Abstract
A collagenase and a neutral protease have been insolated and characterized from primary cultures obtained from rheumatoid subcutaneous nodules. Release of both active enzymes was maximal between the 3rd and 7th days of culture and was stimulated by the presence of small amounts of colchicine (0.1 μg/ml) added to the culture medium.
Both the protease and the collagenase from nodule tissue were active at physiologic pH and were inhibited by chelating agents, sulfhydryl compounds, and 1:40 dilutions of human serum. Both enzymes appeared to have a molcular size equivalent to similar enzymes found in cultures of rheumatoid synovium. The nodule collagenase was purified by chromatography on molecular sieve columns followed by affinity chromatography. The pure enzyme cleaved collagen in solution at 24°C at the locus common for mammalian collagenases to act: three quarters of the distance from the amino-terminus. Under the same conditions the purified enzyme cleaved gelatin (denatured collagen) at the same locus. It is likely therefore that the collagenase in rheumatoid connective tissues functions to produce the initial cleavage of collagen and that after the initial reaction products are denatured, proteases digest them into smaller polypeptides more rapidly than does the collagenase itself.
Since rheumatoid nodules grow centrifugally at the expense of the palisading fibroblast layer it seems possible that the central necrotic areas are caused by release of collagenase and protease from the highly cellular palisading zone resulting in the destruction of the extracellular collagen matrix.
Full text
PDF
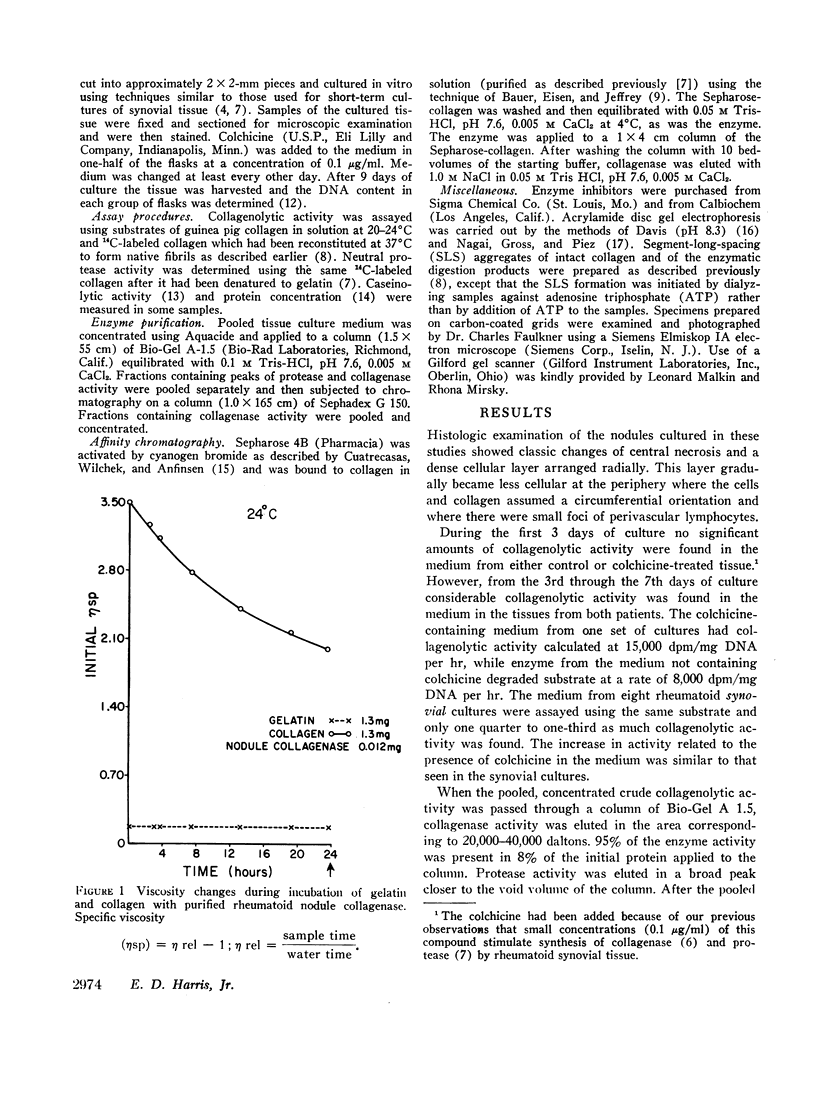
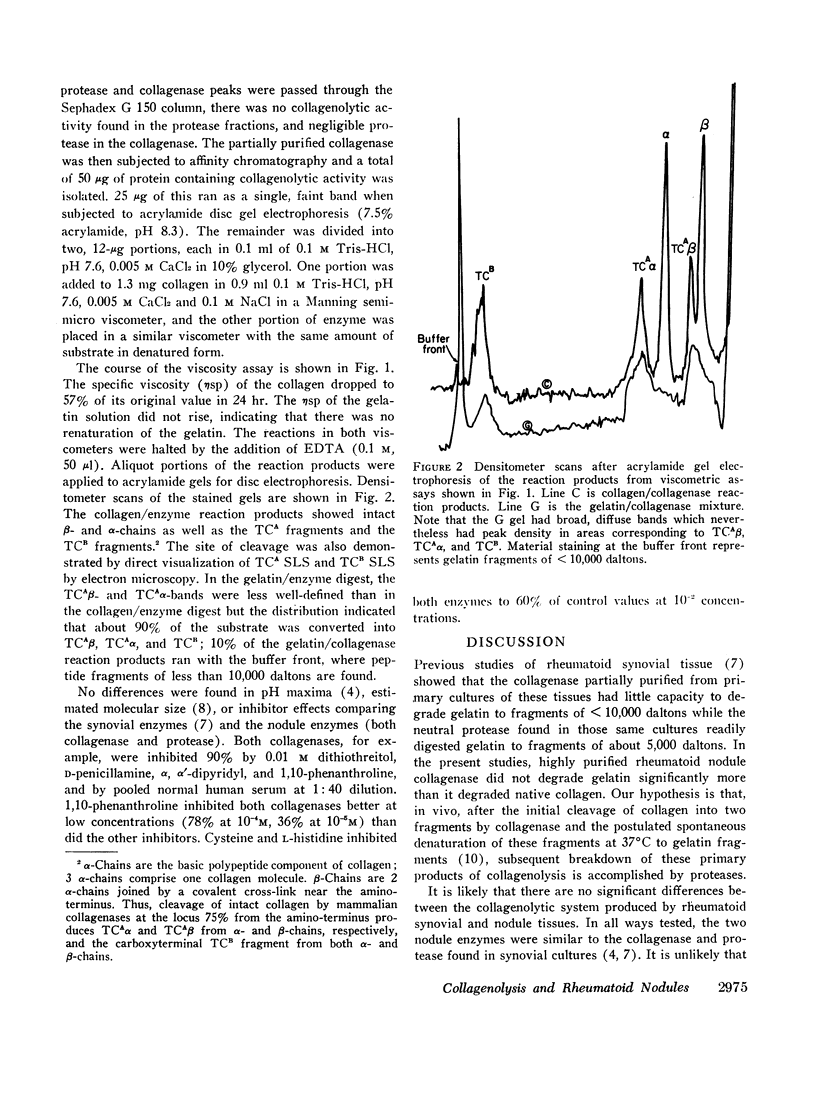

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer E. A., Eisen A. Z., Jeffrey J. J. Studies on purified rheumatoid synovial collagenase in vitro and in vivo. J Clin Invest. 1971 Oct;50(10):2056–2064. doi: 10.1172/JCI106699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE W., DAVIES D. V., DORLING J., BYWATERS E. G. ULTRAMICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF THE RHEUMATOID NODULE. Ann Rheum Dis. 1964 Sep;23:345–363. doi: 10.1136/ard.23.5.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P., Wilchek M., Anfinsen C. B. Selective enzyme purification by affinity chromatography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Oct;61(2):636–643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.2.636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisen A. Z. Human skin collagenase: localization and distribution in normal human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1969 May;52(5):442–448. doi: 10.1038/jid.1969.76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evanson J. M., Jeffrey J. J., Krane S. M. Studies on collagenase from rheumatoid synovium in tissue culture. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2639–2651. doi: 10.1172/JCI105947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, DiBona D. R., Krane S. M. Collagenases in human synovial fluid. J Clin Invest. 1969 Nov;48(11):2104–2113. doi: 10.1172/JCI106177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Evanson J. M., DiBona D. R., Krane S. M. Collagenase and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1970 Jan-Feb;13(1):83–94. doi: 10.1002/art.1780130109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Krane S. M. An endopeptidase from rheumatoid synovial tissue culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):566–576. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Krane S. M. Effects of colchicine on collagenase in cultures of rheumatoid synovium. Arthritis Rheum. 1971 Nov-Dec;14(6):669–684. doi: 10.1002/art.1780140602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGAI Y., GROSS J., PIEZ K. A. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS OF COLLAGEN COMPONENTS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:494–500. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


