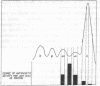
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBRIGHT F., CARROLL E. L., DEMPSEY E. F., HENNEMAN P. H. The cause of hypercalcuria in sarcoid and its treatment with cortisone and sodium phytate. J Clin Invest. 1956 Nov;35(11):1229–1242. doi: 10.1172/JCI103378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ANDERSON J., HARPER C., DENT C. E., PHILPOT G. R. Effect of cortisone on calcium metabolism in sarcoidosis with hypercalcaemia; possibly antagonistic actions of cortisone and vitamin D. Lancet. 1954 Oct 9;267(6841):720–724. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)90492-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W., Marble A. STUDIES ON THE MODE OF ACTION OF IRRADIATED ERGOSTEROL: II. Its Effect on the Calcium and Phosphorus Metabolism of Individuals with Calcium Deficiency Diseases. J Clin Invest. 1932 Jan;11(1):21–35. doi: 10.1172/JCI100403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREERY R. D., NEILL D. W. Idiopathic hypercalcaemia in infants with failure to thrive. Lancet. 1954 Jul 17;267(6829):110–114. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUICKSHANK E. M., KODICEK E., ARMITAGE P. The vitamin D content of tissues of rats given ergocalciferol. Biochem J. 1954 Sep;58(1):172–175. doi: 10.1042/bj0580172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUICKSHANK E. M., KODICEK E. The antagonism between cortisone and vitamin D: experiments on hypervitaminosis D inrats. J Endocrinol. 1958 May;17(1):35–40. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0170035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRUICKSHANK E. M., KODICEK E. Vitamin D balance and distribution in rats given a massive dose of ergocalciferol I. Experimental results. Biochem J. 1953 May;54(2):337–343. doi: 10.1042/bj0540337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE LUCA H. F., STEENBOCK H. An in vitro effect of vitamin D on citrate oxidation by kidney mitochondria. Science. 1957 Aug 9;126(3267):258–258. doi: 10.1126/science.126.3267.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOCK W., FRANK N. R. Cation exchangers: their use and hazards as aids in managing edema. Am Heart J. 1950 Oct;40(4):638–645. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(50)90374-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FELLERS F. X., SCHWARTZ R. Etiology of the severe form of idiopathic hypercalcemia of infancy; a defect in vitamin D metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1958 Nov 27;259(22):1050–1058. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195811272592202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FESTENSTEIN G. N. The effect of ergosterol and ergocalciferol on the anaerobic glycolysis of rat-liver slices. Biochem J. 1955 Apr;59(4):605–609. doi: 10.1042/bj0590605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENMAN L., SHALER J. B., DANOWSKI T. S. Biochemical disturbances and clinical symptoms during prolonged exchange resin therapy in congestive heart failure. Am J Med. 1953 Apr;14(4):391–403. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(53)90196-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRISON H. C., HARRISON H. E., PARK E. A. Vit. D and citrate metabolism; inhibition of vit. D effect by cortisol. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Dec;96(3):768–773. doi: 10.3181/00379727-96-23603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPKINS T., HOWARD J. E., EISENBERG H. Ultrafiltration studies on calcium and phosphorus in human serum. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1952 Jul;91(1):1–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOWARD J. E., CONNOR T. B. Some experiences with the use of vitamin D in the treatment of hypoparathyroidism. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1954;67:199–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris L. J., Innes J. R. The mode of action of vitamin D: Studies on hypervitaminosis D. The influence of the calcium-phosphate intake. Biochem J. 1931;25(1):367–390.5. doi: 10.1042/bj0250367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUERGENS J. L., SCHOLZ D. A., WOLLAEGER E. E. Severe osteomalacia associated with occult steatorrhea due to nontropical sprue; report of five cases. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1956 Dec;98(6):774–782. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1956.00250300092011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., SLATER R. J. Lipoprotein patterns of serum obtained by zone electrophoresis. J Clin Invest. 1952 Jul;31(7):677–684. doi: 10.1172/JCI102649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNKEL H. G., TISELIUS A. Electrophoresis of proteins on filter paper. J Gen Physiol. 1951 Sep;35(1):89–118. doi: 10.1085/jgp.35.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN H. G., MITCHELL R. G., STOWERS J. M., THOMSON J. Metabolic studies on two infants with idiopathic hypercalcaemia. Lancet. 1956 Jun 16;270(6929):925–931. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91518-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAIHA C. E., FORSANDER O. Vitamin D and phosphorylation of thiamin. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 1954;43(100):541–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1954.tb15497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAVILLE P. D., NASSIM J. R., STEVENSON F. H., MULLIGAN L., CAREY M. The effect of A.T. 10 on calcium and phosphorus metabolism in resistant rickets. Clin Sci. 1955 Aug;14(3):489–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS W. C., Jr, MORGAN H. G. The effect of cortisone in experimental hypervitaminosis D. Endocrinology. 1958 Jul;63(1):57–64. doi: 10.1210/endo-63-1-57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERNER J. V., Jr, ENGEL F. L., McPHERSON H. T. Vitamin D intoxication: report of two cases treated with cortisone. Ann Intern Med. 1958 Apr;48(4):765–773. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-48-4-765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOLWILER W. Gastrointestinal malabsorptive syndromes. Am J Med. 1957 Aug;23(2):250–268. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]