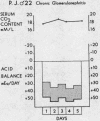
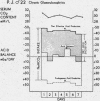
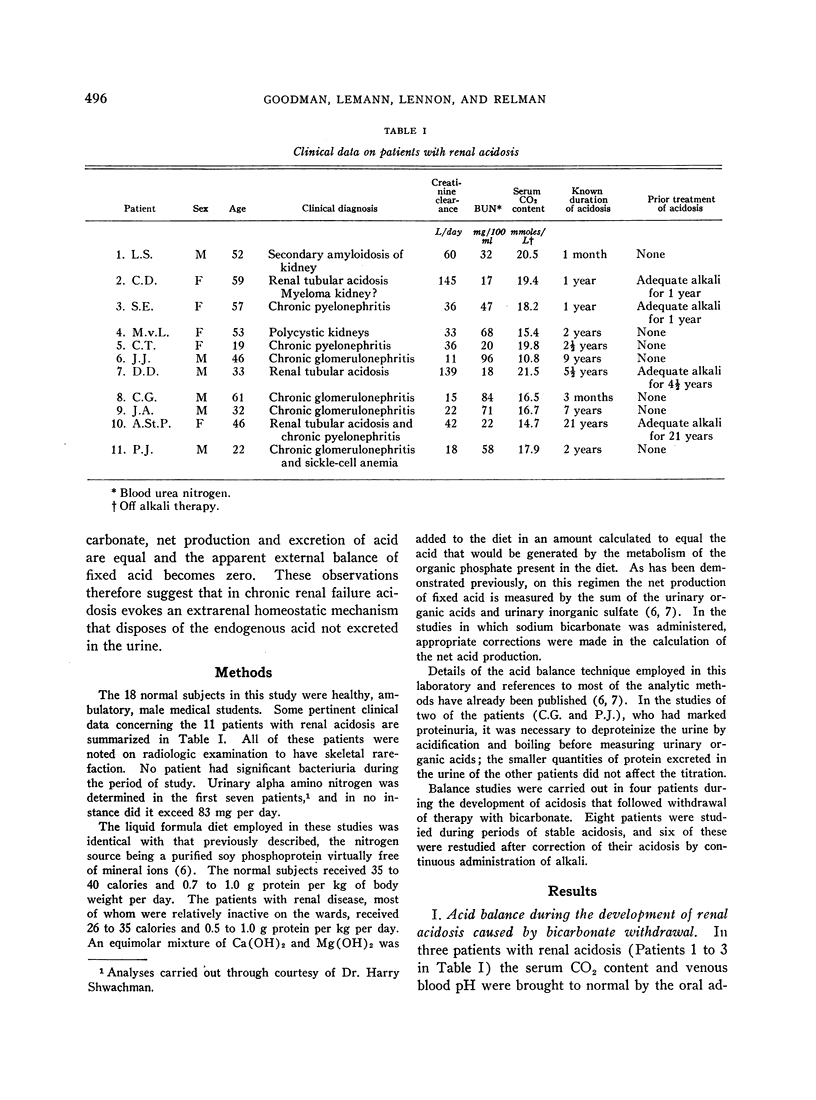
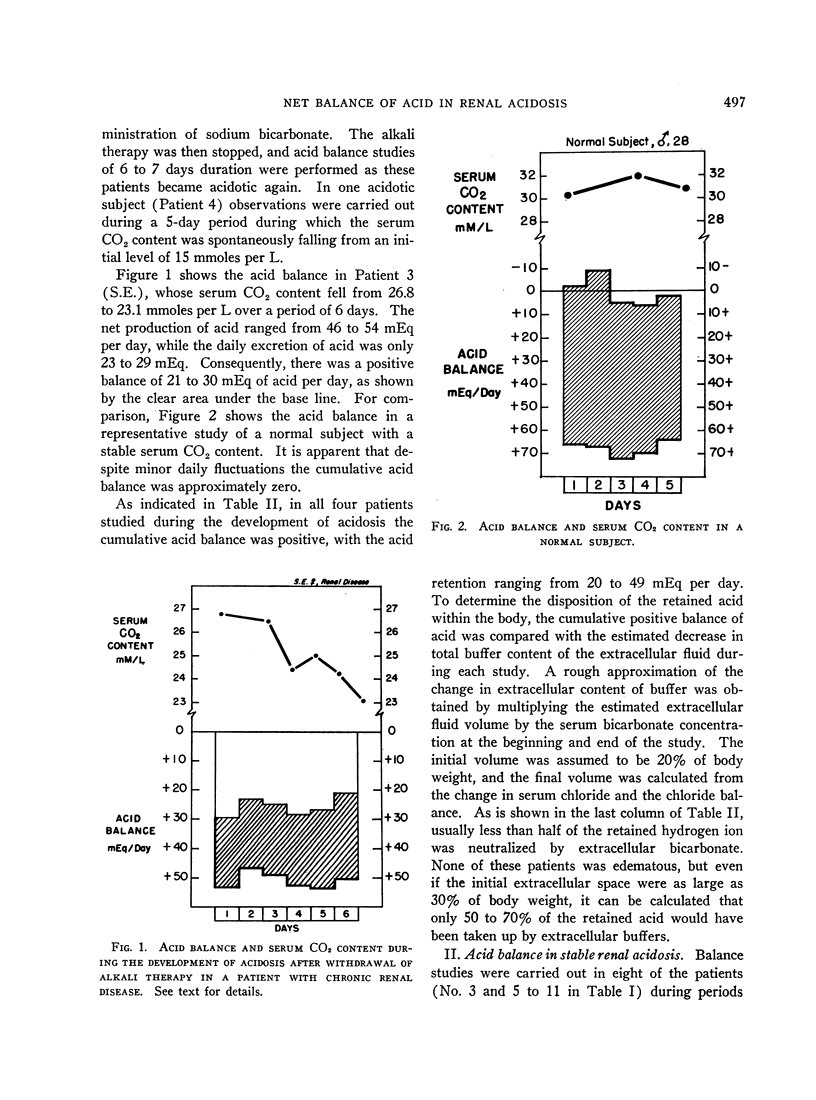
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DENT C. E., HARPER C. M., PHILPOT G. R. The treatment of renal-glomerular osteodystrophy. Q J Med. 1961 Jan;30:1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELKINTON J. R., HUTH E. J., WEBSTER G. D., Jr, McCANCE R. A. The renal excretion of hydrogen ion in renal tubular acidosis. I. quantitative assessment of the response to ammonium chloride as an acid load. Am J Med. 1960 Oct;29:554–575. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON A. R. Clinical and metabolic observations on osteomalacia following ureterosigmoidostomy. Br J Urol. 1958 Dec;30(4):455–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1958.tb03546.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAYE M., PRITCHARD J. E., HALPENNY G. W., LIGHT W. Bone disease in chronic renal failure with particular reference to osteosclerosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1960 May;39:157–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LENNON E. J., LEMANN J., Jr, RELMAN A. S. The effects of phosphoproteins on acid balance in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:637–645. doi: 10.1172/JCI104519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN H. E., JONES R. The effect of ammonium chloride and sodium bicarbonate on the urinary excretion of magnesium, calcium, and phosphate. Am Heart J. 1961 Aug;62:206–210. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(61)90319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RELMAN A. S., LENNON E. J., LEMANN J., Jr Endogenous production of fixed acid and the measurement of the net balance of acid in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1961 Sep;40:1621–1630. doi: 10.1172/JCI104384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., HALL P. W., 3rd, HAYS R. M., RELMAN A. S. On the mechanism of acidosis in chronic renal disease. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):39–52. doi: 10.1172/JCI103794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., RELMAN A. S. Acidosis in renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1957 Jun 20;256(25):1184–1186. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195706202562505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STANBURY S. W., LUMB G. A. Metabolic studies of renal osteodystrophy. I. Calcium, phosphorus and nitrogen metabolism in rickets, osteomalacia and hyperparathyroidism complicating chronic uremia and in the osteomalacia of the adult Fanconi syndrome. Medicine (Baltimore) 1962 Feb;41:1–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRONG O., DAVIES H. E. The excretion of acid in renal disease. Q J Med. 1959 Apr;28(110):259–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]