Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLYTHE W. B., WELT L. G. DISSOCIATION BETWEEN FILTERED LOAD OF SODIUM AND ITS RATE OF EXCRETION IN THE URINE. J Clin Invest. 1963 Sep;42:1491–1496. doi: 10.1172/JCI104833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARPENTER C. C., DAVIS J. O., HOLMAN J. E., AYERS C. R., BAHN R. C. Studies on the response of the transplanted kidney and the transplanted adrenal gland to thoracic inferior vena caval constriction. J Clin Invest. 1961 Feb;40:196–204. doi: 10.1172/JCI104245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. O., HOLMAN J. E., CARPENTER C. C., URQUHART J., HIGGINS J. T., Jr AN EXTRA-ADRENAL FACTOR ESSENTIAL FOR CHRONIC RENAL SODIUM RETENTION IN PRESENCE OF INCREASED SODIUM-RETAINING HORMONE. Circ Res. 1964 Jan;14:17–31. doi: 10.1161/01.res.14.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS J. O., HOWELL D. S., GOODKIND M. J., HYATT R. E. Accumulation of ascites during maintenance of adrenalectomized dogs with thoracic inferior vena cava constriction on a high sodium diet without hormone therapy. Am J Physiol. 1956 Apr;185(1):230–234. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.185.1.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WARDENER H. E., MILLS I. H., CLAPHAM W. F., HAYTER C. J. Studies on the efferent mechanism of the sodium diuresis which follows the administration of intravenous saline in the dog. Clin Sci. 1961 Oct;21:249–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
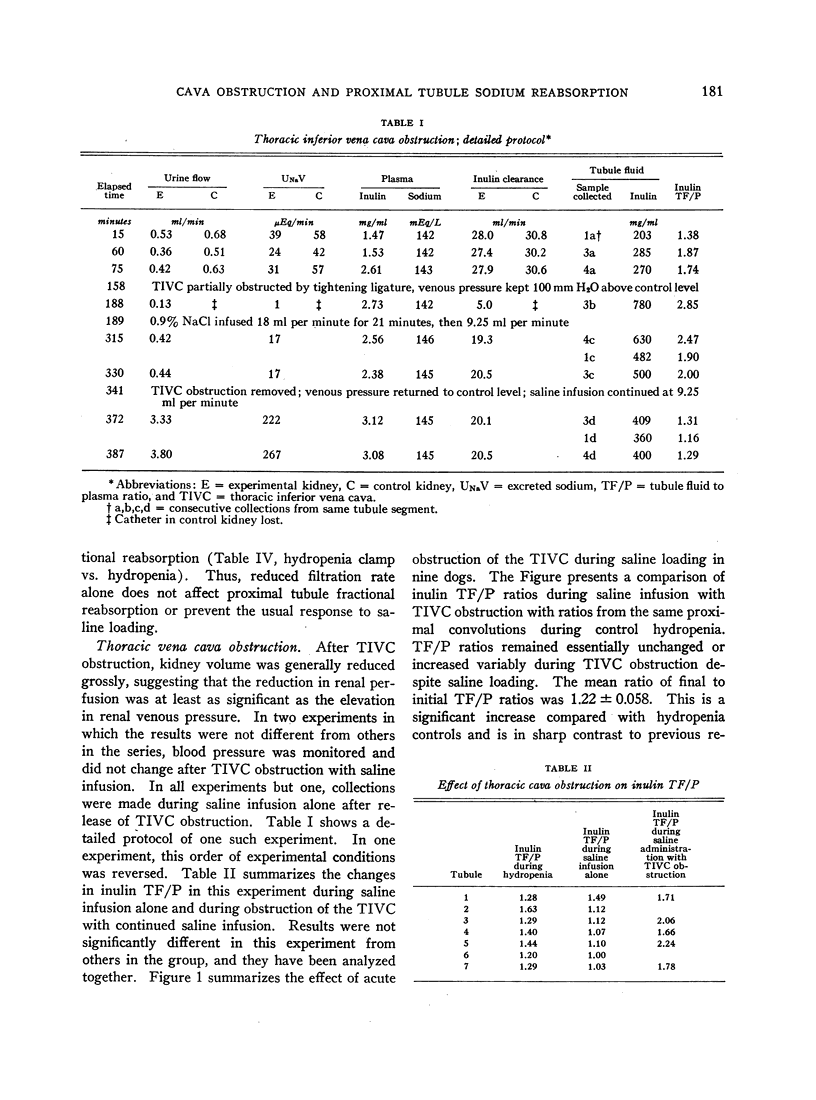
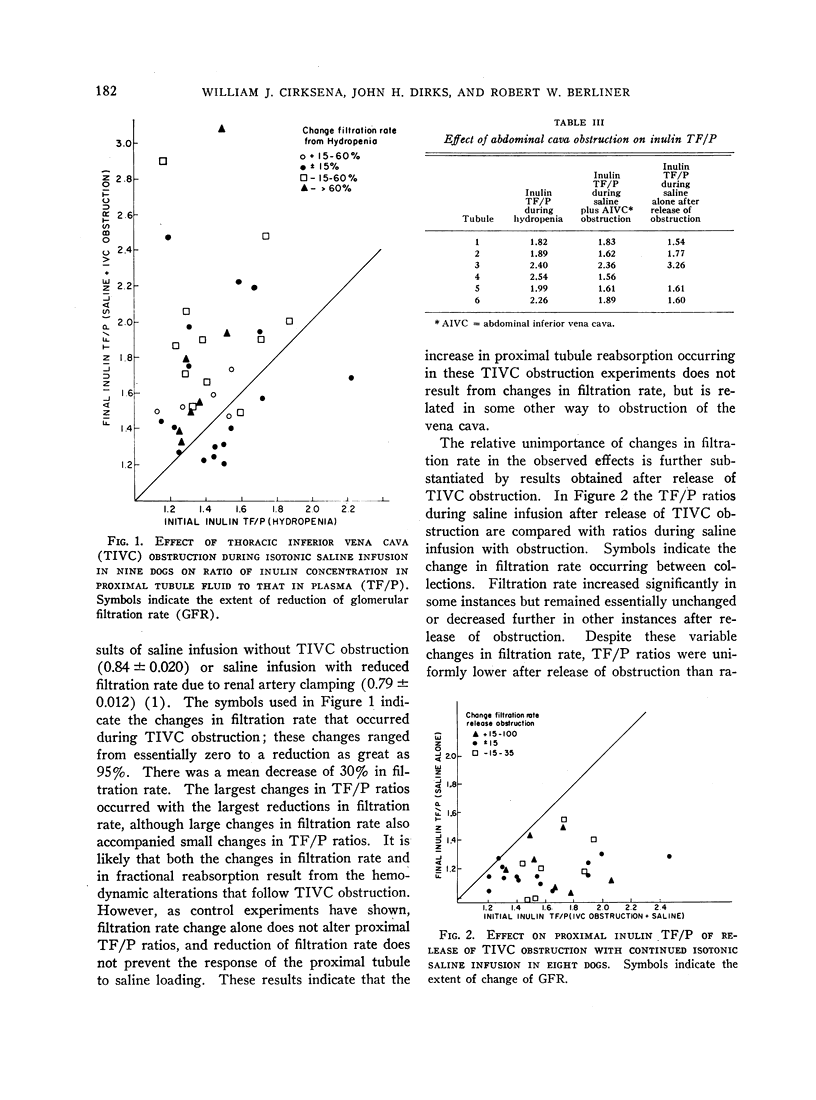
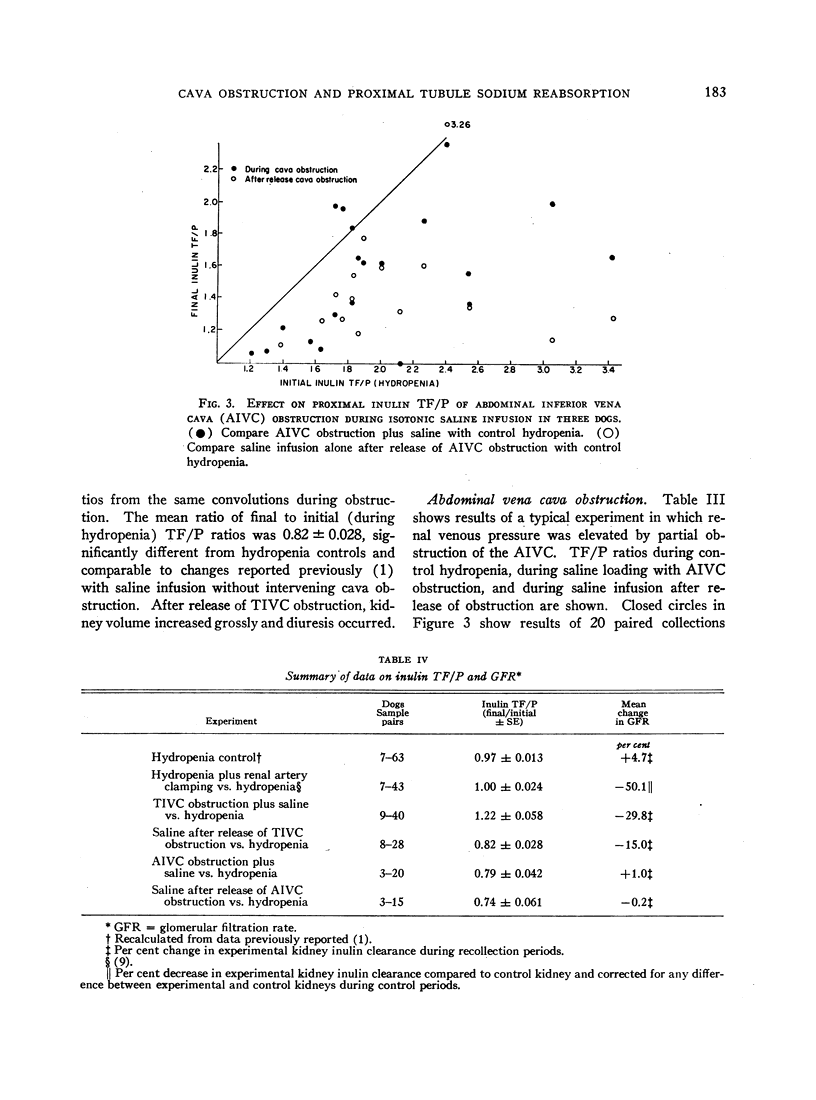
- DIRKS J. H., CIRKSENA W. J., BERLINER R. W. THE EFFECTS OF SALINE INFUSION ON SODIUM REABSORPTION BY THE PROXIMAL TUBULE OF THE DOG. J Clin Invest. 1965 Jul;44:1160–1170. doi: 10.1172/JCI105223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EARLY L. E., FRIEDLER R. M. OBSERVATIONS ON THE MECHANISM OF DECREASED TUBULAR REABSORPTION OF SODIUM AND WATER DURING SALINE LOADING. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1928–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI105067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUHR J., KACZMARCZYK J., KRUTTGEN C. D. Eine einfache colorimetrische Methode zur Inulinbestimmung für Nieren-Clearance-Untersuchungen bei Stoffwechselgesunden und Diabetikern. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 Aug 1;33(29-30):729–730. doi: 10.1007/BF01473295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINSKY N. G., LALONE R. C. SODIUM EXCRETION DURING ACUTE SALINE LOADING IN DOGS WITH VENA CAVAL CONSTRICTION. J Clin Invest. 1965 Apr;44:565–573. doi: 10.1172/JCI105169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINSKY N. G., LALONE R. C. THE MECHANISM OF SODIUM DURESIS AFTER SALINE INFUSION IN THE DOG. J Clin Invest. 1963 Aug;42:1261–1276. doi: 10.1172/JCI104811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLS I. H., DE WARDENER H. E., HAYTER C. J., CLAPHAM W. F. Studies on the afferent mechanism of the sodium chloride diuresis which follows intravenous saline in the dog. Clin Sci. 1961 Oct;21:259–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, VANGIESEN G., KIIL F., SELDIN D. W. INFLUENCE OF EXPANSION OF EXTRACELLULAR VOLUME ON TUBULAR REABSORPTION OF SODIUM INDEPENDENT OF CHANGES IN GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE AND ALDOSTERONE ACTIVITY. J Clin Invest. 1964 Mar;43:341–348. doi: 10.1172/JCI104919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


