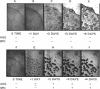
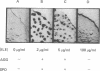
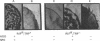
Abstract
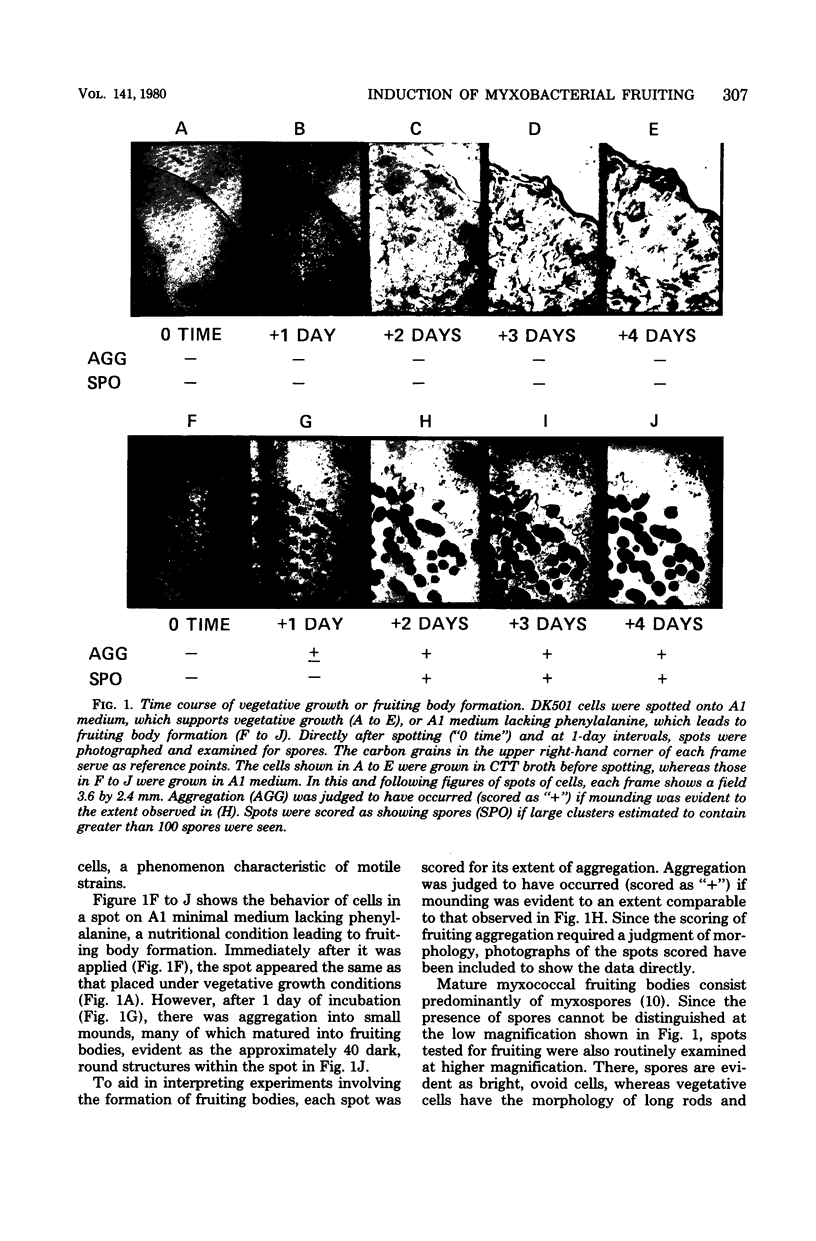
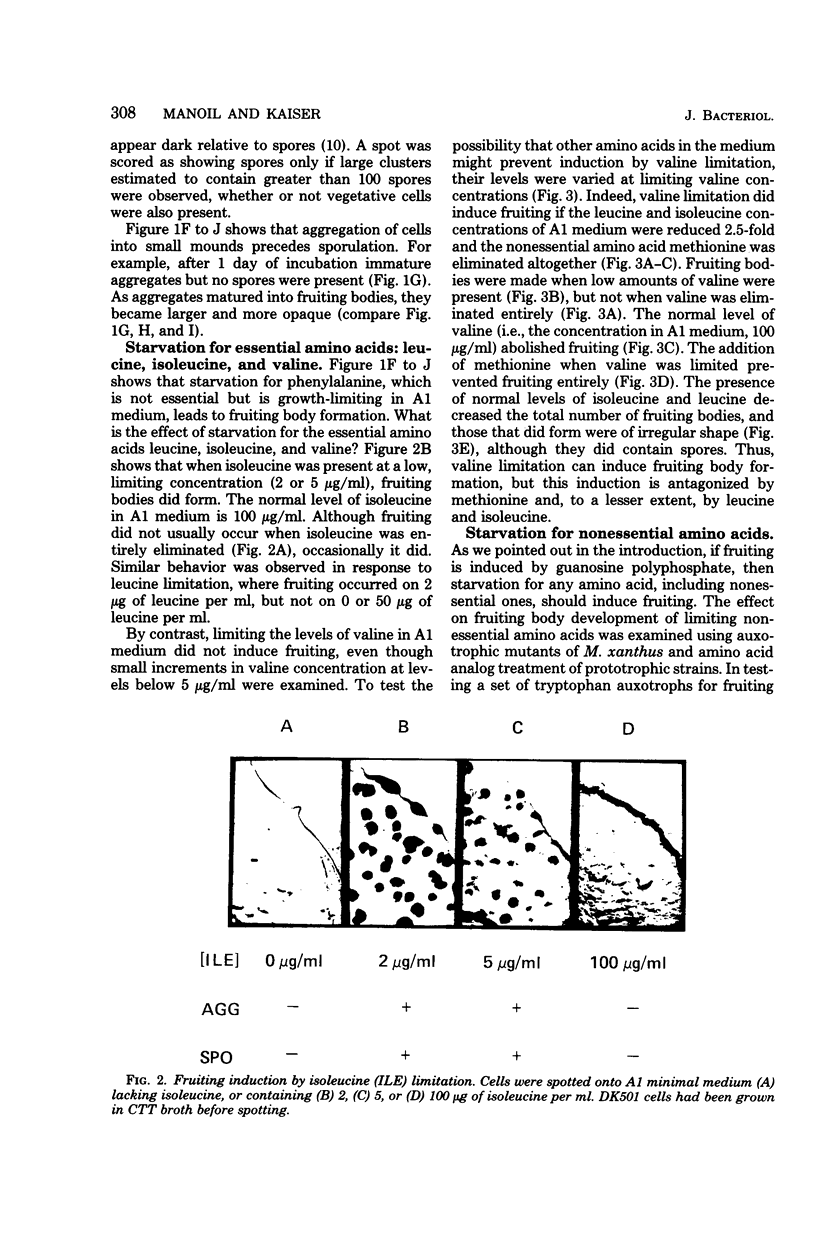
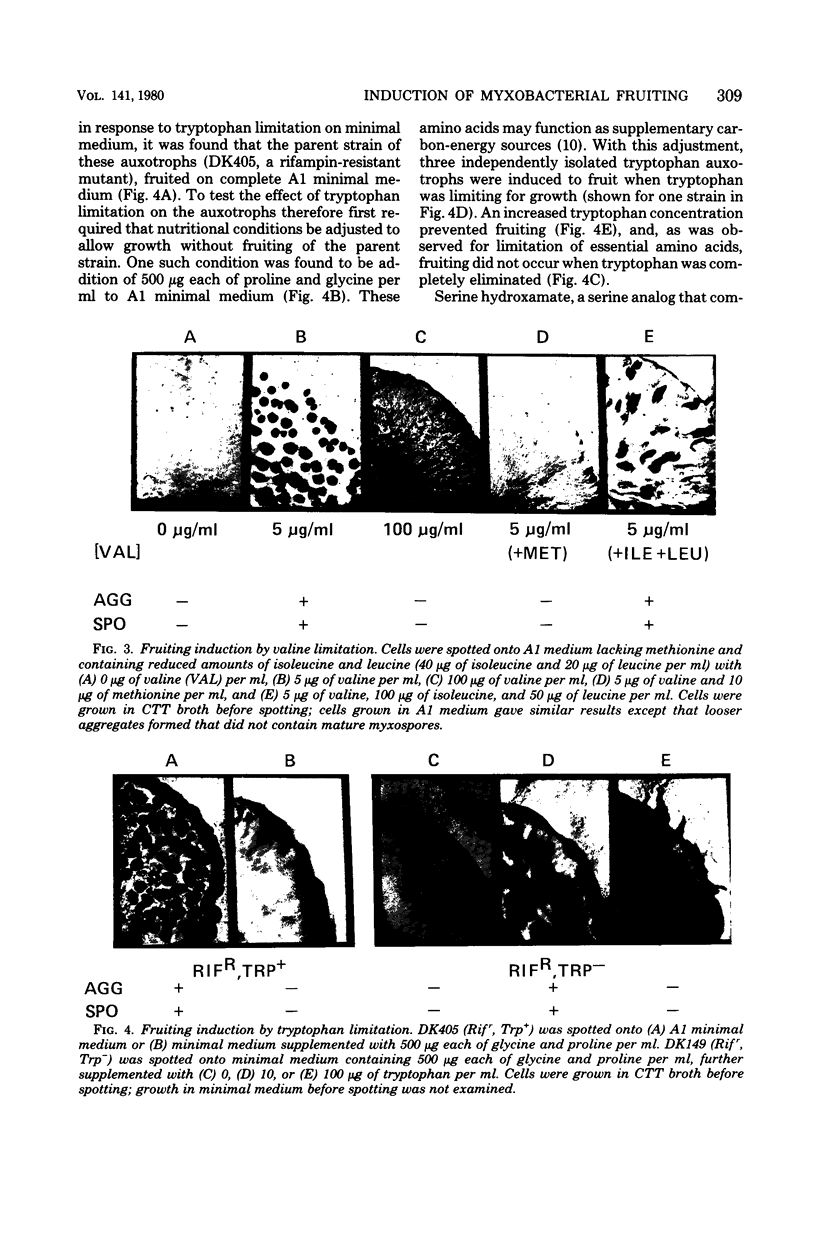
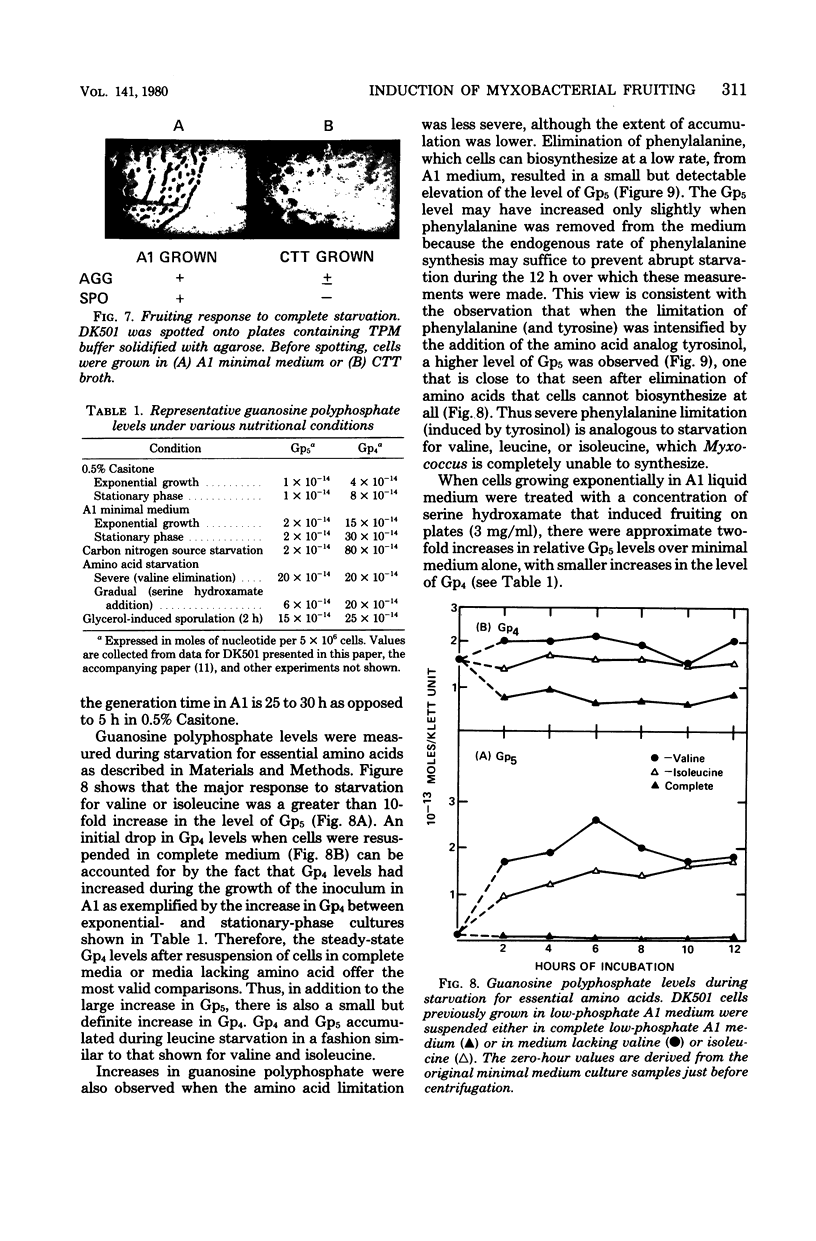
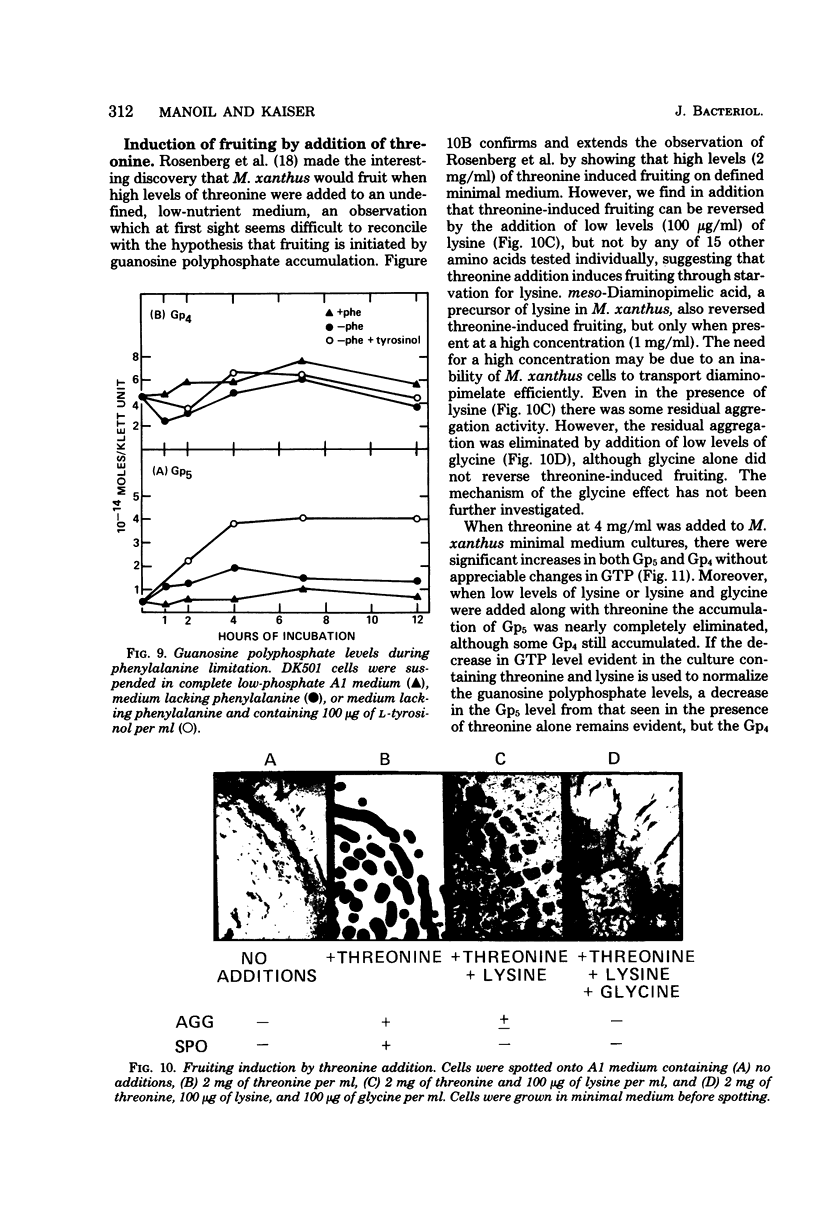
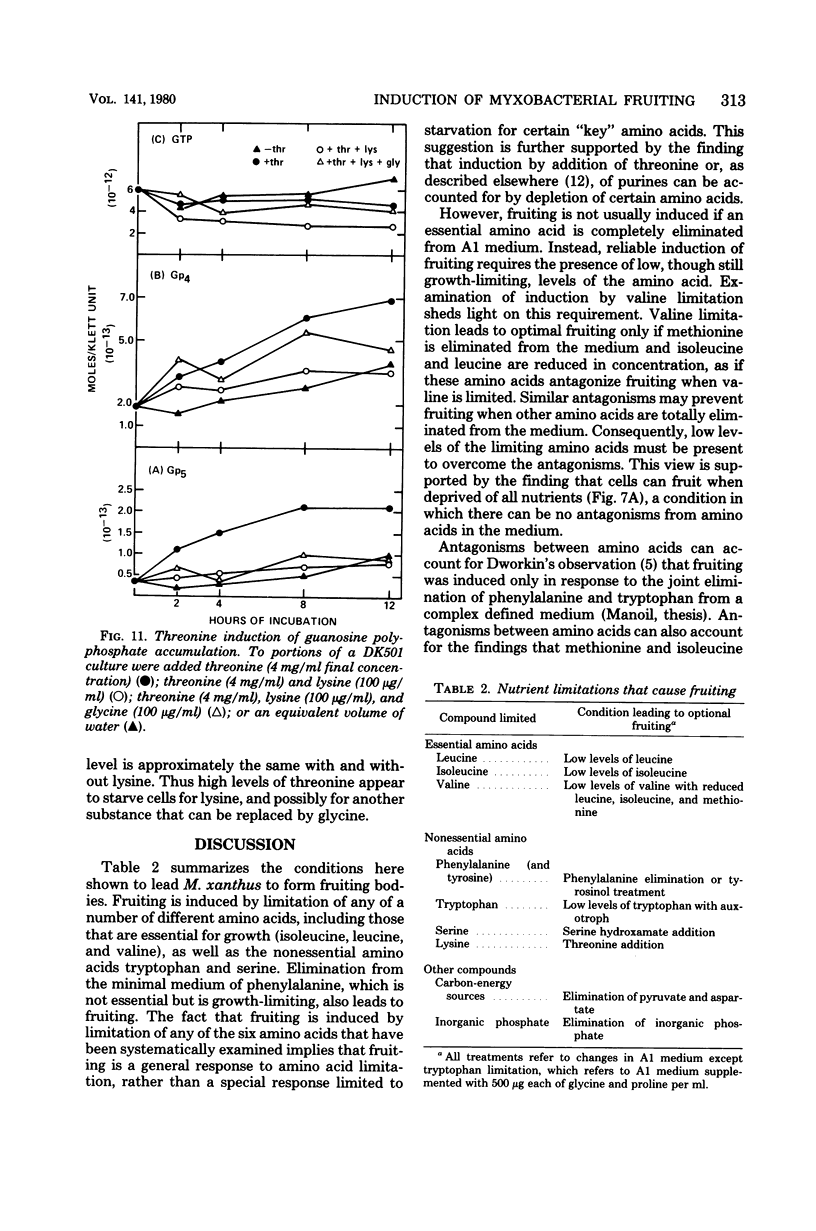
Development of multicellular fruiting bodies of Myxococcus xanthus can be induced by limitation of any of a number of different classes of amino acids. Investigated were amino acids that wild-type strains of M. xanthus are unable to synthesize (isoleucine, leucine, and valine), can synthesize at a low rate (phenylalanine), or can normally synthesize at an adequate rate (tryptophan and serine). In general, gradual rather than abrupt starvation for an essential amino acid was required for the induction of fruiting. Perhaps gradual starvation in general minimizes antagonism between amino acids present in the medium, as was documented for valine starvation. The previously reported induction of fruiting by a high concentration of threonine was shown to be specifically reversed by lysine. Threonine addition may starve cells for lysine by feedback inhibition of aspartokinase activity. Starvation for carbon-energy sources or inorganic phosphate also induced fruiting. As in other bacteria, amino acid starvation of M. xanthus leads to increases in cellular guanosine polyphosphate, usually consisting of large increases in the amount of guanosine pentaphosphate with smaller increases in the level of guanosine tetraphosphate. Guanosine polyphosphate accumulation is thus shown to be correlated with nutritional conditions that induce fruiting, and therefore may serve as an intracellular signal to trigger cells to end vegetative growth and initiate fruiting body development.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Nutrition of Myxococcus xanthus, a fruiting myxobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):763–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.763-768.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campos J. M., Zusman D. R. Regulation of development in Myxococcus xanthus: effect of 3':5'-cyclic AMP, ADP, and nutrition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):518–522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M. Regulation of bacterial ppGpp and pppGpp. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:301–318. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashel M. The control of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli. IV. Relevance of unusual phosphorylated compounds from amino acid-starved stringent strains. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3133–3141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DWORKIN M. NUTRITIONAL REGU.ATION OF MORPHOGENESIS IN MYXOCOCCUS XANTHUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:67–72. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.67-72.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filer D., Rosenberg E., Kindler S. H. Aspartokinase of Myxococcus xanthus: "feedback stimulation" by required amino acids. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):23–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.23-28.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen J. D., An G., Fiil N. P. Nonsense and insertion mutants in the relA gene of E. coli: cloning relA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemphill H. E., Zahler S. A. Nutritional induction and suppression of fruiting in Myxococcus xanthus FBa. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1018–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1018-1023.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D., Manoil C., Dworkin M. Myxobacteria: cell interactions, genetics, and development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:595–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.003115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. The suppression of defective translation by ppGpp and its role in the stringent response. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):545–557. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90241-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao C. C., Gallant J. A gene involved in the metabolic control of ppGpp synthesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jan 17;158(3):271–277. doi: 10.1007/BF00267198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker J., Pollard J. W., Friesen J. D., Stanners C. P. Stuttering: high-level mistranslation in animal and bacterial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1091–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primakoff P., Artz S. W. Positive control of lac operon expression in vitro by guanosine 5'-diphosphate 3'-diphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1726–1730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickenberg H. V. Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1974;28(0):353–369. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.28.100174.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Filer D., Zafriti D., Kindler S. H. Aspartokinase activity and the developmental cycle of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.29-34.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosa T., Pizer L. I. Biochemical bases for the antimetabolite action of L-serine hydroxamate. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jun;106(3):972–982. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.3.972-982.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B. Regulation of the assimilation of nitrogen compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:1127–1162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.005403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]