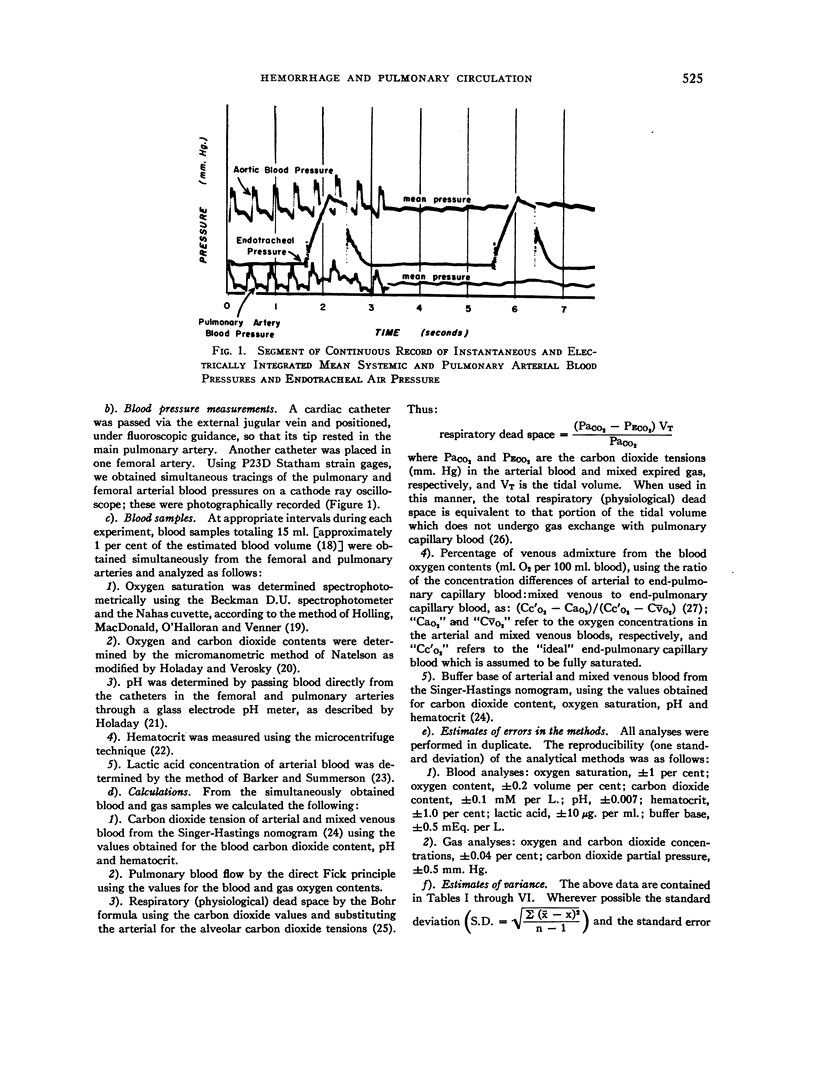
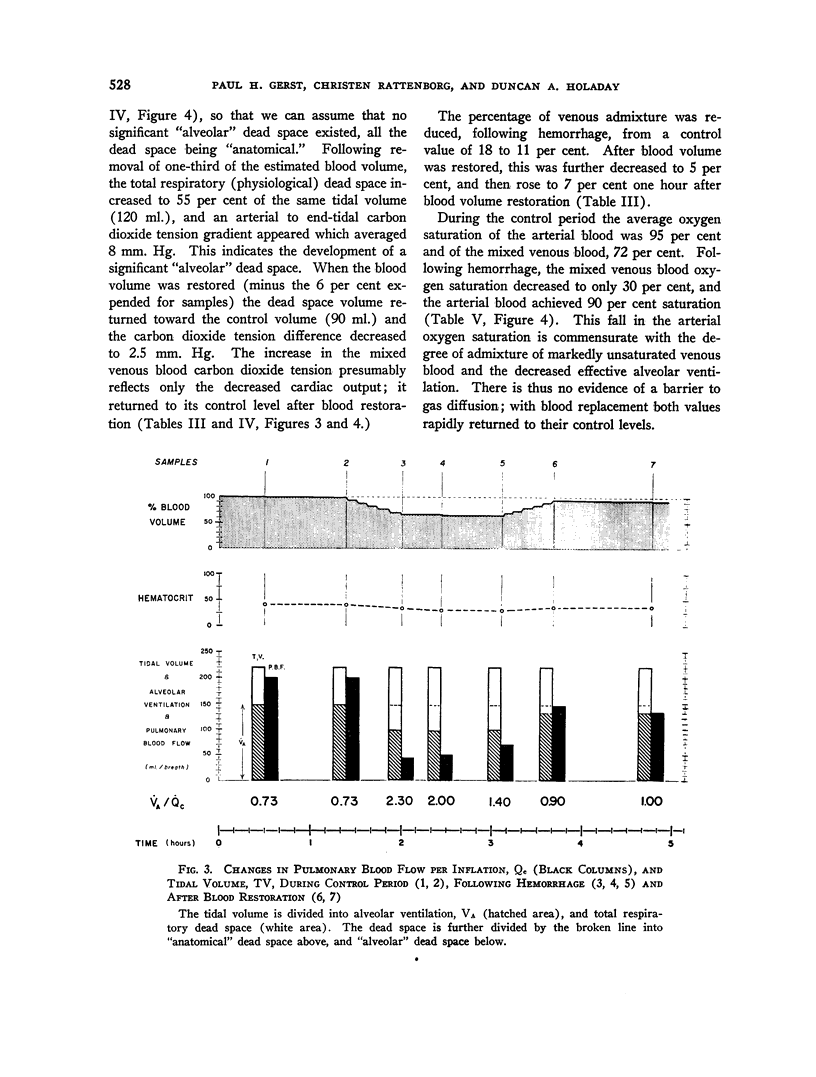
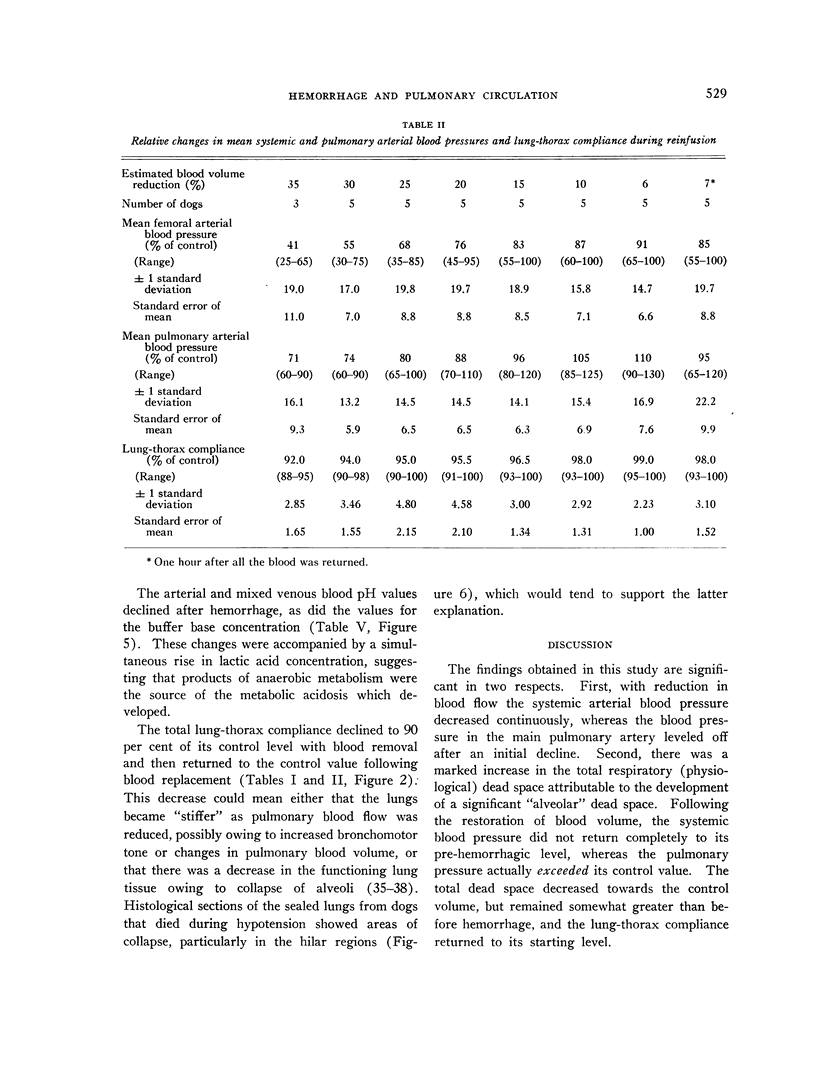
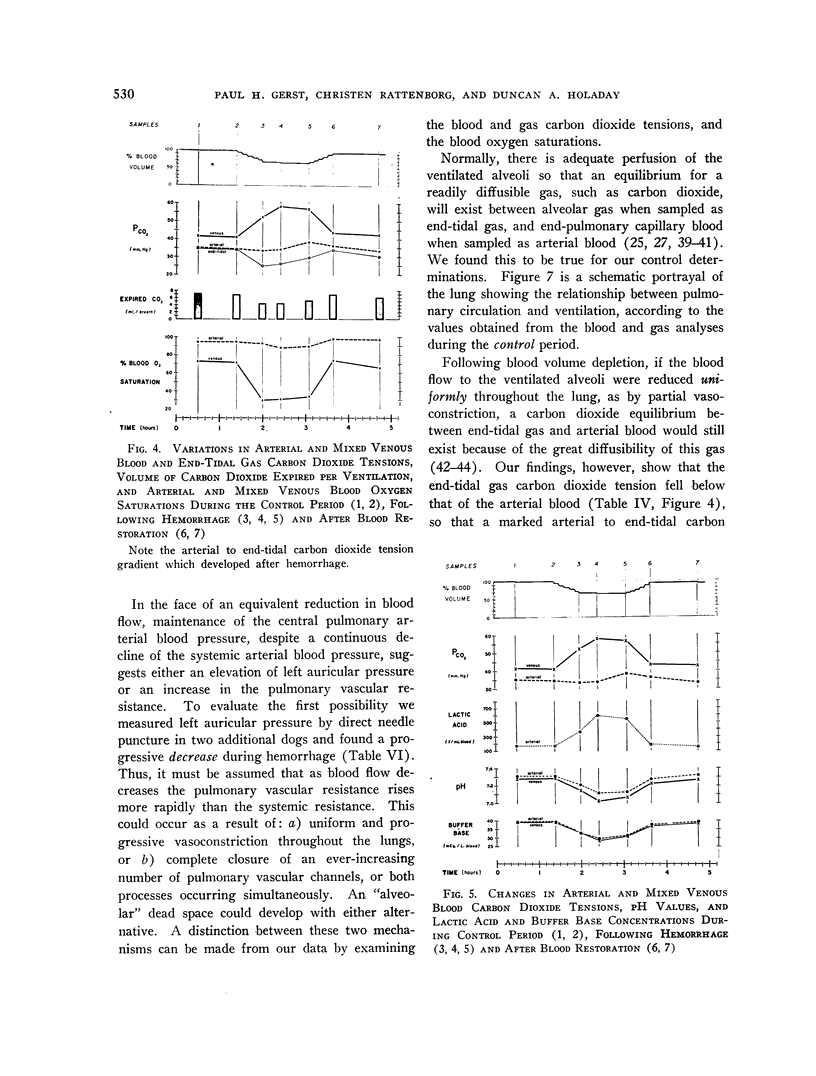
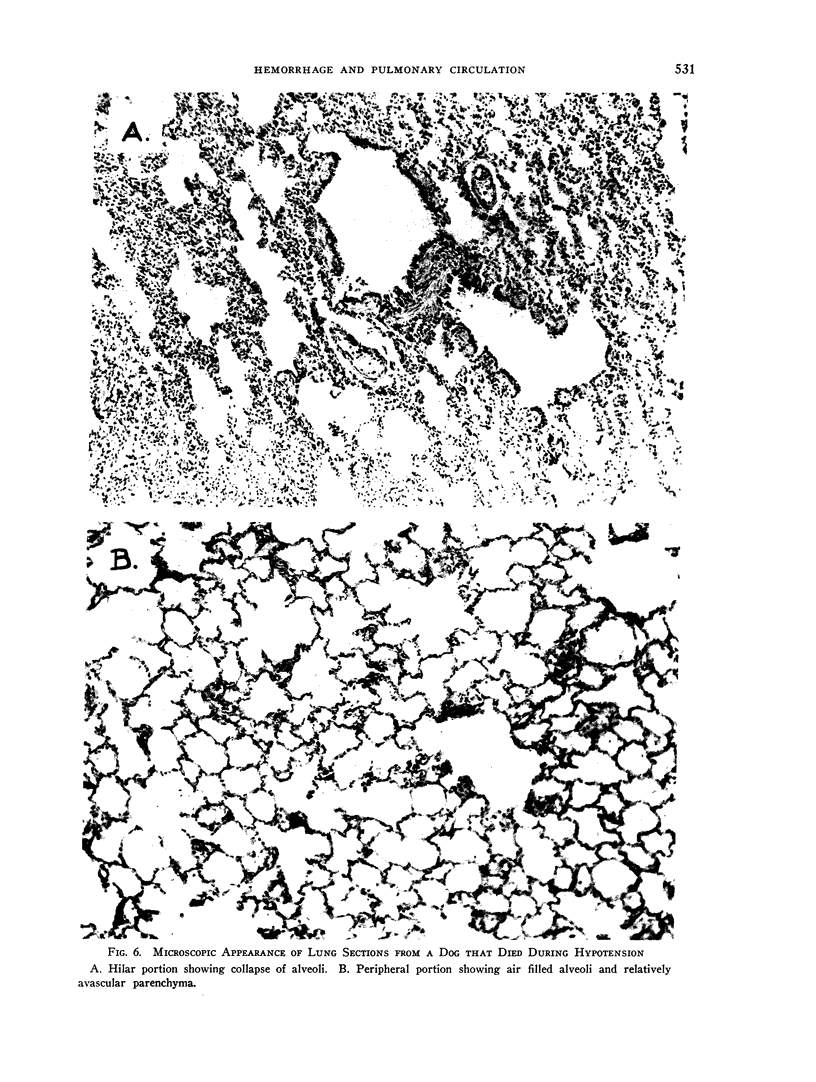
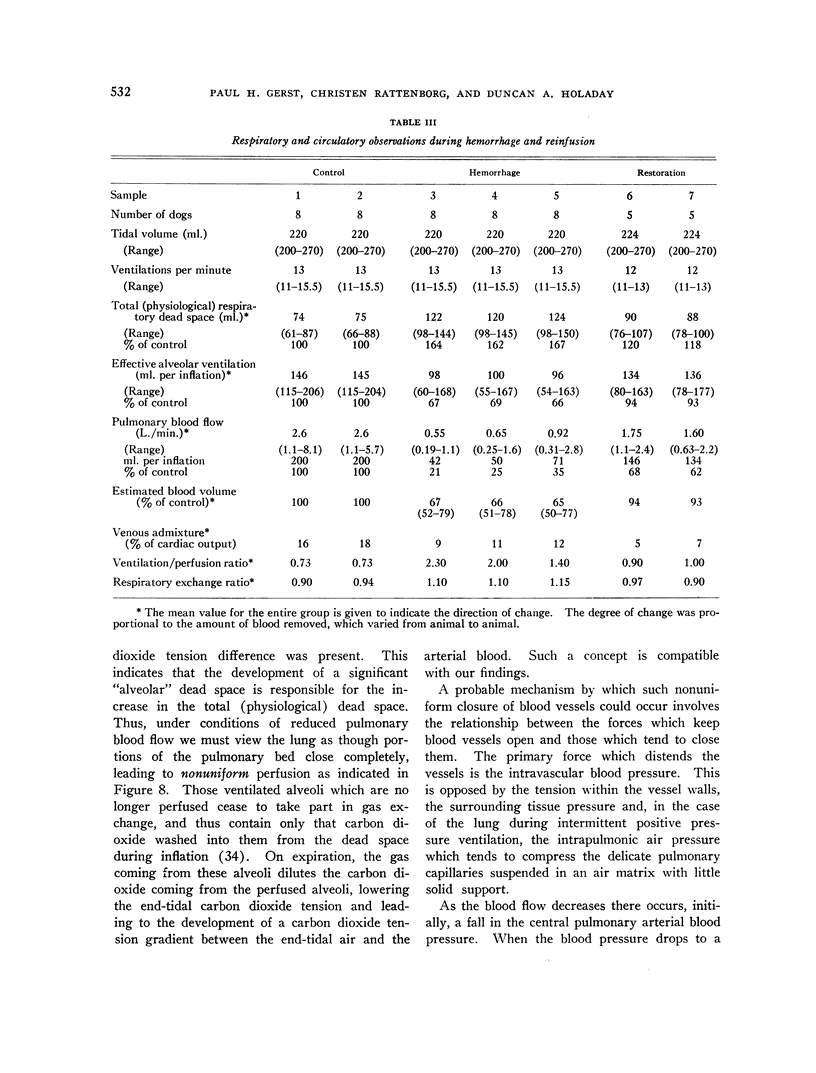
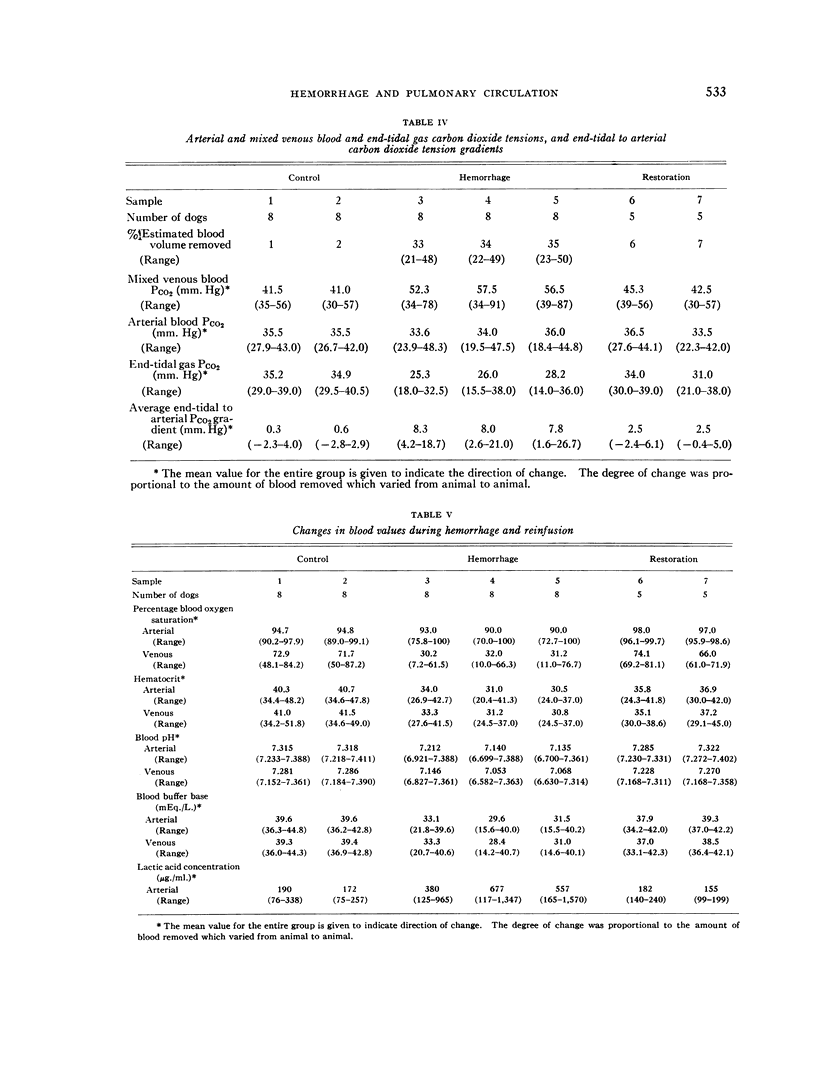
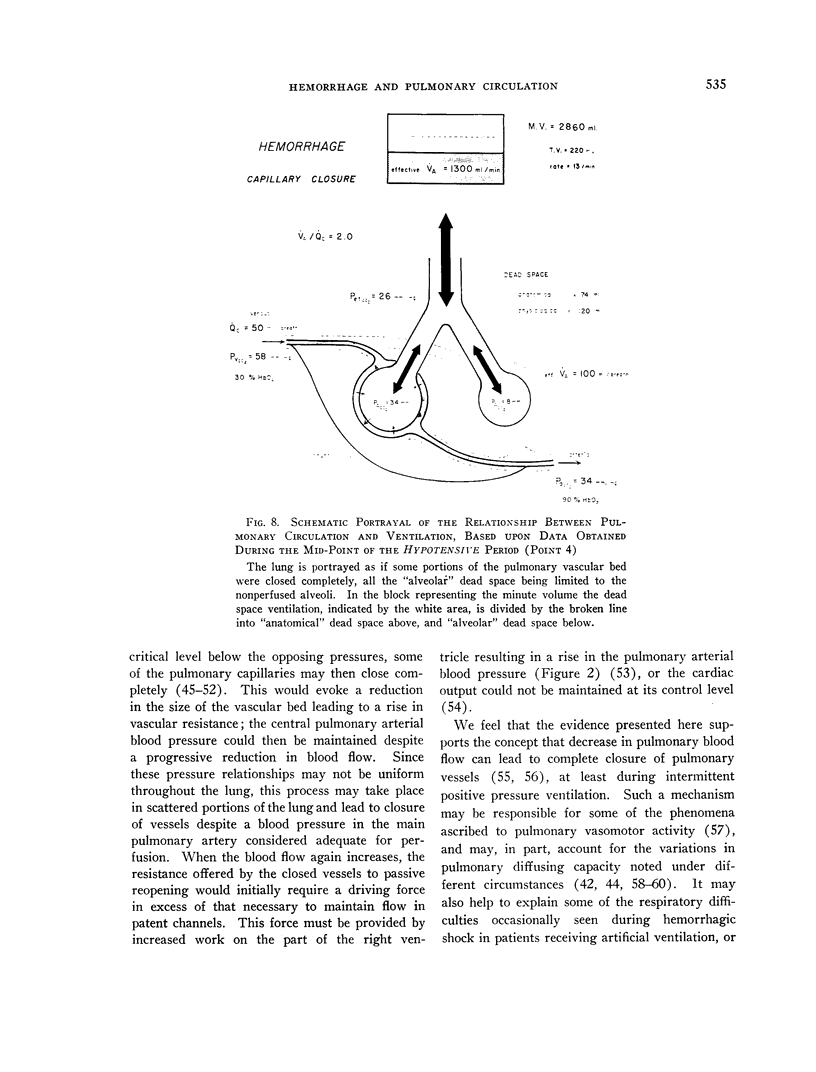
Full text
PDF
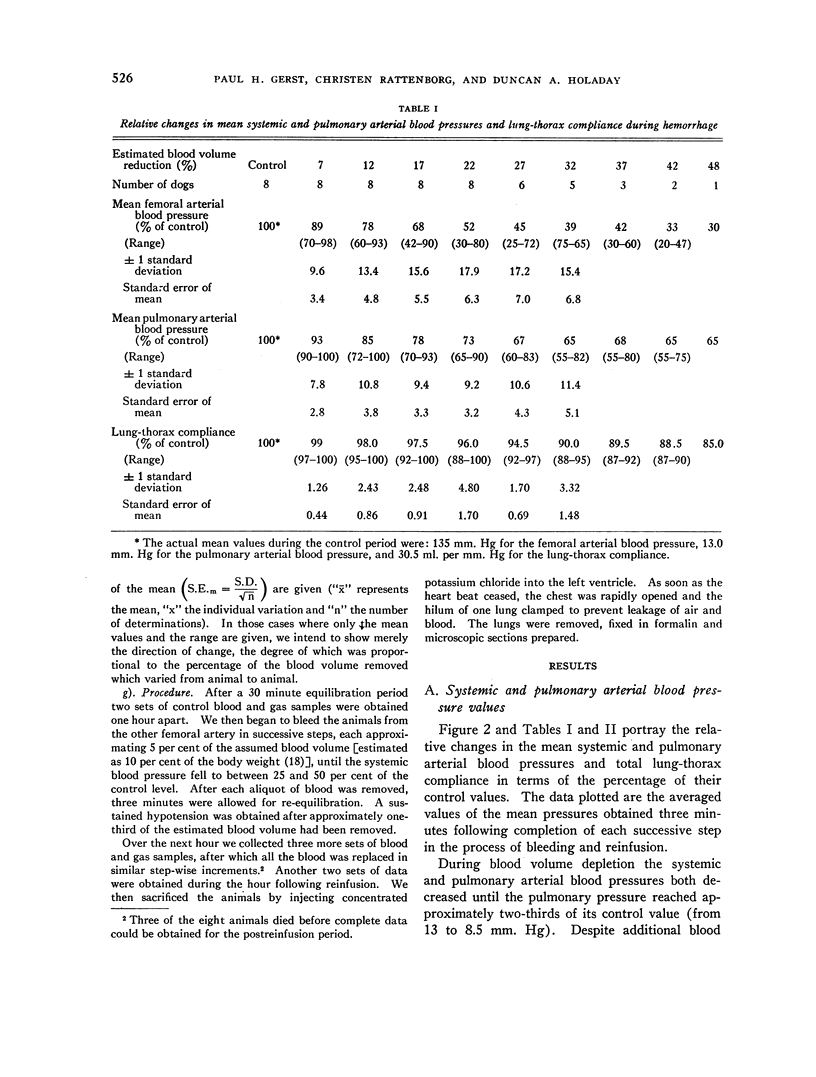
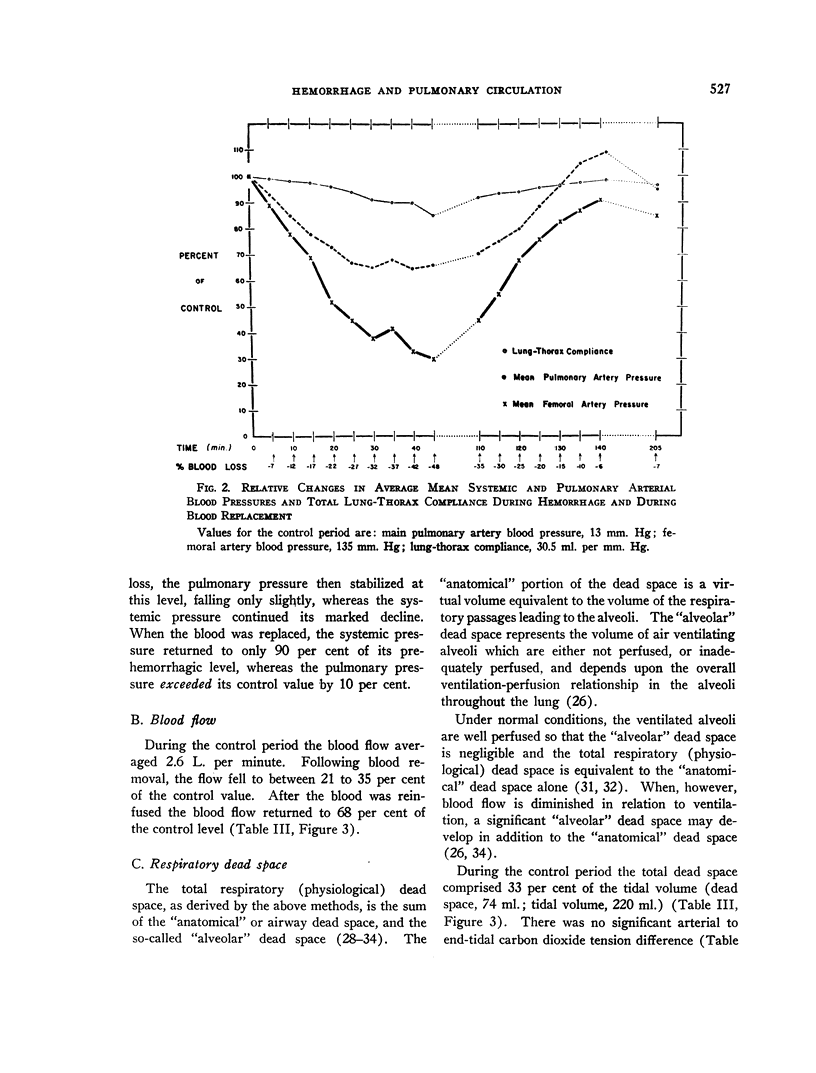



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARER G. R., NUSSER E. Pulmonary blood flow in the cat; the effect of positive pressure respiration. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):103–118. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BJURSTEDT H., HESSER C. M. Effect of lung inflation on the pulmonary circulation in anesthetized dogs. Acta Physiol Scand. 1953 Oct 6;29(2-3):180–189. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1953.tb01013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORST H. G., MCGREGOR M., WHITTENBERGER J. L., BERGLUND E. Influence of pulmonary arterial and left atrial pressures on pulmonary vascular resistance. Circ Res. 1956 Jul;4(4):393–399. doi: 10.1161/01.res.4.4.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROFMAN B. L., CHARMS B. L., KOHN P. M., ELDER J., NEWMAN R., RIZIKA M. Unilateral pulmonary artery occlusion in man; control studies. J Thorac Surg. 1957 Aug;34(2):206–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON A. C. On the physical equilibrium of small blood vessels. Am J Physiol. 1951 Feb;164(2):319–329. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.164.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock A. V., Dill D. B., Edwards H. T., Henderson L. J., Talbott J. H. On the partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide in arterial blood and alveolar air. J Physiol. 1929 Nov 25;68(3):277–291. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1929.sp002613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTER E. T., GRAY J. S., GRODINS F. S. Alveolar and total ventilation and the dead space problem. J Appl Physiol. 1956 Nov;9(3):307–320. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1956.9.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURNAND A., RILEY R. L. Pulmonary circulation and alveolar ventilation perfusion relationships after pneumonectomy. J Thorac Surg. 1950 Jan;19(1):80–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURNAND A. Some aspects of the pulmonary circulation in normal man and in chronic cardiopulmonary diseases. Circulation. 1950 Nov;2(5):641–657. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.2.5.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE BURGH DALY M., LAMBERTSEN D. C. J., SCHWEITZER A. The effects upon the bronchial musculature of altering the oxygen and carbon dioxide tensions of the blood perfusing the brain. J Physiol. 1953 Feb 27;119(2-3):292–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE DALY I B. Intrinsic mechanisms of the lung. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1958 Jan;43(1):2–26. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1958.sp001304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEXTER L., DOW J. W., HAYNES F. W., WHITTENBERGER J. L., FERRIS B. G., GOODALE W. T., HELLEMS H. K. Studies of the pulmonary circulation in man at rest; normal variations and the interrelations between increased pulmonary blood flow, elevated pulmonary arterial pressure, and high pulmonary 'capillary" pressures. J Clin Invest. 1950 May;29(5):602–613. doi: 10.1172/JCI102297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BRITT A. G., FENN W. O. Alveolar CO2 during the respiratory cycle. J Appl Physiol. 1952 Jan;4(7):535–548. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1952.4.7.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., FOWLER R. C., SOFFER A., FENN W. O. Alveolar CO2 measured by expiration into the rapid infrared gas analyzer. J Appl Physiol. 1952 Jan;4(7):526–534. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1952.4.7.526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS W. S. The effects of lung inflation and epinephrine on pulmonary vascular resistance. Am J Physiol. 1951 Dec;167(3):756–762. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.167.3.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FILLEY G. F., MACINTOSH D. J., WRIGHT G. W. Carbon monoxide uptake and pulmonary diffusing capacity in normal subjects at rest and during exercise. J Clin Invest. 1954 Apr;33(4):530–539. doi: 10.1172/JCI102923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN A. P., RICHARDS D. W. The management of cor pulmonale in chronic pulmonary disease, with particular reference to the associated disturbances in the pulmonary circulation. Am Heart J. 1956 Jul;52(1):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(56)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHMAN A. P. Studies in man of the volume of the respiratory dead space and the composition of the alveolar gas. J Clin Invest. 1954 Apr;33(4):469–481. doi: 10.1172/JCI102918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLKOW B., PAPPENHEIMER J. R. Components of the respiratory dead space and their variation with pressure breathing and with bronchoactive drugs. J Appl Physiol. 1955 Jul;8(1):102–110. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1955.8.1.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORSTER R. E. Exchange of gases between alveolar air and pulmonary capillary blood: pulmonary diffusing capacity. Physiol Rev. 1957 Oct;37(4):391–452. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1957.37.4.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HATCH T., COOK K. M., PALM P. E. Respiratory dead space. J Appl Physiol. 1953 Jan;5(7):341–347. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1953.5.7.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
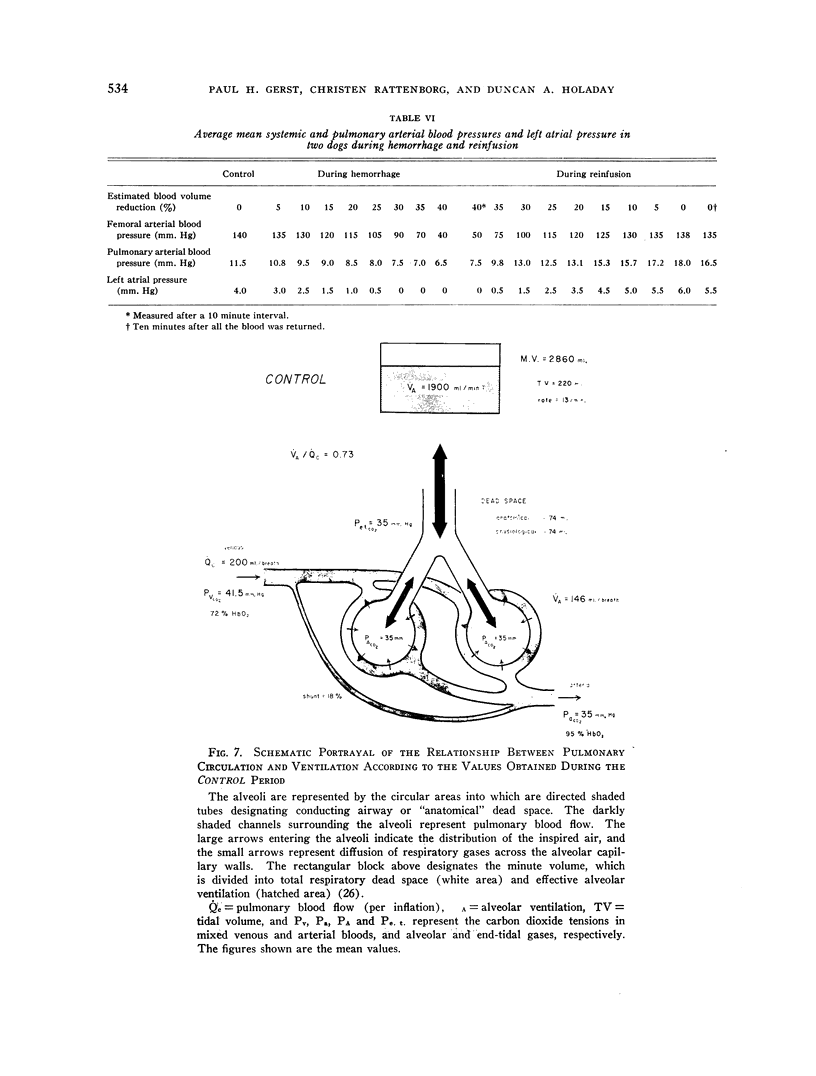
- HOLADAY D. A. An improved method for multiple rapid determinations of arterial blood pH. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Jul;44(1):149–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLADAY D. A., VEROSKY M. Improved micromanometric methods for the analysis of respiratory gases in plasma and whole blood. J Lab Clin Med. 1956 Apr;47(4):634–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLING H. E., MACDONALD I., O'HALLORAN J. A., VENNER A. Reliability of a spectrophotometric method of estimating blood oxygen. J Appl Physiol. 1955 Nov;8(3):249–254. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1955.8.3.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh A. The rate of diffusion of gases through animal tissues, with some remarks on the coefficient of invasion. J Physiol. 1919 May 20;52(6):391–408. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1919.sp001838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krogh M. The diffusion of gases through the lungs of man. J Physiol. 1915 May 12;49(4):271–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1915.sp001710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS B. M., LIN T. H., NOE F. E., KOMISARUK R. The measurement of pulmonary capillary blood volume and pulmonary membrane diffusing capacity in normal subjects; the effects of exercise and position. J Clin Invest. 1958 Jul;37(7):1061–1070. doi: 10.1172/JCI103687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LILIENTHAL J. L., Jr, RILEY R. L. Diseases of the respiratory system; circulation through the lung and diffusion of gases. Annu Rev Med. 1954;5:237–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.05.020154.001321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICHOL J., GIRLING F., JERRARD W., CLAXTON E. B., BURTON A. C. Fundamental instability of the small blood vessels and critical closing pressures in vascular beds. Am J Physiol. 1951 Feb;164(2):330–344. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.164.2.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISELL O. I., DUBOIS A. B. Relationship between compliance and FRC of the lungs in cats, and measurement of resistance to breathing. Am J Physiol. 1954 Aug;178(2):206–210. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.178.2.206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OTIS A. B., FENN W. O., RAHN H. Mechanics of breathing in man. J Appl Physiol. 1950 May;2(11):592–607. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1950.2.11.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPPENHEIMER J. R., FISHMAN A. P., BORRERO L. M. New experimental methods for determination of effective alveolar gas composition and respiratory dead space, in the anesthetized dog and in man. J Appl Physiol. 1952 May;4(11):855–867. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1952.4.11.855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RILEY R. L., COURNAND A. Analysis of factors affecting partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide in gas and blood of lungs; theory. J Appl Physiol. 1951 Aug;4(2):77–101. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1951.4.2.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RILEY R. L., SHEPARD R. H., COHN J. E., CARROLL D. G., ARMSTRONG B. W. Maximal diffusing capacity of the lungs. J Appl Physiol. 1954 Apr;6(10):573–587. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1954.6.10.573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODBARD S. Bronchomotor tone; a neglected factor in the regulation of the pulmonary circulation. Am J Med. 1953 Sep;15(3):356–367. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROUNTHWAITE H. L., SCOTT H. J., GURD F. N. Changes in the pulmonary circulation during hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation. Surg Forum. 1953;(38TH):454–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANCETTA S. M., RAKITA L. Response of pulmonary artery pressure and total pulmonary resistance of untrained, convalescent man to prolonged mild steady state exercise. J Clin Invest. 1957 Jul;36(7):1138–1149. doi: 10.1172/JCI103510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEVERINGHAUS J. W., STUPFEL M. Alveolar dead space as an index of distribution of blood flow in pulmonary capillaries. J Appl Physiol. 1957 May;10(3):335–348. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1957.10.3.335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS M. H., Jr Relationships between pulmonary artery pressure and blood flow in the dog lung. Am J Physiol. 1954 Nov;179(2):243–245. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.179.2.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]