Abstract
The metabolic behavior of C′3 labeled with radioactive iodine was investigated in 10 normal subjects and in 20 patients with diseases in which complement is thought to play a pathophysiological role. The mean fractional catabolic rate of C′3 in normal subjects was 2.3 ± 1.0% of the plasma pool per hr, whereas the fractional catabolic rate of C′3i, the inactive conversion product of C′3 produced by complement activation, was at least five times as great.
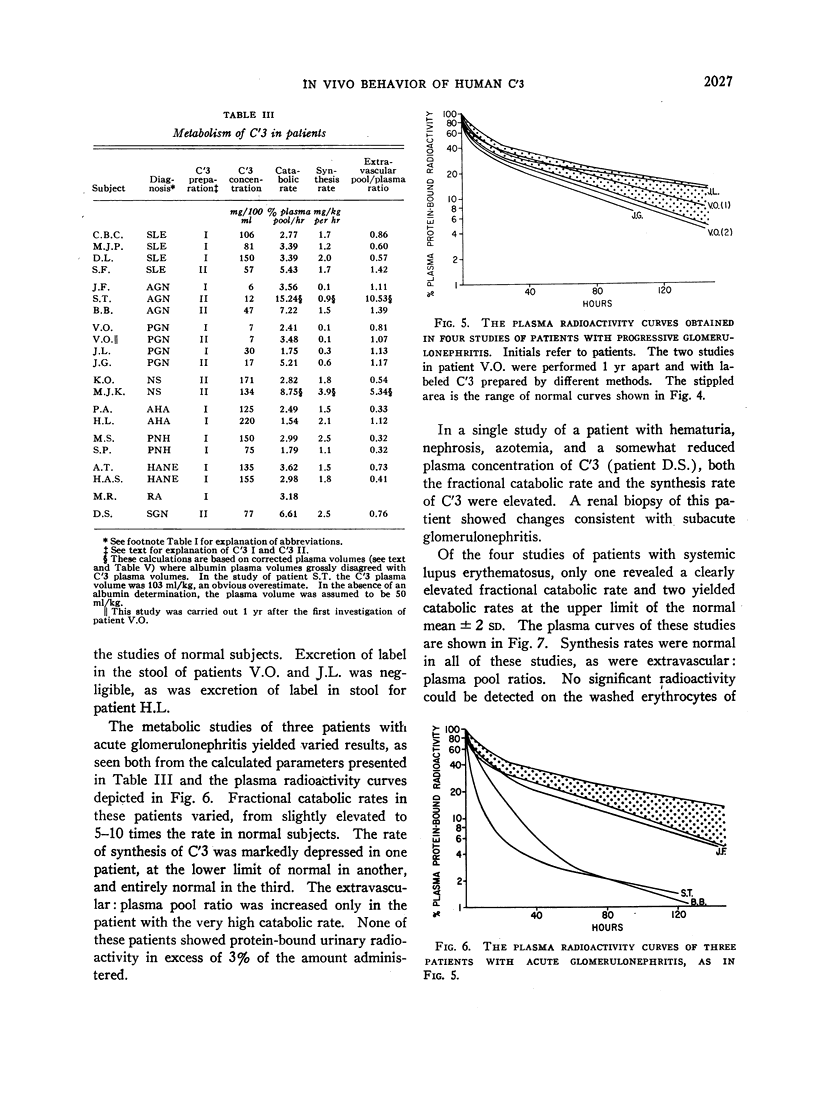
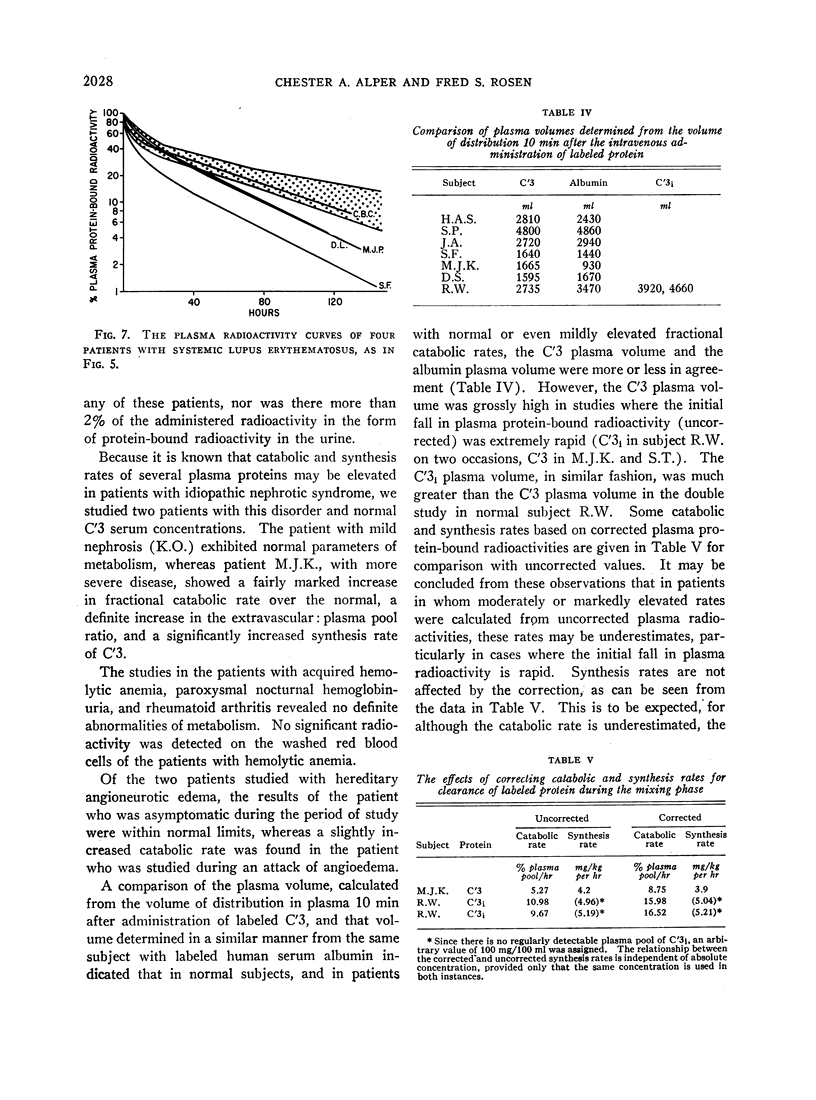
Increased catabolic rates were found in some patients with acute glomerulonephritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, idiopathic nephrotic syndrome of childhood, and progressive glomerulonephritis. Depressed synthesis was found in each of four studies of patients with progressive glomerulonephritis and seemed to be the major factor in the lowering of plasma C′3 concentrations regularly observed in patients with this disease. Of three patients with acute glomerulonephritis, synthesis rates of C′3 were markedly depressed in one subject, at the lower limit of normal in another, and entirely normal in the third. Increased extravascular: plasma pool ratios were observed in the studies of C′3i metabolism in a normal subject, and of C′3 metabolism in two of three patients with acute glomerulonephritis, in one of four patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, and in one patient with idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. The increased pool ratios are possibly compatible with tissue attachment of part of the injected C′3 or its conversion products.
No important abnormalities of metabolism were found in patients with acquired hemolytic anemia, paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria, hereditary angioneurotic edema, or rheumatoid arthritis.
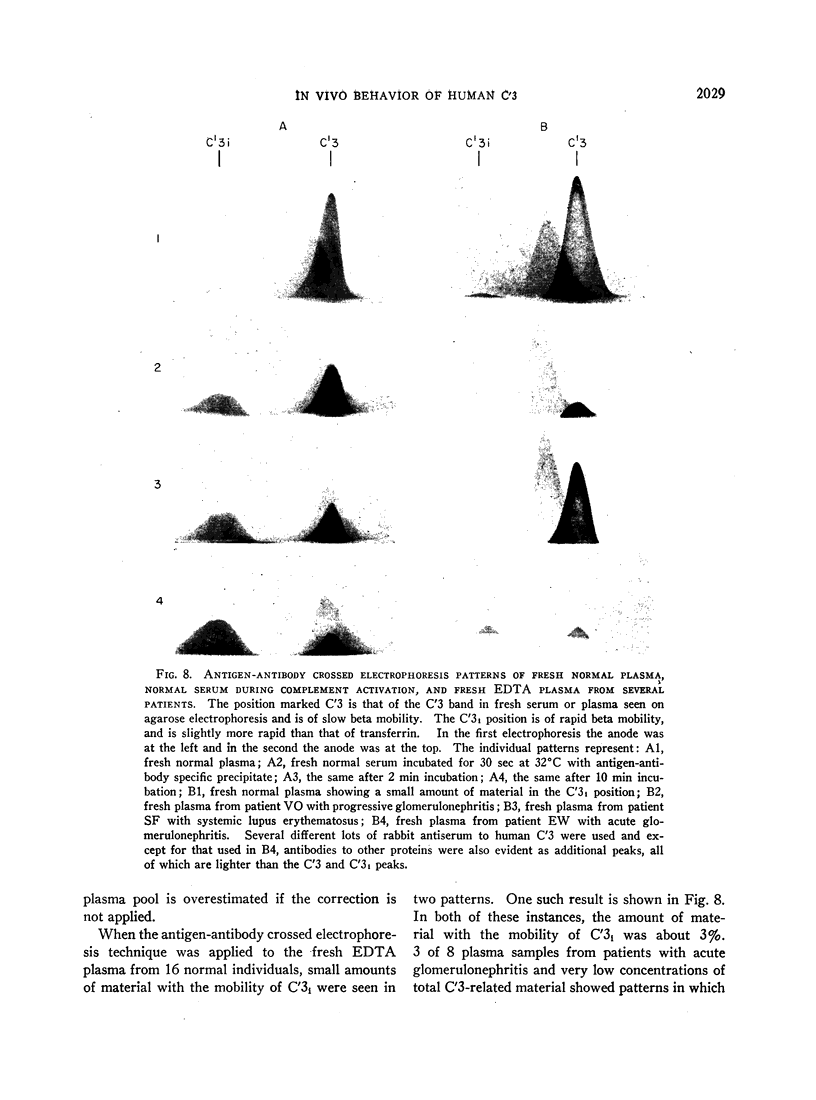
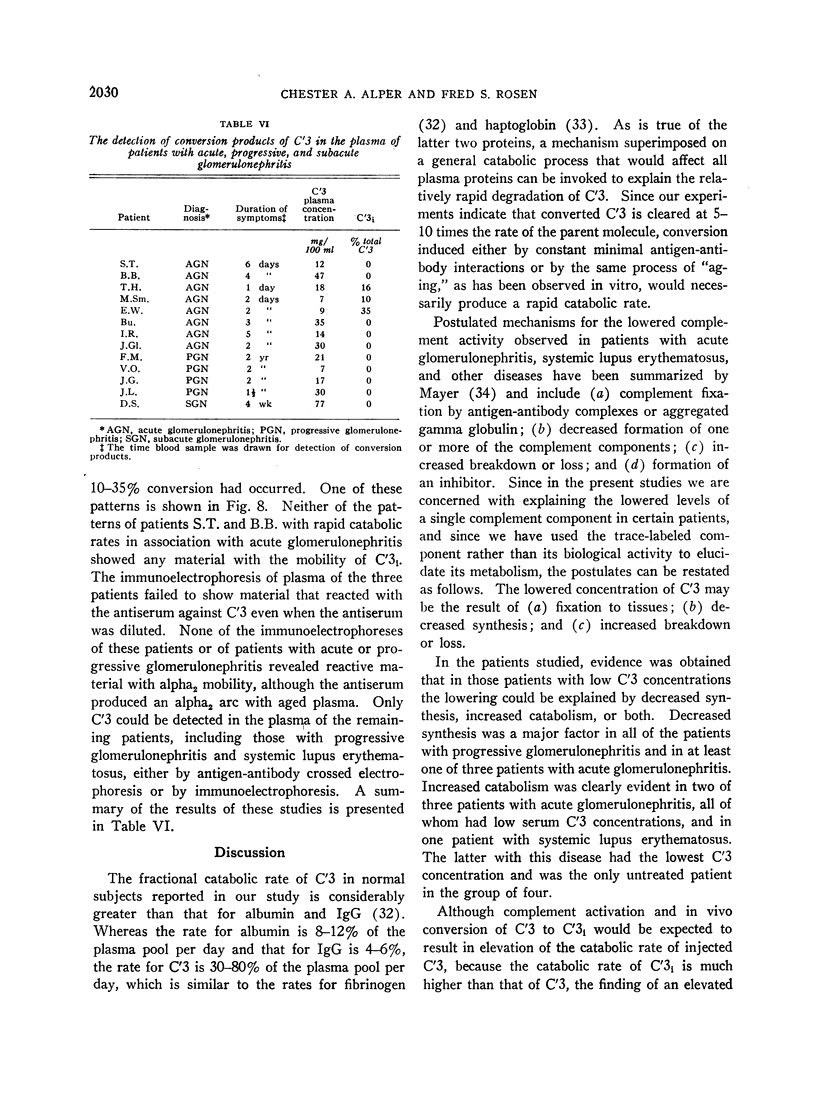
By means of antigen-antibody crossed electrophoresis, C′3i could be demonstrated in the fresh plasma of three of eight patients who had acute glomerulonephritis. This finding was used as evidence for in vivo complement activation in this disease. Since C′3i was demonstrated only in plasma from patients with very low plasma concentrations whose onset of symptoms was very recent, there may be two phases in the metabolism of C′3: early complement activation with resultant increased catabolism and later depressed synthesis, both of which lead to lowered serum concentrations.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALPER C. A., FREEMAN T., WALDENSTROEM J. THE METABOLISM OF GAMMA GLOBULINS IN MYELOMA AND ALLIED CONDITIONS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Dec;42:1858–1868. doi: 10.1172/JCI104870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper C. A., Levin A. S., Rosen F. S. Beta-1C-globulin: metabolism in glomerulonephritis. Science. 1966 Jul 8;153(3732):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.153.3732.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL R. M., CUTHBERTSON D. P., MATTHEWS C. M., MCFARLANE A. S. Behaviour of 14C- and 131I-labelled plasma proteins in the rat. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1956 Jul;1(1-2):66–84. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(56)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINBERG J. G. A specific assay method for biological solution with particular reference to allergen extracts. Immunology. 1959 Oct;2:346–350. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., JANEWAY C. A., FARR L. E. Studies on the metabolism of plasma proteins in the nephrotic syndrome. I. Albumin, gamma-globulin and iron-binding globulin. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jan;35(1):44–56. doi: 10.1172/JCI103251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTOFF S. P., FELLERS F. X., VAWTER G. F., JANEWAY C. A., ROSEN F. S. THE BETA-1C GLOBULIN IN CHILDHOOD NEPHROTIC SYNDROME: LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF PROGRESSIVE GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. N Engl J Med. 1965 Sep 2;273:524–529. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196509022731004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEMPERER M. R., GOTOFF S. P., ALPER C. A., LEVIN A. S., ROSEN F. S. ESTIMATION OF THE SERUM BETA-1C GLOBULIN CONCENTRATION: ITS RELATION TO THE SERUM HEMOLYTIC COMPLEMENT TITER. Pediatrics. 1965 May;35:765–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACHMANN P. J., MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., KUNKEL H. G., PARONETTO F. The localization of in vivo bound complement in tissue section. J Exp Med. 1962 Jan 1;115:63–82. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANGE K., WENK E. J. Complement components in the sera and urines of patients with severe proteinurias. Am J Med Sci. 1954 Oct;228(4):448–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B. ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY CROSSED ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1965 Feb;10:358–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(65)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURELL C. B., LAURELL S., SKOOG N. Buffer composition in paper electrophoresis; considerations on its influence, with special reference to the interaction between small ions and proteins. Clin Chem. 1956 Apr;2(2):99–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDH B. THE EFFECT OF INCUBATION WITH HYDRAZINE AND IMMUNOPRECIPITATE ON BETA-1C-GLOBULIN. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1965;63:266–274. doi: 10.1111/apm.1965.63.2.266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B., Lundh B. Electrophoretic studies of the conversion products of serum beta-1C-globulin. Immunology. 1967 Mar;12(3):313–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B., Niléhn J. E. A new type of inherited serum albumin anomaly. J Clin Invest. 1966 Dec;45(12):1935–1945. doi: 10.1172/JCI105498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATTHEWS C. M. The theory of tracer experiments with 131I-labelled plasma proteins. Phys Med Biol. 1957 Jul;2(1):36–53. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/2/1/305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORSE J. H., MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., KUNKEL H. G. Anti-nuclear factors and serum complement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1962 Oct;38:641–651. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER-EBERHARD H. J., NILSSON U., ARONSSON T. Isolation and characterization of two beta1-glycoproteins of human serum. J Exp Med. 1960 Feb 1;111:201–215. doi: 10.1084/jem.111.2.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. Efficient trace-labelling of proteins with iodine. Nature. 1958 Jul 5;182(4627):53–53. doi: 10.1038/182053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller-Eberhard H. J., Nilsson U. R., Dalmasso A. P., Polley M. J., Calcott M. A. A molecular concept of immune cytolysis. Arch Pathol. 1966 Sep;82(3):205–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J., Polley M. J., Calcott M. A. Formation and functional significance of a molecular complex derived from the second and the fourth component of human complement. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):359–380. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllerèberhard H. J., Dalmasso A. P., Calcott M. A. The reaction mechanism of beta-1C-globulin (C'3) in immune hemolysis. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):33–54. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NILSSON U. R., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. ISOLATION OF BETA IF-GLOBULIN FROM HUMAN SERUM AND ITS CHARACTERIZATION AS THE FIFTH COMPONENT OF COMPLEMENT. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:277–298. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POULIK M. D. Starch gel electrophoresis in a discontinous system of buffers. Nature. 1957 Dec 28;180(4600):1477–1479. doi: 10.1038/1801477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELIGMANN M., HANAU C. Etude immuno-électrophorétique du sérum de malades atteints de lupus érythémateux disséminé. Rev Hematol. 1958 Apr-Jun;13(2):239–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soothill J. F. Altered complement component C3A (beta-1C--beta-1A) in patients with glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1967 Jan;2(1):83–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNANUE E., DIXON F. J. EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. IV. PARTICIPATION OF COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:965–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEST C. D., NORTHWAY J. D., DAVIS N. C. SERUM LEVELS OF BETA-1C GLOBULIN, A COMPLEMENT COMPONENT, IN THE NEPHRITIDES, LIPOID NEPHROSIS, AND OTHER CONDITIONS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Aug;43:1507–1517. doi: 10.1172/JCI105027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West C. D., Winter S., Forristal J., McConville J. M., Davis N. C. Evidence for in vivo breakdown of beta-10-globulin in hypocomplementemic glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):539–548. doi: 10.1172/JCI105555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West C., Davis N. C., Forristal J., Herbst J., Spitzer R. Antigenic determinants of human beta-1c and beta-1g-globulins. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):650–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YACHNIN S. THE HEMOLYSIS OF RED CELLS FROM PATIENTS WITH PAROXYSMAL NOCTURNAL HEMOGLOBINURIA BY PARTIALLY PURIFIED SUB-COMPONENTS OF THE THIRD COMPLEMENT COMPONENT. J Clin Invest. 1965 Sep;44:1534–1546. doi: 10.1172/JCI105260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]