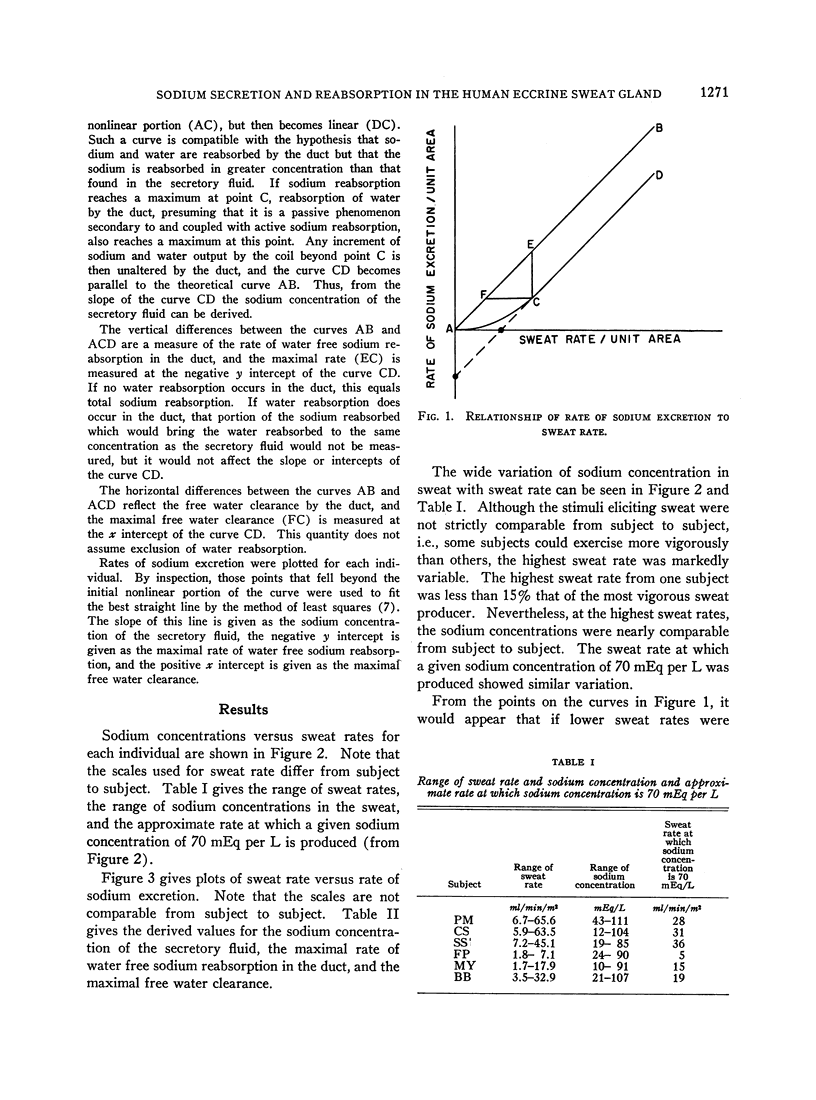
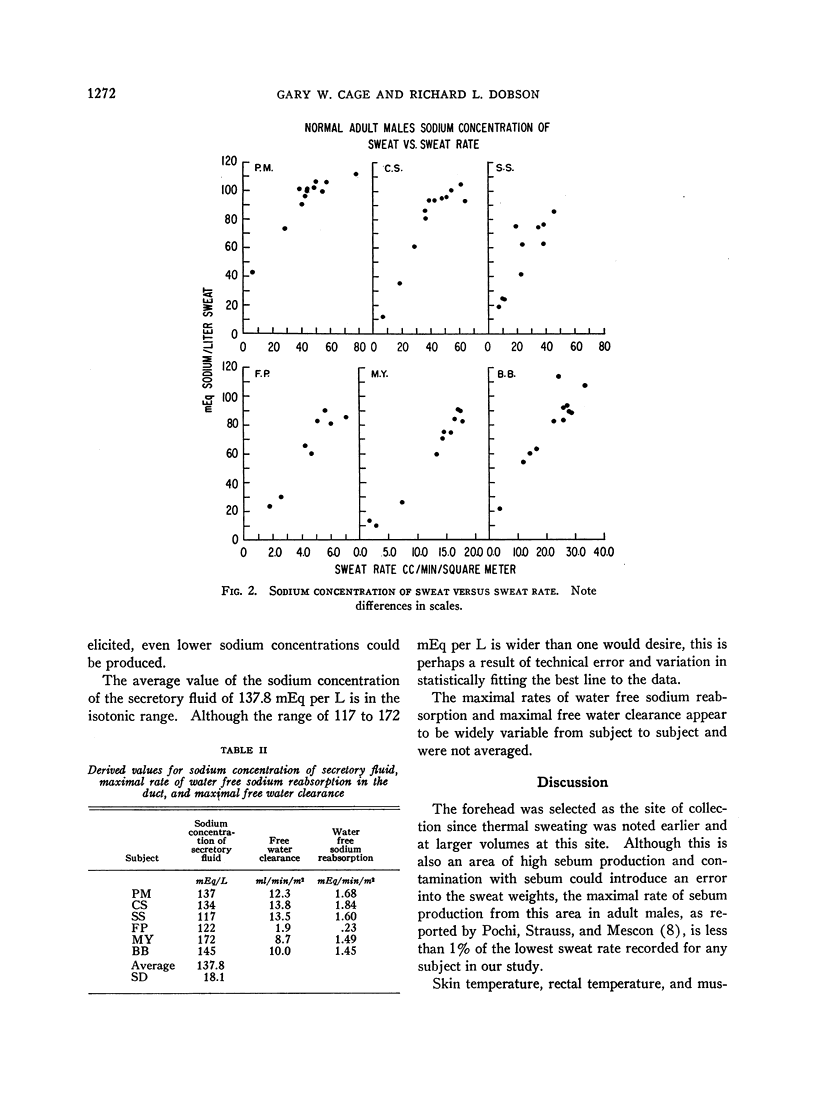
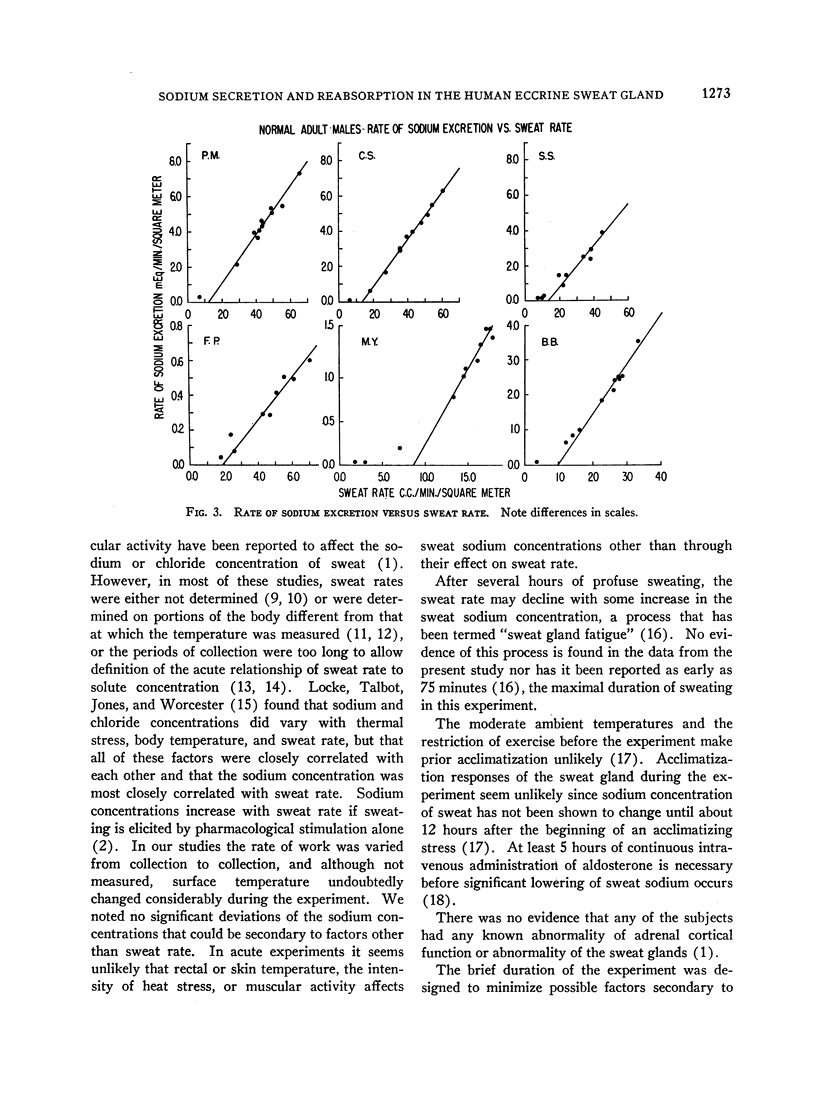
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS R., JOHNSON R. E., SARGENT F., 2nd The osmotic pressure (freezing point) of human sweat in relation to its chemical composition. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1958 Jul;43(3):241–257. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1958.sp001327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUSILOW S. W., MUNGER B. Comparative physiology of sweat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Jun;110:317–319. doi: 10.3181/00379727-110-27503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULMER M. G., FORWELL G. D. The concentration of sodium in thermal sweat. J Physiol. 1956 Apr 27;132(1):115–122. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS K. J., SARGENT F., WEINER J. S. The effect of arterial occlusion on sweat-gland responses in the human forearm. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:615–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON L. E., DISANT AGNESE P. A. Studies of salt excretion in sweat. Relationships between rate, conductivity, and electrolyte composition of sweat from patients with cystic fibrosis and from control subjects. J Pediatr. 1963 Jun;62:855–867. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(63)80099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIEBISCH G., WINDHAGER E. E. RENAL TUBULAR TRANSFER OF SODIUM, CHLORIDE AND POTASSIUM. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:643–669. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90178-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W. OSMOTIC CONCENTRATION AND DILUTION OF THE URINE. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:670–685. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENN O. Der Chloridgehalt des Schweisses bei hoher Temperatur, hoher relativer Feuchtigkeit, aber körperlicher Ruhe. Arbeitsphysiologie. 1953;15(1):93–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKE W., TALBOT N. B., JONES H. S., WORCESTER J. Studies on the combined use of measurements of sweat electrolyte composition and rate of sweating as an index of adrenal cortical activity. J Clin Invest. 1951 Mar;30(3):325–337. doi: 10.1172/JCI102448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCONAHAY T. P., ROBINSON S., NEWTON J. L. D-ALDOSTERONE AND SWEAT ELECTROLYTES. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Jul;19:575–579. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.4.575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNGER B. L., BRUSILOW S. W. An electron microscopic study of eccrine sweat glands of the catfoot and toe pads--evidence for ductal reabsorption in the human. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Nov;11:403–417. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POCHI P. E., STRAUSS J. S., MESCON H. Sebum secretion and urinary fractional 17-ketosteroid and total 17-hydroxycorticoid excretion in male castrates. J Invest Dermatol. 1962 Dec;39:475–483. doi: 10.1038/jid.1962.146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON S., GERKING S. D., TURRELL E. S., KINCAID R. K. Effect of skin temperature on salt concentration of sweat. J Appl Physiol. 1950 Jun;2(12):654–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON S., ROBINSON A. H. Chemical composition of sweat. Physiol Rev. 1954 Apr;34(2):202–220. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1954.34.2.202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ I. L., THAYSEN J. H. Excretion of sodium and potassium in human sweat. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jan;35(1):114–120. doi: 10.1172/JCI103245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THAYSEN J. H., SCHWARTZ I. L. The permeability of human sweat glands to a series of sulfonamide compounds. J Exp Med. 1953 Sep;98(3):261–268. doi: 10.1084/jem.98.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINER J. S., VAN HEYNINGEN R. E. Relation of skin temperature to salt concentration of general body sweat. J Appl Physiol. 1952 Mar;4(9):725–733. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1952.4.9.725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


