Abstract
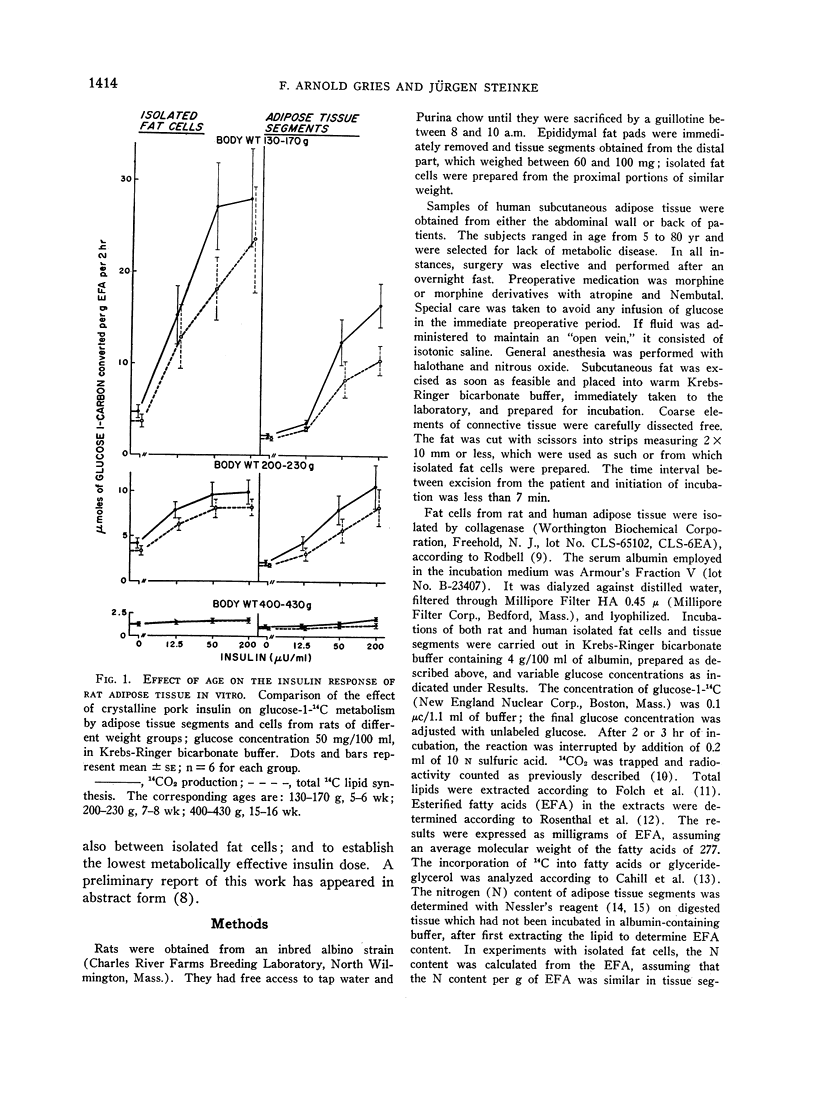
In vitro metabolism of glucose-1-14C by adipose tissue into 14CO2 and total 14C lipids in rat and man was compared employing both adipose tissue segments and isolated fat cells prepared from the same donor. In the rat, the basal glucose metabolism and response to insulin decreased with increasing body weight for both adipose tissue segments and isolated cells. Regardless of age, the isolated cells exhibited a persistently higher metabolic activity. Of the parameters selected, conversion to CO2 was more pronounced than that to lipid.
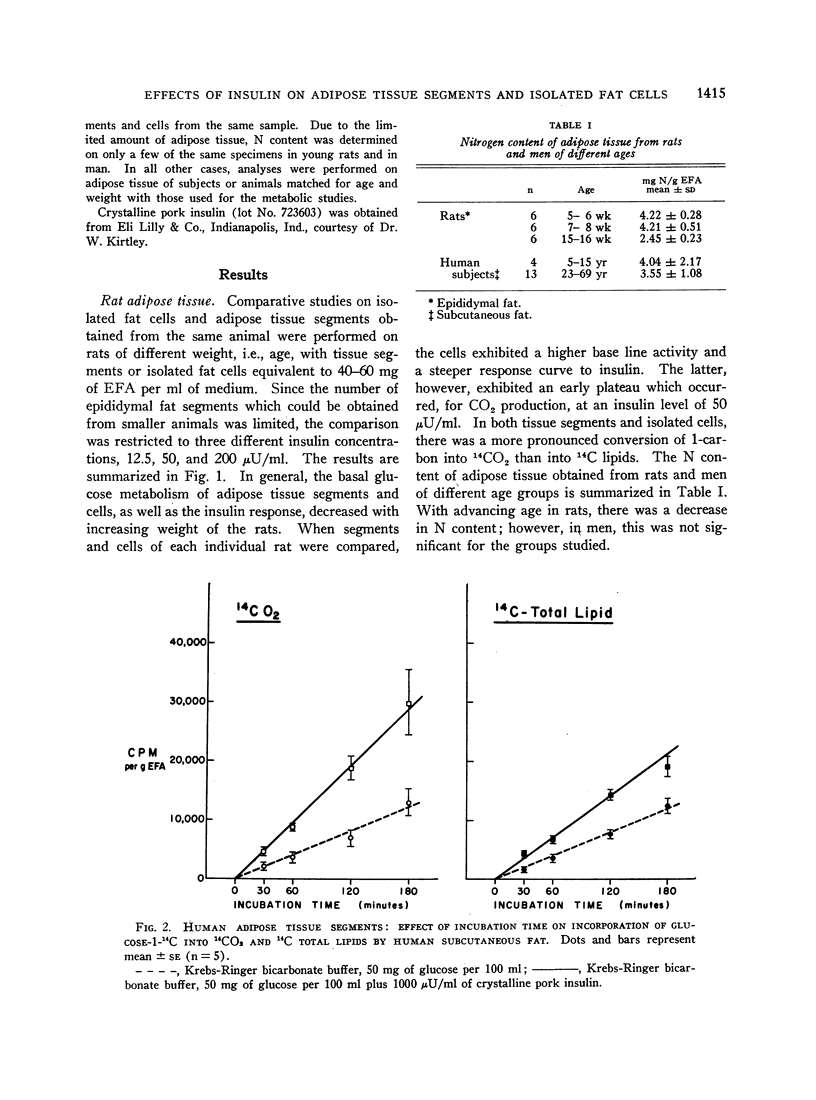
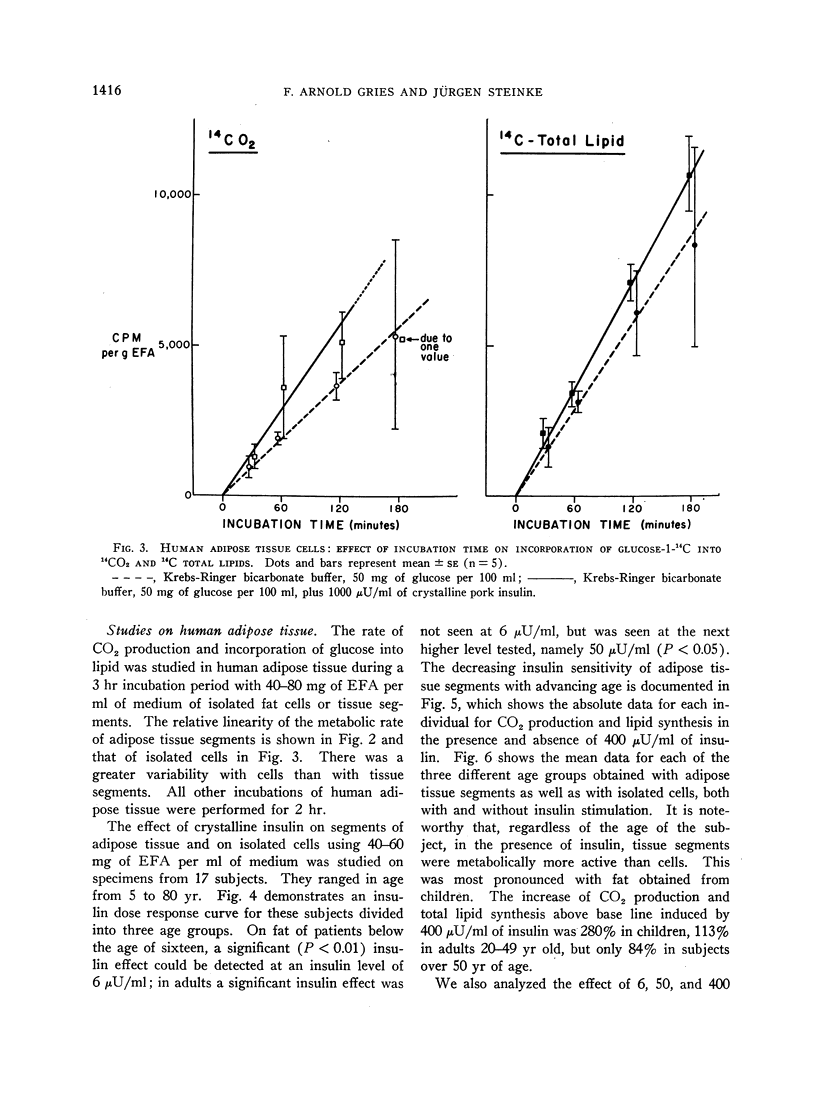
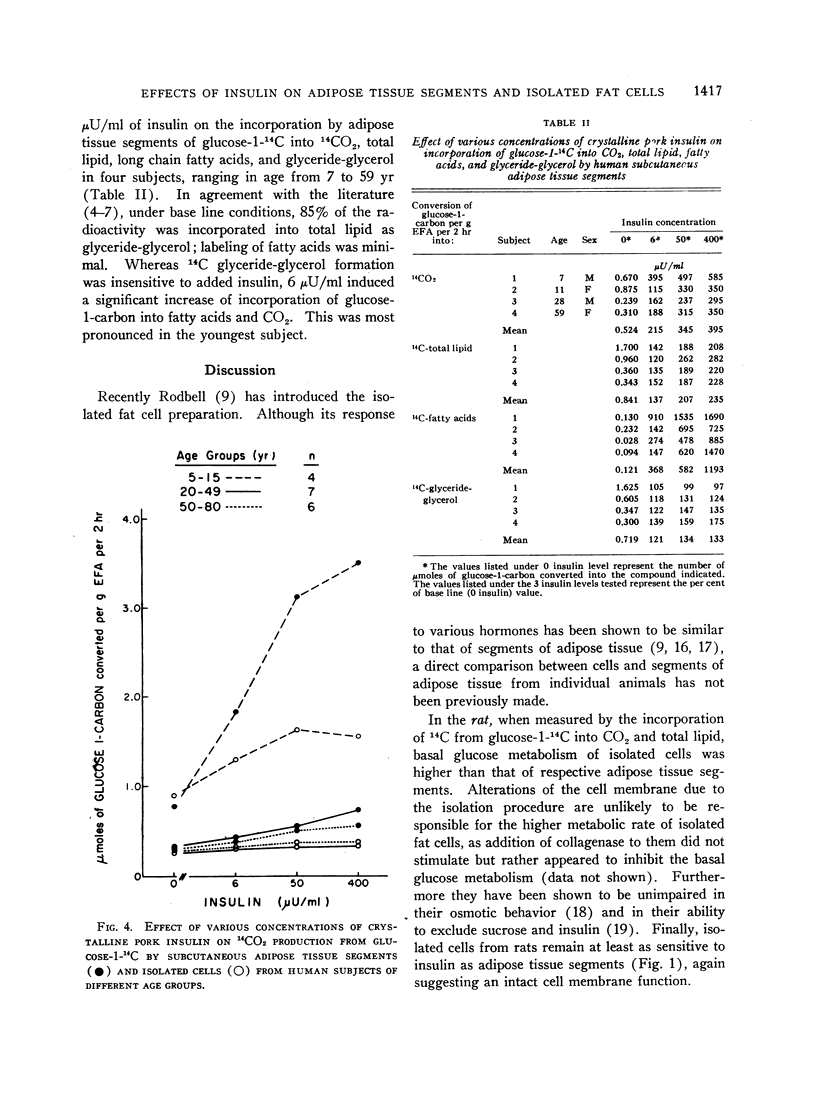
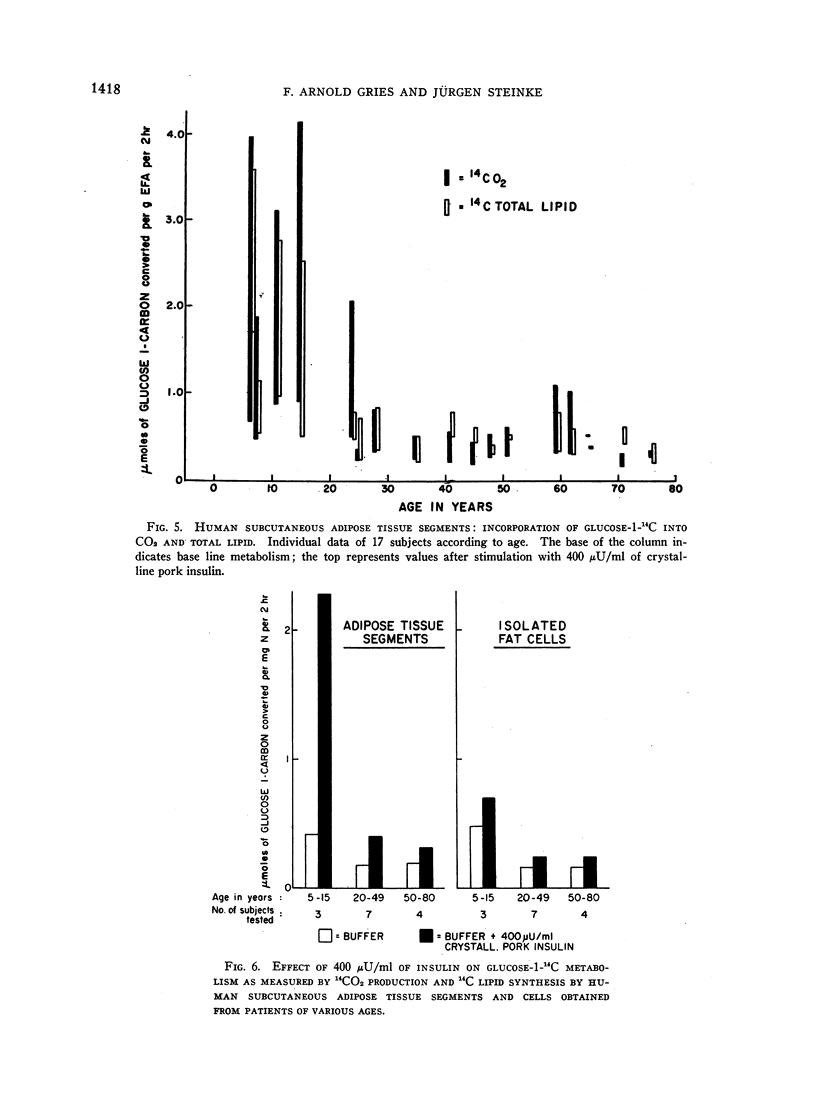
In contrast to the rat, in man adipose tissue segments were more active than isolated cells. In four subjects, the effect of 6, 50, and 400 μU/ml of insulin was analyzed on conversion of glucose-1-carbon to CO2, long chain fatty acids, and glycerides by adipose tissue segments only. In 17 subjects, glucose oxidation and lipid synthesis by adipose tissue segments and isolated fat cells were measured and showed a definite response to physiological doses of crystalline pork insulin. There was, however, an age dependency, and consistent effects were obtained with 6 μU/ml in children and 50 μU/ml in adults. The responsiveness of human adipose tissue to exogenous insulin in concentrations comparable to those detected in blood reemphasizes the importance of adipose tissue as a major site for fatty acid synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALL E. G., COOPER O. Studies on the metabolism of adipose tissue. III. The response to insulin by different types of adipose tissue and in the presence of various metabolites. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:584–588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P. Studies on adipose tissue from obese patients with or without diabetes mellitus. II. Basal and insulin-stimulated glucose metabolism. Acta Med Scand. 1966 Feb;179(2):229–234. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1966.tb05452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAHILL G. F., Jr, LEBOEUF B., RENOLD A. E. Studies on rat adipose tissue in vitro. III. Synthesis of glycogen and glyceride-glycerol. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2540–2543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROFFORD O. B., RENOLD A. E. GLUCOSE UPTAKE BY INCUBATED RAT EPIDIDYMAL ADIPOSE TISSUE. RATE-LIMITING STEPS AND SITE OF INSULIN ACTION. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:14–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Girolamo M., Rudman D. Species differences in glucose metabolism and insulin responsiveness of adipose tissue. Am J Physiol. 1966 Apr;210(4):721–727. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.4.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD J. B., JOHNSON P., HERRING B. Insulin-resistant diabetes associated with increased endogenous plasma insulin followed by complete remission. J Clin Invest. 1961 Sep;40:1672–1683. doi: 10.1172/JCI104390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Galton D. J., Kovacev V. P. Effect of drugs on the lipolytic action of hormones in isolated fat cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1966 May;2(3):237–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fain J. N., Kovacev V. P., Scow R. O. Effect of growth hormone and dexamethasone on lipolysis and metabolism in isolated fat cells of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3522–3529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler A., Beck J. C. The effect of insulin on the metabolism of human adipose tissue in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jul 7;106(1):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(65)90108-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMOSH M., HAMOSH P., BAR-MAOR J. A., COHEN H. FATTY-ACID METABOLISM BY HUMAN ADIPOSE TISSUES. J Clin Invest. 1963 Oct;42:1648–1652. doi: 10.1172/JCI104850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH J., GOLDRICK R. B. SERIAL STUDIES ON THE METABOLISM OF HUMAN ADIPOSE TISSUE. I. LIPOGENESIS AND FREE FATTY ACID UPTAKE AND RELEASE IN SMALL ASPIRATED SAMPLES OF SUBCUTANEOUS FAT. J Clin Invest. 1964 Sep;43:1776–1792. doi: 10.1172/JCI105052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEANRENAUD B., RENOLD A. E. Studies on rat adipose tissue in vitro. IV. Metabolic patterns produced in rat adipose tissue by varying insulin and glucose concentrations independently from each other. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3082–3087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAHLENBERG A., KALANT N. THE EFFECT OF INSULIN ON HUMAN ADIPOSE TISSUE. Can J Biochem. 1964 Nov;42:1623–1635. doi: 10.1139/o64-173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lech J. J., Calvert D. N. Protein content and osmotic behavior of isolated fat cells. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):561–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. A., Jr, Lindsay R. W., Gaskin J. H., Hollifield G. Response of human adipose tissue to endogenous serum insulin-like activity in vitro. Metabolism. 1967 Jan;16(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(67)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POZZA G., GHIDONI A., BASILICO C. Glucose uptake and gas exchange in human adipose tissue incubated in vitro. Lancet. 1963 Apr 13;1(7285):836–836. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)91550-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBELL M. METABOLISM OF ISOLATED FAT CELLS. I. EFFECTS OF HORMONES ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND LIPOLYSIS. J Biol Chem. 1964 Feb;239:375–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENTHAL H. L., PFLUKE M. L., CALLERAMI J. The colorimetric estimation of serum fatty esters. Clin Chim Acta. 1959 May;4(3):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(59)90098-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renold A. E., Gonet A., Crofford O. B., Vecchio D. Metabolic regulation in heterogeneous systems: some new questions about diabetes mellitus. Fed Proc. 1966 May-Jun;25(3):827–831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINKE J., SOELDNER J. S., CAMERINI D AVALOS R. A., RENOLD A. E. STUDIES ON SERUM INSULIN-LIKE ACTIVITY (ILA) IN PREDIABETES AND EARLY OVERT DIABETES. Diabetes. 1963 Nov-Dec;12:502–507. doi: 10.2337/diab.12.6.502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Plasma insulin concentrations in nondiabetic and early diabetic subjects. Determinations by a new sensitive immuno-assay technic. Diabetes. 1960 Jul-Aug;9:254–260. doi: 10.2337/diab.9.4.254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


