Abstract
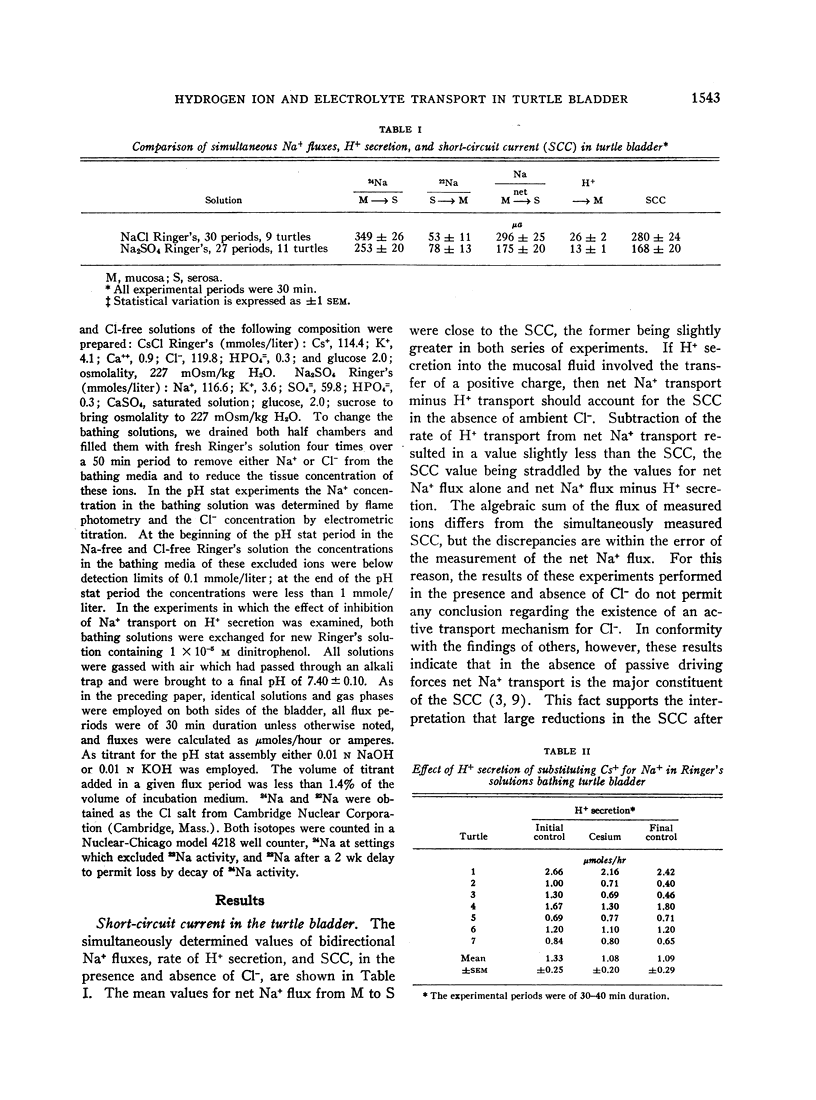
The relationship between hydrogen ion secretion and the transport of other electrloytes was examined in the isolated urinary bladder of the water turtle. Symmetrical solutions which were free from exogenous carbon dioxide and bicarbonate bathed the two surfaces of the preparation, and the spontaneous electrical potential of the bladder was nullified by a voltage clamp. Active transport of sodium from mucosal to serosal medium was confirmed by simultaneous bidirectional flux measurements and found to be slightly, but not significantly, greater than the short-circuit current. In the absence of sodium in the bathing solutions, the normal potential difference across the bladder reversed and the current required to nullify this reversed potential difference had the same magnitude as the simultaneously measured rate of hydrogen ion secretion. The results indicate that, under these experimental conditions, the bladder transports sodium and hydrogen ion actively, but that chloride movement does not contribute to the short-circuit current.
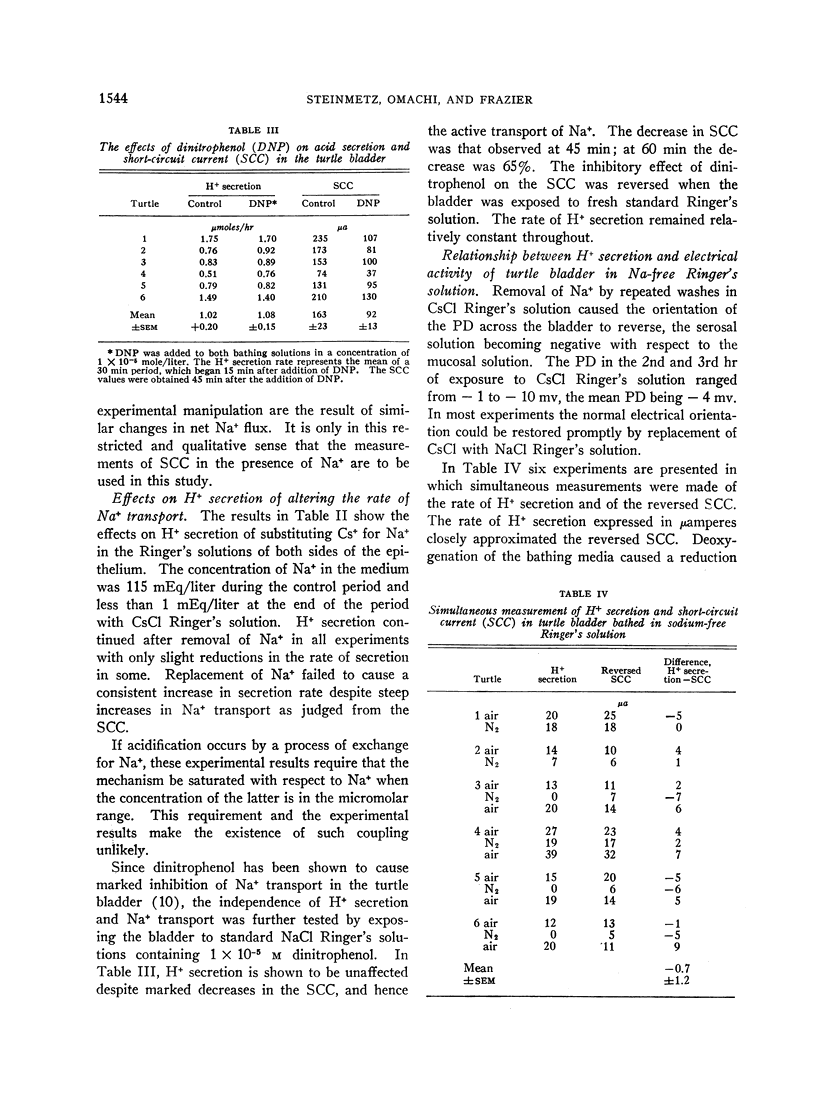
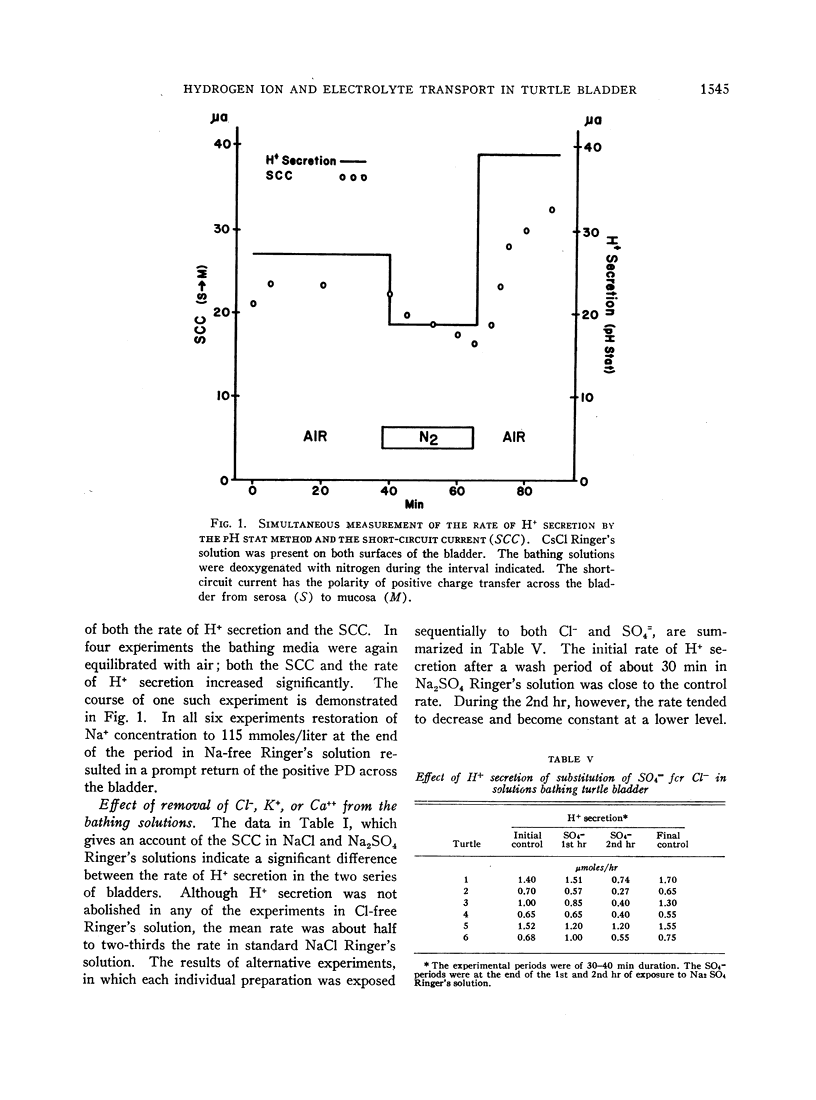
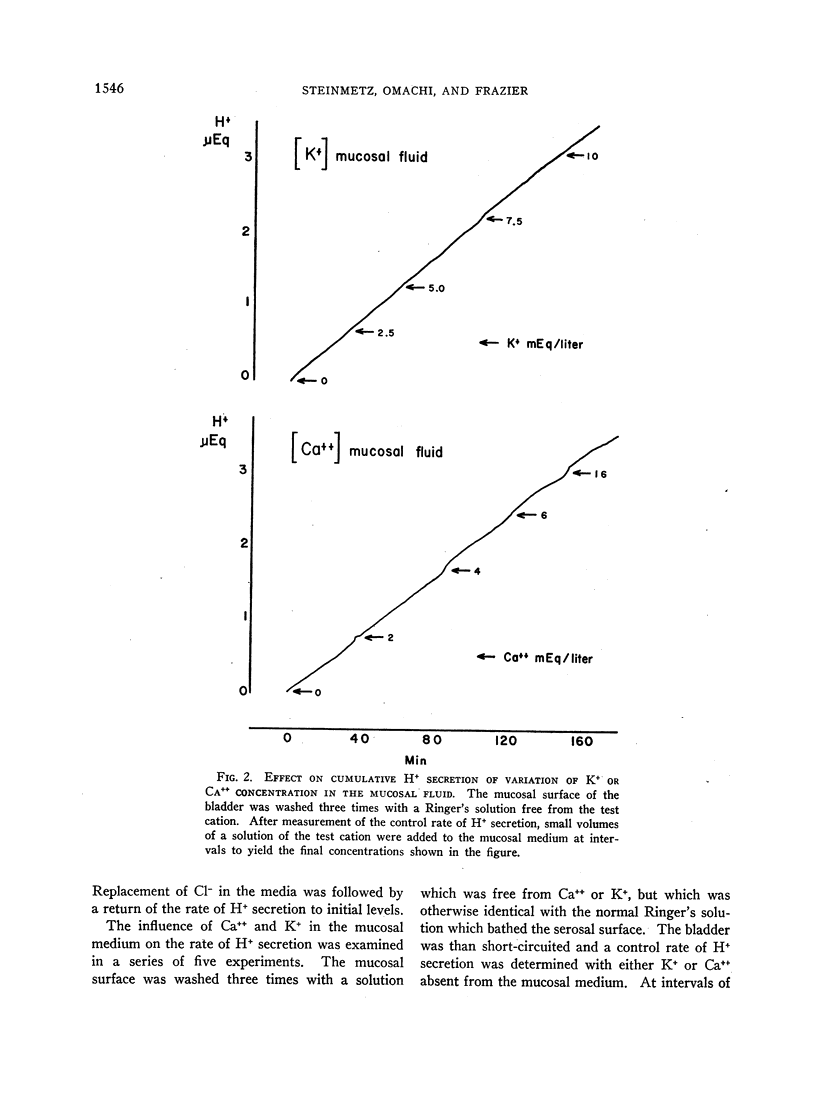
The rate of secretion of hydrogen ion was not affected by replacement of the sodium in the bathing media by cesium, or by inhibition of sodium transport by dinitrophenol. Acidification continued when chloride in the solutions was replaced by sulfate, or when potassium or calcium was removed from the solution bathing the mucosal surface.
Secretion of hydrogen ion by the turtle bladder is not dependent on the simultaneous transport of other electrolytes across the bladder.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bricker N. S., Klahr S. Effects of dinitrophenol and oligomycin on the coupling between anaerobic metabolism and anaerobic sodium transport by the isolated turtle bladder. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jan;49(3):483–499. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.3.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky W. A., Schilb T. P. Ionic mechanisms for sodium and chloride transport across turtle bladders. Am J Physiol. 1966 May;210(5):987–996. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.5.987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civan M. M., Kedem O., Leaf A. Effect of vasopressin on toad bladder under conditions of zero net sodium transport. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):569–575. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F., Shamoo Y. E., Brodsky W. A. Electrical nature of active chloride transport across short-circuited turtle bladders. Am J Physiol. 1967 Mar;212(3):641–650. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.3.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLAHR S., BRICKER N. S. NA TRANSPORT BY ISOLATED TURTLE BLADDER DURING ANAEROBIOSIS AND EXPOSURE TO KCN. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jun;206:1333–1339. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.6.1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOEFOED-JOHNSEN V., USSING H. H. The nature of the frog skin potential. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Jun 2;42(3-4):298–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01563.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINE C. M., FOULKES E. C. SODIUM COMPARTMENTATION IN TURTLE BLADDER. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Dec 13;78:767–768. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., JENSON R. L., RELMAN A. S. Acidification of the urine and increased ammonium excretion without change in acid-base equilibrium: sodium reabsorption as a stimulus to the acidifying process. J Clin Invest. 1955 May;34(5):673–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI103117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINMETZ P. R., BANK N. Effects of acute increases in the excretion of solute and water on renal acid excretion in man. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42:1142–1149. doi: 10.1172/JCI104799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINMETZ P. R., EISINGER R. P., LOWENSTEIN J. THE EXCRETION OF ACID IN UNILATERAL RENAL DISEASE IN MAN. J Clin Invest. 1965 Apr;44:582–591. doi: 10.1172/JCI105171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz P. R. Characteristics of hydrogen ion transport in urinary bladder of water turtle. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1531–1540. doi: 10.1172/JCI105644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz P. R., Eisinger R. P. Influence of posture and diurnal rhythm on the renal excretion of acid: observations in normal and adrenalectomized subjects. Metabolism. 1966 Jan;15(1):76–87. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



