Abstract
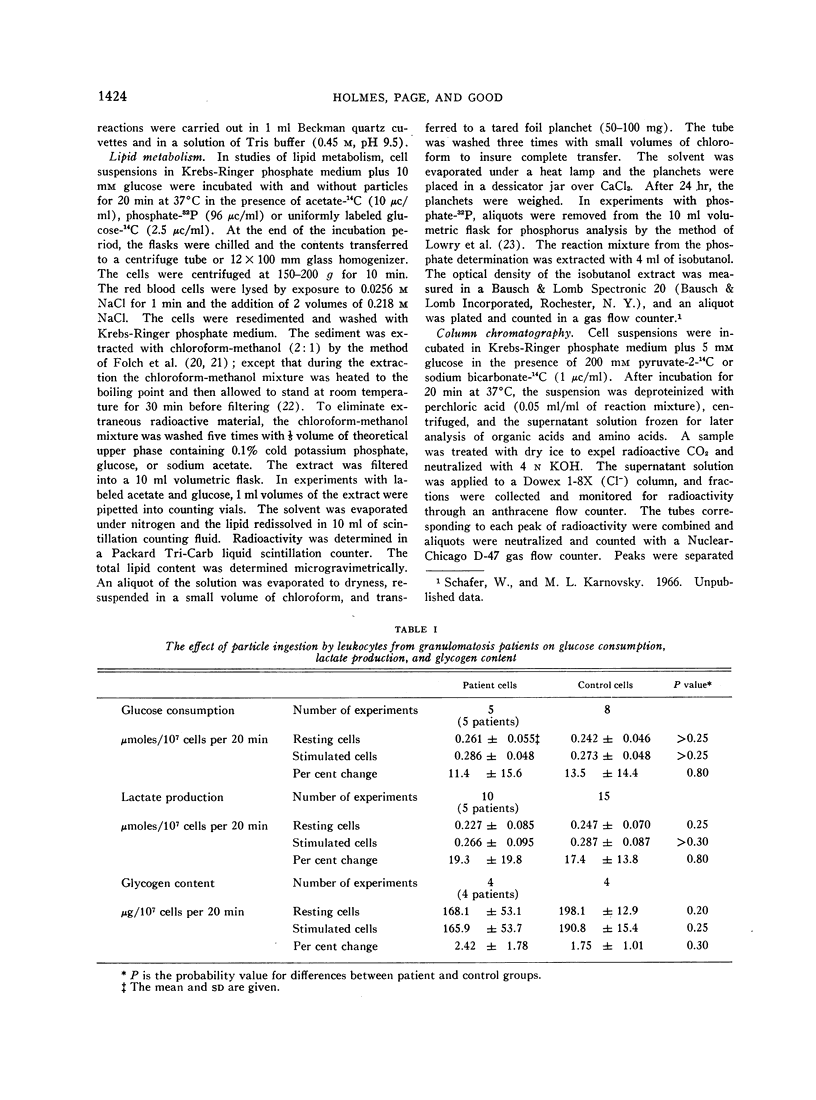
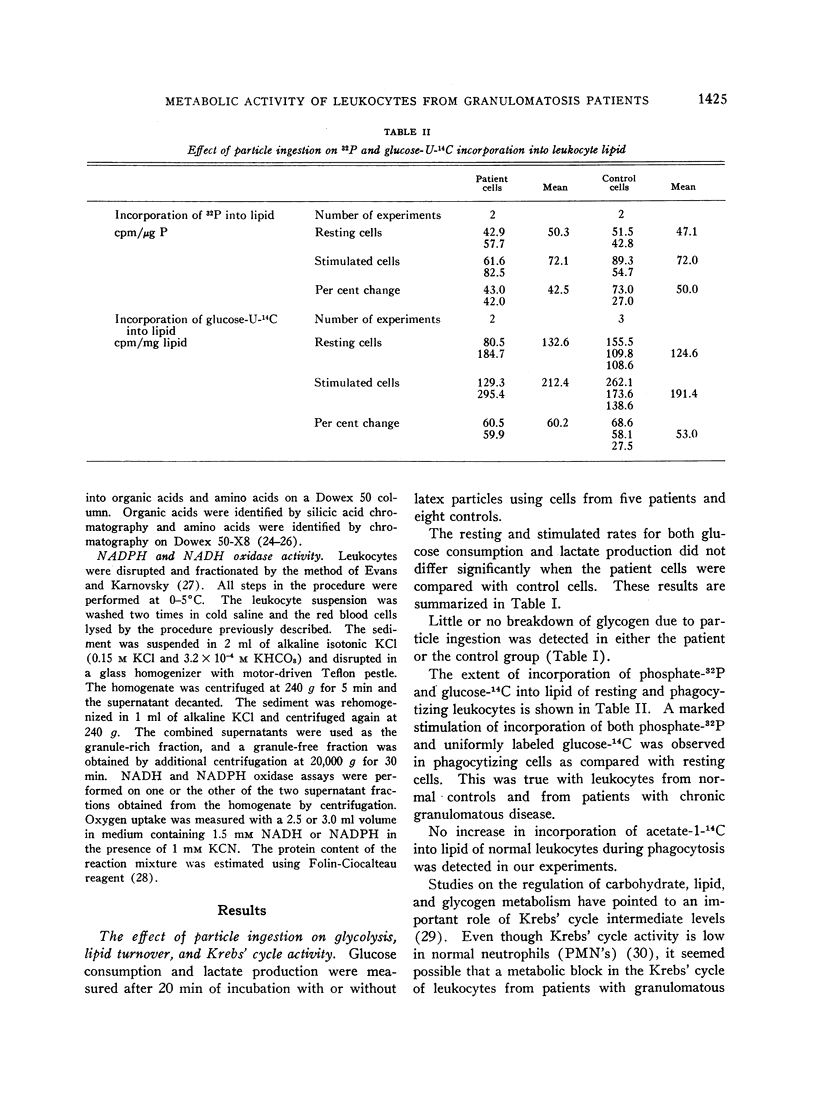
Polymorphonuclear leukocytes from patients with chronic granulomatous disease respond to the phagocytosis of latex particles with normal increments in glucose consumption, lactate production, Krebs' cycle activity, and lipid turnover.
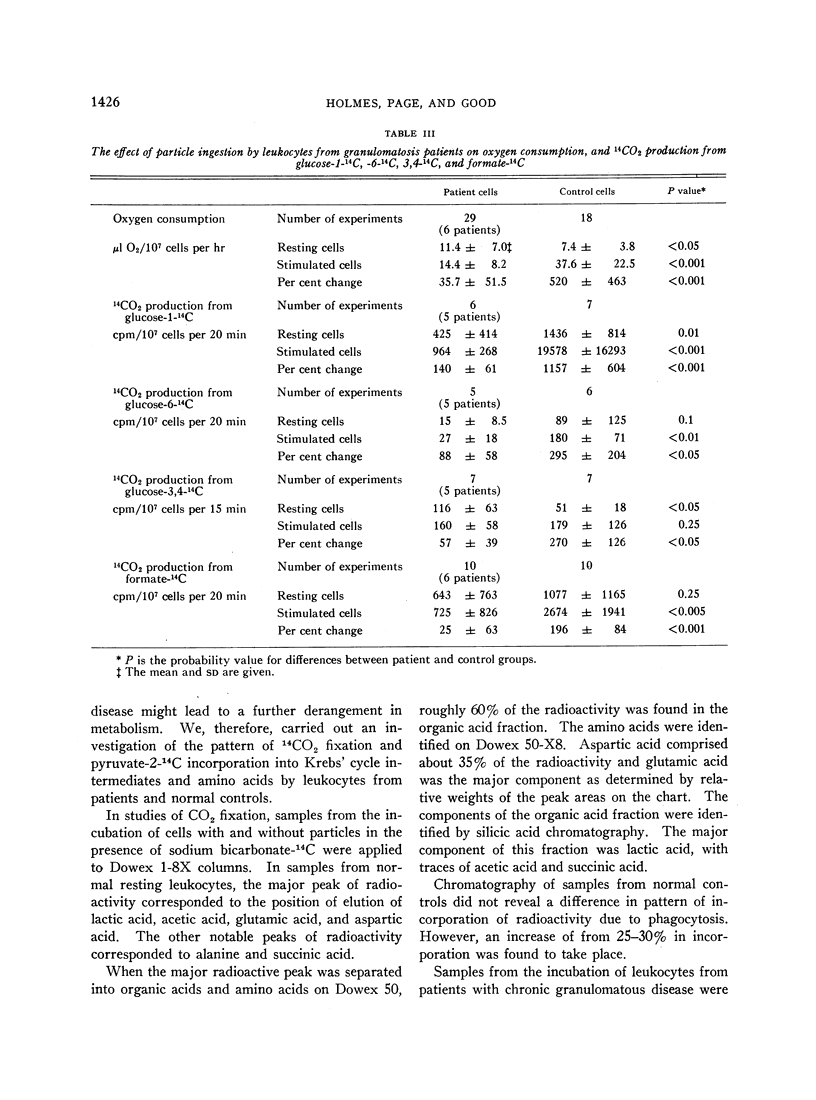
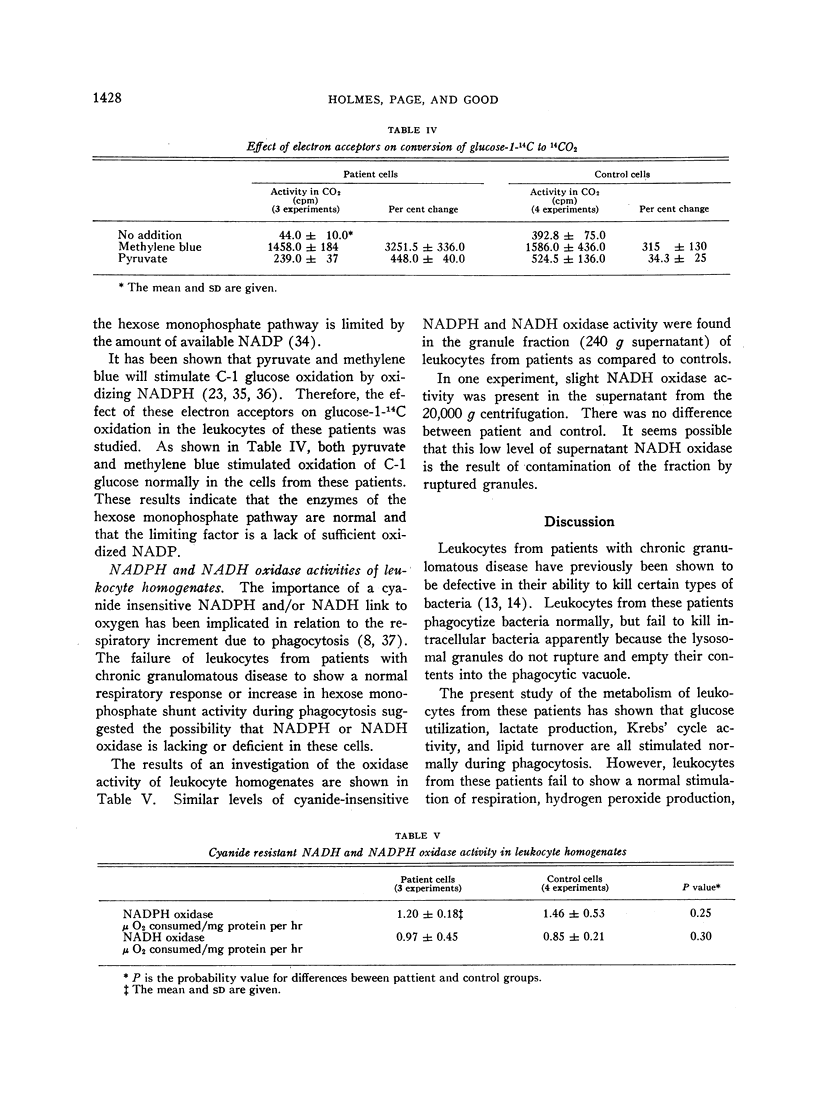
The leukocytes of these patients fail to show normal increments in respiration, direct oxidation of glucose, and hydrogen peroxide formation during particle uptake.
It appears that the stimulation of respiration with the formation of hydrogen peroxide and stimulation of the direct oxidative pathway of glucose metabolism are closely linked to degranulation and intracellular killing of bacteria by polymorphonuclear leukocytes.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson D. E. Biological feedback control at the molecular level. Science. 1965 Nov 12;150(3698):851–857. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3698.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER H., MUNDER G., FISCHER H. Uber den Leukocytenstoffwechsel bei der Phagocytose. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1958;313:266–275. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1958.313.1.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECK W. S. Occurrence and control of the phosphogluconate oxidation pathway in normal and leukemic leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1958 May;232(1):271–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECK W. S., VALENTINE W. N. The aerobic carbohydrate metabolism of leukocytes in health and leukemia. I. Glycolysis and respiration. Cancer Res. 1952 Nov;12(11):818–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERENDES H., BRIDGES R. A., GOOD R. A. A fatal granulomatosus of childhood: the clinical study of a new syndrome. Minn Med. 1957 May;40(5):309–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIDGES R. A., BERENDES H., GOOD R. A. A fatal granulomatous disease of childhood; the clinical, pathological, and laboratory features of a new syndrome. AMA J Dis Child. 1959 Apr;97(4):387–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRIN M., YONEMOTO R. H. Stimulation of the glucose oxidative pathway in human erythrocytes by methylene blue. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jan;230(1):307–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baehner R. L., Nathan D. G. Leukocyte oxidase: defective activity in chronic granulomatous disease. Science. 1967 Feb 17;155(3764):835–836. doi: 10.1126/science.155.3764.835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAGAN R. H., KARNOVSKY M. L. ENZYMATIC BASIS OF THE RESPIRATORY STIMULATION DURING PHAGOCYTOSIS. Nature. 1964 Oct 17;204:255–257. doi: 10.1038/204255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARSON M. J., CHADWICK D. L., BRUBAKER C. A., CLELAND R. S., LANDING B. H. THIRTEEN BOYS WITH PROGRESSIVE SEPTIC GRANULOMATOSIS. Pediatrics. 1965 Mar;35:405–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHN Z. A., MORSE S. I. Functional and metabolic properties of polymorphonuclear leucocytes. I. Observations on the requirements and consequences of particle ingestion. J Exp Med. 1960 May 1;111:667–687. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.5.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELBACH P. Composition and synthesis of lipids in resting and phagocytizing leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1959 Dec 1;110:969–980. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.6.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS W. H., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. IV. Some aspects of carbohydrate metabolism during phagocytosis. Biochemistry. 1962 Jan;1:159–166. doi: 10.1021/bi00907a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., ASCOLI I., LEES M., MEATH J. A., LeBARON N. Preparation of lipide extracts from brain tissue. J Biol Chem. 1951 Aug;191(2):833–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes B., Quie P. G., Windhorst D. B., Good R. A. Fatal granulomatous disease of childhood. An inborn abnormality of phagocytic function. Lancet. 1966 Jun 4;1(7449):1225–1228. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)90238-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IYER G. Y., QUESTEL J. H. NADPH and NADH oxidation by guinea pig polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1963 Feb;41:427–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARNOVSKY M. L. Metabolic basis of phagocytic activity. Physiol Rev. 1962 Jan;42:143–168. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1962.42.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINNORY D. S., TAKEDA Y., GREENBERG D. M. Chromatography of carboxylic acids on a silica gel column with a benzene-ether solvent system. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jan;212(1):379–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDING B. H., SHIRKEY H. S. A syndrome of recurrent infection and infiltration of viscera by pigmented lipid histiocytes. Pediatrics. 1957 Sep;20(3):431–438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROBERTS N. R., LEINER K. Y., WU M. L., FARR A. L. The quantitative histochemistry of brain. I. Chemical methods. J Biol Chem. 1954 Mar;207(1):1–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MENDEL B., KEMP A., MYERS D. K. A colorimetric micro-method for the determination of glucose. Biochem J. 1954 Apr;56(4):639–646. doi: 10.1042/bj0560639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Chromatography of amino acids on sulfonated polystyrene resins. J Biol Chem. 1951 Oct;192(2):663–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malawista S. E., Bodel P. T. The dissociation by colchicine of phagocytosis from increased oxygen consumption in human leukocytes. J Clin Invest. 1967 May;46(5):786–796. doi: 10.1172/JCI105579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., White J. G., Holmes B., Good R. A. In vitro bactericidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: diminished activity in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):668–679. doi: 10.1172/JCI105568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBERTS J., QUASTEL J. H. OXIDATION OF REDUCED TRIPHOSPHOPYRIDINE NUCLEOTIDE BY GUINEA PIG POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUCOCYTES. Nature. 1964 Apr 4;202:85–86. doi: 10.1038/202085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSSI F., ZATTI M. CHANGES IN THE METABOLIC PATTERN OF POLYMORPHO-NUCLEAR LEUCOCYTES DURING PHAGOCYTOSIS. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Oct;45:548–559. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Zatti M. Biochemical aspects of phagocytosis in polymorphonuclear leucocytes. NADH and NADPH oxidation by the granules of resting and phagocytizing cells. Experientia. 1964 Jan 15;20(1):21–23. doi: 10.1007/BF02146019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. 2. Incorporation of C14-labeled building blocks into lipid, protein, and glycogen of leukocytes during phagocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2224–2229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SBARRA A. J., KARNOVSKY M. L. The biochemical basis of phagocytosis. I. Metabolic changes during the ingestion of particles by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1355–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEIFTER S., DAYTON S. The estimation of glycogen with the anthrone reagent. Arch Biochem. 1950 Jan;25(1):191–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPERRY W. M. Lipide analysis. Methods Biochem Anal. 1955;2:83–111. doi: 10.1002/9780470110188.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAHELIN H., KARNOVSKY M. L., FARNHAM A. E., SUTER E. Studies on the interaction between phagocytes and tubercle bacilli. III. Some metabolic effects in guinea pigs associated with infection with tubercle bacilli. J Exp Med. 1957 Mar 1;105(3):265–277. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.3.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraj R. J., Sbarra A. J. Relationship of glycolytic and oxidative metabolism to particle entry and destruction in phagocytosing cells. Nature. 1966 Sep 17;211(5055):1272–1276. doi: 10.1038/2111272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WENNER C. E. Oxidation of reduced triphosphopyridine nucleotide by ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1959 Sep;234:2472–2479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windhorst D. B., Holmes B., Good R. A. A newly defined X-linked trait in man with demonstration of the Lyon effect in carrier females. Lancet. 1967 Apr 8;1(7493):737–739. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91360-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



