Abstract
RNA editing in flowering plant mitochondria post-transcriptionally alters several hundred nucleotides from C to U, mostly in mRNAs. Several factors required for specific RNA-editing events in plant mitochondria and plastids have been identified, all of them PPR proteins of the PLS subclass with a C-terminal E-domain and about half also with an additional DYW domain. Based on this information, we here probe the connection between E-PPR proteins and RNA editing in plant mitochondria. We initiated a reverse genetics screen of T-DNA insertion lines in Arabidopsis thaliana and investigated 58 of the 150 E-PPR-coding genes for a function in RNA editing. Six genes were identified to be involved in mitochondrial RNA editing at specific sites. Homozygous mutants of the five genes MEF18-MEF22 display no gross disturbance in their growth or development patterns, suggesting that the editing sites affected are not crucial at least in the greenhouse. These results show that a considerable percentage of the E-PPR proteins are involved in the functional processing of site-specific RNA editing in plant mitochondria.
Keywords: Arabidopsis, Mitochondria, Plant, RNA Editing, RNA Modification, RNA Processing, PPR Proteins
Introduction
RNA editing in mitochondria of flowering plants changes 400–500 selected cytosines to uridines mostly in coding regions of mRNAs and some tRNAs (1–3). In non-flowering plants such as Isoetes species, the number of edited nucleotides is estimated to be more than 1,500 (4), raising the question of how the to-be-edited nucleotides are distinguished from other unaltered moieties.
Specific sequence contexts in the pre-mRNA yield the first part of an answer; such cis-elements are required to identify a bona fide editing site as in vivo, in organelle, and in vitro analyses of several mitochondrial RNA-editing sites have shown (5–11). The second part of the answer seems to be provided by the identification of nuclear encoded specificity factors in Arabidopsis thaliana such as MEF1, MEF9, and MEF11 (mitochondrial-editing factor (MEF)2), which are required intact for correct editing of specific different sites (12–15).
The present theory is that the cis-elements in the mitochondrial RNA molecules are individually recognized by RNA-binding proteins, which may be these MEF proteins. This model makes several predictions, which need to be tested to correct or substantiate this connection. First, the nuclear-encoded MEF proteins must show an evolutionary diversity and a variation sufficient to recognize and target the more than 400 editing sites in plant mitochondria in, for example, A. thaliana. Secondly, the MEF proteins must be able to bind RNA and do so selectively to specific RNA sequences, the identified cis-elements. Specific RNA binding has been experimentally verified for one of the proteins required for a plastid RNA-editing event, the CRR4 protein (16) in addition to similar proteins involved in other RNA maturation steps (see Refs. 17, 18; for reviews, see Refs. 19, 20).
In this study, we addressed the first question and initiated an analysis to test if other proteins similar to MEF1, MEF9, and MEF11 are involved in RNA editing in plant mitochondria. The Arabidopsis mitochondrial-editing factors MEF1 and MEF11 as well as the OGR1 factor in rice (13–15, 21), are pentatricopeptide repeat proteins (PPR proteins) of the DYW subgroup as are several PPR proteins required for specific RNA-editing events in plastids. These DYW-PPR proteins are extended by the about 100-amino acid long DYW region at the C terminus beyond the preceding E-domain. The mitochondrial protein MEF9 as well as several plastid RNA-editing factors do not contain the DYW C terminus and terminate with the E-domain (12, 20, 22–29). Thus, all of the RNA-editing factors identified today belong to the E-class, suggesting that this E-domain is important for their function in the editing process.
In this reported analysis, we, therefore, focus on this E-subgroup of the 450 PPR proteins encoded in the nuclear genome of Arabidopsis (30–32). About 150 of the PPR proteins contain the E region and 87 of these also the DYW domain (19, 30, 33). Consequently we consider the DYW-containing PPR proteins a subgroup of the E-domain-containing PPR proteins. The DYW C-terminal extension is particularly intriguing in proteins involved in organellar RNA editing in plants because it displays a signature characteristic of Zn-containing cytidine deaminases. The enzymatic activity involved in the C to U RNA editing has not yet been identified, and the DYW domain has been proposed to potentially mediate this reaction (34, 35). On the other hand, truncated proteins without the DYW domain can still be competent in editing in vivo (36, 37).
To investigate whether more of the about 150 E-group proteins with 65 E-only and 87 DYW-E-PPR proteins are involved in RNA editing at specific sites in plant mitochondria, we here screened 58 T-DNA insertion lines of genes coding for DYW-E-PPR proteins and E-domain PPR proteins in Arabidopsis by a direct analysis for impaired RNA editing with the recently developed multiplexed SNaPshot procedure (38).
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Plant Material and Preparation of Nucleic Acids
A. thaliana seeds for the Columbia (Col) ecotype were kind gifts from J. Forner and S. Binder (Universität Ulm). The T-DNA insertion lines of A. thaliana were obtained from TAIR resources. Growth of the A. thaliana plants and preparation of DNA or RNA from leaves were as described (39). Seeds were sown as obtained and used for the initial screening in material from pools of eight plants. Young leaves were harvested from each plant line, single leaves from eight lines were pooled, and RNA was extracted. Identified mutants were selfed, and the T-DNA insertion sites and homozygocity of individuals were verified by PCR and sequence analysis. Development of the homozygous plants and pollen viability were monitored and documented as detailed in the respective figure legends.
SNaPshot Assays and Mutant Analysis
The 58 T-DNA insertion lines in E-PPR-proteins and the 3 in PLS-PPRs were screened by multiplexed single base extension (38) for plants with altered RNA editing at specific sites. Plants were first analyzed in pools of eight from which the deviant plants were recovered. In the identified individual plants, the compromised RNA-editing phenotype was verified by cDNA sequence analysis for the status of the respective investigated editing site. Oligonucleotides were from biomers.net, Ulm, Germany. Most sequences were obtained commercially from 4base lab, Reutlingen, Germany or from Macrogen, Seoul, Korea.
Analysis of RNA-editing Sites
Specific cDNA fragments were generated by RT-PCR amplification by established protocols (39). The cDNA sequences were compared for C to T differences resulting from RNA editing.
Protoplast Complementation Assays
Protoplasts were prepared from 3–4-week-old plantlets by the method of Yoo et al. (40). Transfected genes, including GFP as control and the respective wt Col reading frames, were expressed from the 35S promoter in the cloning site of vector pSMGFP4. Efficiency of the transfection was monitored by the signals from separately introduced or co-transfected GFP genes in the cytoplasm. Typically the GFP fluorescence was detected in more than 80% of the transfected protoplasts. Total RNA was isolated after 20–24 h of incubation at room temperature. Sequences of cDNAs were determined after RT-PCR with the respective specific primers. RNA-editing levels were estimated by the relative areas of the respective nucleotide peaks in the sequence analyses.
RESULTS
Selection of T-DNA Insertion Lines
From the SALK collection of T-DNA insertion lines, we selected 61 plant lines for which insertions were annotated in genes for PPR proteins of the DYW extension subclass (32 lines), of the E-domain-containing subgroup (26 lines) and of the PLS group without any further C-terminal extensions (3 lines and Table 1). The primary selection criterion was the availability (i.e. the annotation) of homozygous mutant plants in the lines to be analyzed. At the beginning of this project, only these 58 lines were described as homozygous for T-DNA insertions in (DYW-)E-class PPR genes in the databases. So far, none of the identified plastid or mitochondrial RNA-editing factors belongs to the PLS group; therefore, these latter three are unlikely candidates and are not expected to be involved in RNA editing. As genuine negative controls we included several lines, which had been identified as bona fide factors of plastid RNA editing such as CRR28 (37) and YS1 (29), and one which had been identified to be involved in other RNA maturation processes such as CRR2 (41). These three lines should thus not show any defect in mitochondrial RNA editing. Two other genes selected have in the meantime been identified as plastid-editing factors; these are OTP81 and OTP86 (42). Overall, within the 61 selected T-DNA insertion lines annotated as containing homozygous plants, 3 are mutated in PPR proteins not involved in mitochondrial editing, 3 have insertions in genes for PLS proteins, and 55 plant lines are mutated in E-domain-containing PPR protein-coding candidate genes.
TABLE 1.
The 61 T-DNA insertion lines of PPR proteins investigated are listed in the SALK collection as being homozygous
Lines are ordered according to the genomic locus in the Arabidopsis genome. The subclass characterized by the C-terminal extension is given in the next column. 58 of the PPR proteins analysed contain an E-domain, 32 of these also a DYW extension. For controls, 3 PLS-PPR proteins were included. Predictions by the two target analysis programs TargetP and predotar are given in the following columns: C indicating a plastid (chloroplast) and M a mitochondrial prediction. Names of genes with known functions are given in bold for those newly found in this investigation, and their target sites are identified. Citations are given for those identified by others before or during the course of this work. The last two columns give the SALK numbers, and show the location of the T-DNA insert.
| Arabidopsis locus | Subclass | TargetP | Predotar | Gene name | Editing defect in mitochondria (position in CDS) | Editing defect in Chloroplast (genome position) | Refs. | T-DNA insertion lines | T-DNA location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| At1g04840 | DYW | M | SALK_020491C | CDS | |||||
| At1g08070 | DYW | C | C | SALK_084804C | CDS | ||||
| At1g29710 | DYW | M | M | SALK_102463C | Promoter | ||||
| At1g47580 | E+ | M | M | SALK_038140C | Promoter | ||||
| At1g50270 | E+ | SALK_036097C | CDS | ||||||
| At1g59720 | DYW | C | CRR28 | ndhB (96698), ndhD (116290) | SALK_115133C | CDS | |||
| At1g64310 | E | M | C | SALK_069611C | CDS | ||||
| At1g68930 | DYW | M | SALK_085526C | Promoter | |||||
| At1g71420 | DYW | C | M | SALK_083202C | CDS | ||||
| At1g71490 | PLS | C | SALK_132831C | CDS | |||||
| At1g74600 | E | C | C | SALK_112173C | Promoter | ||||
| At2g20540 | E+ | MEF21 | cox3-257 | SALK_123212C | CDS | ||||
| At2g25580 | DYW | M | M | MEF8 | nad5-676 | SALK_106391C | CDS | ||
| At2g27610 | DYW | M | SALK_067071C | CDS | |||||
| At2g29760 | DYW | C | C | OTP81 | rps12 intron (69553) | Hammani et al. (42) | SALK_092402C | CDS | |
| At2g40720 | E+ | SALK_039787C | CDS | ||||||
| At3g02330 | E+ | M | C | SALK_097270C | CDS | ||||
| At3g03580 | DYW | C | C | SALK_025107C | Promoter | ||||
| At3g05240 | E | M | MEF19 | ccb206-566 | SALK_131274C | CDS | |||
| At3g11460 | DYW | M | M | SALK_061966C | Promoter | ||||
| At3g12770 | DYW | MEF22 | nad3-149 | SALK_107216C | CDS | ||||
| At3g14330 | DYW | M | SALK_077977C | CDS | |||||
| At3g14730 | E+ | M | C | SALK_093086C | Promoter | ||||
| At3g18970 | E | M | M | MEF20 | rps4-226 | SALK_051287C | CDS | ||
| At3g22690 | DYW | C | C | YS1 | rpoB (25992) | Zhou et al. (29) | SALK_123515C | CDS | |
| At3g24000 | DYW | M | M | SALK_055539C | 5′UTR | ||||
| At3g25970 | E+ | S | SALK_070881C | Promoter | |||||
| At3g26630 | PLS | C | C | SALK_124331C | 5′UTR | ||||
| At3g46790 | DYW | C | CRR2 | Hashimoto et al. (41) | SALK_030786C | CDS | |||
| At3g50420 | E+ | SALK_062063C | CDS | ||||||
| At3g51320 | E | M | M | SALK_022718C | 5′UTR | ||||
| At4g01990 | E | M | M | SALK_088721C | CDS | ||||
| At4g14050 | DYW | M | M | SALK_052078C | CDS | ||||
| At4g14820 | DYW | C | SALK_128858C | CDS | |||||
| At4g15720 | DYW | SALK_089468C | Promoter | ||||||
| At4g18520 | PLS | C | M | SALK_054374C | CDS | ||||
| At4g18750 | DYW | C | C | SALK_106218C | Promoter | ||||
| At4g19220 | E | M | M | SALK_032609C | Promoter | ||||
| At4g20770 | E | M | M | SALK_061964C | CDS | ||||
| At4g22760 | E | S | M | SALK_046917C | Promoter | ||||
| At4g30700 | DYW | M | SALK_059311C | CDS | |||||
| At4g32450 | DYW | M | M | SALK_047005C | CDS | ||||
| At4g33170 | DYW | C | SALK_043048C | CDS | |||||
| At4g35130 | DYW | C | C | SALK_0649 49C | CDS | ||||
| At4g37170 | DYW | M | SALK_021806C | Promoter | |||||
| At4g38010 | E | SALK_062576C | CDS | ||||||
| At4g39530 | E+ | M | M | SALK_130673C | 3′UTR | ||||
| At5g15340 | DYW | M | M | SALK_033610C | CDS | ||||
| At5g16860 | DYW | M | SALK_126201C | Promoter | |||||
| At5g19020 | E | M | M | MEF18 | nad4-1355 | SALK_126644C | CDS | ||
| At5g27110 | E+ | M | C | SALK_053627C | CDS | ||||
| At5g43790 | E | SALK_064501C | CDS | ||||||
| At5g46460 | DYW | M | M | SALK_033891C | 5′UTR | ||||
| At5g47460 | E | M | SALK_079594C | CDS | |||||
| At5g50390 | DYW | C | C | SALK_076606C | Promoter | ||||
| At5g52850 | DYW | C | C | SALK_085242C | CDS | ||||
| At5g59200 | E+ | C | C | OTP86 | rps14(37161) | Hammani et al., (42) | SALK_060533C | CDS | |
| At5g59600 | E | SALK_072473C | 5′UTR | ||||||
| At5g61800 | E | M | M | SALK_109464C | CDS | ||||
| At5g66500 | E | M | M | SALK_044034C | CDS | ||||
| At5g66520 | DYW | SALK_078415C | CDS |
Intracellular location predictions of all 61 mutated proteins were analyzed separately with the TargetP and Predotar programs, respectively. Both programs predicted 11 of these PPR proteins to be targeted to the plastid. Six more proteins were predicted by one of the two programs to the plastid, while the other program could not make a decision. Four proteins were targeted to mitochondria by one program, while plastid locations were predicted by the other program. For 8 PPRs, predictions for mitochondria were made by one program, while both programs targeted 16 polypeptides to the mitochondria. The other PPR proteins could not be sorted or gave other compartments (Table 1). These predictions turned out to be rather accurate, especially when both programs predicted the same organelle, mitochondrion or plastid, because no case was observed in which the prediction was erroneous. Two of the proteins for which no predictions were possible are identified here as mitochondrial RNA-editing factors (MEF21 and MEF22). Insertions of the T-DNA were annotated to be in coding sequences in 35 lines, of which 19 were predicted for a mitochondrial location by either or both of the prediction programs and 16 could not be assigned to either organelle (Table 1).
For the RNA-editing analysis with the SNaPshot screen, all 61 lines were grown from the seed sample as obtained from the collections. RNA was extracted for the analysis from young leaves of individual plants from this first generation. This rapid direct approach will thus include erroneous identification of T-DNA insertion sites as well as cases of problematic differentiation between homo- and heterozygous plants. To reduce the number of candidate lines to be tested in a more focused next generation approach, it would be advantageous to first confirm the T-DNA sites in each of the plant lines and to identify genuine homozygous individuals.
Identification of Mitochondrial RNA-editing Defects in the T-DNA Insertion Lines
The selected T-DNA insertion lines were screened for deficiencies in RNA editing at specific sites in plant mitochondria with the recently developed multiplexed SNaPshot approach (38). With this assay, 269 annotated editing sites were probed in RNAs prepared from pooled leaves picked from individuals of eight lines. The 269 editing sites were thus probed in seven pools of eight and one of five plants to test each of the 61 T-DNA lines for mutant plants impaired in RNA editing at one or more of the investigated sites.
RNA-editing defects were found for 6 of the 61 insertion lines in different mitochondrial mRNAs, 5 of which are documented in Fig. 1. The editing sites affected by disruption of the gene coding for MEF8 will be detailed and discussed elsewhere; this gene was identified in parallel by screening and mapping of EMS-induced mutations in an A. thaliana population (38). The five mutant plants mef18-mef22 were identified in their respective “horizontal” pools of 8 plants by an analysis of “vertically” pooled plants as described (38). These individual plants were then investigated for the insertion site of the T-DNA and were confirmed to be homozygous by PCR assays across the insertion (detailed below). The defect in RNA editing in each mutant was documented by direct sequence analysis of the affected mitochondrial cDNAs (Fig. 1B). These sequence tracings reveal a complete loss of RNA editing at specific sites in the mef18-mef21 mutant plants and lowered editing at site nad3-149 in mef22.
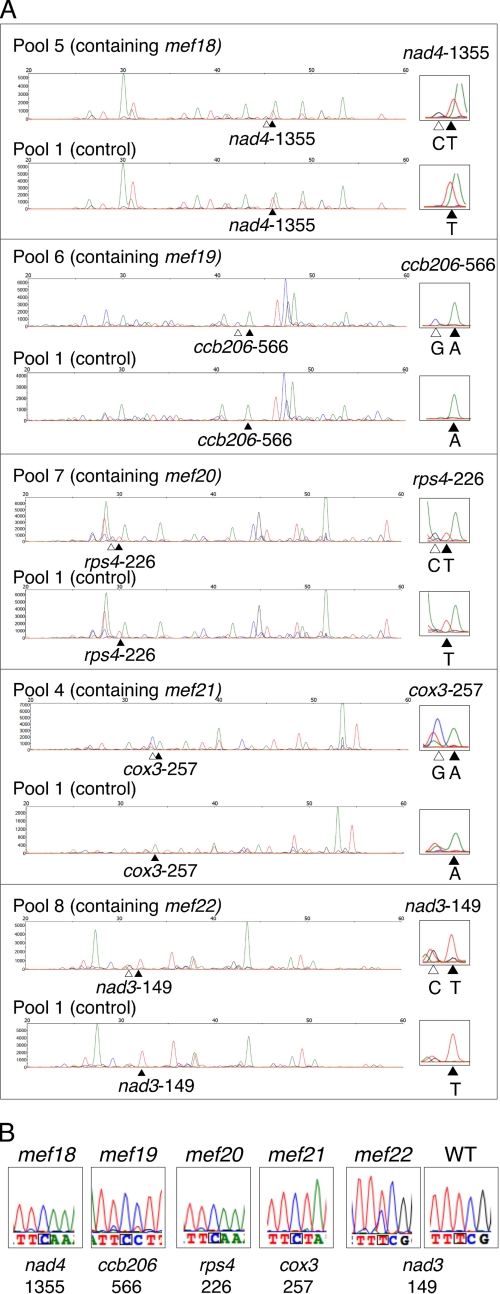
FIGURE 1.
A SNaPshot screen of 58 T-DNA insertion lines of E-class PPR proteins identifies five lines defective in RNA editing at specific sites in mitochondrial RNAs of the mutant plants. A, SNaPshot analyses of RNA-editing sites in the cDNAs of the indicated mitochondrial mRNAs are shown for the identification of the five mutants mef18-mef22 in A. thaliana. The left parts show an analysis of the RNA prepared from pooled leaves of 8 plants each, the top lines contain the mutant line indicated and for comparison of the tracing of pool 1, which contain none of these mutants as a negative control. The relevant sites are shown enlarged on the right hand side with the C and G traces derived from one unedited (or partially edited) plant in the pool indicated by open arrowheads. The filled arrowheads point to the respective T or A traces of the edited nucleotide. The open triangles indicate the respective C or G traces of the nucleotide unedited in the mutant plant. The mutant will be present as one in eight plants and will therefore yield a proportionally lower signal. A sixth T-DNA mutant, MEF8, was identified in parallel by mapping of EMS mutants and will be described elsewhere. B, direct sequence analysis of the disturbed RNA-editing sites in the cDNAs of the five mutants mef18-mef22 shows a complete loss of editing at the sites identified in mutants mef18-mef21, whereas mutant mef22 displays in comparison to a Col wild-type A. thaliana plant (WT) reduced editing of about 40% detectable C to U conversion. The mutant plants were confirmed by PCR to be homozygous for the T-DNA insertion. Color traces are C, blue; T, red; G, black; A, green.
Complementation of the mef18 to mef22 T-DNA Insertion Mutants
The connection between the annotated T-DNA insertions in the MEF18 to MEF22 genes, and the absence or reduction of RNA editing at the specific target sites was further assayed by exploring the ability of the respective wild type (wt)-A. thaliana ecotype Columbia (Col) genes to complement the corresponding mutants. The Col wt genes were cloned under the control of the [35S]CaMV promoter, and the plasmid DNAs were transfected into the respective mutant protoplasts (40, 15). The four wt genes MEF18 to MEF21 restored the ability for RNA editing at the respective editing sites in the transfected mutant protoplasts and the fifth gene MEF22 increased the reduced editing at site nad3-149 (Fig. 2). Control transfections with only a GFP sequence in the vector did not alter editing at the sites monitored. These protoplast complementation results confirm that the intact MEF18 to MEF21 genes are required for the RNA editing events found missing in the respective T-DNA insertion lines and that the MEF22 protein enhances editing at least at site nad3-149.
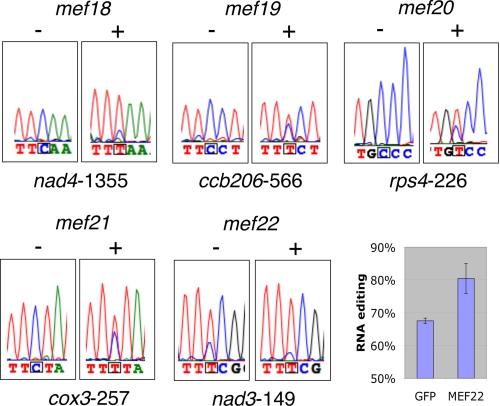
FIGURE 2.
Introduction of the Col WT version of the genes MEF18 -MEF22 into the respective mutant protoplasts restores the ability for RNA editing in the mutants. Untransfected mutant protoplasts mef18-mef21 (−) show no detectable editing at the cognate sites. Competence for editing of these sites is recovered upon introduction of the respective Col wild-type gene (+). In mutant mef22 the level of the diminished editing at site nad3-149 is enhanced by the introduction of the Col wild-type MEF22 gene. The inset on the right shows the average increase in editing by the Col wt MEF22 gene in three experiments (MEF22) in comparison to the respective control transfections with GFP (GFP). Nucleotide assignment represents the strongest signal displayed. Color traces are C, blue; T, red; G, black; A, green.
Phenotypes of the mef18 to mef22 Mutant Plants
The five T-DNA insertion lines are annotated to yield viable homozygous seeds and plants. Individual plants were grown from each of these five lines and were investigated by PCR for the presence of the respective mutant alleles. In all five lines, products of the mutant alleles but not of the respective wild-type PPR genes were obtained, confirming that these plants are homozygous for the mutant alleles.
To investigate the physiological requirements of the affected editing sites, we analyzed the developing plantlets and documented their habitus and overall growth parameters. As already suggested by the production of homozygous mutant seeds, all mef18 to mef22 mutant plants grow normally (Fig. 3 and supplemental Fig. S1). Growth habitus, time of bolting, aging of leaves, flower set, shapes of infloresceces, and appearances of the seed pods appear indistinguishable from the wild-type Columbia plants. Pollen maturation and viability were investigated specifically because in plants mitochondrial malfunction is known to affect pollen development. Stains of anthers and pollen showed the same viability patterns as the wild-type plants (Fig. 3C and supplemental Fig. S2). Fertility does not seem to be affected because self-pollination of individual plants yielded the normal full seed pods as did the wt plants.
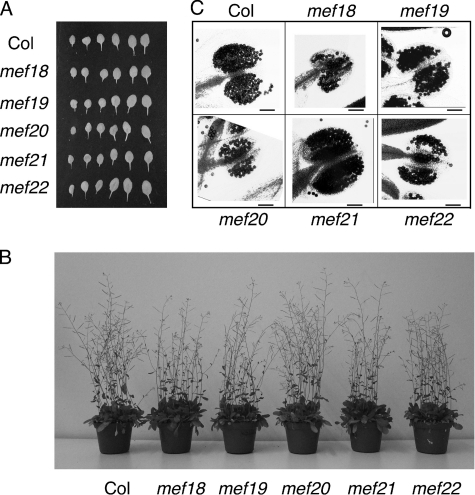
FIGURE 3.
Mutant plants develop similar to wild-type plants. Homozygous mutant plants with the T-DNA insertions in the genes MEF18 -MEF22 grow normally and are, in the greenhouse, indistinguishable from the Col wild-type plants. A, the six largest leaves were collected from Col wt and the mutant plants 3 weeks after seeding and aligned for comparison. Overall numbers of leaves (supplemental Fig. S1), their shapes, and sizes are similar between the mutants and the Col wt plants. B, pictures of several plants per pot are shown after 6 weeks of growth. C, the anthers from Col wt and the mutant plants were prepared and stained for viability (12). Staining of individual pollen kernels and further pictures of plants are shown in the supplemental figures.
Even though these gross phenotypic characters appear normal, minor disturbances of mitochondrial functions caused by the deviant proteins synthesized from the respective unedited mRNAs may become apparent under different conditions. While these potentially detrimental effects may be largely compensated for under greenhouse conditions, such disturbances of the affected respiratory chain complexes or the ribosome, respectively, will be worth investigating in detail. In depth biochemical and functional studies of mitochondrial activities of one or the other of these in effect point mutations in mitochondrial mRNAs and thus the respectively encoded proteins may be useful to yield information on the assembly, structure, and/or function of the mitochondrial multiprotein complexes.
Processing and RNA Stability Are Not Affected by the Mutations in mef18-mef22
To investigate whether the observed RNA-editing defects in the mutant lines are caused by indirect effects such as altered RNA processing or modified RNA stability, the transcript patterns of the respectively affected mitochondrial genes cox3, ccb206, rps4, nad3, and nad4 were analyzed in the homozygous mutant plants (Fig. 4). The RNA blot hybridization reveals comparable quantities of the respective mature transcripts from all five genes between Col wild-type plants and the respective mutants, suggesting that the mutations in the MEF18-MEF22 genes do not affect the accumulation of these transcripts. An increased amount of a given mRNA by an altered RNA stability could for example outtitrate a limited amount of the RNA-editing factor required for the affected site in this transcript. Processing of the various mRNAs likewise does not seem to be affected in the mutants, because the stoichiometry of precursor and mature transcripts are not detectably influenced in any of the mutants. These observations support direct and specific roles of the MEF18-MEF22 genes in RNA editing at the identified sites.
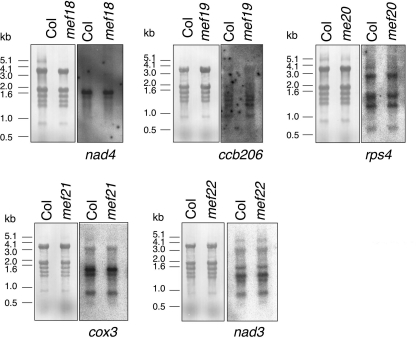
FIGURE 4.
Transcript patterns of the mitochondrial target RNAs in Col wild type and the mef18-mef22 mutants. The transcript patterns of the mitochondrial nad4, ccb206, rps4, cox3, and nad4 genes in the respective mutant plants are compared by RNA blot analyses. The hybridization signals of the gene-specific probes show comparable patterns and similar amounts of the respective precursors and mature transcripts from all five genes in Col and in the respective mef18 to mef22 mutants. The source of the respective total cellular RNA preparation is given above each lane. Stained gels in the left panels show the intactness of each RNA preparation. The right panels show the Northern assays with the labeled mitochondrial gene probes indicated underneath. The positions of DNA size standards are indicated alongside in kbp.
Target Sequences at the RNA-editing Sites
For several editing sites in mitochondria and plastids, in vitro and in organello investigations have identified the cis-elements in the RNA context to occupy the region between 20 or 25 nucleotides upstream (5′) and 1 or 3 nucleotides downstream (3′) of the edited C (5, 6, 8, 10, 11, 43–46). Therefore, for the sites affected in the mef18 to mef22 mutants, a similar extent of the recognition sequences may be expected. The comparison of this region between different plant species shows that at the five editing sites, a U is conserved in most land plants (supplemental Fig. S3).
Searching in silico the sequence of the mitochondrial genome of Arabidopsis for motifs similar to the sequences surrounding each of the edited C nucleotides, scattered shared nucleotide identities are found with 6–10 coinciding residues but with no common pattern. The most similar sites were tested in the respective mutants, but none of these show any defect in editing. If such further similar editing sites are addressed by either of the MEF18-MEF22 PPR proteins, their roles or requirements are readily substituted by other factors. Yet other target sites may show less overall but crucial shared cis-motifs and may be additional targets for the MEF18–22-editing factors.
DISCUSSION
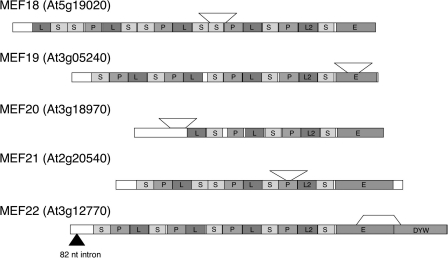
Here we functionally assign the five PPR proteins MEF18-MEF22 to be involved in RNA editing in plant mitochondria and identify target sites for each of these proteins. The five T-DNA insertions disrupt the respective reading frames and have induced the deletion of fragments of the coding sequences (Fig. 5). The insertions in MEF18 and MEF21 are within the PPR repeats, the insert in MEF20 is just upstream of the ATG codon. These three insertions and sequence deletions appear to disable gene functions because editing is lost at their target sites. The insertion in MEF22 in the E-domain and the thus disabled partial E-domain potentially does not completely abolish the function of the mutant protein. If stably transcribed and translated, the mutant protein may still be partially functional and thus may cause the only partial reduction of editing at the target site. The insertion in the MEF19 mutant is also in the E-domain, but most likely abolishes the competence in RNA editing because no nucleotide conversion is observed at the target site of MEF19.
FIGURE 5.
Comparison of the modular structural composition of the proteins MEF18-MEF22 as deduced from their gene sequences. MEF18-MEF21 contain only an E-domain, MEF22 has in addition a C-terminal adjacent DYW-domain. The P-L2-S repeats preceding the E-domains in MEF18-MEF22 are rather well conserved and are labeled according to recent nomenclature (29). The sites of the T-DNA insertions confirmed by PCR and sequence analysis are indicated by arrowheads. Open brackets depict the borders of the deletions at the T-DNA insertion sites. Further details of the insertions are shown online (supplemental Fig. S5). MEF20 is annotated to be interrupted by an intron (filled triangle), but this is not given in TAIR, and two EST clones are colinear with the genomic sequence.
We detected no gross detrimental phenotypic effect on plant growth and development in the homozygous T-DNA insertion lines in which no editing is seen at the target sites for MEF18-MEF21. The second finding in common for these five factors is that as yet only single targets have been identified for each of them. Both common features may be connected to the selection of homozygous and basically healthy T-DNA plants, because loss of a single editing event may be less likely to be detrimental to plant health than the elimination of several editing events. However, fully functional mitochondrial proteins specified by fully edited mRNAs may be crucial under more stressful growth conditions in the wild.
Analogous observations have been reported for plastid-editing sites, several of which, although highly conserved, show no phenotypical consequences when their cognate-editing factors are disabled by T-DNA mutations (42). These congruent findings in both organelles impact considerations underlying analyses of evolutionarily conserved editing sites and their loss in individual plant lineages (47).
The Target Sites of MEF18-MEF22 Alter Conserved Amino Acids
All target-editing sites alter the encoded amino acid sequence; none of the events is silent. The nad4-1355 site of MEF18 alters a serine to a conserved leucine codon in the NAD4 protein, the ccb206-566-editing event of MEF19 results in encoding a conserved phenylalanine rather than a serine in CCB206, the rps4-226 site requires MEF20 to change a proline amino acid to a serine residue codon at amino acid residue 76 in RPS4. The cox3-257 site targeted by MEF21 changes a serine amino acid to a conserved phenylalanine residue at amino acid 86 in COX3 and MEF22 enhances editing at nad3-149 to code for a conserved phenylalanine rather than a serine.
At most of these positions, all land plants including the moss and the liverwort incorporate the amino acid into the protein specified after the respective editing event in Arabidopsis (supplemental Fig. S3), suggesting that these conserved residues are important for proper function. From this high degree of conservation, one would expect impaired proteins synthesized from mRNA intermediates unedited at these positions and thus detectable physiological consequences on the growth pattern and phenotypes of the plants. The apparently normal growth and absence of any gross malformation in the greenhouse is similar to the phenotypes seen for MEF1 and MEF9 (12, 15). These observations suggest that the criterion of conservation of an amino acid (and an underlying editing event) between different plant species is not a straightforward indicator of functional importance.
The Five Identified MEF Proteins Have Different Compositions
The predicted gene structures of the five PPR proteins and their annotated T-DNA insertion sites show that only one, MEF22, belongs to the DYW subclass of the E-PPR proteins. The other four predicted PPR proteins, MEF18-MEF21, are also members of the E-group, but do not contain the C-terminal DYW extension (Fig. 5). The five proteins MEF18-MEF22 show very little structural similarity in the order and sizes of the various PPRs. MEF20 is, with about 8 repeats, the shortest, MEF18 with 17 predicted repeats the longest. These two proteins display a rather degenerated E-domain, in which only a C-terminal part is fairly well conserved, whereas the region between the C-terminal discernible PPR and this conserved E-internal region displays little similarity. Furthermore, MEF18 and MEF20 terminate within the actual E-domain just beyond the conserved E-internal region. MEF19 is only few amino acids longer than MEF18 and MEF20 and of the same size as MEF9 (12). The P, L2, and S repeats (nomenclature according to Ref. 48) just upstream of the E-domain are much better conserved between these and the other MEF proteins than any of the further N-terminal PPR repeats. Assignments of further PPR proteins to the functional group of RNA-editing factors will show which of these similar features is a characteristic feature of MEF-PPR proteins distinguishing these from non-MEF-PPRs. Recently, a PPR protein of the P subfamily without E- or DYW domain has been found to influence RNA-editing levels, in fact to lower the percentage of edited steady state mRNAs for a ribosomal protein (49).
When searching the genomic databases of other plant species for orthologs of the five proteins MEF18-MEF22, an interesting distribution emerges for MEF20: the three fully sequenced dicot plants Arabidopsis, Brassica oleracea, and Vitis vinifera encode clearly assigned orthologs and show this editing event at the mitochondrial rps4-226 site. In rice, where the mitochondrial genome already encodes a T residue, no ortholog of MEF20 is detected. This finding may suggest that since this editing event is not required in rice, the dedicated factor MEF20 has been lost from the genome. This scenario would support the assumption that MEF20 is required only for this single editing event in the mitochondrial transcriptome of Arabidopsis.
On the other hand, orthologs of MEF22 are detected in all four flowering plants, although Vitis does not require this editing event since a U corresponding to the editing site can be directly transcribed from the mitochondrial genomic sequence. In Arabidopsis, we observe that disruption of MEF22 only lowers editing at this site, and there may be another target site not yet identified that requires this factor in Arabidopsis and also in the grape. Alternatively, if stably transcribed and translated, the mutant protein of mef22 may still be partially functional and thus may cause only partial reduction of the editing at the target site. Orthologs can be found for MEF18, 19, and 21 in the four vascular plants, with the most similar grapevine PPR protein varying more from Arabidopsis MEF18 than the orthologs in the other plants.
Further E-class PPR Proteins May Be Required for Functionally Important Editing Events
The selection criterion of having yielded viable homozygous T-DNA insertion mutants will have preselected for editing events with minor biochemical and physiological impact. The other about 90 E-class PPR proteins may be required for editing reactions resulting in amino acid changes with major structural and functional consequences. This may be the reason why no homozygous lines had been annotated for these other genes. A number of the E-class proteins will not be involved in RNA editing at all but in other functionally important RNA-processing steps (20, 27, 50–52).
Nevertheless many more E-class PPR proteins, also within the group analyzed, may be involved in mitochondrial-editing sites. Several lines of reasoning contribute to this assumption: Foremost, one-third of the T-DNA lines investigated here are annotated to have a T-DNA insertion outside of the actual reading frames and may not be affected in the function of the respective PPR protein. Likewise not or little affected may be proteins from genes with insertions near their C termini (14). Further factors may have been missed if homozygous seeds were not present, and the original seed batches contained only heterozygous seeds. Other, small effects of specific PPR proteins like that observed for MEF22 at nad3-149 may have escaped our screen. Furthermore, we screened only 2/3 of the editing sites in the Arabidopsis mitochondrial transcriptome and thus will have missed the E-class PPR proteins involved in the editing events that are not included.
Outside of the T-DNA insertion lines of genes for E-class PPR proteins annotated as yielding homozygous plants, there will be more of such proteins involved in RNA editing in plant mitochondria. These other factors may affect more than one editing site as observed for some of the previously identified plant mitochondrial-editing factors MEF1, MEF11, and OGR1 (13–15, 21). Chances are that knock-out mutants of such factors will accumulate additive effects from disturbances of several unedited mitochondrially encoded proteins and therefore will show defects in their physiology even in the greenhouse. These genes will then not be amenable to identification by T-DNA insertions, which abolish gene function, but will require the analysis of more mild mutations such as the EMS mutants we are investigating in parallel (38). These may allow access to such further trans-factors dedicated to editing sites, which need to be processed for proper mitochondrial function.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Dagmar Pruchner for excellent experimental help. We are grateful to Stefan Binder, Joachim Forner, Angela Hölzle, and Christian Jonietz (All at Molekulare Botanik, Universität Ulm, Germany) for gifts of plant lines and other materials.
This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (to M. T. and A. B.).

The on-line version of this article (available at http://www.jbc.org) contains supplemental Figs. S1–S5.
- MEF
- mitochondrial-editing factor
- PPR
- pentatricopeptide repeat protein
- Col
- Columbia.
REFERENCES
- 1.Giegé P., Brennicke A. (1999) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96, 15324–15329 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Handa H. (2003) Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 5907–5916 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Takenaka M., Verbitskiy D., van der Merwe J. A., Zehrmann A., Brennicke A. (2008) Mitochondrion 8, 35–46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Grewe F., Viehoever P., Weisshaar B., Knoop V. (2009) Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 5093–5104 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bock R., Hermann M., Kössel H. (1996) EMBO J. 15, 5052–5059 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bock R., Koop H. U. (1997) EMBO J. 16, 3282–3288 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chateigner-Boutin A. L., Hanson M. R. (2002) Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 8448–8456 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Farré J. C., Leon G., Jordana X., Araya A. (2001) Mol. Cell. Biol. 21, 6731–6737 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kempken F., Bolle N., Bruhs A. (2009) Endocytobiosis Cell Res. 19, 1–10 [Google Scholar]
- 10.Neuwirt J., Takenaka M., van der Merwe J. A., Brennicke A. (2005) RNA 11, 1563–1570 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.van der Merwe J. A., Takenaka M., Neuwirt J., Verbitskiy D., Brennicke A. (2006) FEBS Lett. 580, 268–272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Takenaka M. (2010) Plant Physiol. 152, 939–947 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Tang J., Kobayashi K., Suzuki M., Matsumoto S., Muranaka T. (2010) Plant J. 61, 456–466 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Verbitskiy D., Zehrmann A., van der Merwe J. A., Brennicke A., Takenaka M. (2010) Plant J. 61, 446–455 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zehrmann A., Verbitskiy D., van der Merwe J. A., Brennicke A., Takenaka M. (2009) Plant Cell 21, 558–567 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Okuda K., Nakamura T., Sugita M., Shimizu T., Shikanai T. (2006) J. Biol. Chem. 281, 37661–37667 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Beick S., Schmitz-Linneweber C., Williams-Carrier R., Jensen B., Barkan A. (2008) Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 5337–5347 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Williams-Carrier R., Kroeger T., Barkan A. (2008) RNA 14, 1930–1941 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Delannoy E., Stanley W. A., Bond C. S., Small I. D. (2007) Biochem. Soc. Trans. 35, 1643–1647 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Schmitz-Linneweber C., Small I. D. (2008) Trends Plant Sci. 13, 663–670 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim S. R., Yang J. I., Moon S., Ryu C. H., An K., Kim K. M., Yim J., An G. (2009) Plant J. 59, 738–749 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Cai W., Ji D., Peng L., Guo J., Ma J., Zou M., Lu C., Zhang L. (2009) Plant Physiol. 150, 1260–1271 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Chateigner-Boutin A. L., Ramos-Vega M., Guevara-García A., Andrés C., Gutierrez-Nava M., Cantero A., Delannoy E., Jiménez L. F., Lurin C., Small I. D., León P. (2008) Plant J. 56, 590–602 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kotera E., Tasaka M., Shikanai T. (2005) Nature 433, 326–330 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Okuda K., Myouga F., Motohashi R., Shinozaki K., Shikanai T. (2007) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 8178–8183 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Robbins J. C., Heller W. P., Hanson M. R. (2009) RNA 15, 1142–1153 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shikanai T. (2006) Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 63, 689–708 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yu Q. B., Jiang Y., Chong K., Yang Z. N. (2009) Plant J. 59, 1011–1023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhou W., Cheng Y., Yap A., Chateigner-Boutin A. L., Delannoy E., Hammani K., Small I. D., Huang J. (2009) Plant J. 58, 82–96 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Andrés C., Lurin C., Small I. D. (2007) Physiol. Plant. 129, 14–22 [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lurin C., Andrés C., Aubourg S., Bellaoui M., Bitton F., Bruyère C., Caboche M., Debast C., Gualberto J. M., Hoffmann B., Lecharny A., Le Ret M., Martin-Magniette M. L., Mireau H., Peeters N., Renou J. P., Szurek B., Taconnat L., Small I. (2004) Plant Cell 16, 2089–2103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Small I. D., Peeters N. (2000) Trends Biochem. Sci. 25, 46–47 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nakamura T., Sugita M. (2008) FEBS Lett. 582, 4163–4168 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rüdinger M., Polsakiewicz M., Knoop V. (2008) Mol. Biol. Evol. 25, 1405–1414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Salone V., Rüdinger M., Polsakiewicz M., Hoffmann B., Groth-Malonek M., Szurek B., Small I., Knoop V., Lurin C. (2007) FEBS Lett. 581, 4132–4138 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Okuda K., Hammani K., Tanz S. K., Peng L., Fukao Y., Myouga F., Motohashi R., Shinozaki K., Small I., Shikanai T. (2010) Plant J. 61, 339–349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Okuda K., Chateigner-Boutin A. L., Nakamura T., Delannoy E., Sugita M., Myouga F., Motohashi R., Shinozaki K., Small I., Shikanai T. (2009) Plant Cell 21, 146–156 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Takenaka M., Brennicke A. (2009) Nucleic Acids Res. 37, e13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Takenaka M., Brennicke A. (2007) Methods Enzymol. 424, 439–458 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yoo S. D., Cho Y. H., Sheen J. (2007) Nature Protocols 2, 1565–1572 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hashimoto M., Endo T., Peltier G., Tasaka M., Shikanai T. (2003) Plant J. 36, 541–549 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hammani K., Okuda K., Tanz S. K., Chateigner-Boutin A. L., Shikanai T., Small I. (2009) Plant Cell 21, 3686–3699 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Chaudhuri S., Maliga P. (1996) EMBO J. 15, 5958–5964 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hegeman C. E., Hayes M. L., Hanson M. R. (2005) Plant J. 42, 124–132 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Miyamoto T., Obokata J., Sugiura M. (2002) Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 6726–6734 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sasaki T., Yukawa Y., Wakasugi T., Yamada K., Sugiura M. (2006) Plant J. 47, 802–810 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Tillich M., Le Sy V. L., Schulerowitz K., von Haeseler A., Maier U. G., Schmitz-Linneweber C. (2009) BMC Evol. Biol. 9, 201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rivals E., Bruyère C., Toffano-Nioche C., Lecharny A. (2006) Plant Physiol. 141, 825–839 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Doniwa Y., Ueda M., Ueta M., Wada A., Kadowaki K., Tsutsumi N. (2010) Gene 454, 39–46 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.de Longevialle A. F., Meyer E. H., Andrés C., Taylor N. L., Lurin C., Millar A. H., Small I. D. (2007) Plant Cell 19, 3256–3265 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Schmitz-Linneweber C., Williams-Carrier R., Barkan A. (2005) Plant Cell 17, 2791–2804 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schmitz-Linneweber C., Williams-Carrier R. E., Williams-Voelker P. M., Kroeger T. S., Vichas A., Barkan A. (2006) Plant Cell 18, 2650–2663 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.