 Mar 23;1(7282):621–626. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Brain M. C. Organ distribution of fibrin in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Br J Haematol. 1969 Jul;17(1):73–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1969.tb05665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Gergely J., McFarlane A. S. In vivo effects of Agkistrodon rhodostoma venom: studies with fibrinogen-131I. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jul;45(7):1202–1212. doi: 10.1172/JCI105426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E. Interference of lysed fibrin with coagulation: a quantifying approach using isotopic techniques. Br J Haematol. 1971 Aug;21(2):209–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb03431.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid H. A., Chan K. E. The paradox in therapeutic defibrination. Lancet. 1968 Mar 9;1(7541):485–486. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91463-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Erdmann F., Carpenter C. B., Galvanek E. G. Experimental dysfibrinogenemia: in vivo studies with arvin. Blood. 1971 Jun;37(6):664–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenberg M. L., Bull B. S., Regoeczi E., Dacie J. V., Brain M. C. Experimental production of microangiopathic haemolytic anaemia in vivo. Lancet. 1967 Nov 25;2(7526):1121–1123. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90622-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The effect of fibrin-stabilizing factor on the subunit structure of human fibrin. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1506–1513. doi: 10.1172/JCI106636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Pizzo S. V., Hill R. L., McKee P. A. The subunit structures of human plasma and platelet factor XIII (fibrin-stabilizing factor). J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 25;246(18):5851–5854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp A. A., Warren B. A., Paxton A. M., Allington M. J. Anticoagulant therapy with a purified fraction of Malayan pit viper venom. Lancet. 1968 Mar 9;1(7541):493–499. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91466-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turpie A. G., Prentice C. R., McNicol G. P., Douglas A. S. In-vitro studies with ancrod ('Arvin'). Br J Haematol. 1971 Feb;20(2):217–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1971.tb07030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler H. M. Studies on the activation of purified human factor XIII. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 24;222(2):396–404. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]