Abstract
Histamine and IL-1 have been implicated in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory diseases, such as pulmonary allergic reactions and rheumatoid arthritis. We therefore investigated whether histamine modulated the synthesis of IL-1 beta. Human PBMC were stimulated with IL-1 alpha (10 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of histamine (10(-9)-10(-4) M). Histamine alone did not induce protein synthesis or mRNA accumulation for IL-1 beta. IL-1 alpha-induced IL-1 beta synthesis was enhanced two to threefold by histamine concentrations from 10(-6)-10(-4) M. Cimetidine, an H2 receptor antagonist, reversed the histamine (10(-5) M)-mediated increase in IL-1 alpha-induced IL-1 beta synthesis. Diphenhydramine, an H1 receptor antagonist, had no effect. Indomethacin, a cyclooxygenase inhibitor, significantly reduced IL-1 alpha-induced IL-1 beta synthesis, but had no effect on the histamine-mediated increase in IL-1 alpha-induced IL-1 beta synthesis. Histamine (10(-5) M) enhanced and sustained IL-1 beta mRNA levels in IL-1 alpha-stimulated PBMC. However, histamine reduced IL-1 beta mRNA half-life (2.4 vs 1.2 h), suggesting that histamine enhances IL-1 alpha-induced IL-1 beta synthesis at the level of transcriptional activation. On the other hand, histamine (10(-5) M) did not affect IL-1 alpha-induced synthesis of IL-1 receptor antagonist. These results suggest that mast cells may sustain chronic inflammatory processes by upregulating self-induction of IL-1 through histamine release.
Full text
PDF
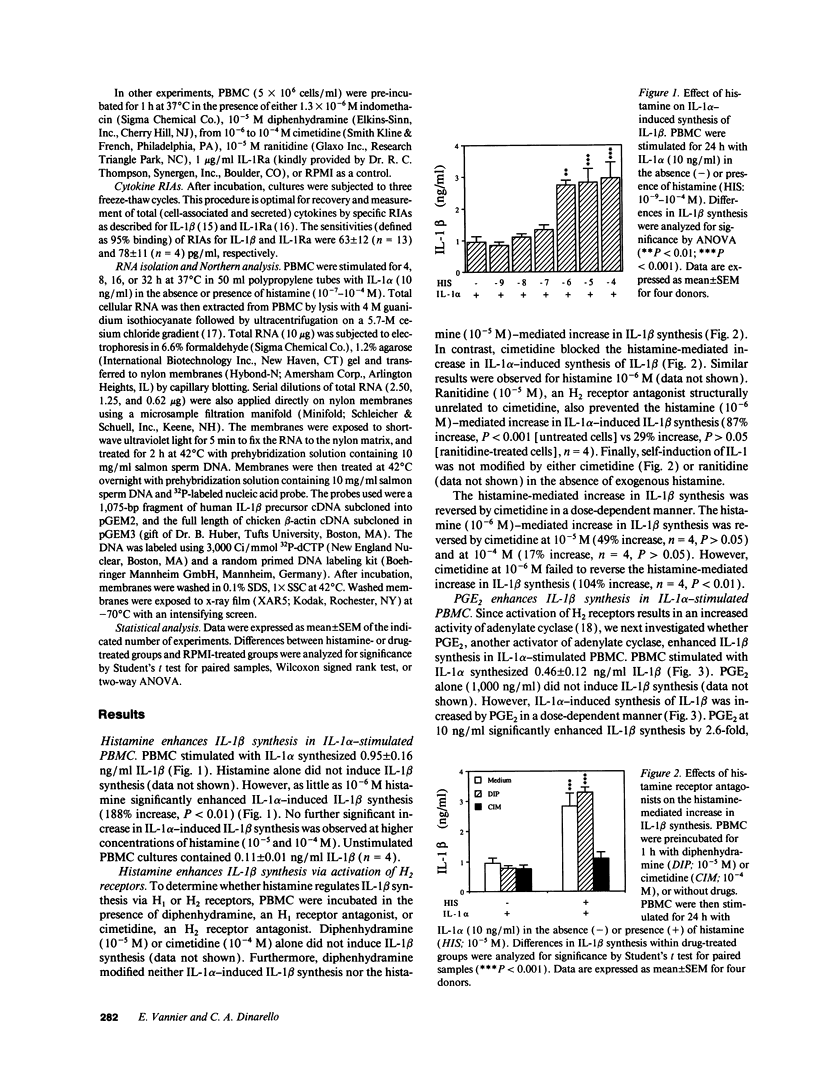
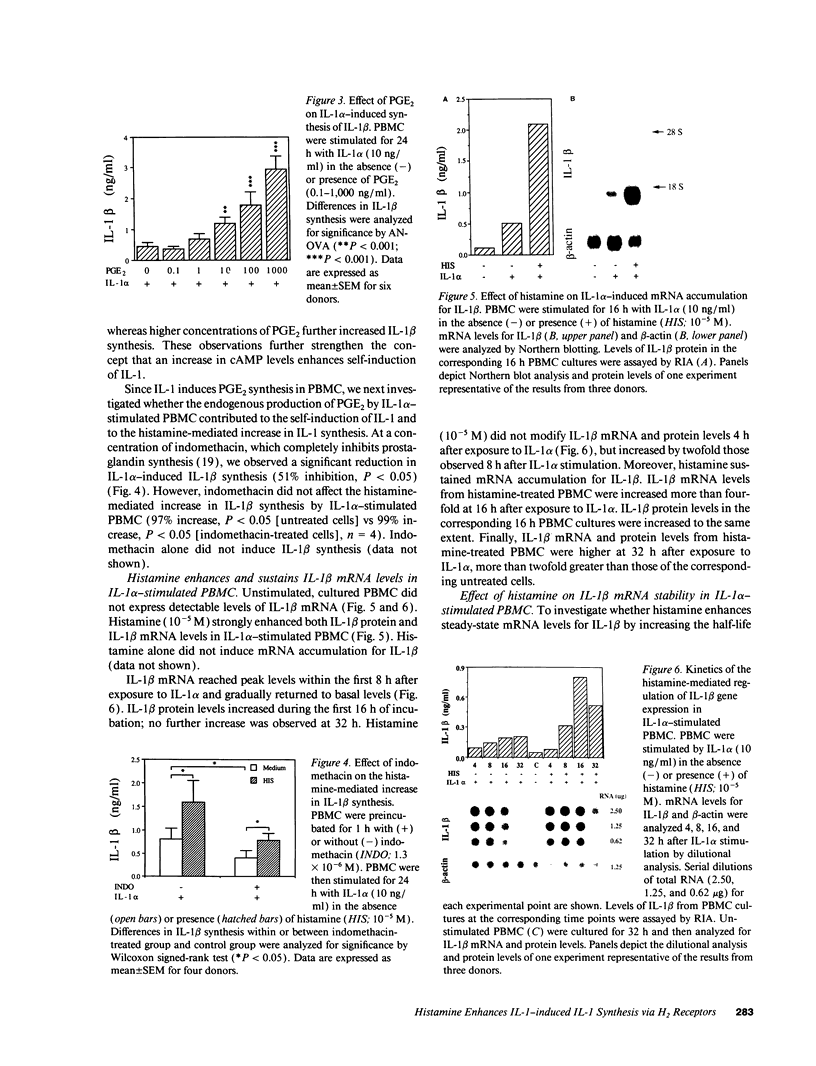
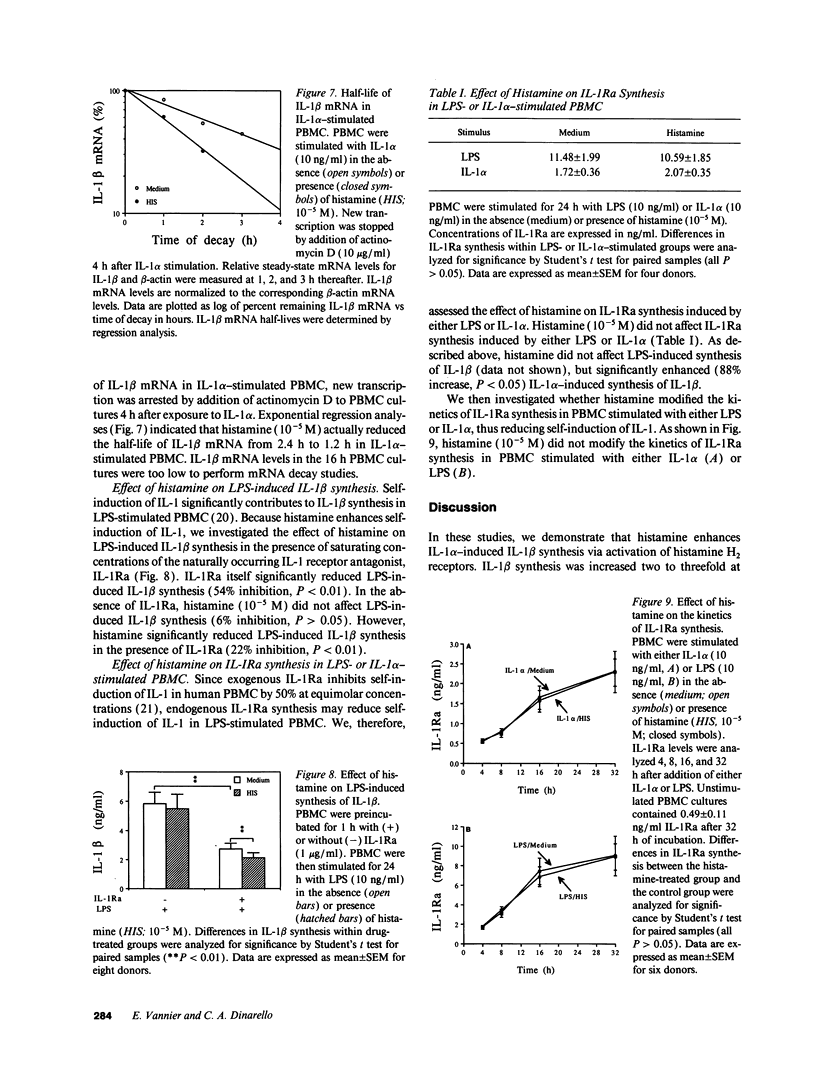



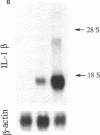
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Smith M. F., Jr, Janson R. W., Joslin F. G. IL-1 receptor antagonist and IL-1 beta production in human monocytes are regulated differently. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1530–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bomsztyk K., Toivola B., Emery D. W., Rooney J. W., Dower S. K., Rachie N. A., Sibley C. H. Role of cAMP in interleukin-1-induced kappa light chain gene expression in murine B cell line. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9413–9417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borish L., Mascali J. J., Rosenwasser L. J. IgE-dependent cytokine production by human peripheral blood mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):63–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Melmon K. L., Lichtenstein L. M. Histamine augments leukocyte adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and blocks antigenic histamine release. Science. 1971 Aug 20;173(3998):743–745. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3998.743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandwein S. R. Regulation of interleukin 1 production by mouse peritoneal macrophages. Effects of arachidonic acid metabolites, cyclic nucleotides, and interferons. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 5;261(19):8624–8632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burd P. R., Rogers H. W., Gordon J. R., Martin C. A., Jayaraman S., Wilson S. D., Dvorak A. M., Galli S. J., Dorf M. E. Interleukin 3-dependent and -independent mast cells stimulated with IgE and antigen express multiple cytokines. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):245–257. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron W., Doyle K., Rocklin R. E. Histamine type I (H1) receptor radioligand binding studies on normal T cell subsets, B cells, and monocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2116–2120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Dohlsten M., Sjögren H. O. Histamine modulates the production of interferon-gamma and interleukin-2 by mitogen-activated human mononuclear blood cells. Cell Immunol. 1985 Nov;96(1):104–112. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casale T. B., Wescott S., Rodbard D., Kaliner M. Characterization of histamine H-1 receptors on human mononuclear cells. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1985;7(5):639–645. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(85)90147-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlsten M., Kalland T., Sjögren H. O., Carlsson R. Histamine inhibits interleukin 1 production by lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human peripheral blood monocytes. Scand J Immunol. 1988 May;27(5):527–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb02379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Brewer M. T., Verderber E., Heimdal P., Brandhuber B. J., Thompson R. C. Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist is a member of the interleukin 1 gene family: evolution of a cytokine control mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5232–5236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Osborn L., Takada Y., Crouse C., Luhowskyj S., Hemler M. E., Lobb R. R. VCAM-1 on activated endothelium interacts with the leukocyte integrin VLA-4 at a site distinct from the VLA-4/fibronectin binding site. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):577–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90661-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres S., Ghorbani R., Lonnemann G., van der Meer J. W., Dinarello C. A. Measurement of immunoreactive interleukin-1 beta from human mononuclear cells: optimization of recovery, intrasubject consistency, and comparison with interleukin-1 alpha and tumor necrosis factor. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1988 Dec;49(3):424–438. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(88)90130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gespach C., Courillon-Mallet A., Launay J. M., Cost H., Abita J. P. Histamine H2 receptor activity and histamine metabolism in human U-937 monocyte-like cells and human peripheral monocytes. Agents Actions. 1986 Apr;18(1-2):124–128. doi: 10.1007/BF01988001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. R., Galli S. J. Release of both preformed and newly synthesized tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha)/cachectin by mouse mast cells stimulated via the Fc epsilon RI. A mechanism for the sustained action of mast cell-derived TNF-alpha during IgE-dependent biological responses. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):103–107. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granowitz E. V., Clark B. D., Vannier E., Callahan M. V., Dinarello C. A. Effect of interleukin-1 (IL-1) blockade on cytokine synthesis: I. IL-1 receptor antagonist inhibits IL-1-induced cytokine synthesis and blocks the binding of IL-1 to its type II receptor on human monocytes. Blood. 1992 May 1;79(9):2356–2363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granowitz E. V., Vannier E., Poutsiaka D. D., Dinarello C. A. Effect of interleukin-1 (IL-1) blockade on cytokine synthesis: II. IL-1 receptor antagonist inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine synthesis by human monocytes. Blood. 1992 May 1;79(9):2364–2369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurme M. Modulation of interleukin-1 beta production by cyclic AMP in human monocytes. FEBS Lett. 1990 Apr 9;263(1):35–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80699-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurme M., Serkkola E., Ronni T., Silvennoinen O. Control of interleukin-1 beta expression by protein kinase C and cyclic adenosine monophosphate in myeloid leukemia cells. Blood. 1990 Dec 1;76(11):2198–2203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Sato N., Arai K., Miyajima A. Expression cloning of the human IL-3 receptor cDNA reveals a shared beta subunit for the human IL-3 and GM-CSF receptors. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1165–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Takaku F., Miyajima A. IL-1 up-regulates the expression of cytokine receptors on a factor-dependent human hemopoietic cell line, TF-1. Int Immunol. 1991 Jun;3(6):571–577. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.6.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel S. L., Chensue S. W., Phan S. H. Prostaglandins as endogenous mediators of interleukin 1 production. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):186–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier J. A., Hla T., Maciag T. Cyclooxygenase is an immediate-early gene induced by interleukin-1 in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10805–10808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizel S. B. How does interleukin 1 activate cells? Cyclic AMP and interleukin 1 signal transduction. Immunol Today. 1990 Nov;11(11):390–391. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90154-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill L. A., Barrett M. L., Lewis G. P. Induction of cyclo-oxygenase by interleukin-1 in rheumatoid synovial cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 9;212(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81551-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill L. A., Bird T. A., Saklatvala J. How does interleukin 1 activate cells? Interleukin 1 signal transduction. Immunol Today. 1990 Nov;11(11):392–394. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90155-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmori Y., Strassman G., Hamilton T. A. cAMP differentially regulates expression of mRNA encoding IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta in murine peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3333–3339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Hession C., Tizard R., Vassallo C., Luhowskyj S., Chi-Rosso G., Lobb R. Direct expression cloning of vascular cell adhesion molecule 1, a cytokine-induced endothelial protein that binds to lymphocytes. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1203–1211. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90775-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaut M., Pierce J. H., Watson C. J., Hanley-Hyde J., Nordan R. P., Paul W. E. Mast cell lines produce lymphokines in response to cross-linkage of Fc epsilon RI or to calcium ionophores. Nature. 1989 May 4;339(6219):64–67. doi: 10.1038/339064a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Lapierre L. A., Mendrick D. L., Fiers W., Rothlein R., Springer T. A. Overlapping patterns of activation of human endothelial cells by interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and immune interferon. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 15;137(6):1893–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poutsiaka D. D., Clark B. D., Vannier E., Dinarello C. A. Production of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist and interleukin-1 beta by peripheral blood mononuclear cells is differentially regulated. Blood. 1991 Sep 1;78(5):1275–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz A., Wyche A., Siegel N., Needleman P. Regulation of fibroblast cyclooxygenase synthesis by interleukin-1. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):3022–3028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roszkowski W., Plaut M., Lichtenstein L. M. Selective display of histamine receptors on lymphocytes. Science. 1977 Feb 18;195(4279):683–685. doi: 10.1126/science.190677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Anderle S. K., Brown R. R., Dalldorf F. G., Thompson R. C. Pro- and anti-inflammatory roles of interleukin-1 in recurrence of bacterial cell wall-induced arthritis in rats. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4436–4442. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4436-4442.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Chedid M., Suttles J., Pollok B. A., Mizel S. B. Interleukin 1 and cyclic AMP induce kappa immunoglobulin light-chain expression via activation of an NF-kappa B-like DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):959–964. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung S. S., Walters J. A. Increased cyclic AMP levels enhance IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta mRNA expression and protein production in human myelomonocytic cell lines and monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1915–1923. doi: 10.1172/JCI115515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavernier J., Devos R., Cornelis S., Tuypens T., Van der Heyden J., Fiers W., Plaetinck G. A human high affinity interleukin-5 receptor (IL5R) is composed of an IL5-specific alpha chain and a beta chain shared with the receptor for GM-CSF. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1175–1184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Woolley D. E. Evidence for both histamine H1 and H2 receptors on human articular chondrocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jun;46(6):431–435. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.6.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. J., Woolley D. E. Histamine H1 receptors on adherent rheumatoid synovial cells in culture: demonstration by radioligand binding and inhibition of histamine-stimulated prostaglandin E production by histamine H1 antagonists. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Jun;46(6):425–430. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.6.425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier E., Miller L. C., Dinarello C. A. Histamine suppresses gene expression and synthesis of tumor necrosis factor alpha via histamine H2 receptors. J Exp Med. 1991 Jul 1;174(1):281–284. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh G. M., Mermod J. J., Hartnell A., Kay A. B., Wardlaw A. J. Human eosinophil, but not neutrophil, adherence to IL-1-stimulated human umbilical vascular endothelial cells is alpha 4 beta 1 (very late antigen-4) dependent. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3419–3423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner C. D., Gundel R. H., Reilly P., Haynes N., Letts L. G., Rothlein R. Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in the pathogenesis of asthma. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):456–459. doi: 10.1126/science.1967851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wodnar-Filipowicz A., Heusser C. H., Moroni C. Production of the haemopoietic growth factors GM-CSF and interleukin-3 by mast cells in response to IgE receptor-mediated activation. Nature. 1989 May 11;339(6220):150–152. doi: 10.1038/339150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]