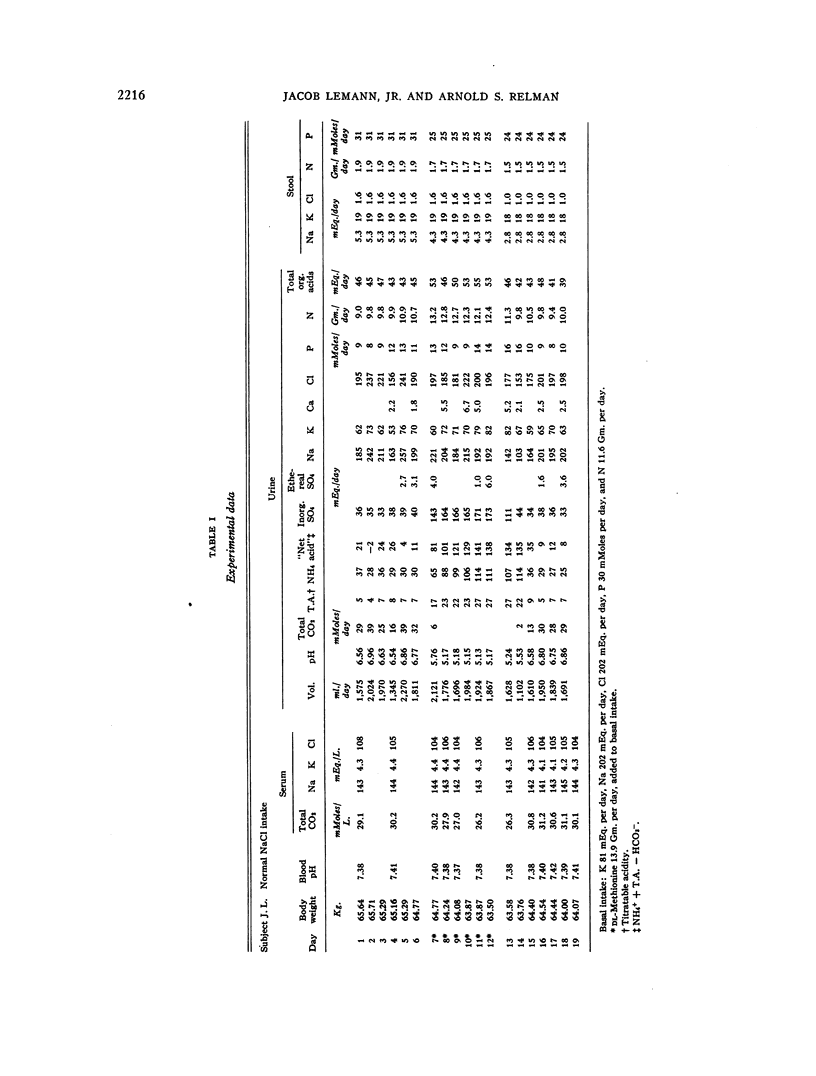
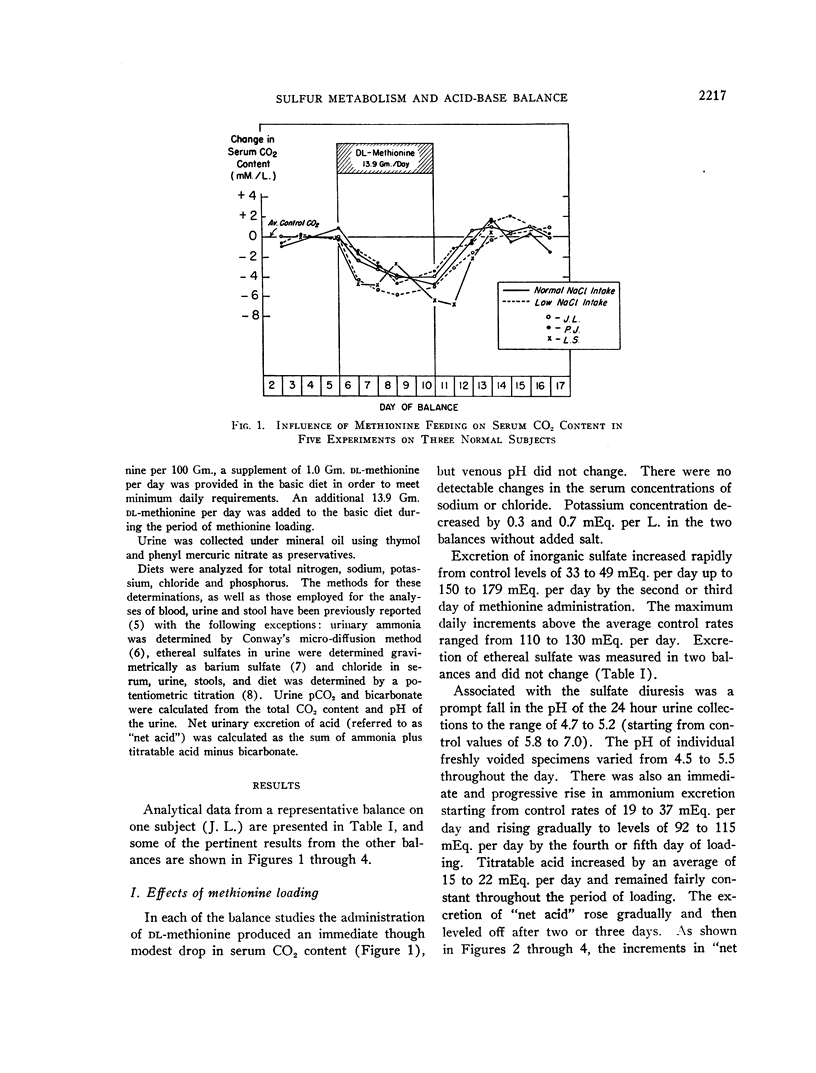
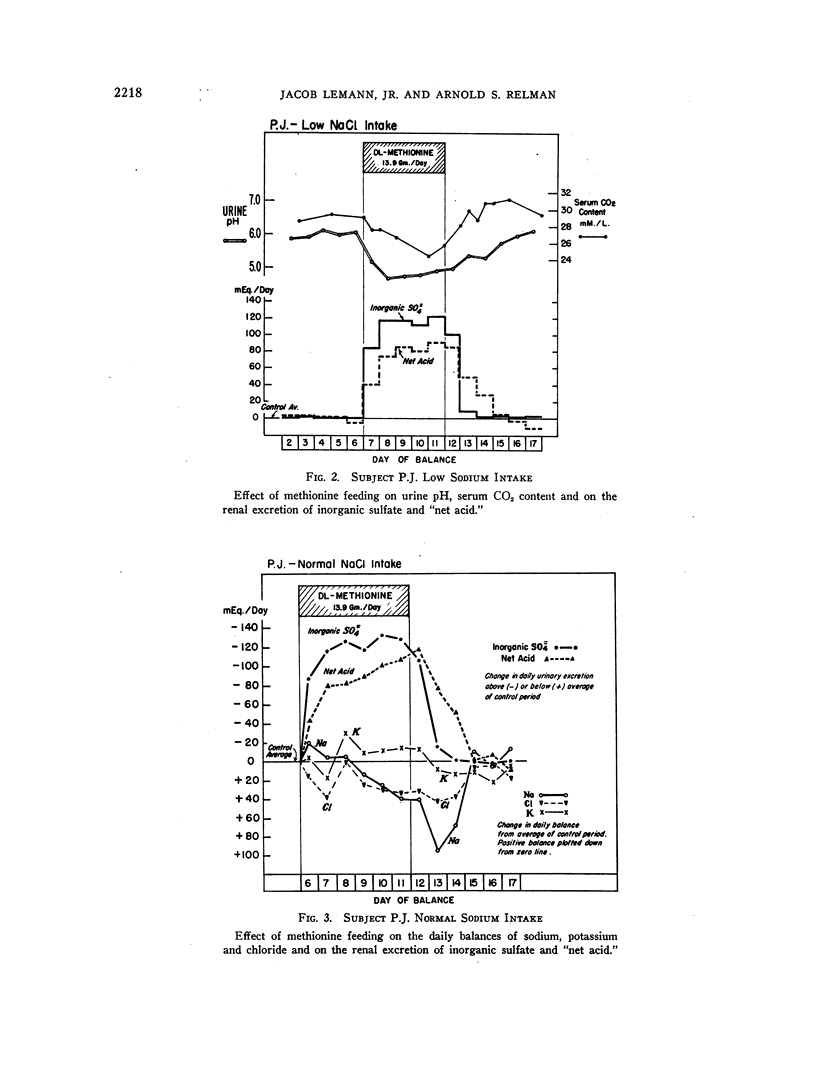
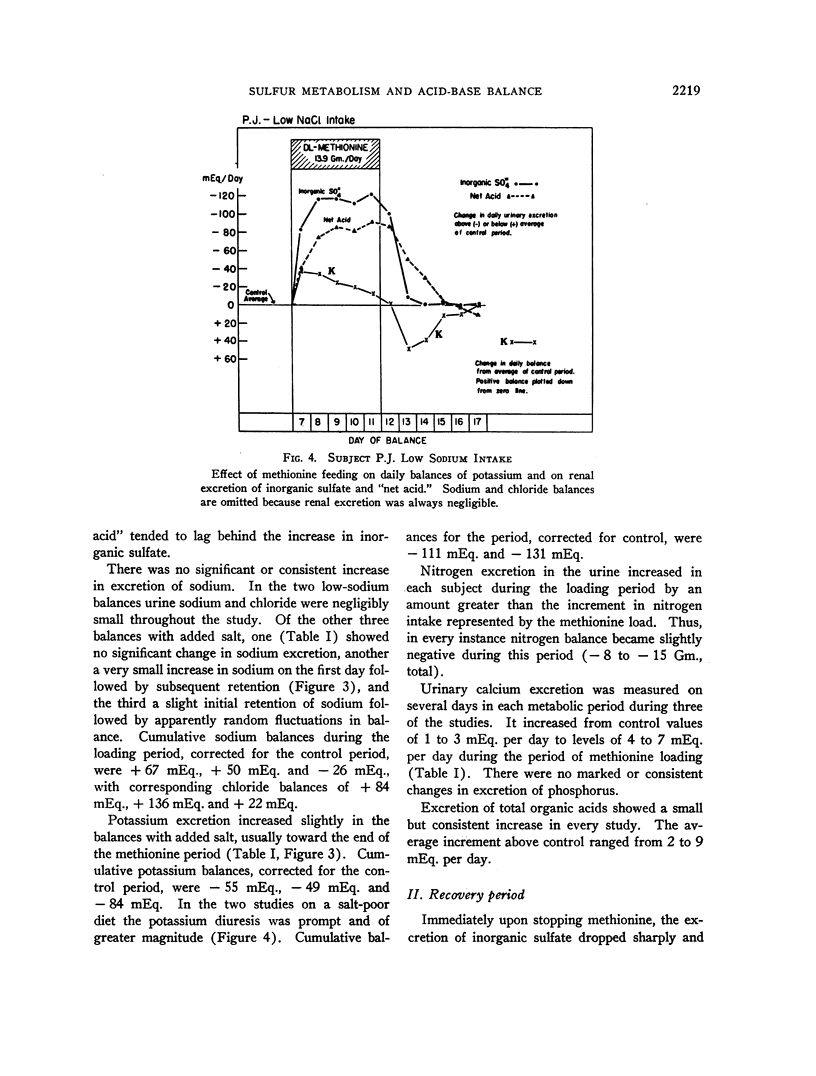
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHALLENGER F., WALSHE J. M. Methyl mercaptan in relation to foetor hepaticus. Biochem J. 1955 Mar;59(3):372–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNT J. N. The influence of dietary sulphur on the urinary output of acid in man. Clin Sci. 1956 Feb;15(1):119–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASS E. H. Bacteriuria and the diagnosis of infections of the urinary tract; with observations on the use of methionine as a urinary antiseptic. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1957 Nov;100(5):709–714. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1957.00260110025004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHEAR E. A., RUEBNER B., SHERLOCK S., SUMMERSKILL W. H. Methionine toxicity in liver disease and its prevention by chlortetracycline. Clin Sci. 1956 Feb;15(1):93–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RELMAN A. S., SCHWARTZ W. B. The effect of DOCA on electrolyte balance in normal man and its relation to sodium chloride intake. Yale J Biol Med. 1952 Jun;24(6):540–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERSON P. H. Potentiometric determination of chloride in biological fluids. Biochem J. 1952 Nov;52(3):502–505. doi: 10.1042/bj0520502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ W. B., JENSON R. L., RELMAN A. S. Acidification of the urine and increased ammonium excretion without change in acid-base equilibrium: sodium reabsorption as a stimulus to the acidifying process. J Clin Invest. 1955 May;34(5):673–680. doi: 10.1172/JCI103117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



