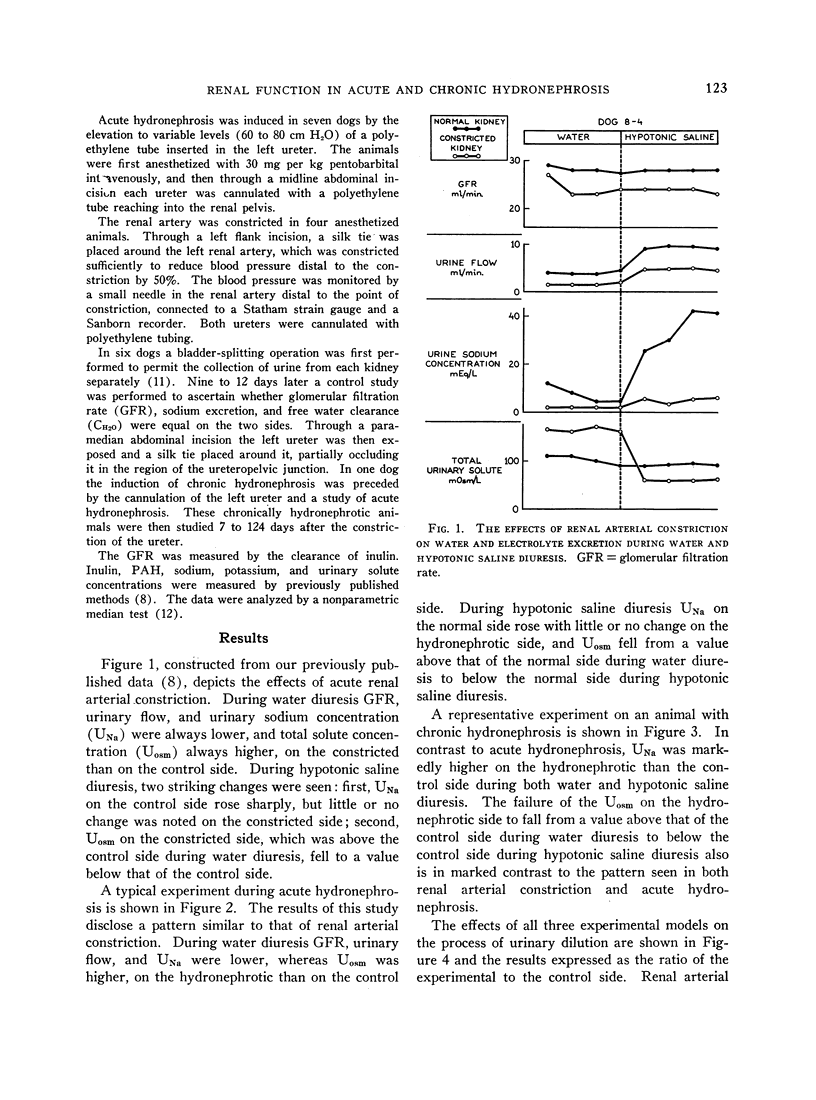
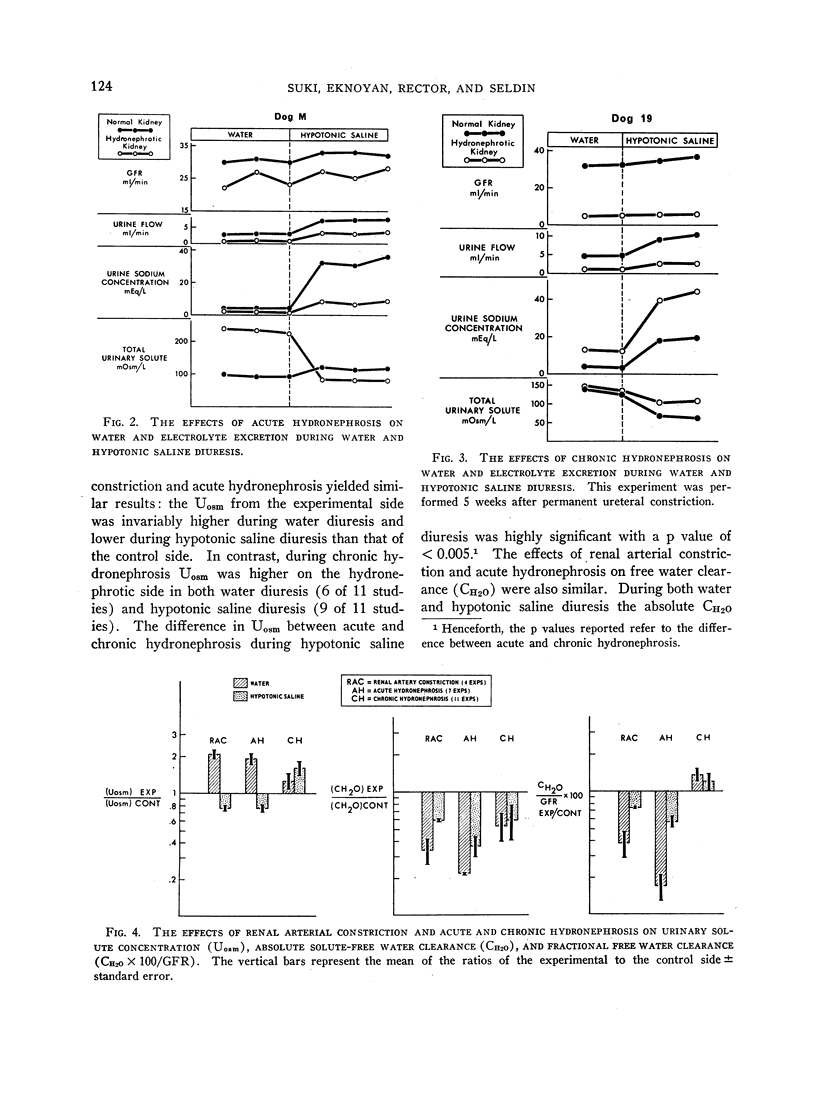
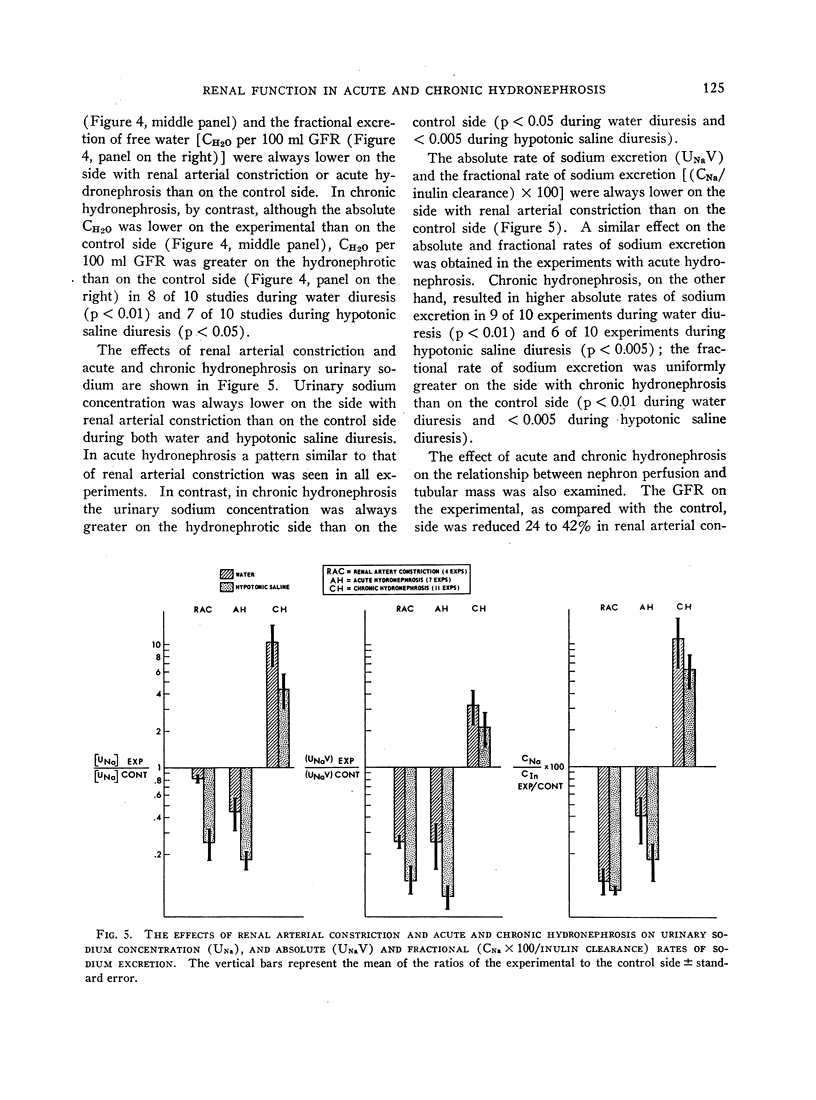
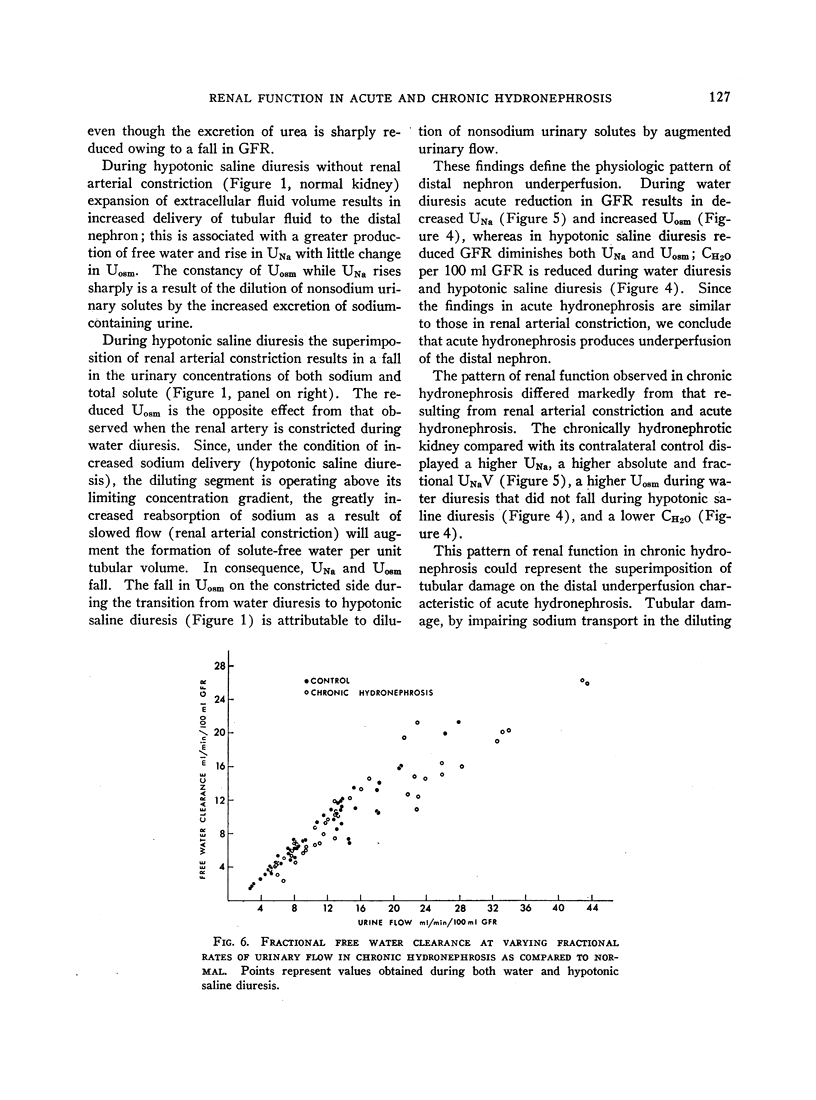
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERLINER R. W., DAVIDSON D. G. Production of hypertonic urine in the absence of pituitary antidiuretic hormone. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1416–1427. doi: 10.1172/JCI103541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERLYNE G. M. Distal tubular function in chronic hydronephrosis. Q J Med. 1961 Oct;30:339–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRICKER N. S., MORRIN P. A., KIME S. W., Jr The pathologic physiology of chronic Bright's disease. An exposition of the "intact nephron hypothesis". Am J Med. 1960 Jan;28:77–98. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRICKER N. S., SHWAYRI E. I., REARDAN J. B., KELLOG D., MERRILL J. P., HOLMES J. H. An abnormality in renal function resulting from urinary tract obstruction. Am J Med. 1957 Oct;23(4):554–564. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARONE F. A., EPSTEIN F. H. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus caused by amyloid disease. Evidence in man of the role of the collecting ducts in concentrating urine. Am J Med. 1960 Sep;29:539–544. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIRKS J. H., CIRKSENA W. J., BERLINER R. W. THE EFFECTS OF SALINE INFUSION ON SODIUM REABSORPTION BY THE PROXIMAL TUBULE OF THE DOG. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jul;44:1160–1170. doi: 10.1172/JCI105223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DORHOUT MEES E. J. Reversible water loosing state, caused by incomplete ureteric obstruction. Acta Med Scand. 1960 Nov 1;168:193–196. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1960.tb06661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EARLEY L. E. Extreme polyuria in obstructive uropathy; report of a case of water-losing nephritis in an infant, with a discussion of polyuria. N Engl J Med. 1956 Sep 27;255(13):600–605. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195609272551305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EARLY L. E., FRIEDLER R. M. OBSERVATIONS ON THE MECHANISM OF DECREASED TUBULAR REABSORPTION OF SODIUM AND WATER DURING SALINE LOADING. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1928–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI105067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLABMAN S., AYNEDJIAN H. S., BANK N. MICROPUNCTURE STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF ACUTE REDUCTIONS IN GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE ON SODIUM AND WATER REABSORPTION BY THE PROXIMAL TUBULES OF THE RAT. J Clin Invest. 1965 Aug;44:1410–1416. doi: 10.1172/JCI105246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIIL F., AUKLAND K. Renal tubular localization of water and sodium reabsorption in antidiuresis and water diuresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1960;12:277–289. doi: 10.3109/00365516009062438. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEEMAN C. R., EPSTEIN F. H. An illustrative case of chronic pyelonephritis with persistently hypotonic urine. Am J Med. 1957 Sep;23(3):488–492. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90327-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEEMAN C. R., HEWITT W. L., GUZE L. B. Pyelonephritis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1960 Feb;39:3–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINSKY N. G., DAVIDSON D. G., BERLINER R. W. Effects of reduced glomerular filtration on urine concentration in the presence of antidiuretic hormone. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):730–740. doi: 10.1172/JCI103853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALVIN R. L., KUTCHAI H., OSTERMANN F. DECREASED NEPHRON POPULATION RESULTING FROM INCREASED URETERAL PRESSURE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Oct;207:835–839. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.4.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUSSAK N. J., OLEESKY S. Waterlosing nephritis, a syndrome simulating diabetes insipidus. Q J Med. 1954 Apr;23(90):147–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMPSON D. D., BARRETT M. J., PITTS R. F. Significance of glomerular perfusion in relation to variability of filtration rate. Am J Physiol. 1951 Nov;167(2):546–552. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.2.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANGIESEN G., REESE M., KIIL F., RECTOR F. C., Jr, SELDIN D. W. THE CHARACTERISTICS OF RENAL HYPOPERFUSION IN DOGS WITH ACUTE AND CHRONIC REDUCTIONS IN GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE AS DISCLOSED BY THE PATTERN OF WATER AND SOLUTE EXCRETION AFTER HYPOTONIC SALINE INFUSIONS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Mar;43:416–424. doi: 10.1172/JCI104926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON B., REISMAN D. D., MOYER C. A. Fluid balance in the urological patient: disturbances in the renal regulation of the excretion of water and sodium salts following decompression of the urinary bladder. J Urol. 1951 Dec;66(6):805–815. doi: 10.1016/S0022-5347(17)74418-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WINBERG J. Renal function in water-losing syndrome due to lower urinary tract obstruction before and after treatment. Acta Paediatr. 1959 Mar;48(2):149–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1959.tb16030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


