Abstract
We compared the occurrence and timing of divorce in 391 parents of children with an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and a matched representative sample of parents of children without disabilities using a survival analysis. Parents of children with an ASD had a higher rate of divorce than the comparison group (23.5% vs. 13.8%). The rate of divorce remained high throughout the son/daughter’s childhood, adolescence, and early adulthood for parents of children with an ASD, whereas it decreased following the son/daughter’s childhood (after about age 8 years) in the comparison group. Younger maternal age when the son/daughter with ASD was born and having the son/daughter born later in the birth order were positively predictive of divorce for parents of children with an ASD. Findings have implications for interventions focused on ameliorating ongoing and long term marital strains for parents of children with an ASD.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorders, Divorce, Marital Relationship, and Parent
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) are lifelong neurodevelopmental disorders involving a triad of impairments in communication, social reciprocity, and repetitive/restricted interests and behaviors (American Psychiatric Association, 2000). Parenting a son or daughter with an ASD poses several unique challenges (e.g., Seltzer, Krauss, Orsmond, & Vestal, 2001), which may take a toll on marriages. The extent of this toll in terms of divorce has been the topic of wide speculation in the media, with divorce rates of 80% and higher mentioned (Doherty, 2008; Solomon & Thierry, 2006), but the issue has not yet been addressed by empirical research. In this study, we compare the occurrence and timing of divorce among parents with an adolescent or adult with an ASD to a closely matched sample of parents of adolescents and adults without a disability drawn from a nationally representative sample. Family characteristics predictive of divorce are also identified.
Several studies have examined parental divorce in heterogeneous samples of children with a variety of disabilities or specific populations of children with disabilities other than ASD. Some of these studies indicate that parents of children with a disability have an increased risk of divorce as compared to parents of children without a disability (Breslau & Davis, 1986; Witt, Riley, & Coiro, 2003; Wymbs, Pelhma, Molina, Gnagy, Wilson, & Greenhouse, 2008). Other studies, however, have not shown an adverse impact of having a child with a disability on divorce (Josech & Smith, 1997; Urbano & Hodapp, 2007), possibly suggesting that some disabilities exact a heavy toll on marriages, while others have little impact (Josech & Smith, 1997; Risdal & Singer, 2004).
Few disabilities appear to be more taxing on parents than ASDs (Seltzer et al., 2001). Parents of children with an ASD fare worse on a variety of measures of wellbeing than parents of children without disabilities as well as parents of children with other types of disabilities (e.g., Abbeduto et al., 2004; Eisenhower, Baker, & Blacher, 2005). Several factors have been proposed to account for the poorer wellbeing of parents of children with an ASD including the uncertainty surrounding ASD diagnosis and the long-term prognosis of individuals with an ASD, the stressful nature of autistic symptoms and associated behavior problems, and the lack of public understanding of and tolerance for the behaviors of children with an ASD (Gray & Holden, 1992). Moreover, because of familial linkages, these parents may be caring for multiple children with special needs (Orsmond, Lin, & Seltzer, 2007), and are themselves at risk for evidencing a broader autism phenotype, which includes subtle impairments in social, communication, and restricted/repetitive interests and behaviors (e.g., Piven, 2001), and psychiatric symptoms (e.g., Szatmari et al., 1995). Thus, in addition to the challenging nature of ASD, some parents may have more limited resources to cope with these demands which may elevate their risk of family disruption, including marital dissolution.
In addition to examining the rate of divorce, it is important to understand the timing of divorce in families of children with an ASD to detect when couples may be most vulnerable to marital dissolution. Parents in the general population have the greatest risk of divorce during their son or daughters’ childhood, prior to the teenage years (Bramlett & Mosher, 2002; Cherlin, 1992; Shiono & Quinn, 1994). This vulnerability to divorce is believed to be related to the high-level of parenting demands and stress of having children and the subsequent reduction in responsiveness to the needs of one’s spouse during these years (e.g., Shapiro, Gottman, & Carrere, 2000; Shiono & Quinn, 1994). If couples can survive these early years, however, their risk of divorce decreases, although there may be another smaller increase in risk of divorce during midlife (Furstenberg & Kiernan, 2001; Cherlin, 1992). In contrast to this typical pattern, parents of sons and daughters with an ASD continue to experience a high-level of parenting demands and report elevated levels of stress beyond their son or daughter’s childhood and into their adolescence and adulthood (Abbeduto et al., 2004; Smith, Hong, Seltzer, Greenberg, Almeida, & Bishop, 2009). Thus, these parents may experience a prolonged period of vulnerability to divorce that starts in their son or daughter’s childhood and persists into their adolescence and adulthood.
It is also important to explore the family characteristics which place parents of children with an ASD at risk for divorce. In families of children without a disability, maternal ethnicity/race has been shown to be related to divorce, with some minority groups (e.g., African-Americans) evidencing an increased risk of divorce (Bramlett & Mosher, 2002; Tzerg & Mare, 1995). Risk of divorce is also higher if the parents are less educated, marry younger, and have children early in the marriage (Bramlett & Mosher, 2002; Karney & Bradbury, 1995; Ono, 2009). Younger maternal age and lower maternal education were also risk factors for divorce in parents of children with Down syndrome and other types of congenital disabilities (Urbano & Hodapp, 2007), and thus may have similar effects in families of children with an ASD.
Characteristics related to the child with an ASD may also be important predictors of parental divorce. Studies of children with disabilities indicate that parental stress and marital satisfaction are more strongly associated with the child’s behavior problems than his or her intellectual delay (e.g., Baker, Blacher, Crnic, & Edelbrock, 2002). Thus, while the presence of intellectual disability (ID) in addition to an ASD may not increase the risk of divorce, severity of aberrant behaviors may be related to marital dissolution. Having multiple children with an ASD in the family may also increase divorce, as parenting resources may be particularly taxed (Orsmond et al., 2007). Birth order of the child with an ASD may also play a role in the parental divorce. Urbano and Hodapp (2007) found that divorce was less likely in families of children with Down syndrome when the child was born later (i.e., second versus first born) in the birth order. It is unknown whether birth order is similarly predictive of divorce in families of children with an ASD.
In this study, we examined the occurrence and timing of divorce in 391 parents who have an adolescent or adult with an ASD, collected as part of an ongoing longitudinal study, as compared to a closely matched sample of 391 parents of adolescents and adults without a disability, drawn from a nationally-representative sample, using a survival analysis. We also examined whether correlates of divorce reported in the literature for parents in the general population and children with other types of disabilities also predicted divorce in parents of children with an ASD. We hypothesized that parents of children with an ASD would evidence more divorce than parents of children without a disability, and that the risk of divorce would remain high as their son or daughter moved through childhood, adolescence, and into adulthood. Mothers who were younger when they had their child and less educated were predicted to have a higher rate of divorce. The severity of the child’s aberrant behaviors and having multiple children with ASD in the family were also expected to be associated with an increased risk of divorce.
Method
Adolescents and Adults with Autism Study (AAA)
AAA is an ongoing longitudinal study of families of 406 adolescents and adults with an ASD in Massachusetts and Wisconsin (Lounds, Seltzer, Greenberg, & Shattuck, 2007; Seltzer, Krauss, Shattuck, Orsmond, Swe, & Lord, 2003). The present report uses data from the first (collected in 1998 – 1999) through fourth (collected in 2003 – 2004) waves of data collection, as data from the normative comparison group were also available for this same time period. Criteria for inclusion in the AAA study were that the son or daughter was age 10 or older at the beginning of the study, had received an ASD diagnosis (Autistic Disorder, Asperger Disorder, or PDD-NOS) from an educational or health professional, and had a research-administered Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R; Lord, Rutter, & Le Couteur, 1994) profile consistent with an ASD diagnosis. Almost all (94.6%) of the sons and daughters met the ADI-R lifetime criteria for a diagnosis of Autistic Disorder, and the remainder met criteria for Asperger Disorder or PDD-NOS. Approximately half of the participants lived in Wisconsin (n = 202), and half in Massachusetts (n = 204) and were recruited through service agencies, schools, and clinics.
The 406 adolescents and adults with an ASD included 11 children from families with more than one child with an ASD. In such families, one son or daughter with an ASD was selected to be the target child for the present analysis, according to the following criteria: 1) the child who lived in the family home; 2) the older child if both children were living at home, and 3) a child was randomly selected in the case of triplets, all of whom lived at home. In an additional 4 families, mothers had never married the biological father of the son or daughter with an ASD and these families were excluded from the present analyses, resulting in a sample for the present analysis of 391 families.
National Survey of Midlife in the United States (MIDUS)
The normative comparison group came from the Midlife in the United States(MIDUS) national survey of 7,108 English-speaking adults aged 25 to 74 years first completed in 1994–1996 (MIDUS I; Brim et al., 2004). A national random digit dialing sampling procedure was used. For each household contacted, a household member between 25 and 74 years of age was randomly selected and invited to participate in the study. Additionally, subsamples of siblings of these individuals and twins pairs, and oversamples from metropolitan areas were included (additional information can be found at http://www.midus.wisc.edu/). Follow-up data were collected in 2004–2006 (MIDUS II) from 4,963 (70%) of the MIDUS I participants. MIDUS II data were used to construct the comparison group for the present study because it coincided with the timing of the fourth wave of data collection in the AAA sample. Compared to the U.S. Census Bureau, the MIDUS sample was similar in demographics, with the exception of being slightly underrepresentive of adults with a high school education or less and African-Americans (Brim et al., 2004).
Of the MIDUS II participants, 4,316 (87.0%) were parents, but 433 (10.03%) reported that they had at least one child with a disability or mental health condition and were excluded, leaving 3,883 MIDUS participants as potential members of the comparison group for the present analysis. The following procedure was used to create a matched comparison group with the AAA sample. First, because we were interested in examining divorce related to a particular child (i.e., the child with an ASD), we randomly selected a target child within each MIDUS II family. Then the MIDUS II sample was stratified based on mother’s ethnicity (Caucasian vs. Non-Caucasian) and education level (less than high school, high school, some college, and more than college). Within each stratum, we created a random number associated with each case and ordered the cases according to their random number. Using this new random order of cases, we selected the first case that matched an AAA family based on mother’s ethnicity, education level, age (within 4 years) and index child’s sex, age (within 3 years) and birth order (first versus later born) until all of the AAA families were matched. Table 1 displays the participant characteristics of the 391 families in the MIDUS II comparison group.
Table 1.
Subject Characteristics of Families
| Characteristic | ASD (N = 391) | No Disability (N = 391) |
|---|---|---|
| Mother | ||
| Age in yrs (M, SD) | 56.1 (10.5) | 57.4 (10.0) |
| Range | 37.6 – 86.2 | 38.0 –84.9 |
| White, non-Hispanic (n, %) | 364 (93.1%) | 364 (93.1%) |
| > High school education (n, %) | 11 (2.8%) | 11 (2.8%) |
| High school graduate (n, %) | 95 (24.3%) | 95 (24.3%) |
| Some college/Bachelor’s degree (n, %) | 110 (28.1%) | 110 (28.1%) |
| Post Bachelor’s/Graduate degree (n, %) | 175 (44.8%) | 175 (44.8%) |
| Child | ||
| Biological (n, %) | 382 (97.7%) | 382 (97.7%) |
| Adoptive | 9 (2.3%) | 9 (2.3%) |
| Male (n, %) | 287 (73.4%) | 287 (73.4%) |
| Female | 104 (26.6%) | 104 (26.6%) |
| Age in yrs (M, SD) | 26.9 (9.5) | 27.8 (9.7) |
| Range | 14.6 – 56.9 | 13.88– 58.12 |
| First born (n, %) | 184 (47.1%) | 184 (47.1%) |
| Total # Children (M, SD) | 2.8 (1.3) | 2.8 (1.5) |
| Range | 1 –8 | 1 – 11 |
Note. Race/ethnicity breakdown for ASD: African-American (8), Hispanic (7), American Indian (2), Asian or Pacific Islander (6), and other (4). Race/ethnicity breakdown for No Disability: African-American (10), Hispanic (7), American Indian (2), Asian or Pacific Islander (2), and other (6).
There was not a significant difference on any of the matched variables between the AAA and MIDUS II comparison groups. Although not used in matching, there also was not a significant difference in total number of children between the AAA and MIDUS II comparison groups. There was not a significant difference in the average length of marriages (in years) of the biological/adoptive parents of the target child for couples who did not divorce between the AAA (M = 26.56, SD = 9.50) and MIDUS II (M = 27.54, SD = 9.47) groups.
Procedure and Measures
Mothers in the AAA sample participated in 2-to-3 hour, in-home interviews and completed self-administered measures. Parents in the MIDUS II sample participated in an hour-long telephone interview and completed self-administered measures.
Divorce
Information on divorce was collected through self-reported questionnaires in the AAA sample and telephone interviews in the MIDUS II sample. Only divorce involving the biological/adoptive parents of the target child was examined. The month and year the divorce was finalized was used in analyses. Of the 391 AAA families, 84 dropped out of the study prior to the fourth wave of data collection. Drop outs occurred because the family decided to no longer participate in the study (n = 64) or the family could not be located (n = 20). In an additional 6 families, either the mother or child with an ASD died. Information on divorce in these 90 cases was obtained through searching the publicly accessible divorce records using the online Wisconsin Circuit Court Access system and the Massachusetts county court records. Records were searched using mothers’ first and last names and then verified using mother’s date of birth, address, and husband’s first and last name.
There were 10 cases in the AAA sample for which mothers reported being divorced, but the date of divorce could not be obtained by searching the Massachusetts or Wisconsin divorce records. It is likely that these families divorced in another state. Similarly, there were 6 cases in the MIDUS II comparison group for which mothers reported being divorced but did not report the date of divorce. These cases were not included in analyses regarding the timing of divorce.
Characteristics of Families
We examined characteristics of the family as predictors of divorce, including mother’s age, race/ethnicity (White, non-Hispanic versus other), education (less than a high school degree, high school degree or some college, college graduate, and more than college degree), and age when the target child was born. We also examined the target child’s age, sex, and birth order (first versus later born) and family size (single child versus multiple children).
For families of children with an ASD, the presence of ID was determined by assessing cognitive functioning on the Wide Range Intelligence Test (Glutting, Adams, & Sheslow, 2000) and adaptive behavior on the Vineland Screener (Sparrow, Carter, & Cicchetti, 1993). These assessments were administered in 2004. Children with scores above 75 on both measures were classified as not having ID and those with scores below 75 on both measures were classified as having ID. For children with scores below 75 on only one of the two measures, or for whom there were missing data, a review of available records (historical assessments; parent report of prior diagnoses; clinical and school records) combined with a clinical consensus procedure was used to determine ID status.
Aberrant behaviors were assessed through two measures of the child’s autism symptoms: report of their child’s age when problems were first noticed and the Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised (ADI-R; Lord, Rutter, & Le Couteur, 1994) lifetime rating, or rating of autism symptoms at their most severe manifestation (mainly rated at age 4 –5 years). These measures were chosen because they capture the child’s aberrant behavior preceding the divorce in most cases. The ADI-R has good test-retest reliability, and diagnostic and convergent validity, (Hill, Bolte, Petrova, Beltcheva, Tacheva, & Poustka, 2001; Lord et al., 1997). The average inter-rater agreement between interviewers and two supervising psychologists in the present study was 88%. Items on the ADI-R are coded as 0 (symptom not present), 1 (symptom present but not severe/frequent enough to meet criterion), 2 (symptom present and meets criterion). A score of 3 is recoded as a 2 in the algorithm. In order to include nonverbal children with ASD, as well as verbal children, verbal items were excluded from this summary score.
Data Analysis Plan
The prevalence of divorce in the 391 parents of children with an ASD was statistically compared against the matched sample of 391 parents of children without a disability using Pearson’s chi-square test. A Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was conducted to evaluate differences in the marriage survival distributions of parents of children with an ASD and parents of children without a disability. This is a method for modeling time to event data; in this context, divorce is the event and years of marriage following the birth of the target child (i.e., latency to divorce following the birth of the child) is the time variable. The Kaplan-Meier survival analysis has the advantage of accounting for “censored” data (i.e., likelihood that divorce occurs subsequent to the end of data collection). The 381 families of children with an ASD and 385 families of children without a disability for whom years married following the birth of the target child could be determined were included in the survival analysis. The Breslow statistic was used to test for differences in latency to divorce between parents of children with an ASD and parents of children without a disability (Breslow, 1979).
Binary logistic regression analyses were conducted to examine the impact of family characteristics on divorce in parents of children with an ASD and parents of children without a disability. This analysis provides the relative risk ratios (i.e., likelihood of divorce) given the presence of a specific risk factor, controlling other risk factors. Mother’s education (0 = less than college degree, 1 = College degree of more), race/ethnicity (0 = White, non-Hispanic, 1 = other), maternal age when the target child was born (in years), target child sex (0 = female, 1 = male), family size (0 = single child, 1 = multiple children), and birth order (0 = first born, 1 = later born) were entered into the regression model for both parents of children with and without an ASD. The following ASD-specific variables were also entered into the model for parents of children with an ASD: age when problems were first noticed (in months), ADI-R lifetime score, and presence of other children with an ASD in the family (0 = no, 1 = yes).
Results
Prevalence and Timing of Divorce
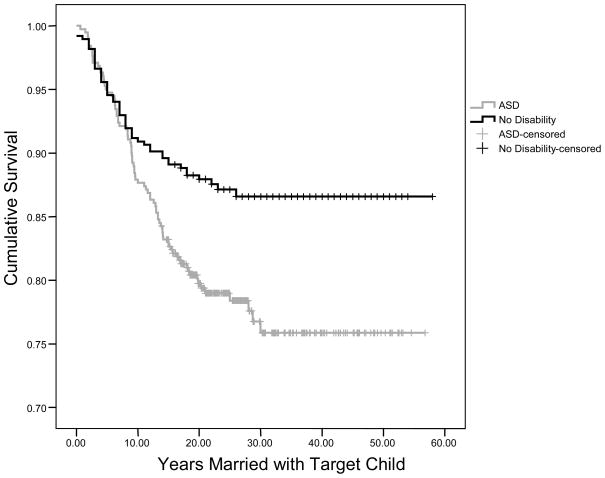
The prevalence of divorce was significantly higher among the parents of children with an ASD (n = 92, 23.53%) than the parents of children without a disability (n = 54, 13.81%), Pearson’s χ2 (df = 1, n = 781) = 12.16, p < .001). As shown in Figure 1, there was a significant difference in the survival distributions of parents of children with an ASD and parents of children without a disability (Breslow χ2 = 8.55, df = 1, p = .003). The rate of decline in remaining marriages for parents of children without a disability tapers off in the target child’s late childhood (i.e., about age 8 years), and continues to flatten out until the target child has reached age 26 years, when the rate of divorce is virtually non-existent. In other words, the risk of divorce begins to decrease in the son/daughter’s late childhood for parents of children without a disability, and is extremely low by the time the son/daughter is a young adult. In contrast, the risk of divorce for parents of children with an ASD remains steep throughout the son/daughter’s adolescence and early adulthood and does not decrease until the target child has reached age 30 years. Thus, parents of children with an ASD continue to have a high risk of divorce through the son/daughter’s childhood, adolescence, and early adulthood.
Figure 1.
Survival plot for divorce in parents of children with an autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and parents of children without a disability.
Follow-up Analyses
Follow-up analyses were conducted to ensure that results were robust against possible selection differences between the two samples. First, we examined the impact of parent death on the prevalence of divorce. Of the couples who did not experience a divorce, a parent death occurred in 33 (8.43%) AAA families and 37 (9.46%) MIDUS II families, which is not a significant difference. Because divorce is no longer an option for these families, we re-ran the survival analysis excluding these cases. Parents of children with an ASD continued to have a shorter latency to divorce than parents of children without a disability (Breslow χ2 = 9.24, df = 1, p = .002). The pattern of decline in marriages did not change.
Second, we performed a series of calculations to estimate the impact of differences in the way that dropouts were handled within our two samples. To obtain complete divorce information through 2004 for both groups, our comparison group of families of children without a disability was selected from the second wave of MIDUS data collection (MIDUS II) and thus families who dropped out of the study prior to 2004 were not included. In contrast, all families of children with an ASD originally enrolled in the AAA study were included in this sample by searching divorce records for the 84 families who dropped out of the study prior to 2004. We recalculated the Pearson chi-square statistic for the overall likelihood of divorce using the smaller sample of 307 AAA families who remained in the study through 2004 and 307 matched MIDUS II families. The prevalence of divorce continued to be significantly higher among the parents of children with an ASD (n = 72, 23.92%) than the parents of children without a disability (n = 47, 15.60%), Pearson’s χ2 (df = 1, n = 601) = 6.03, p = .01. Results from the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis for this smaller sample continued to indicate that parents of children with an ASD had a shorter latency to divorce than parents of children without a disability (Breslow χ2 = 4.90, df = 1, p = .03). The pattern of decline in marriages was also similar.
Third, we examined whether the prevalence of divorce differed within the states from which the two samples were drawn. The MIDUS II comparison group included families living in 45 states, whereas the AAA families resided in Wisconsin or Massachusetts. The averaged divorce rate (per 1,000 total population residing in the state) reported by the Division of Vital Statistics, National Center for Health Statistics, Center for Disease Control (Center for Disease Control, 2007) for Wisconsin and Massachusetts, is lower than the national average divorce rate by a magnitude of 0.38. Thus, the heightened prevalence of divorce in parents of children with an ASD as compared to parents of children without a disability may be more pronounced than what was captured in our study. However, by closely matching our samples on maternal characteristics, regional differences in divorce rates may have been accounted for in our analyses.
Family Characteristic Predictors of Divorce
Table 2 presents the binary logistic regression results for the impact of family characteristics on divorce in parents of children with an ASD and without a disability. For parents of children with an ASD, maternal age at which she had the target child and birth order significantly predicted divorce. The rate of divorce was greater when mothers were younger when they had the child with an ASD and when the child with an ASD was born later in the birth order. The effect size is reported with respect to the odds ratio (i.e., exp (B), indicating how the odds of divorce change for each unit change in the predictor). For example, the odds ratio effect size of .90 for maternal age at childbirth implies that the odds ratio of divorce decreases by multiples of .90 for each year increase in maternal age, assuming all other variables are equal. There were no significant family characteristic predictors of divorce in the comparison group.
Table 2.
Statistics for Binary Logistic Regression Assessing Prospective Prediction of Divorce
| B | SE | Wald | Odds Ratio Exp (B) | CI (95%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASD | |||||
| Constant | 2.69 | 1.71 | 2.49 | 14.76 | --------- |
| Mother | |||||
| Education | −0.06 | 0.27 | 0.05 | 1.06 | 0.63 – 1.80 |
| Race/ethnicity | −0.07 | 0.52 | 0.02 | 0.93 | 0.33 – 2.56 |
| Age had child | −0.11 | 0.03 | 12.94** | 0.90 | 0.85 – 0.95 |
| Child | |||||
| Sex | 0.58 | 0.31 | 3.41 | 1.78 | 0.97 – 3.27 |
| Birth order | 0.82 | 0.31 | 7.19** | 0.44 | 0.24 – 0.80 |
| Family size | −0.49 | 0.45 | 1.15 | 1.63 | 0.67 – 3.95 |
| ID | 0.33 | 0.30 | 1.19 | 0.72 | 0.40 – 1.30 |
| Age first noticed problems | −0.01 | 0.01 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.97 – 1.01 |
| ADI-R lifetime | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.80 | 0.98 | 0.94 – 1.02 |
| Siblings with an ASD | 0.17 | 0.85 | 0.04 | 1.18 | 0.23 – 6.19 |
| No Disability | |||||
| Constant | −1.50 | 1.20 | 1.57 | 0.22 | --------- |
| Mother | |||||
| Education | −0.56 | 0.34 | 2.68 | 1.74 | 0.84 – 3.08 |
| Race/ethnicity | −0.93 | 0.49 | 3.63 | 2.53 | 0.97 – 6.55 |
| Age had child | −0.04 | 0.03 | 1.64 | 0.96 | 0.89 – 1.01 |
| Child | |||||
| Sex | 0.71 | 0.41 | 2.99 | 2.03 | 0.91 – 4.52 |
| Birth order | −0.06 | 0.36 | 0.02 | 0.95 | 0.47 – 1.90 |
| Family size | 0.31 | 0.60 | 0.27 | 0.73 | 0.23 – 2.38 |
| ID | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
| Age first noticed problems | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
| ADI-R lifetime | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
| Siblings with an ASD | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ | ------ |
Note.
P ≤ .05,
P ≤ .01.
ASD: overall χ2 (n =382, df = 8) = 23.90, p =.01, Nagelkerke R2 = 0.09. + P ≤ .10. No ASD: χ2 (n =385, df = 5) = 15.46, p =.02, Nagelkerke R2 = 0.07. Education: Less than a college degree = 0, College degree or more = 1. Race/ethnicity: White, non-Hispanic = 0, other = 1. Child Sex: Females = 0, Males = 1. Birth order: First born = 0, Later born = 1. Family Size: Single child = 0, Multiple children = 1. ID: No ID = 0, ID = 1. Siblings with ASD: No = 0, Yes = 1.
Discussion
This study is the first systematic examination of the relative risk and timing of divorce in a large sample of parents of children with an ASD. The present study also constitutes the first step toward identifying family characteristic predictors of divorce within families of children with an ASD. Fully three-fourths of the marriages of parents of children with an ASD in our sample remained intact, at least through the time of the present analysis, indicating that most marriages survive despite having a child with an ASD. Nevertheless, the rate of divorce was nearly twice the rate of the comparison group, which was closely matched on key characteristics and drawn from a nationally representative sample. The heightened risk of divorce in parents of children with an ASD is consistent with findings that these families experience an extraordinary level of stress (e.g., Seltzer et al., 2001; Smith et al., 2009). This finding is similar to the heightened rate of divorce found in parents of children with ADHD, who were also twice as likely to divorce as parents of typically developing children (Wymbs et al., 2008).
As expected, parents of children with an ASD had a prolonged period of vulnerability to divorce. Specifically, there was a relatively high, and equivalent, risk of divorce for both the comparison group and families of children with an ASD during the son or daughter’s early childhood (until age 8 years). However, the risk of divorce markedly decreased in the son or daughter’s late childhood for our comparison group. A similar pattern has been found in the general population; the risk of divorce has been shown to be highest during the first several years of marriage, when children are young (e.g., Bramlett & Mosher, 2002; Shino & Quinn, 1994), and in part, is attributed to the high-level of parenting demands and stress and subsequent lack of attention devoted to one’s spouse during these years (Shapiro et al., 2000). As children without a disability age they launch into their own independent lives and parenting demands and stress often decrease, affording a renewed focus on the marital relationship. In contrast to this normative pattern, the risk of divorce remained high into the son or daughter’s early adulthood (age 30 years) for parents of children with an ASD. Parents of children with an ASD often continue to have a “full nest” (i.e., children living at home) (Seltzer et a., 2000) and high-levels of parenting demands and stress (e.g., Smith et al., 2010), and subsequently may continue to experience marital strain, into their son or daughter’s early adulthood. In our sample, nearly all (94.6%) of the parents who divorced, co-resided with their son/daughter with ASD at the time of their divorce. Moreover, parents are faced with a unique set of challenges as their son or daughter with an ASD ages into adolescence and adulthood, including assisting their son or daughter in transitioning out of school and into job and community settings and planning for long-term care, which may add new strain on parents’ marriages. Interestingly, there was not a significant difference in the prevalence of divorce between parents of children with an ASD and our comparison group during the son or daughter’s early childhood (prior to age 8 years). Although different in nature, the challenges of having a young child with an ASD may not place more strain on marriages than the challenges of having a young child without a disability, given that parenting demands and stress are high in both cases.
There were significant family characteristic predictors of divorce. As expected, mothers of children with an ASD who were younger when they had their child were at greater risk of divorce. This finding has also been shown in studies of parents of children without a disability (e.g., Bramlett & Mosher, 2002) as well as parents of children with Down syndrome (Urbano & Hodapp, 2007), although it was not significantly associated with divorce in our comparison group. An elevated rate of divorce was also related to having a child with an ASD later in the birth order (i.e., second or later born). This finding is in contrast to findings of an increased risk of divorce being related to earlier birth order in families of children with Down syndrome (Urbano & Hodapp, 2007). The mechanisms driving this syndrome difference are not clear and should be examined in future studies. Birth order of the target child was not significantly related to divorce in families of children without a disability. Unexpectedly, there was not a significant relation between having multiple children with an ASD and divorce, which may be due to the small number of families (n = 10) with more than one child with an ASD in our sample.
In contrast to our prediction, onset and severity of early autism symptoms were also not significantly predictive of divorce. This finding may be related to several factors. First, dimensions of autism symptoms (e.g., predictability and course over-time) other than onset and severity of early autism symptoms may take a greater toll on parents’ marriages. Moreover, among parents of children with an ASD parenting stress is often more related to co-occurring behavior problems (e.g., aggression and hyperactivity) than autism symptoms (e.g., Lecavalier, Leone, & Wiltz, 2006). Thus, it may be that these co-occurring behavior problems are also more predictive of divorce within families of children with an ASD than autism symptoms. Second, parents’ coping strategies and or their own presence of a broader autism phenotype (i.e., milder autism features and impairments) and psychiatric problems may greatly moderate the degree to which their child’s autism symptoms impact marriages. The mechanisms leading to divorce likely involve cascading effects of the interplay of these and other family characteristics with spousal behaviors and life experiences over time and should be the focus of future studies with larger sized samples and a longer follow-up period.
There are several other limitations to this study. Our comparison group, which was selected from a large study of adults in their midlife (MIDUS), has the advantage of offering a normative sample of families of children without a disability. A disadvantage of this comparison group is that the sampling procedures differed from those used in the AAA study. However, several follow-up analyses were conducted and these sampling difference were estimated to have little impact on the overall pattern of findings in the survival analysis. The prevalence of divorce may have been slightly underestimated in our sample of parents of children with an ASD. Our sample of families of children with an ASD resided in Wisconsin and Massachusetts, states with relatively low rates of divorce, whereas our comparison group was located throughout the United States. The heightened risk of divorce in parents of children with an ASD may be more pronounced when controlling for this regional difference. However, by closely matching on several maternal characteristics, we likely accounted for some of the regional difference between our groups. It is also possible that divorced parents were less likely to volunteer for the study. Also, parents who dropped out the study may have gotten a divorce in a state other than Wisconsin and Massachusetts and were thus falsely counted as not divorced. Moreover, the prevalence of divorces occurring at later stages (i.e., during the child’s middle to late adulthood) may not have been fully captured in this study. Generalizations of findings from this study should be made cautiously. The rate, timing, and correlates of divorce in families who do not participate in research studies may differ from those of families who do participate. Families in this study were also predominately White, non-Hispanic and college-educated, and thus findings may not generalize to less educated, and minority families of children with an ASD. Finally, family characteristics including the onset and severity of the child’s autism symptoms were reported on by mothers and may be open to bias and representative of fathers’ perspectives. However, the likelihood that maternal perceptions biased ratings of autism symptoms is low given that the ADI-R has a standardized interview procedure and trained coding system.
Even given these limitations, this study provides the first large-scale examinations of divorce in parents of children with an ASD using a closely matched comparison group. Findings have important implications for enhancing services for families of children with an ASD. Service providers should be educated about the heightened risk and timing of divorce in families of children an ASD. Parents should be guided in identifying strategies to enhance their marital relationship in an ongoing way, such as learning how to best communicate with and support their spouse and carving out “couple time.” Given their prolonged period of vulnerability to divorce, couples may need to remain vigilant to recurring and compounding marital strains throughout the course of their child’s development, including into adulthood. Finally, it may be reassuring for parents to know that most marriages survive and thus their marriage is not destined for divorce, as is often incorrectly presented in the media.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants R01 HD24356, P01 HD03352, and T32 HD07489. We are grateful to the families who participated for their continued support and generosity.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: The following manuscript is the final accepted manuscript. It has not been subjected to the final copyediting, fact-checking, and proofreading required for formal publication. It is not the definitive, publisher-authenticated version. The American Psychological Association and its Council of Editors disclaim any responsibility or liabilities for errors or omissions of this manuscript version, any version derived from this manuscript by NIH, or other third parties. The published version is available at www.apa.org/pubs/journals/fam
Contributor Information
Sigan L. Hartley, Waisman Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Erin T. Barker, Waisman Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison
Marsha Mailick Seltzer, Waisman Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Frank Floyd, Georgia State University.
Jan Greenberg, Waisman Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Gael Orsmond, Boston University.
Daniel Bolt, Waisman Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison.
References
- Abbeduto L, Seltzer MM, Shattuck P, Krauss MW, Orsmond G, Murphey M. Stress and coping in mothers of youths with Down syndrome, autism, and Fragile X syndrome. American Journal on Mental Retardation. 2004;109:237–254. doi: 10.1352/0895-8017(2004)109<237:PWACIM>2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. Washington, DC: Author; 2000. Text Revision. [Google Scholar]
- Baker BL, Blacher J, Crnic KA, Edelbrock C. Behavior problems and parenting stress in families of three-year-old children with and without developmental delays. American Journal of Mental Retardation. 2002;107:433–444. doi: 10.1352/0895-8017(2002)107<0433:BPAPSI>2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bramlett MD, Mosher WD. Cohabitation, marriage, divorce, and remarriage in the United States. Vol. 23. Washington, DC: National Center for Health Statistics; 2002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslau NN, Davis GC. Chronic stress and major depression. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1986;43:309–314. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1986.01800040015003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brim OG, Ryff CD, Kessler RC. The MIDUS national survey: An overview. In: Brim OG, Ryff CD, Kessler RC, editors. How healthy are we?: A national study of well-being at midlife. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 2004. pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Bristol MM, Gallagher JJ, Schopler E. Mothers and fathers of young developmentally disabled and nondisabled boys: Adaptation and spousal support. Developmental Psychology. 1988;24:441–451. [Google Scholar]
- Cherlin A. Marriage, Divorce, and Remarriage. Cambridge: Harvard University Press; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Center for Disease Control, National Center for Health Statistics, Division of Vital Statistics. Retrieved on February 20 from www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvss/Divorce%20Rates%2090%2095%20and%2099-07.pdf.
- Doherty S. Arrested development the day-to-day struggles of autistic children affect entire family. The Capital Times. 2008 July 2;:25. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhower AS, Baker BL, Blacher J. Preschool children with intellectual disability: Syndrome specificity, behaviour problems, and maternal well-being. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research. 2005;49:657–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.2005.00699.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furtenberg FF, Kiernan KE. Delayed parental divorce: How much do children benefit? Journal of Marriage and the Family. 2001;63:446–457. [Google Scholar]
- Gray DE, Holden WJ. Psycho-social well-being among parents of children with autism. Australia and New Zealand Journal of Developmental Disabilities. 1992;18:83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Glutting J, Adams W, Sheslow D. Wide Range Intelligence Test. Wilmington, D.E: Wide Range, Inc; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hodapp RM, Urbano RC. Adult siblings of individuals with Down syndrome versus with autism: Findings from a large-scale US survey. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research. 2007;51:1018–1029. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.2007.00994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlin P, Asgharian A. The diagnosis of autism and Asperger syndrome: Findings from a survey of 770 families. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology. 1999;41:834–839. doi: 10.1017/s0012162299001656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joesch JM, Smith KR. Children’s health and their mother’s risk of divorce or separation. Social Biology. 1997;44:159–169. doi: 10.1080/19485565.1997.9988944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karney BR, Bradbury TN. The longitudinal course of marital quality and stability: A review of theory, method, and research. Psychological Bulletin. 1995;118:3–34. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.118.1.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecavalier L, Leone S, Wiltz J. The impact of behaviour problems on caregiver stress in young people with autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research. 2006;50:172–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2788.2005.00732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lord C, Rutter M, LeCouteur A. Autism Diagnostic Interview-Revised: A revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 1994;24:659–685. doi: 10.1007/BF02172145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lounds J, Seltzer MM, Greenberg JS, Shattuck P. Transition and change in adolescent and young adults with autism: Longitudinal effects on maternal well-being. American Journal on Mental Retardation. 2007;112:401–417. doi: 10.1352/0895-8017(2007)112[401:TACIAA]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono H. Husbands’ and wives’ education divorce in the United States and Japan, 1946–2000. Journal of Family History. 200;34:292–322. [Google Scholar]
- Orsmond GI, Lin LY, Seltzer MM. Mothers of adolescents and adults with autism: Parenting multiple children with disabilities. Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities. 2007;45:257–260. doi: 10.1352/1934-9556(2007)45[257:MOAAAW]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piven J. The broad autism phenotype: A complementary strategy for molecular genetic studies of autism. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 2001;105:34–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risdal D, Singer GH. Marital adjustment in parents of children with disabilities: A historical review and meta-analysis. Research and Practice for Persons with Severe Disabilities. 2004;29:95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer MM, Krauss MW, Orsmond GI, Vestal C. Families of adolescents and adults with autism: Uncharted territory. In: Glidden LM, editor. International review of research on mental retardation. Vol. 23. San Diego: Academic Press; 2001. pp. 267–294. [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer MM, Krauss MW, Shattuck PT, Orsmond G, Swe A, Lord C. The symptoms of Autism Spectrum Disorders in adolescence and adulthood. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 2003;33:565–581. doi: 10.1023/b:jadd.0000005995.02453.0b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro AF, Gottman JM, Carrere S. The baby and the marriage: Identifying factors that buffer against decline in marital satisfaction after the first baby arrives. Journal of Family Psychology. 2000;14:59–70. doi: 10.1037//0893-3200.14.1.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiono PH, Quinn LS. Epidemiology of divorce. Future of Children. 1994;4:15–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith LE, Hong J, Seltzer MM, Greenberg JS, Almeida DM, Bishop SL. Daily Experiences Among Mothers of Adolescents and Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 2009 doi: 10.1007/s10803-009-0844-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, E., & Thierry, L. (Producer) and Thierry, L. (Director). (2006). Autism everyday [motion picture]. USA. Autism Speaks.
- Sparrow SS, Carter AS, Cicchetti DV. Vineland Screener: Overview, reliability, validity, administration, and scoring. New Haven, CT: Yale University Child Study Center; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Szatmari P, Jones MB, Fisman S, Tuff L, Bartulucci G, Mahoney WJ, et al. Parent and collateral relatives of children with pervasive developmental disorders: A family history study. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 1995;60:282–290. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320600405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzeng JM, Mare RD. Labor market and socioeconomic effects on marital stability. Social Science Research. 1995;24:329–351. [Google Scholar]
- Urbano RC, Hodapp RM. Divorce in families of children with Down syndrome: A population-based study. American Journal on Mental Retardation. 2007;112:61–274. doi: 10.1352/0895-8017(2007)112[261:DIFOCW]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiggins LD, Baio J, Rice C. Examination of the time between first evaluation and first autism spectrum diagnosis in a population-based sample. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics. 2006;27:S79–87. doi: 10.1097/00004703-200604002-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt WP, Riley AW, Coiro MJ. Childhood functional status, family stressors, and psychological adjustment among school-aged children with disabilities in the United States. Archives of Pediatric Adolescent Medicine. 2003;157:687–695. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.157.7.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wymbs BT, Pelham WE, Molina BSG, Gnagy EM, Wilson TK. Rate and predictors of divorce among parents of youths with ADHD. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 2008;76:735–744. doi: 10.1037/a0012719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]