Full text
PDF







Selected References
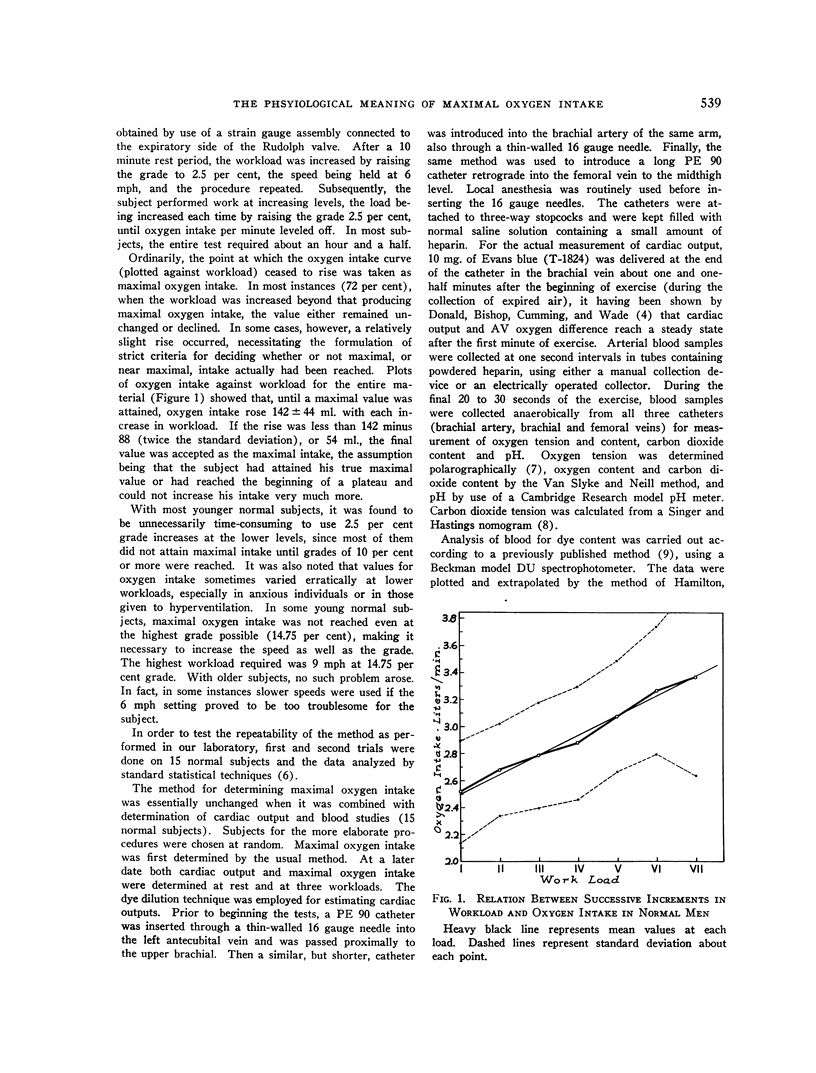
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASMUSSEN E., NIELSEN M. Cardiac output during muscular work and its regulation. Physiol Rev. 1955 Oct;35(4):778–800. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1955.35.4.778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASMUSSEN E., NIELSEN M. The cardiac output in rest and work determined simultaneously by the acetylene and the dye injection methods. Acta Physiol Scand. 1952;27(2-3):217–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb00937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARRATT-BOYES B. G., WOOD E. H. Hemodynamic response of healthy subjects to exercise in the supine position while breathing oxygen. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Jul;11(1):129–135. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.11.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLOUNT S. G., Jr, MCCORD M. C., ANDERSON L. L. The alveolar-arterial oxygen pressure gradient in mitral stenosis. J Clin Invest. 1952 May;31(9):840–842. doi: 10.1172/JCI102670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUSKIRK E., TAYLOR H. L. Maximal oxygen intake and its relation to body composition, with special reference to chronic physical activity and obesity. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Jul;11(1):72–78. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.11.1.72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN C. B., FRASER R. S. Studies on the effect of exercise on cardiovascular function. I. Cardiac output and mean circulation time. Circulation. 1954 Jan;9(1):57–62. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.9.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALD K. W., BISHOP J. M., CUMMING G., WADE O. L. The effect of exercise on the cardiac output and circulatory dynamics of normal subjects. Clin Sci. 1955 Feb;14(1):37–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DONALD K. W., BISHOP J. M., WADE O. L. A study of minute to minute changes of arterio-venous oxygen content difference, oxygen uptake and cardiac output and rate of achievement of a steady state during exercise in rheumatic heart disease. J Clin Invest. 1954 Aug;33(8):1146–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI102988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill D. B., Fölling A. Studies in muscular activity: II. A nomographic description of expired air. J Physiol. 1928 Oct 10;66(2):133–135. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1928.sp002513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FILLEY G. F., GREGOIRE F., WRIGHT G. W. Alveolar and arterial oxygen tensions and the significance of the alveolar-arterial oxygen tension difference in normal men. J Clin Invest. 1954 Apr;33(4):517–529. doi: 10.1172/JCI102922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN M. E., SNIDER G. L., BROSTOFF P., KIMELBLOT S., KATZ L. N. Effect of training on response of cardiac output to muscular exercise in athletes. J Appl Physiol. 1955 Jul;8(1):37–47. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1955.8.1.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKAM J. B., PRYOR W. W., PAGE E. B., ATWELL R. J. Respiratory regulation during exercise in unconditioned subjects. J Clin Invest. 1951 May;30(5):503–516. doi: 10.1172/JCI102466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
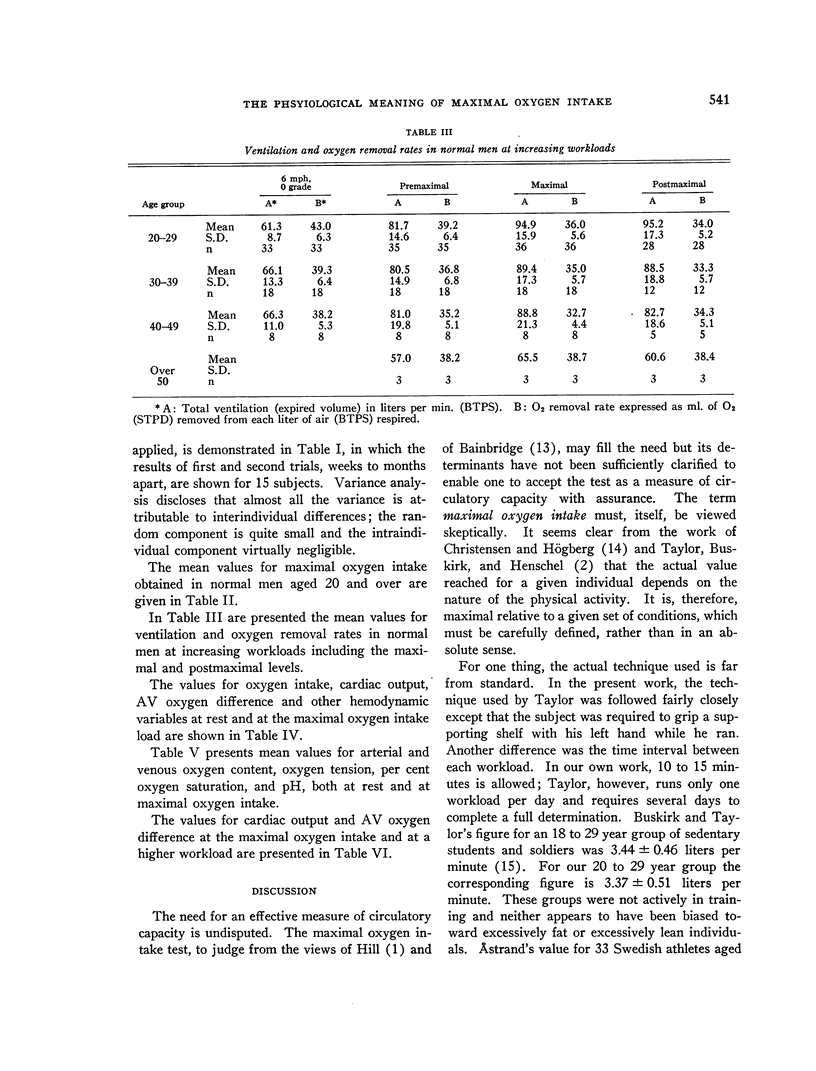
- HOHWU CHRISTENSEN E., HOGBERG P. Physiology of skiing. Arbeitsphysiologie. 1950;14(3):292–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00933847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLONIM N. B., GILLESPIE D. G., HAROLD W. H. Peak oxygen uptake of healthy young men as determined by a treadmill method. J Appl Physiol. 1957 May;10(3):401–404. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.10.3.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPROULE B. J., MILLER W. F., CUSHING I. E., CHAPMAN C. B. An improved polarographic method for measuring oxygen tension in whole blood. J Appl Physiol. 1957 Nov;11(3):365–370. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.11.3.365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSKIND M., BRUCE R. A., McDOWELL M. E., YU P. N. G., LOVEJOY F. W., Jr, VERNARELLI S. J. Normal variations in end-tidal air and arterial blood carbon dioxide and oxygen tensions during moderate exercise. J Appl Physiol. 1950 Nov;3(5):282–290. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1950.3.5.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR H. L., BUSKIRK E., HENSCHEL A. Maximal oxygen intake as an objective measure of cardio-respiratory performance. J Appl Physiol. 1955 Jul;8(1):73–80. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1955.8.1.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYNDHAM C. H., WARD J. S. An assessment of the exercise capacity of cardiac patients. Circulation. 1957 Sep;16(3):384–393. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.16.3.384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


