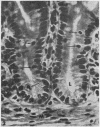
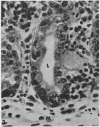
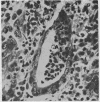
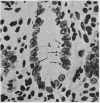
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOOM M. A. Acquired radioresistance of the crypt epithelium of the duodenum. Radiology. 1950 Jul;55(1):104–115. doi: 10.1148/55.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRANDBORG L. L., RUBIN G. E., QUINTON W. E. A multipurpose instrument for suction biopsy of the esophagus, stomach, small bowel, and colon. Gastroenterology. 1959 Jul;37(1):1–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSEN C. R., BOND V. P., RAI K. R., LIPPINCOTT S. W. ABSCOPAL EFFECTS OF LOCALIZED IRRADIATION BY ACCELERATOR BEAMS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Mar 31;114:302–315. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb53584.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPKIN M., SHERLOCK P., BELL B. CELL PROLIFERATION KINETICS IN THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT OF MAN. II. CELL RENEWAL IN STOMACH, ILEUM, COLON, AND RECTUM. Gastroenterology. 1963 Dec;45:721–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD W. C., TRIER J. S., EVERETT N. B. CELL PROLIFERATION AND MIGRATION IN THE STOMACH, DUODENUM, AND RECTUM OF MAN: RADIOAUTOGRAPHIC STUDIES. Gastroenterology. 1964 Apr;46:405–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADANAGOPALAN N., SHINER M., ROWE B. MEASUREMENTS OF SMALL INTESTINAL MUCOSA OBTAINED BY PERORAL BIOPSY. Am J Med. 1965 Jan;38:42–53. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90158-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLONIG G. A modified procedure for lead staining of thin sections. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Dec;11:736–739. doi: 10.1083/jcb.11.3.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PADYKULA H. A., STRAUSS E. W., LADMAN A. J., GARDNER F. H. A morphologic and histochemical analysis of the human jejunal epithelium in nontropical sprue. Gastroenterology. 1961 Jun;40:735–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUASTLER H., HAMPTON J. C. Effects of ionizing radiation on the fine structure and function of the intestinal epithelium of the mouse. I. Villus epithelium. Radiat Res. 1962 Dec;17:914–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUBIN C. E., BRANDBORG L. L., PHELPS P. C., TAYLOR H. C., Jr Studies of celiac disease. I. The apparent identical and specific nature of the duodenal and proximal jejunal lesion in celiac disease and idiopathic sprue. Gastroenterology. 1960 Jan;38:28–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAUER W. G. Factitial enteritis: an unusual cause of intestinal obstruction, chronic blood loss or malabsorption syndrome. J Iowa State Med Soc. 1960 Jan;50:1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHINER M., DONIACH I. Histopathologic studies in steatorrhea. Gastroenterology. 1960 Mar;38:419–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRIER J. S. Morphologic alterations induced by methotrexate in the mucosa of human proximal intestine. I. Serial observations by light microscopy. Gastroenterology. 1962 Mar;42:295–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROWELL O. A. The sensitivity of lymphocytes to ionising radiation. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Oct;64(4):687–704. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUMP B. F., SMUCKLER E. A., BENDITT E. P. A method for staining epoxy sections for light microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res. 1961 Aug;5:343–348. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(61)80011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YARDLEY J. H., BAYLESS T. M., NORTON J. H., HENDRIX T. R. Celiac disease. A study of the jejunal epithelium before and after a gluten-free diet. N Engl J Med. 1962 Dec 6;267:1173–1179. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196212062672303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]