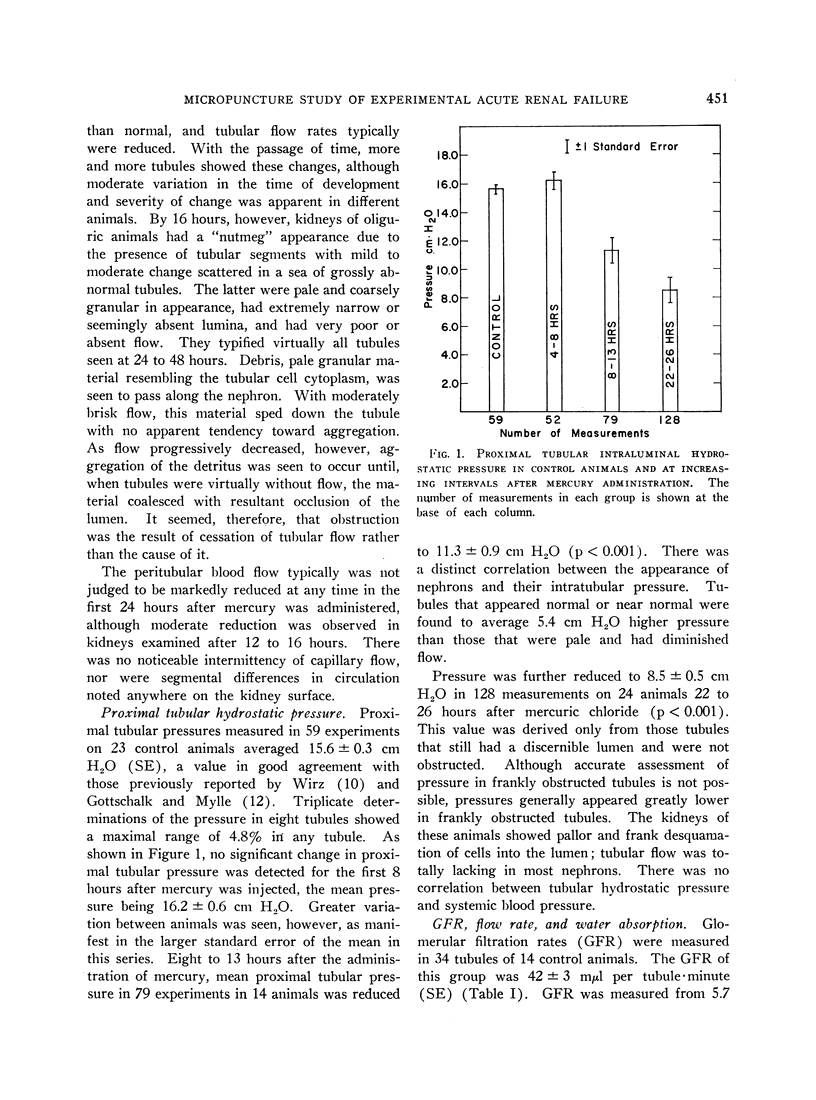
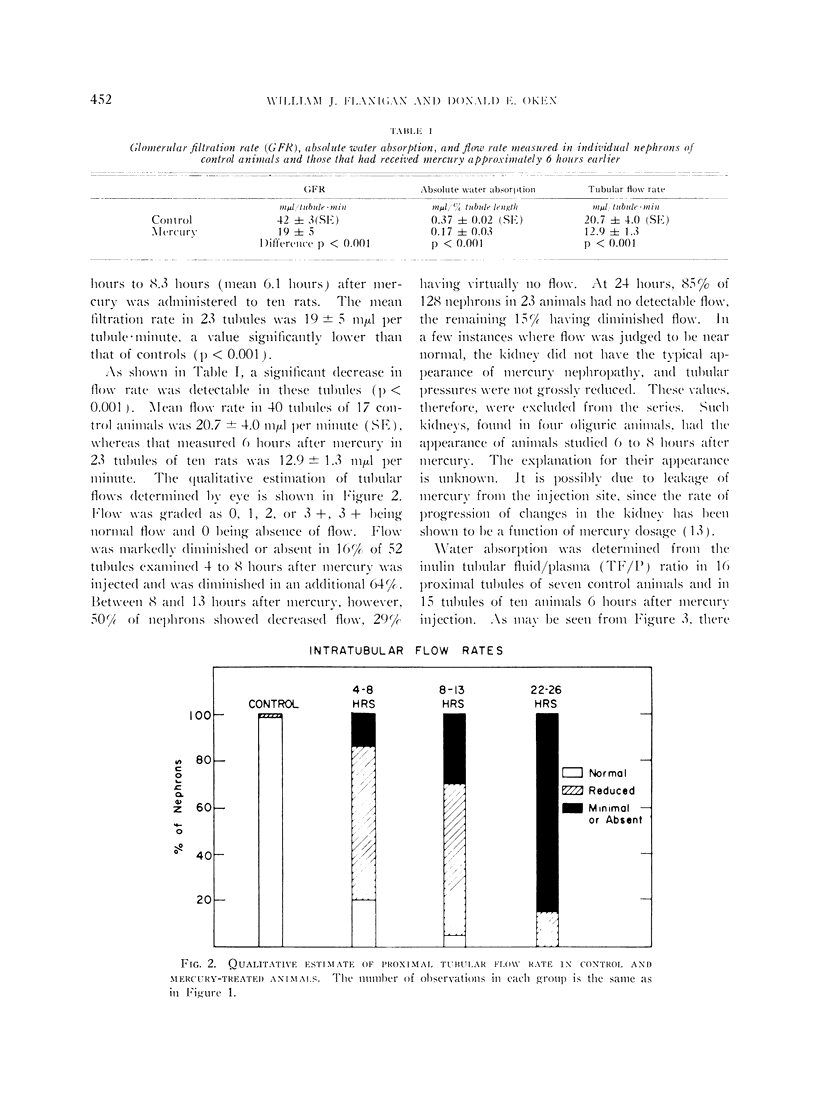
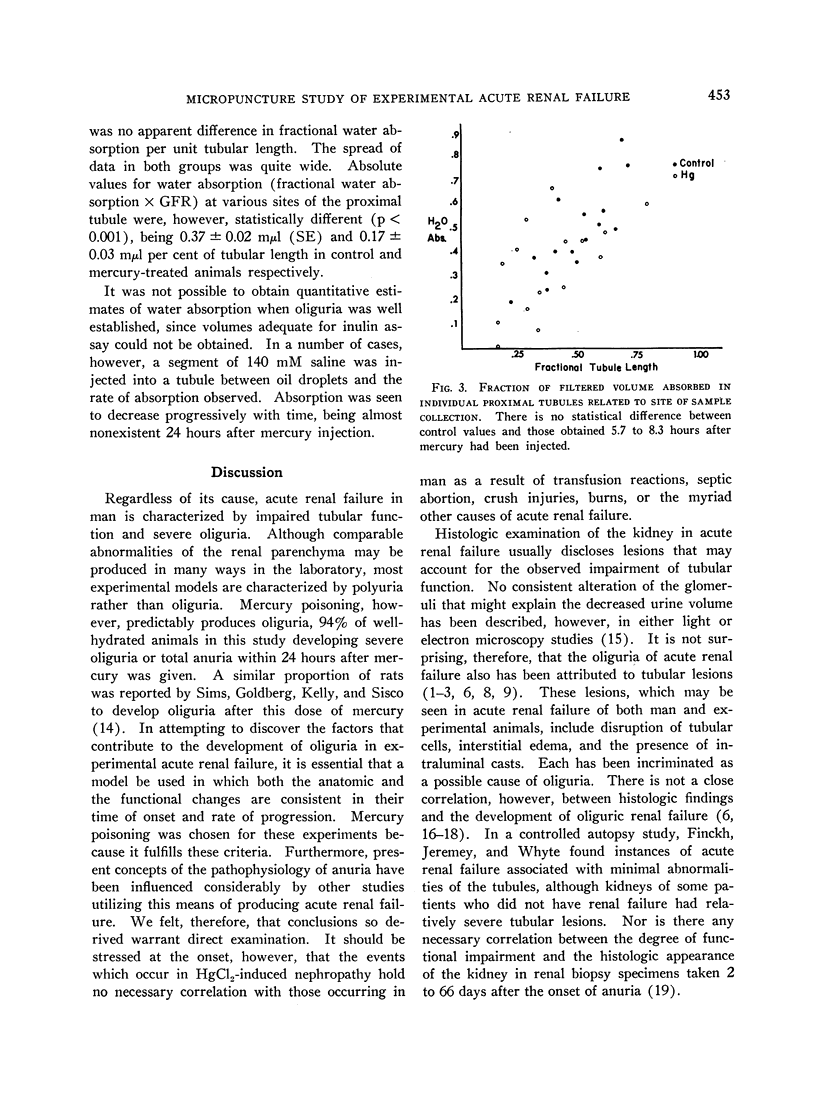
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOTT P. A. Renal excretion of creatinine in Necturus; a reinvestigation by direct analysis of glomerular and tubule fluid for creatinine and inulin. Am J Physiol. 1952 Jan;168(1):107–113. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.168.1.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUN C., MUNCK O. Lesions of the kidney in acute renal failure following shock. Lancet. 1957 Mar 23;272(6969):603–607. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91069-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALGAARD O. Z., PEDERSEN K. J. Renal tubular degeneration. Electron microscopy in ischaemic anuria. Lancet. 1959 Oct 3;2(7101):484–488. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90607-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINCKH E. S., JEREMY D., WHYTE H. M. Structural renal damage and its relatin to clinical features in acute oliguric renal failure. Q J Med. 1962 Oct;31:429–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of pressures in proximal and distal tubules and peritubular capillaries of the rat kidney during osmotic diuresis. Am J Physiol. 1957 May;189(2):323–328. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1957.189.2.323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of pressures in proximal tubules and peritubular capillaries of the rat kidney and their relation to ureteral and renal venous pressures. Am J Physiol. 1956 May;185(2):430–439. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.185.2.430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINZELLER A., CORT J. H. The mechanism of action of mercurial preparations on transport processes and the role of thiol groups in the cell membrane of renal tubular cells. Biochem J. 1957 Sep;67(1):15–24. doi: 10.1042/bj0670015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERONEY W. H., RUBINI M. E. Kidney function during acute tubular necrosis: clinical studies and a theory. Metabolism. 1959 Jan;8(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKEN D. E., WHITTEMBURY G., WINDHAGER E. E., SOLOMON A. K. Single proximal tubules of Necturus kidney. V. Unidirectional sodium movement. Am J Physiol. 1963 Mar;204:372–376. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.204.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLIVER J., MacDOWELL M., TRACY A. The pathogenesis of acute renal failure associated with traumatic and toxic injury; renal ischemia, nephrotoxic damage and the ischemic episode. J Clin Invest. 1951 Dec;30(121):1307–1439. doi: 10.1172/JCI102550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVITT S. Pathogenesis of traumatic uraemia: a revised concept. Lancet. 1959 Aug 22;2(7095):135–141. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90557-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIMS E. A., GOLDBERG H. I., KELLY J. R., SISCO B. Glomerular perfusion during acute renal insufficiency from mercury poisoning in the rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Sep;54:440–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANDER A. J., WILDE W. S., MALVIN R. L., SULLIVAN L. P. Re-examination of salt and water retention in congestive heart failure: significance of renal filtration fraction. Am J Med. 1958 Oct;25(4):497–502. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGEL G., HEYM E. Untersuchungen zur Bedeutung kolloidosomotischer Druckdifferenzen für den Mechanismus der isosmotischen Flüssigkeitsresorption in der Niere. Pflugers Arch. 1956;262(3):226–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00369703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINDHAGER E. E., GIEBISCH G. Micropuncture study of renal tubular transfer of sodium chloride in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1961 Mar;200:581–590. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.3.581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIRZ H. Druckmessung in Kapillaren und Tubuli der Niere durch Mikropunktion. Helv Physiol Pharmacol Acta. 1955;13(1):42–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


