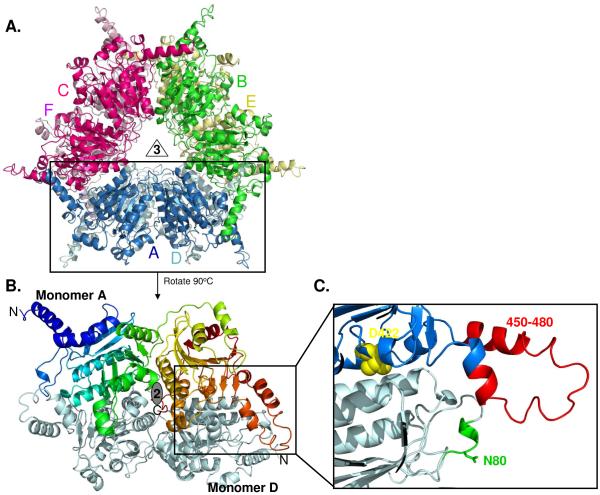
Fig. 2.
(A) The overall structures of all PccB mutants are highly similar as a hexamer, with each monomer in different color. (B) The PccB active site lies in between two monomers (in color and gray, respectively). (C) Zoom to the acyl-CoA binding pocket, showing the position of residue D422 at the “end” of the active site and the conformation of loops that contain N80 and R456 and R457, which define part of the acyl-CoA pocket entrance.