Abstract
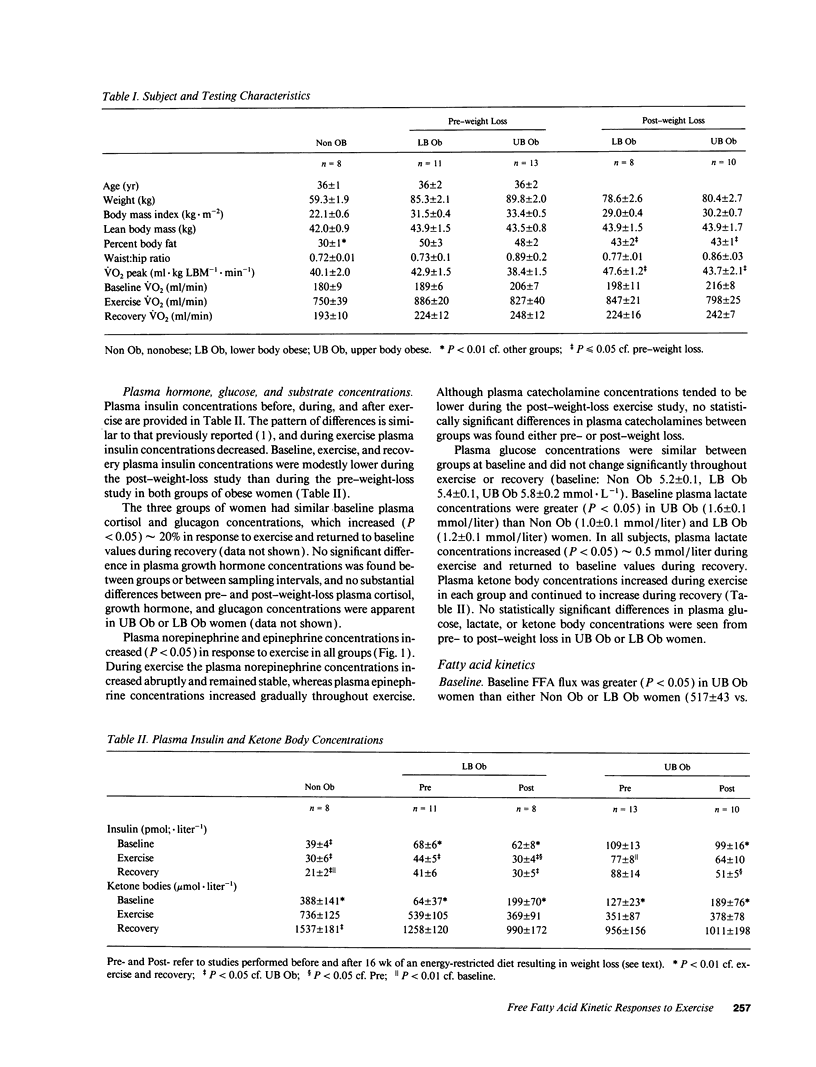
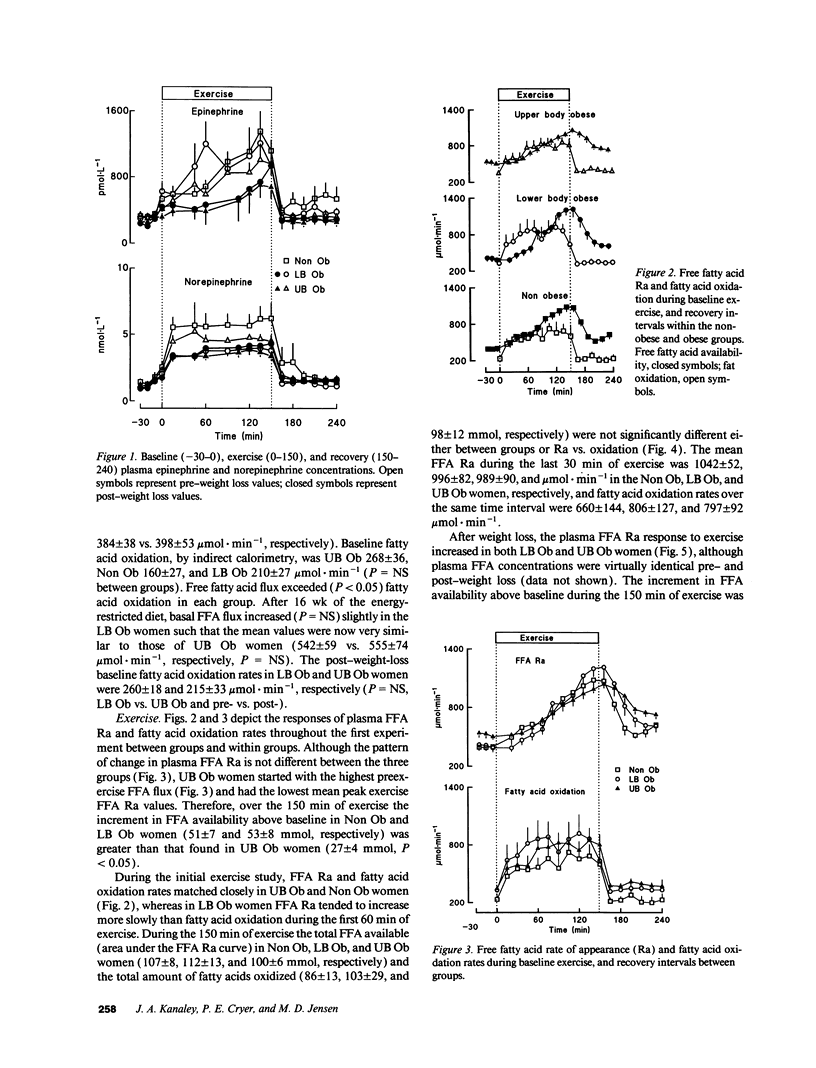
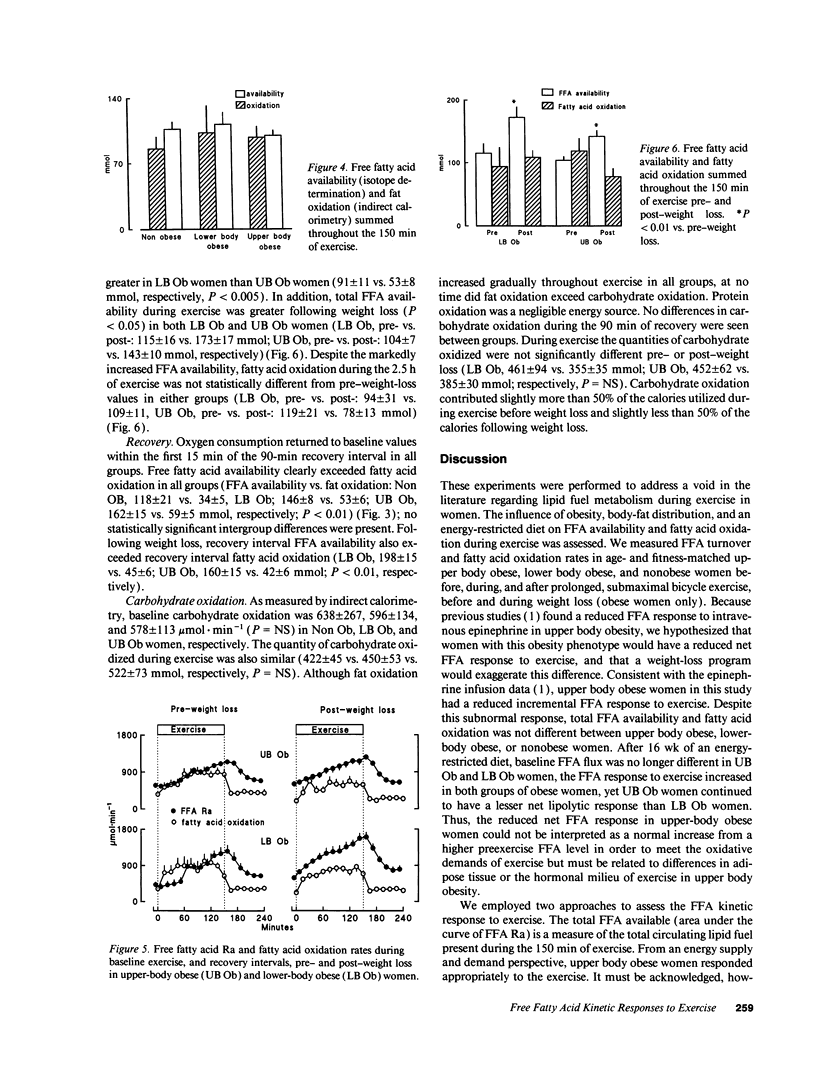
Upper body obesity (UB Ob) is associated with a reduced net free fatty acid (FFA) response to epinephrine compared with nonobese (Non Ob) and lower-body obese (LB Ob) women. Because catecholamines regulate some of the metabolic responses to exercise, we hypothesized that UB Ob would have a reduced net FFA response to exercise. Plasma FFA rate of appearance (Ra) ([1-14C]palmitate) and fatty acid oxidation (indirect calorimetry) were therefore measured during 2.5 h of stationary bicycle exercise (45% VO2 peak) in 13 UB Ob, 11 LB Ob, and 8 Non Ob premenopausal women. 10 UB Ob and 8 LB Ob women were retested after an approximately 8-kg weight loss. Results: During exercise Non Ob and LB Ob women had greater increments in FFA availability (51 +/- 7 and 53 +/- 8 mmol, respectively) than UB Ob women (27 +/- 4 mmol, P < 0.05). Total exercise FFA availability and fatty acid oxidation were not different between Non Ob, LB Ob, and UB Ob women, however. Following weight loss (approximately 8 kg), the FFA response to exercise increased (P < 0.01) and remained greater (P < 0.05) in LB Ob than in UB Ob women. In conclusion, the FFA response to exercise was reduced in UB Ob women before and after weight loss, but no effects on fatty acid oxidation were apparent.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlborg G., Felig P., Hagenfeldt L., Hendler R., Wahren J. Substrate turnover during prolonged exercise in man. Splanchnic and leg metabolism of glucose, free fatty acids, and amino acids. J Clin Invest. 1974 Apr;53(4):1080–1090. doi: 10.1172/JCI107645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basso L. V., Havel R. J. Hepatic metabolism of free fatty acids in normal and diabetic dogs. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):537–547. doi: 10.1172/JCI106264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P., Bergman H., Varnauskas E. Plasma free fatty acid turnover rate in obesity. Acta Med Scand. 1969 Apr;185(4):351–356. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1969.tb07347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowiecki L., Lupien J., Follea N., Paradis A., Richard D., LeBlanc J. Mechanism of enhanced lipolysis in adipose tissue of exercise-trained rats. Am J Physiol. 1980 Dec;239(6):E422–E429. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.6.E422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill G. F., Jr, Herrera M. G., Morgan A. P., Soeldner J. S., Steinke J., Levy P. L., Reichard G. A., Jr, Kipnis D. M. Hormone-fuel interrelationships during fasting. J Clin Invest. 1966 Nov;45(11):1751–1769. doi: 10.1172/JCI105481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frayn K. N. Calculation of substrate oxidation rates in vivo from gaseous exchange. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Aug;55(2):628–634. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.2.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galster A. D., Clutter W. E., Cryer P. E., Collins J. A., Bier D. M. Epinephrine plasma thresholds for lipolytic effects in man: measurements of fatty acid transport with [l-13C]palmitic acid. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jun;67(6):1729–1738. doi: 10.1172/JCI110211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollnick P. D. Free fatty acid turnover and the availability of substrates as a limiting factor in prolonged exercise. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1977;301:64–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1977.tb38186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., CARLSON L. A., EKELUND L. G., HOLMGREN A. TURNOVER RATE AND OXIDATION OF DIFFERENT FREE FATTY ACIDS IN MAN DURING EXERCISE. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Jul;19:613–618. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.4.613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., NAIMARK A., BORCHGREVINK C. F. Turnover rate and oxidation of free fatty acids of blood plasma in man during exercise: studies during continuous infusion of palmitate-1-C14. J Clin Invest. 1963 Jul;42:1054–1063. doi: 10.1172/JCI104791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J., Ekelund L. G., Holmgren A. Kinetic analysis of the oxidation of palmitate-1-14C in man during prolonged heavy muscular exercise. J Lipid Res. 1967 Jul;8(4):366–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch I. B., Marker J. C., Smith L. J., Spina R. J., Parvin C. A., Holloszy J. O., Cryer P. E. Insulin and glucagon in prevention of hypoglycemia during exercise in humans. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):E695–E704. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.5.E695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloszy J. O., Coyle E. F. Adaptations of skeletal muscle to endurance exercise and their metabolic consequences. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Apr;56(4):831–838. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.4.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz B., Jr, Bortz W. M., Miller H. I., Wroldsen A. Plasma free fatty acid response to exercise in obese humans. Metabolism. 1967 Jun;16(6):492–502. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(67)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. D., Braun J. S., Vetter R. J., Marsh H. M. Measurement of body potassium with a whole-body counter: relationship between lean body mass and resting energy expenditure. Mayo Clin Proc. 1988 Sep;63(9):864–868. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)62688-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. D., Haymond M. W., Gerich J. E., Cryer P. E., Miles J. M. Lipolysis during fasting. Decreased suppression by insulin and increased stimulation by epinephrine. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):207–213. doi: 10.1172/JCI112785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. D., Haymond M. W., Rizza R. A., Cryer P. E., Miles J. M. Influence of body fat distribution on free fatty acid metabolism in obesity. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1168–1173. doi: 10.1172/JCI113997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. D., Heiling V., Miles J. M. Measurement of non-steady-state free fatty acid turnover. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 1):E103–E108. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.1.E103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen M. D., Rogers P. J., Ellman M. G., Miles J. M. Choice of infusion-sampling mode for tracer studies of free fatty acid metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):E562–E565. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.254.5.E562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. L., Heigenhauser G. J., Kuksis A., Matsos C. G., Sutton J. R., Toews C. J. Fat metabolism in heavy exercise. Clin Sci (Lond) 1980 Dec;59(6):469–478. doi: 10.1042/cs0590469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissebah A. H., Vydelingum N., Murray R., Evans D. J., Hartz A. J., Kalkhoff R. K., Adams P. W. Relation of body fat distribution to metabolic complications of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Feb;54(2):254–260. doi: 10.1210/jcem-54-2-254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koivisto V., Hendler R., Nadel E., Felig P. Influence of physical training on the fuel-hormone response to prolonged low intensity exercise. Metabolism. 1982 Feb;31(2):192–197. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(82)90135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marker J. C., Hirsch I. B., Smith L. J., Parvin C. A., Holloszy J. O., Cryer P. E. Catecholamines in prevention of hypoglycemia during exercise in humans. Am J Physiol. 1991 May;260(5 Pt 1):E705–E712. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1991.260.5.E705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. L., Jensen M. D. Effects of body fat distribution on regional lipolysis in obesity. J Clin Invest. 1991 Aug;88(2):609–613. doi: 10.1172/JCI115345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles J. M., Ellman M. G., McClean K. L., Jensen M. D. Validation of a new method for determination of free fatty acid turnover. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 1):E431–E438. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.252.3.E431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minuk H. L., Hanna A. K., Marliss E. B., Vranic M., Zinman B. Metabolic response to moderate exercise in obese man during prolonged fasting. Am J Physiol. 1980 Apr;238(4):E322–E329. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.4.E322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheen A., Cession-Fossion A., Scheen-Lavigne M., Luyckx A. Effect of protein-supplemented fasting on metabolic and hormonal responses to epinephrine infusion in obese subjects. Horm Metab Res. 1982 May;14(5):240–245. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1018982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah S. D., Clutter W. E., Cryer P. E. External and internal standards in the single-isotope derivative (radioenzymatic) measurement of plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Dec;106(6):624–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarnopolsky L. J., MacDougall J. D., Atkinson S. A., Tarnopolsky M. A., Sutton J. R. Gender differences in substrate for endurance exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Jan;68(1):302–308. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.1.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren J., Sato Y., Ostman J., Hagenfeldt L., Felig P. Turnover and splanchnic metabolism of free fatty acids and ketones in insulin-dependent diabetics at rest and in response to exercise. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1367–1376. doi: 10.1172/JCI111340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahrenberg H., Engfeldt P., Bolinder J., Arner P. Acute adaptation in adrenergic control of lipolysis during physical exercise in humans. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):E383–E390. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.4.E383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe R. R., Klein S., Carraro F., Weber J. M. Role of triglyceride-fatty acid cycle in controlling fat metabolism in humans during and after exercise. Am J Physiol. 1990 Feb;258(2 Pt 1):E382–E389. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.258.2.E382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood P. D., Stefanick M. L., Williams P. T., Haskell W. L. The effects on plasma lipoproteins of a prudent weight-reducing diet, with or without exercise, in overweight men and women. N Engl J Med. 1991 Aug 15;325(7):461–466. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199108153250703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



