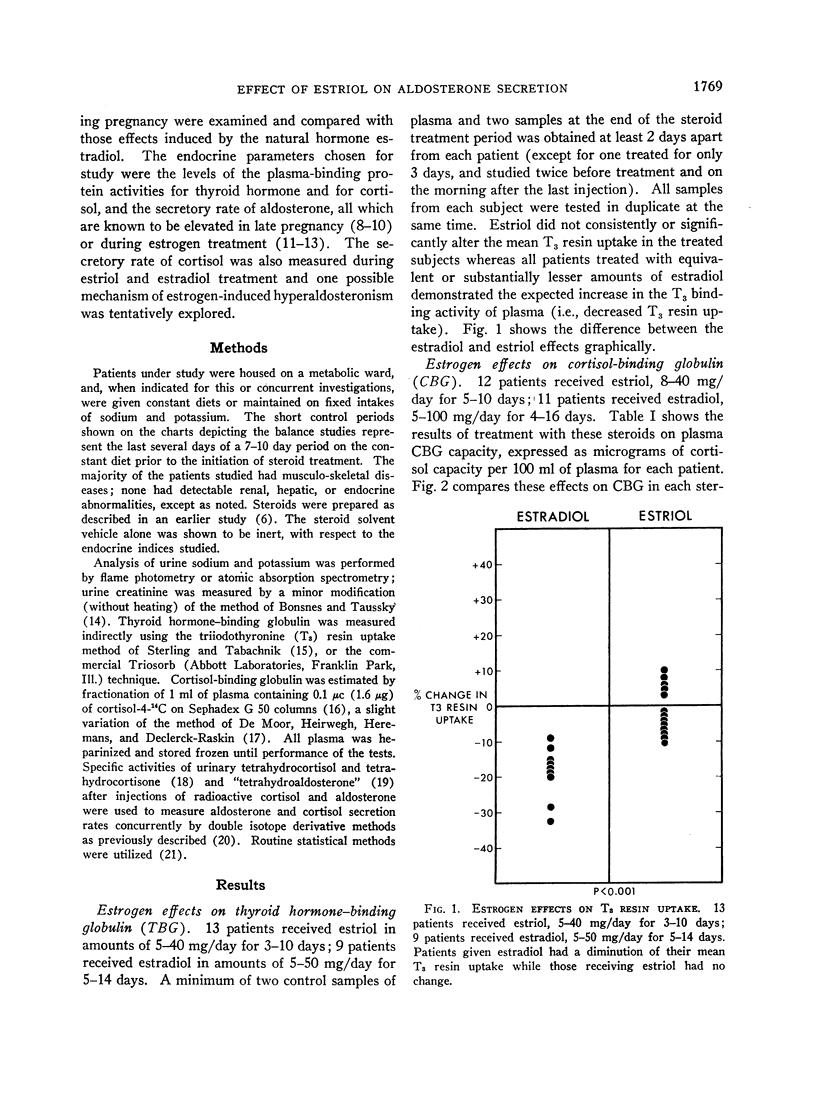
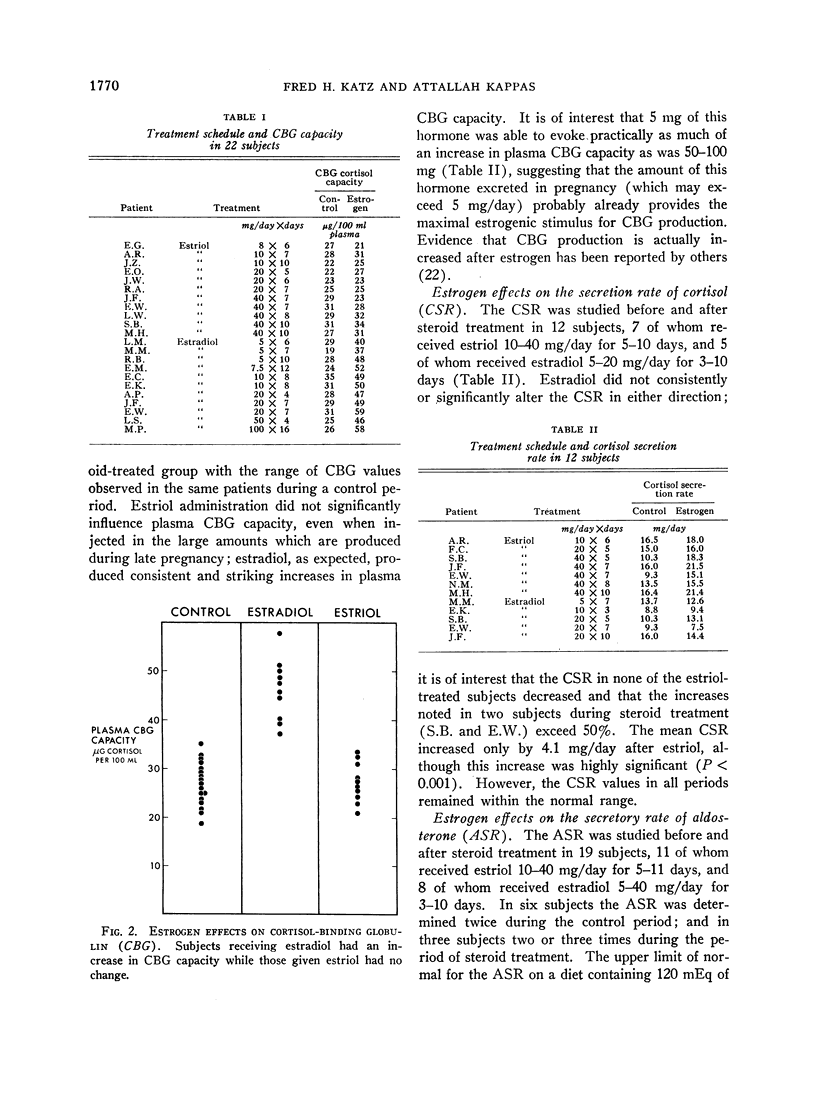
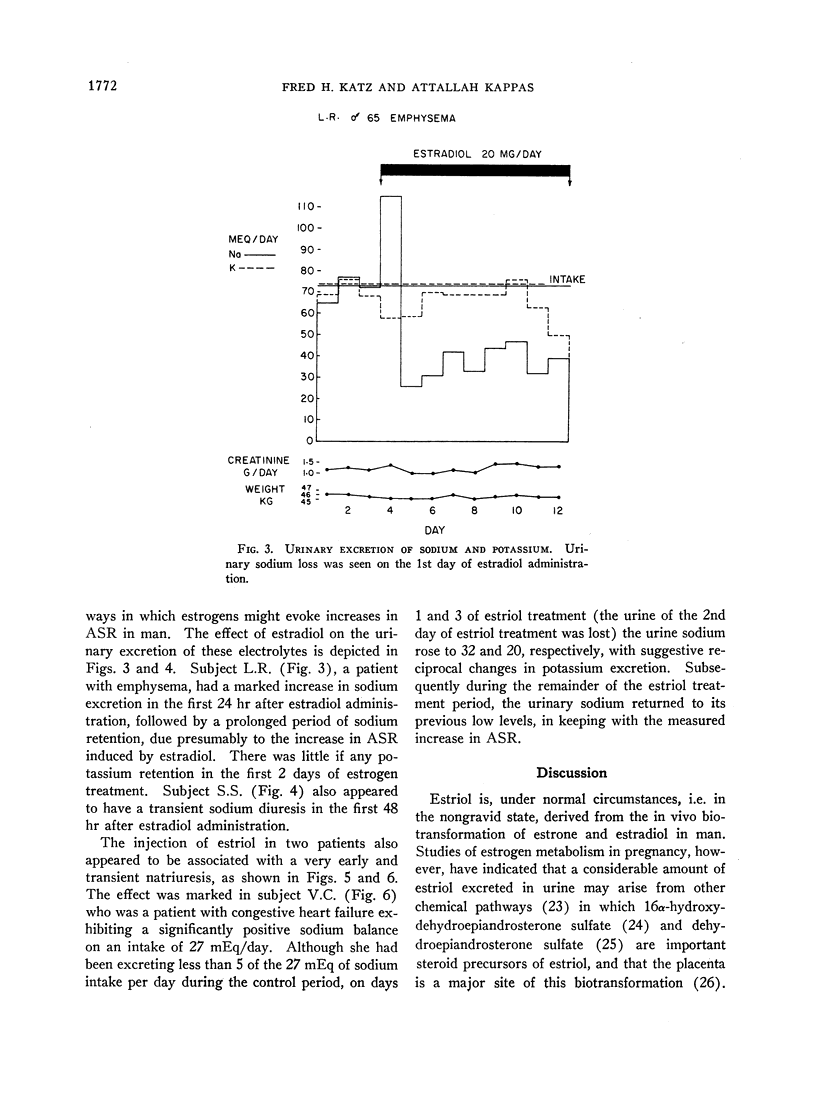
Abstract
The effects of estriol and estradiol on the plasma levels of cortisol- and thyroxine-binding globulin activity, and on the secretion rates of aldosterone and cortisol were studied in man. The metabolite estriol had no consistent or significant influence on plasma levels of the hormone-binding globulin activities; the hormone estradiol increased these binding capacities significantly, as expected. Cortisol secretion rate rose slightly after estriol but was unchanged after estradiol. Both compounds induced substantial increases in the aldosterone secretion rate of most treated subjects. The mechanism of this apparently paradoxical effect of estrogens is not clear; it is suggested that the “salt-retaining” action of estrogens is mediated in part by the rapid enhancement of aldosterone output which follows their administration in man. Balance experiments in four subjects suggest that both estradiol and estriol may induce a transient early natriuresis in man; but other mechanisms for estrogen stimulation of aldosterone secretion may be operative as well.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AUGUST J. T., NELSON D. H., THORN G. W. Response of normal subjects to large amounts of aldosterone. J Clin Invest. 1958 Nov;37(11):1549–1555. doi: 10.1172/JCI103747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLTE E., MANCUSO S., ERIKSSON G., WIQVIST N., DICZFALUSY E. STUDIES ON THE AROMATISATION OF NEUTRAL STEROIDS IN PREGNANT WOMEN. I. AROMATISATION OF C-19 STEROIDS BY PLACENTAS PERFUSED IN SITU. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1964 Apr;45:535–559. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0450535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN C. H., SAFFAN B. D., HOWARD C. M., PREEDY J. R. THE RENAL CLEARANCE OF ENDOGENOUS ESTROGENS IN LATE PREGNANCY. J Clin Invest. 1964 Feb;43:295–303. doi: 10.1172/JCI104914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN J. J., DAVIES D. L., DOAK P. B., LEVER A. F., ROBERTSON J. I. PLASMA-RENIN IN NORMALPREGNANCY. Lancet. 1963 Nov 2;2(7314):900–901. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90614-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN J. J., DAVIES D. L., DOAK P. B., LEVER A. F., ROBERTSON J. I., TREE M. THE PRESENCE OF RENIN IN HUMAN AMNIOTIC FLUID. Lancet. 1964 Jul 11;2(7350):64–66. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. J., Davies D. L., Doak P. B., Lever A. F., Robertson J. I. Serial estimation of plasma renin concentration during pregnancy and after parturition. J Endocrinol. 1966 Aug;35(4):373–378. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0350373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE MOOR P., HEIRWEGH K., HEREMANS J. F., DECLERCK-RASKIN M. Protein binding of corticoids studied by gel filtration. J Clin Invest. 1962 Apr;41:816–827. doi: 10.1172/JCI104539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWLING J. T., FREINKEL N., INGBAR S. H. Effect of diethylstilbestrol on the binding of thyroxine in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1956 Nov;16(11):1491–1506. doi: 10.1210/jcem-16-11-1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOWLING J. T., FREINKEL N., INGBAR S. H. Thyroxine-binding by sera of pregnant women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1956 Feb;16(2):280–282. doi: 10.1210/jcem-16-2-280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easterling W. E., Jr, Simmer H. H., Dignam W. J., Frankland M. V., Naftolin F. Neutral C19-steroids and steroid sulfates in human pregnancy. II. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, 16-alpha-hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone, and 16-alpha-hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in maternal and fetal blood of pregnancies with anencephalic and normal fetuses. Steroids. 1966 Aug;8(2):157–178. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(66)90090-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN J., BROWN J. B., HELLMAN L., ZUMOFF B., GALLAGHER T. F. Estrogen metabolism in normal and pregnant women. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1489–1494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris T. F., Gorden P., Mulrow P. J. Rabbit uterus as a source of renin. Am J Physiol. 1967 Mar;212(3):698–702. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.3.698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS F., SCHAECHTELIN G., ZIEGLER M., BERGER M. A RENIN-LIKE SUBSTANCE IN THE PLACENTA AND UTERUS OF THE RABBIT. Lancet. 1964 Apr 25;1(7339):914–916. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)91637-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GURPIDE E., ANGERS M., VANDE WIELE R. L., LIEBERMAN S. Determination of secretory rates of estrogens in pregnant and nonpregnant women from the specific activities of urinary metabolites. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Sep;22:935–945. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-9-935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. F., Jr, Mueller M. N., Kappas A. Studies on the mechanism and structural specificity of the estrogen effect on BSP metabolism. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1965;78:187–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorden P., Ferris T. F., Mulrow P. J. Rabbit uterus as a possible site of renin synthesis. Am J Physiol. 1967 Mar;212(3):703–706. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.3.703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMER O. M., GRIFFITH R. S. The effect of the administration of estrogens on the renin-substrate (hypertensinogen) content of rat plasma. Endocrinology. 1952 Nov;51(5):421–426. doi: 10.1210/endo-51-5-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAGAWA C. M., JACOBS R. S., Jr Action of testosterone in blocking urinary electrolyte effects of desoxycorticosterone. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1959 Nov;102:521–523. doi: 10.3181/00379727-102-25304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ F. H. ADRENAL FUNCTION DURING BED REST. Aerosp Med. 1964 Sep;35:849–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAIDLAW J. C., RUSE J. L., GORNALL A. G. The influence of estrogen and progesterone on aldosterone excretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Feb;22:161–171. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-2-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANDAU R. L., LUGIBIHL K. Inhibition of the sodium-retaining influence of aldosterone by progesterone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Nov;18(11):1237–1245. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-11-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAYNE D. S., MEYER C. J., VAISHWANAR P. S., PINCUS G. The secretion and metabolism of cortisol and aldosterone in normal and in steroid-treated women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1962 Feb;22:107–118. doi: 10.1210/jcem-22-2-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACDONALD P. C., SITERI P. K. ORIGIN OF ESTROGEN IN WOMEN PREGNANT WITH AN ANENCEPHALIC FETUS. J Clin Invest. 1965 Mar;44:465–474. doi: 10.1172/JCI105160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIYAKE T. Inhibitory effect of various steroids on gonadotrophin hypersecretion in parabiotic mice. Endocrinology. 1961 Sep;69:534–546. doi: 10.1210/endo-69-3-534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER M. N., KAPPAS A. ESTROGEN PHARMACOLOGY. I. THE INFLUENCE OF ESTRADIOL AND ESTRIOL ON HEPATIC DISPOSAL OF SULFOBROMOPHTHALEIN (BSP) IN MAN. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1905–1914. doi: 10.1172/JCI105064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUELLER M. N., KAPPAS A. ESTROGEN PHARMACOLOGY. II. SUPPRESSION OF EXPERIMENTAL IMMUNE POLYARTHRITIS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Dec;117:845–847. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSON R. E., NOKES G., CHEN P. S., Jr, BLACK R. L. Estrogens and adrenocortical function in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1960 Apr;20:495–514. doi: 10.1210/jcem-20-4-495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREEDY J. R., AITKEN E. H. The effect of estrogen on water and electrolyte metabolism. I. The normal. J Clin Invest. 1956 Apr;35(4):423–429. doi: 10.1172/JCI103293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDBERG A. A., SLAUNWHITE W. R., Jr Transcortin: a corticosteroid-binding protein of plasma. II. Levels in various conditions and the effects of estrogens. J Clin Invest. 1959 Aug;38(8):1290–1297. doi: 10.1172/JCI103904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDBERG A. A., WOODRUFF M., ROSENTHAL H., NIENHOUSE S., SLAUNWHITE W. R., Jr TRANSCORTIN: A CORTICOSTEROID-BINDING PROTEIN OF PLASMA. VII. HALF-LIFE IN NORMAL AND ESTROGEN-TREATED SUBJECTS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Mar;43:461–466. doi: 10.1172/JCI104931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEAL U. S., DOE R. P. CORTICOSTERIOD-BINDING GLOBULIN: SPECIES DISTRIBUTION AND SMALL-SCALE PURIFICATION. Endocrinology. 1963 Sep;73:371–376. doi: 10.1210/endo-73-3-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLAUNWHITE W. R., Jr, SANDBERG A. A. Transcortin: a corticosteroid-binding protein of plasma. J Clin Invest. 1959 Feb;38(2):384–391. doi: 10.1172/JCI103812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ULICK S., LARAGH J. H., LIEBERMAN S. The isolation of a urinary metabolite of aldosterone and its use to measure the rate of secretion of aldosterone by the adrenal cortex of man. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1958;71:225–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE M., MEEKER C. I., GRAY M. J., SIMS E. A., SOLOMON S. SECRETION RATE OF ALDOSTERONE IN NORMAL PREGNANCY. J Clin Invest. 1963 Oct;42:1619–1631. doi: 10.1172/JCI104847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson H. E. Natriuretic action of certain adrenocortical androgens. Steroids. 1965 Sep;6(3):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(65)90012-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOUSEM H. L. SIMPLE GAS CHROMATOGRAPHIC METHOD FOR ESTIMATION OF URINARY ESTRIOL IN PREGNANT WOMEN. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1964 Feb 1;88:375–380. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(64)90438-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


