Abstract
Background
The goal of the present study was to analyze associations between depression and mortality of cancer patients and to test whether these associations would vary by study characteristics.
Method
Meta-analysis was used for integrating the results of 105 samples derived from 76 prospective studies.
Results
Depression diagnosis and higher levels of depressive symptoms predicted elevated mortality. This was true in studies that assessed depression before cancer diagnosis as well as in studies that assessed depression following cancer diagnosis. Associations between depression and mortality persisted after controlling for confounding medical variables. The depression–mortality association was weaker in studies that had longer intervals between assessments of depression and mortality, in younger samples and in studies that used the Beck Depression Inventory as compared with other depression scales.
Conclusions
Screening for depression should be routinely conducted in the cancer treatment setting. Referrals to mental health specialists should be considered. Research is needed on whether the treatment of depression could, beyond enhancing quality of life, extend survival of depressed cancer patients.
Keywords: Cancer, depression, meta-analysis, mortality, oncology
Introduction
There is scientific and public interest in whether psychological factors could change the course of cancer and other life-threatening diseases (Coyne et al. 2007). Clinical depression is prevalent among cancer patients with rates ranging between 13 and 40% (Sellick & Crooks, 1999). Many patients experience subthreshold or subsyndromal symptoms without meeting criteria for a depression diagnosis (e.g. Grassi et al. 1996). Depression has been shown to confer risk for all-cause mortality (Wulsin et al. 1999), but its implications for cancer mortality are unclear. Previous narrative reviews have been inconsistent (Shekele et al. 1981; Cwinkel et al. 1997; Giese-Davis & Spiegel, 2003). A prior meta-analysis on the prospective association of depression with the development of cancer found that depression marginally increased the risk for developing cancer (McGee et al. 1994) but recent meta-analyses suggest that the association between depression and cancer mortality is robust (Chida et al. 2008; Satin et al. 2009). One showed that depression was associated with higher cancer mortality, both in community-based samples [eight studies, risk ratio (RR) 1.34] and cancer patients (15 studies, RR 1.08; Chida et al. 2008). Another found that depression predicted higher mortality (25 studies, RR 1.25–1.39; Satin et al. 2009). However, many available studies on depression and cancer mortality were excluded from these meta-analyses and moderator analyses could not be conducted. By expanding the number of included studies, the present meta-analysis explored potentially important moderators. We addressed two questions. First, is there an association between depression and mortality of cancer patients in this broader sample of studies? Second, are these effects more likely to be observed in particular subgroups of patients or in studies that used particular methods or instrumentation?
Depression and cancer mortality
Spiegel & Giese-Davis (2003) identify three reasons why depression may enhance mortality risk in cancer patients. First, depression may have a pathophysiological effect via neuroendocrine and immunological functions that influence mortality (e.g. dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, especially diurnal variation in cortisol and melatonin). Second, depressed patients may be less likely to adhere to preventive screening procedures, cancer treatments or recommendations for maintaining health. For example, depressed patients may be less likely to engage in regular exercise or other forms of physical activity, may be more likely to smoke and drink alcohol to excess (Wulsin et al. 1999) and may not adhere to prescribed medication regimens or miss therapy appointments (DiMatteo et al. 2000). However, not all available studies found poorer treatment adherence in depressed cancer patients (e.g. Ayres et al. 1994). Third, many of the symptoms of cancer and the side-effects of its treatment are similar to those of depression, including the vegetative symptoms of sleep and appetite disturbance, fatigue and concentration difficulties. Thus, depressive symptoms may be a proxy for disease severity. Indeed, depressive symptoms appear to be more prevalent in advanced cancer than in earlier stages (Massie & Popkin, 1998). Whereas the first two explanations invoke substantive mechanisms (pathophysiology, treatment adherence), the third refers to a statistical and measurement issue, symptom overlap. Interpretive problems posed by symptom overlap can be ruled out by longitudinal studies initiated prior to cancer diagnosis and they can be mitigated by controlling statistically for confounding medical variables such as disease stage.
Beyond the explanations considered for the associations between depression and mortality (Spiegel & Giese-Davis, 2003), others are also plausible. Depressed patients may be less likely than non-depressed patients to recruit, retain and benefit from social support and from other forms of social capital. Similarly, they may be less effective at eliciting or cultivating healing relationships with healthcare providers (Epstein & Street, 2007) and navigating complex healthcare delivery systems. Furthermore, effects of depression may be mediated through the use of ineffective coping strategies, such as passive coping or showing helpless resignation. In this case, depression would increase the level of ineffective coping, which again would lead to increased mortality (Faller & Schmidt, 2004). Finally, depression may confer risk for non-cancer causes of death, such as suicide (Akechi et al. 2004).
A narrative review reported positive associations between depression and cancer progression or mortality in 15 of 24 studies (Giese-Davis & Spiegel, 2003). For example, Derogatis et al. (1979) and Watson et al. (1999) reported associations between depression and elevated mortality of cancer patients, but Cody et al. (1994) did not. The apparently null findings may simply reflect a small as opposed to nil association because effects are more difficult to detect in smaller samples. Thus, in line with Chida et al. (2008) and Satin et al. (2009), we expected that there would be an overall positive association between depression and cancer mortality when the effects are pooled across available studies. Based on the assumption that depression's effect on cancer mortality is not a measurement artefact based on symptom overlap with severity of cancer, we expected that the effect of depression on cancer mortality would also be found when controlling for indicators of severity of the disease, such as stage of cancer.
Moderating effects of study characteristics
Moderating effects occur when the size of the association between depression and mortality is influenced by a third variable. Several study characteristics may serve as moderators.
Recruitment site
As community-based studies on mortality usually start with people having no known cancer diagnosis, initially measured depression may affect disease onset, disease progression and mortality. In contrast, studies that follow a cohort of cancer patients analyze effects of depression on disease progression and mortality. Depression may affect both cancer incidence and course. Effects may be larger in community samples because depression is more likely to have affected both cancer incidence and course. In fact, Chida et al. (2008) found slightly stronger associations of depression with mortality in community-based studies than in clinical samples. Thus, we hypothesized that depression's combined effect (on incidence and course) may lead to stronger associations of depression with cancer mortality in community studies than in cancer samples.
Statistical control for confounding variables
Patients with more advanced disease will have higher depression scores. Failing to control for indicators of disease severity could lead to an inflated estimate of depression's effect if disease severity is a more important driver of mortality than depression. In Satin et al.'s meta-analysis, the results were inconclusive as only one out of their three analyses found a significant association of depression and mortality after controlling for confounders. However, Watson et al. (1999) found that the association of depression with mortality was strengthened after statistically controlling for prognostic somatic factors.
Stage of the disease
It has been suggested that, in advanced stages of cancer, biological functions may become increasingly important in regard to patient mortality (Cwinkel et al. 1997) while psychosocial factors may play a larger role in the outcomes of less progressed cancer. Thus, if depression is considered to have psychosocial origins and consequences, we might expect smaller effects when patients have more advanced disease. On the other hand, if the measurement of depression taps symptoms of the disease, which could be magnified in more advanced disease stages, then we might expect larger effect of depression when patients have more advanced disease.
Cancer site
It has been suggested that psychological factors may play less of a role in lung cancers and others with virulent cell histopathology because these cancers rarely deviate from an expected course (Levy & Roberts, 1992). Onitilo et al. (2006) found no differences in the association of depression and mortality when comparing five cancer sites.
Length of study interval
As the severity of depressive symptoms may change over time, depression scores at the first time of data collection may lose predictive power with increasing time interval. In fact, Spiegel and Giese-Davis (2003) reported that prospective studies that found no association between depression and cancer progression had, on average, 10-year intervals, whereas the other studies had, on average, only 5-year intervals. Similarly, Satin et al. (2009) found significant associations of depression and cancer mortality in studies with time intervals <5 years but the results of studies with longer intervals were inconclusive. Thus, we hypothesized that studies with shorter intervals show stronger associations of depression and cancer mortality.
Measurement of depression
Whereas some studies assessed depression diagnosis, other focused on depressive symptoms. Clinical depression may have stronger effects on mortality because depressive symptoms in the lower range may be less likely to affect the suggested moderators of the depression–mortality relationship, such as low compliance (Spiegel & Giese-Davis, 2003). In fact, depression as a clinical syndrome, in contrast with less severe depressions, may more often involve the loss of the will to live, which may cause the rejection of cancer treatments, low compliance and elevated risk for suicide (Schulz et al. 1996; Wulsin et al. 1999). Satin et al. (2009) found that depression diagnosis showed slightly larger associations with mortality than depressive symptoms, but the difference did not reach statistical significance in that smaller database.
Age
The dilemma here is similar to that for offering a hypothesis about disease stage. If depression is considered psychosocial in origin and symptomatology, we might expect smaller effects in samples with a greater proportion of older patients because age-associated somatic risk factors for death, cancer plus co-morbid medical burden, would play a larger role in older patients due to their greater medical burden. Alternatively, if the measurement of depression primarily taps neurovegetative and other somatic symptoms, then we might expect larger effects when patients are older because such symptoms may be an indicator of a co-morbid disease that could cause death.
Gender
As depression is more prevalent in women than in men, we were also interested in whether the size of the association between depression and mortality may vary by gender. Results of available studies not specific to cancer have been inconsistent regarding whether the association of depression and mortality would be stronger in women (e.g. Kawamura et al. 2007) or men (e.g. Anstey & Luszcz, 2002).
Summary
In sum, with regard to moderators, we compared the effects on mortality of depression as a function of when and how depression was assessed, disease stage, patient age, gender and whether confounds were controlled statistically. We did not assign quality scores to individual studies as this practice is controversial (e.g. Juni et al. 1999). Relevant aspects of study quality are considered when computing effect sizes and their weights (sample size) and when analyzing moderating effects (e.g. statistical control for confounding variables).
Method
We identified a comprehensive sample of studies searching electronic databases (Medline, Cochrane Data Base, Psyclit, PSYNDEX); search terms: [(malignant or cancer or carcinoma) and depression and (survival or mortality or death or Kaplan–Meier or Cox)] and cross-referencing. Criteria for inclusion in the meta-analysis were:
The participants were cancer patients or were enrolled in a prospective community-based sample for which cancer mortality is reported.
Depressive disorders were diagnosed according to standard diagnostic criteria in the ICD-10, DSM-III, III-R or IV or depressive symptoms were assessed with self-rating scales or interviewer ratings.
Information on mortality is provided.
Statistics could be computed or estimated for associations between depression and mortality [e.g. RRs and their confidence intervals (CI), survival curves, p values of Cox regression or Kaplan–Meier analysis].
Of the 88 empirical studies initially identified, 76 met all inclusion criteria (N=176 863). The remainder were excluded because they combined data on cancer progression and mortality (five studies) or provided insufficient information for computing effect sizes (seven studies). Of the 76 studies, 11 reported results for more than one sample (e.g. for men and women or for different cancer sites), yielding a total of 105 samples.
Coding of variables
We entered the year of publication, the numbers of participants, age, gender, method for assessing depression (1=clinical diagnosis, 0=rating scales), rating scales used [1=CES-D (Radloff, 1977); 2=Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS; Zigmond & Snaith, 1983; 3=Beck Depression Inventory (BDI; Beck & Steer, 1979); 4=others], sample composition (1=cancer patients only, 0=community sample), cancer site (1=breast, 2=leukemia/lymphoma, 3=lung, 4=brain, 5=other sites, 6=mixed sites), cancer stage [1=early (I, II), 2=mixed/not reported, 3=late (III, IV)], timing of depression assessment (1=prior to cancer diagnosis, 2=after diagnosis) and study interval (years). With regard to control for confounding variables, we created six dummy variables (1=yes, 0=no), indicating whether the study controlled for cancer site, stage, functional status, medical comorbidities, age and socio-economic status. Associations between depression and mortality were coded as RRs. The RR is a summary of the difference between two Kaplan–Meier curves or Cox regression curves and represents the overall increase in the risk of death over the period of follow-up. It has been especially useful for comparing two survival curves because it allows for censoring and time of an event.
For studies reporting on different periods of follow-up, we included the results of all follow-ups but adjusted their weight so that the sum of the subresults' weight would be equal to the weight when only including one result (Lipsey & Wilson, 2004).
Statistical integration of research findings
Calculations for the meta-analysis were performed using random-effects models and the non-iterative method of moments (Hedges & Vevea, 1998), given the expected variability in effect sizes between studies beyond subject-level sampling error. Calculations were conducted as follows.
RRs were calculated. If the RR was not reported, it was computed from information about the numbers of deceased and living patients with low versus high levels of depressive symptoms (or depression diagnosis versus lack of such diagnosis, respectively), the logrank statistics, and survival curves, based on Parmar et al. (1998). For example, if only survival curves are available, the numbers of deaths and persons at risk for death are computed for each time unit for the depressed and non-depressed groups, followed by the computation of the log RR for each time unit and the overall log RR as the weighted sum of the individual estimates. Outliers that were >2 S.D. from the mean of the effect sizes were recoded to the value at 2 S.D. (Lipsey & Wilson, 2004).
Effect sizes were weighted by the inverse of the S.D. and combined to compute an overall weighted mean effect size. The homogeneity of effect sizes was tested by use of the homogeneity statistics Q. The significance of the mean was tested by dividing the weighted mean effect size by the estimated standard error of the mean. Then CI that include 95% of the effects were computed for each effect size.
An analog to the analysis of variance was applied for testing whether the effect sizes would differ between conditions, such as early and late stage of cancer. A significant Q score indicates that the size of the effects differs significantly between studies. Differences between two conditions were interpreted as significant when the 95% CI did not overlap.
Summary statistics of the effect size and the 95% CI were converted back to RRs by taking the anti-logarithms.
Results
Of the 76 prospective studies, 26 included patients with mixed cancer sites and did not report results for individual sites; 15 reported results for leukaemia and lymphomas, 14 for breast cancer, 10 for lung cancer, five for brain cancer and eight studies for other cancer sites (e.g. colon, pancreas). The majority combined patients with early and late stages of the disease (N=59); six focused on patients with early stage cancer (I/II) and 11 on late stage disease (III/IV). Most (n=62) assessed depression after cancer diagnosis; 14 examined the influence of depression prior to cancer diagnosis. Most of the latter studies were community-based cohort studies that assessed risk for different sources of mortality. For the present analyses, only data on cancer mortality were used. In addition, 59 studies used ratings of depressive symptoms and 17 studies assessed depression diagnoses based on structured clinical interviews. The most often used rating scales were the HADS (Zigmond & Snaith, 1983; 15 studies), the CES-D (11 studies) and the BDI (Beck & Steer, 1979; seven studies). A total of 58 studies reporting bivariate associations and 37 studies reporting multivariate analyses were available. The latter controlled for (some) confounding variables, such as age (k=33), stage (k=29), functional status (k=9), socio-economic status (k=8), medical comor-bidities (k=6), and cancer site (k=4). The included studies are identified in the Reference section.
Respondents were, on average, 64.5 years old (S.D.=11.6). About 72% of the respondents (S.D.=42) were women and 49% were married (S.D.=13).
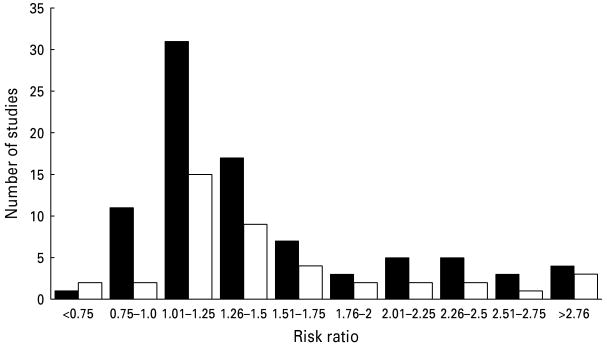
As shown in Fig. 1, effect sizes varied considerably between studies. Nonetheless, 91% of the bivariate associations between depression and mortality as well as 90.5% of the multivariate analyses that controlled for confounding variables reported RRs >1.0, thus indicating that depression was associated with higher mortality. Separate effect sizes were computed for uncontrolled and controlled studies. In line with our expectations, both groups of studies showed that depression was associated with elevated mortality (Table 1). For example, the uncontrolled RR of 1.19 in studies that did not control for confounding variables indicates that the relative risk for mortality increases by 19% in the depressed as compared with the non-depressed group. As indicated by the non-overlap of the 95% CI, the size of the association between depression and cancer mortality did not vary significantly between studies that controlled for confounding variables and studies that did not. In the next step we analyzed whether the effect sizes may vary by moderator variables.
Fig. 1.
Distribution of effect sizes of the individual studies. ■, Uncontrolled; □, controlled.
Table 1. Association of depression with cancer mortality.
| Study characteristic | k | N | RR | 95% CI | Z | Q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uncontrolled effect sizes | 86 | 70 160 | 1.19 | 1.13–1.25 | 6.48*** | 101.94 |
| Controlled effect sizes | 43 | 126 869 | 1.22 | 1.14–1.30 | 5.88*** | 62.31 |
| Averaged effect size | 105 | 176 863 | 1.17 | 1.12–1.22 | 7.23*** | 94.58 |
| Time of collection of depression data/sample composition | 0.15 | |||||
| Prior to cancer diagnosis | 37 | 150 213 | 1.14 | 1.06–1.23 | 3.52*** | 29.76 |
| Following diagnosis | 68 | 26 694 | 1.18 | 1.12–1.24 | 6.45*** | 86.74 |
| Cancer stage | 1.84 | |||||
| Early (I, II) | 6 | 11 828 | 1.31 | 1.10–1.57 | 2.97** | 12.58 |
| mixed/not specified | 85 | 153 026 | 1.16 | 1.10–1.21 | 6.25*** | 89.38 |
| Late (III, IV) | 14 | 12 052 | 1.16 | 1.04–1.29 | 2.79** | 15.02 |
| Cancer site | 1.19 | |||||
| leukemia/lymphoma | 16 | 2507 | 1.13 | 1.03–1.24 | 2.53* | 23.13 |
| breast | 18 | 74 278 | 1.18 | 1.07–1.29 | 3.52*** | 29.27* |
| brain | 6 | 7118 | 1.23 | 1.04–1.47 | 2.36* | 10.02 |
| lung | 12 | 24 116 | 1.17 | 1.03–1.34 | 2.36* | 10.63 |
| other sites (e.g. esophagus) | 22 | 29 984 | 1.14 | 1.04–1.24 | 2.90** | 10.88 |
| mixed sites | 31 | 38 904 | 1.16 | 1.08–1.24 | 4.24*** | 40.78 |
| Length of study intervala | 5.62* | |||||
| ≤2 years | 28 | 9506 | 1.26 | 1.16–1.36 | 5.57*** | 42.03* |
| 2–4 years | 16 | 27 420 | 1.10 | 1.02–1.20 | 2.40* | 15.10 |
| 4–6 years | 35 | 97 586 | 1.14 | 1.05–1.24 | 3.06** | 33.27 |
| >6 years | 26 | 42 394 | 1.14 | 1.07–1.23 | 3.77*** | 26.83 |
| Method of assessing depression | 0.04 | |||||
| Clinical diagnosis | 45 | 45 603 | 1.17 | 1.10–1.35 | 4.79*** | 39.51 |
| Self-rating (depressive symptoms) | 61 | 131 303 | 1.16 | 1.10–1.22 | 5.59*** | 80.35* |
| CES-D | 13 | 15 751 | 1.24 | 1.11–1.40 | 3.54*** | 21.73 |
| HADS | 16 | 7329 | 1.17 | 1.07–1.28 | 3.42*** | 24.42 |
| BDI | 10 | 918 | 1.05 | 0.97–1.14 | 1.18 | 7.41 |
| Mean age of participantsa | 6.02* | |||||
| <55 years | 35 | 22 616 | 1.11 | 1.06–1.17 | 3.99*** | 44.11 |
| 55–69.9 years | 36 | 18 903 | 1.15 | 1.09–1.21 | 5.47*** | 59.61** |
| ≥70 years | 7 | 41 253 | 1.37 | 1.17–1.60 | 3.92*** | 8.85 |
| Gender compositionb (% women) | 2.48 | |||||
| 0 | 16 | 38 523 | 1.20 | 1.06–1.36 | 2.93** | 15.55 |
| 1–49 | 36 | 6860 | 1.13 | 1.06–1.21 | 3.69*** | 44.07 |
| 50–99 | 15 | 11 187 | 1.24 | 1.12–1.38 | 4.02*** | 21.46 |
| 100 | 33 | 112 183 | 1.14 | 1.07–1.23 | 3.79*** | 33.08 |
k, Number of samples; N, number of participants; RR, risk ratio; CI, confidence interval; Z, test for the significance of the mean effect size; Q, test for heterogeneity of effect sizes; HADS, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale; BDI, Beck Depression Inventory.
Values >1 indicate that the risk for cancer mortality is increased in subjects with higher levels of depressive symptoms.
The age of participants was not reported for 27 samples.
Gender composition was not reported in six samples.
p<0.05,
p<0.01,
p<0.001.
To do so, we combined the controlled and uncontrolled effect sizes. When both were reported in the same study, the controlled effect sizes were used because they are presumed to be more valid. This averaged effect size also showed that depression increased the risk for cancer mortality (Table 1).
Effect sizes did not differ significantly between prospective studies that assessed depression prior to cancer diagnosis and those that did so following cancer diagnosis. Nor did effect sizes differ as a function of disease stage. The magnitude of the association between depression and survival was similar across samples with early stage, late stage and mixed stages of cancer.
With regard to cancer site, depression predicted shorter survival in leukemia/lymphoma patients, in breast cancer patients, in lung cancer patients, brain cancer patients and in patients with other homogeneous sites, and in mixed samples. All the CI overlapped.
With regard to the length of the interval between the assessments of depression and survival, we compared studies with time intervals up to 2 years, intervals of 2–4 years, 4–6 years and longer intervals. The Q-statistics indicates that the size of the association between depression and mortality varies by the length of study interval. Strongest associations were found in studies with the shortest time interval, although the 95% CI overlapped with those of the other groups.
Depression diagnosis as well as the level of depression predicted mortality of cancer patients and the size of association did not vary between these two methods of assessment. We also checked whether the size of association between depression and mortality would vary by the use of different rating scales. Significant associations emerged in studies that used the CES-D and the HADS. However, no significant associations emerged in studies that used the BDI.
With regard to the age distribution of the samples, we found stronger associations of age and cancer mortality in the oldest subgroup than in the youngest subgroup (Table 1). The size of the association between depression and mortality did not vary by the gender composition of the sample.
Discussion
The present meta-analysis showed that depression, defined categorically or dimensionally, is associated with elevated risk for mortality in cancer patients and those who develop cancer. Associations were stronger in studies with shorter time intervals and in older samples. Among the self-report instruments used to assess depression, only the BDI yielded a non-significant effect size.
Whereas some individual studies have found no evidence for the idea that depression is associated with elevated mortality in cancer patients (e.g. Cody et al. 1994), the present meta-analysis provides clear evidence for such a relationship. The present study further supports prior meta-analyses (Chida et al. 2008; Satin et al. 2009) with a much larger dataset. It has been suggested that associations between depression and mortality may, at least in part, reflect the effect of illness severity (e.g. Spiegel & Giese-Davis, 2003). In this scenario, the effect of depression is more apparent than real, a result of shared method variance and overlapping symptomatology, such as fatigue and appetite disturbance. Little evidence for this measurement confound argument was uncovered in this meta-analysis. Studies that assessed depression years before cancer diagnosis found similar associations with mortality than studies that assessed depression following cancer diagnosis. Nor were effects stronger in more advanced disease stages. Studies that controlled statistically for disease-related confounds had similar effect sizes than those that did not. Nonetheless, we recognize that these statistical controls were limited. In fact, most controlled studies used only global measures of severity of illness (most often stage).
Several authors have suggested that psychological variables may have a stronger effect on disease progression and mortality in early stages of cancer (e.g. Cwinkel et al. 1997). Although we observed a somewhat stronger effect in studies on early stages than on mixed and later stages of cancer, these differences did not reach statistical significance, perhaps due to the paucity of samples on early stage (k=6) and late stage (k=14) cancer. At present, the most parsimonious conclusion is that depression's influence on mortality is independent of disease stage. Similarly, comparable associations were found for leukemia/lymphoma, breast cancer, brain cancer and lung cancer. The most parsimonious explanation is that depression's influence on mortality is independent of site.
Associations between depression and mortality are strongest in studies with intervals of ≤2 years between assessment of depression and assessment of mortality. Because the correlative stability of depression declines with increasing study intervals (e.g. Lovibold, 1998), T1-depression scores lose predictive power over time. In addition, as survival time is extended, other intervening factors are more likely to account for mortality, thereby obscuring any possible relationships between depression and mortality of cancer patients.
Contrary to our expectations, we did not find stronger associations with mortality in studies on clinical depression, defined categorically, than in studies that used continuous measures of self-rated depressive symptoms. However, the effect of clinical diagnosis may have been underestimated as some studies used crude diagnostic indicators, such as whether the patients had ever been hospitalized or have had outpatient contact for clinical depression (e.g. Dalton et al. 2008). Thus, depression may have been undiagnosed in some cases, which would, again, attenuate the size of association with mortality.
Interestingly, associations between depressive symptoms and mortality were not significant in studies that used the BDI. Note that eight out of the 21 items of the BDI assess somatic symptoms, whereas only four out of the 20 CES-D items assess these symptoms. As somatic symptoms may, at least in part, indicate cancer-related symptoms, somatic co-morbidity, or side-effects of the treatment, the BDI is less well suited for studies interested in isolating the influence of psychological (cognitive, affective) as opposed to neurovegetative processes on health outcomes in cancer, even though evidence for its validity in the cancer setting has been provided (Mystakidou et al. 2007).
Whereas Schulz et al. (1996) had observed stronger associations of pessimism and mortality in younger patients than in older patients, the present meta-analysis found some evidence for stronger associations of depression and mortality in the oldest cancer patients. Older cancer patients may be less likely to receive adequate treatment for depression (Roth & Modi, 2003). This may be true for a host of reasons, including greater stigma (Sirey et al. 2001), competing demands (Klinkman, 1997), lower motivation to seek depression treatment and the concern that frail elderly patients cannot tolerate antidepressant treatment due to side-effects or interactions with other medications (King et al. 2005).
Some limitations of the present study have to be mentioned. First, although our meta-analysis included 76 studies, subanalyses could only be made for four cancer sites. Second, some potential moderators of the size of the association between depression and mortality could not be tested due to the lack of sufficient data (e.g. chronicity of depression, receipt of depression treatment, cancer history, time interval between cancer diagnosis and assessment of depression, performance status). Third, because most available studies did not differ between cancer-related mortality and other causes of mortality in cancer patients, we were not able to test for effects on specific causes of death. Finally, we did not include unpublished studies that were not cited in the electronic databases. Although non-significant results from small studies may be less likely to be published, their lack of significance is often based on small sample sizes rather than on below-average effect sizes. Thus, it is unlikely that our findings would have differed had we included unpublished studies.
Several directions for future research could be pursued. First, more studies on associations of depression with mortality are welcomed for those cancer sites that could not be included in the analysis of site-specific associations.
Second, more efforts are needed for identifying moderators and mediators of the relationship between depression and mortality in cancer patients. Future studies should include more differentiated measures of confounding medical variables, such as performance status, co-morbidity and receipt of curative versus palliative treatment. In addition, they should report whether there is a bivariate association of depression status with cancer mortality and whether this association persists after a more comprehensive control for the severity and type of cancer, use of different forms of cancer therapies, general physical status and other confounding variables. Surprisingly few studies assessed physical function and treatment-related side-effects, health-related behaviours, or personality variables (such as neuroticism) as potential confounders. Consensus regarding which control variables should be included in the analysis would also increase the comparability of results across studies.
With regard to clinical practice, we conclude that the association of depression with mortality is of clinical significance. Practitioners should, first, be more aware of depressive symptoms and depressive disorders of cancer patients. Careful consideration should be given to routine screens for depression as part of the multidisciplinary assessment of cancer patients (Lloyd-Williams et al. 2007). Recognizing the limitations of routine depression screening programs in primary care (Gilbody et al. 2006), the assessment of depression may be construed as a central element in patient-centered cancer care (Epstein & Street, 2007). Referrals to mental health specialists should be considered. Second, as effective treatments of depression in cancer patients are available (e.g. Hopko et al. 2005; Stockler et al. 2007), early recognition and adequate treatment of depression could, beyond enhancing quality of life, potentially improve medical outcomes, such as functional status. Questions have been raised about whether psychosocial interventions have life-prolonging effects (see Smedslund & Ringdahl, 2004; Coyne et al. 2007). The present results indicate that if such effects do indeed exist (Coyne et al. 2007), they are likely to be found among patients with elevated levels of depression and/or depressive disorders. Systematic research on effects of such interventions on survival of depressed cancer patients is needed.
Acknowledgments
Work on this manuscript was supported by the following grants from the United States Public Health Service: K24MH072712 and R24AG031089.
Appendix: Overview of included studies
| Authors | Sample size (cancer) | Cancer site | Assessment of depression | Time of assessing depression | Length of study interval (years) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Akechi et al. 2009 | 122 | Lung | POMS | Post | 2 |
| Andrykowski et al. 1994 | 42 | Leukemia | POMS | Post | 3 |
| Beresford et al. 2006 | 86 | Mixed | BDI | Post | 5 |
| Bergquist et al. 2007 | 94 | Eosophagus | HADS | Post | 1 |
| Black & Markides, 1999 | 2489 | Mixed | CES-D | Pre | 2 |
| Broers et al. 1998 | 123 | Leukemia | SCL-90 | Post | 7.2 |
| Brown et al. 2003 | 205 | Mixed | CES-D | Post | 10 |
| Buccheri, 1998 | 95 | Lung | SDS | Post | 2 |
| Chang, 2004a | 122 | Leukemia | BDI | Post | 1 |
| Chang, 2004b | 114 | Leukemia | BDI | Post | 2.5 |
| Colon et al. 1991 | 100 | Leukemia | Diagnosis | Post | 2 |
| Coryell 1981 | 76 | Mixed | Diagnosis | Pre | 40 |
| Dalton et al. 2008 | 601 | Lymphoma, leukemia | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Dalton et al. 2008 | 24 391 | Breast | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Dalton et al. 2008 | 20 490 | Lung | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Dalton et al. 2008 | 2854 | Mouth | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Dalton et al. 2008 | 1982 | Stomach, esophagus, pancreas | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Dalton et al. 2008 | 9590 | Colon, rectum | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Dalton et al. 2008 | 2774 | Kidney, bladder | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Dalton et al. 2008 | 2871 | Female genital | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Dalton et al. 2008 | 1724 | Male genital | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Dalton et al. 2008 | 6755 | Melanoma | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Dalton et al. 2008 | 5316 | Brain, CNS | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Derogatis et al. 1979 | 35 | Breast | SCL-90 | Post | 2 |
| Edwards et al. 1985 | 26 | Testes | BSI | Post | 7 |
| Ehlers, 2002 | 130 | Head, neck | BDI | Post | 2.7 |
| Faller et al. 1999 | 103 | Lung | Zerssen | Post | 7.5 |
| Faller & Schmidt, 2004 | 59 | Lung | HADS | Post | 4 |
| Forsén, 1991 | 87 | Breast | Home made | Pre | 8 |
| Frick et al. 2005 | 99 | Lymphoma, myeloma | POMS | Post | 2.4 |
| Gantinji et al. 2009 | 1052 | Brain | Diagnosis | Pre | 5 |
| Giraldi et al. 1997 | 95 | Breast | CES-D | Pre | 6 |
| Goodwin et al. 2004 | 24 696 | Breast | Diagnosis | Pre | 3 |
| Gripp et al. 2007 | 184 | Mixed | HADS | Post | .5 |
| Groenvold et al. 2007 | 1588 | Breast | HADS | Post | 12.9 |
| Grulke et al. 2008 | 138 | Leukemia, lymphoma | HADS | Post | 1.5 |
| Herrmann et al. 1998 | 96 | Mixed | HADS | Post | 1.8 |
| Hislop et al. 1987 | 133 | Breast | Home made | Post | 4 |
| Hjerl et al. 2003 | 5191 | Breast | Diagnosis | Pre, post | 6.2 |
| Jamison et al. 1987 | 49 | Breast | SDS | Post | 2.5 |
| Hoodin et al. 2004 | 305 | Leukemia, lymphoma | MMPI | Post | 3.5 |
| Kaplan & Reynolds, 1988 | 6801 | Mixed | Roberts | Pre | 17 |
| Karvonen-Gutierrez et al. 2008 | 495 | Head, neck | GDS | Post | 5.1 |
| Kawamura et al. 2007 | 86 | Mixed | Diagnosis | Pre | 15 |
| Kissane et al. 2007 | 485 | Breast | Diagnosis | Post | 2 |
| Lam et al. 2007 | 162 | Mixed | Hamilton | Post | 0.5 |
| Lehto et al. 2006 | 102 | Breast | Salokangas | Post | 10 |
| Lehto et al. 2007 | 59 | Melanoma | DEPS | Post | 7.5 |
| Leigh et al. 1987 | 101 | Mixed | BDI | Post | 3 |
| Litofsky et al. 2004 | 598 | Brain | Diagnosis | Post | 2 |
| Lloyd-Williams et al. 2009 | 87 | Mixed | EDS | Post | 1 |
| Loberiza et al. 2002 | 193 | Leukemia | Home made | Post | 1 |
| Mainio et al. 2005 | 77 | Brain | BDI | Post | 5 |
| Mainio et al. 2006 | 75 | Brain | BDI | Post | 10 |
| Murphy et al. 1996 | 56 | Leukemia, lymphoma | CIDI | Post | 2.5 |
| Nakaya et al. 2006 | 229 | Lung | POMS, SCID | Post | 5.75 |
| Nakaya et al. 2008 | 1178 | Lung | HADS | Post | 2 |
| Naughton et al. 2002 | 67 | Lung | CES-D | Post | 1 |
| Onitilo et al. 2006 | 876 | Mixed | CES-D | Post | 8 |
| Osborne et al. 2004 | 61 | Breast | HADS | Post | 7 |
| Ösby et al. 2001 | 1404 | Mixed | Diagnosis | Pre | 10 |
| Palmer & Fisch, 2005 | 225 | Mixed | TQSS | Post | 2 |
| Penninx et al. 1998 | 4825 | Mixed | CES-D | Pre | 6 |
| Persky et al. 1987 | 2107 | Mixed | MMPI | Pre | 22 |
| Philipps et al. 2008 | 708 | Breast | HADS | Post | 8.2 |
| Pirl et al. 2009 | 43 | Lung | HADS | Post | 2.5 |
| Prieto et al. 2005 | 199 | Leukemia, lymphoma | Diagnosis | Post | 5 |
| Ratcliffe et al. 1995 | 63 | Lymphoma | HADS | Post | 5 |
| Richardson et al. 1990 | 92 | Leukaemia | SDS | Post | 4.8 |
| Richardson et al. 1990 | 47 | Colon | BDI | Post | 4.8 |
| Ringdahl et al. 1996 | 231 | Mixed | HADS | Post | 2 |
| Saito-Nakaya et al. 2006 | 816 | Lung | HADS | Post | 2 |
| Schulz et al. 1996 | 238 | Mixed | CES-D | Post | 0.7 |
| Sheibani-Rad & Velanovich, 2006 | 258 | Pancreas | Diagnosis | Post | 0.75 |
| Shekele et al. 1981 | 2020 | Mixed | CES-D | Pre | 17 |
| Steel et al. 2007 | 103 | Liver | CES-D | Post | 2 |
| Stein et al. 1989 | 90 | Mixed | Psychiatric Outpatient Mood Scale | Post | 0.25 |
| Stockler et al. 2007 | 189 | Mixed | CES-D, HADS | Post | 4.33 |
| Stommel et al. 2002 | 871 | Mixed | CES-D | Post | 1.6 |
| Tian et al. 2009 | 113 | Mixed | DSI | Post | 1 |
| Tschuschke et al. 2001 | 52 | Leukemia | SCL-90 | Post | 5 |
| Watson et al. 1999 | 578 | Breast | HADS | Post | 5 |
| Watson et al. 2005 | 578 | Breast | HADS | Post | 11 |
| Whooley & Browner, 1998 | 7406 | Mixed | GDS | Pre | 7 |
| Wilson et al. 2007 | 381 | Mixed | Diagnosis | Post | 0.5 |
| Zonderman et al. 1989 | 5793 | Mixed | CES-D, GWB-D | Pre | 8.8 |
| Zonderman et al. 1989 | 1812 | Mixed | CES-D, GWB-D | Pre | 13.8 |
CNS, Central nervous system; BDI, Beck Depression Inventory; BSI, Brief Symptom Inventory; CIDI, Composite Diagnostic Interview; DEPS, Depression Scale; DSI, Depression Status Inventory; EDS, Edinburgh Depression Scale; HADS, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale; MMPI, Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory; POMS, Profile of Mood States; SCID, Structured Clinical Interview – Depression; SCL-90, Symptom Checklist 90; SDS, Zung′s Self Rating Depression Scale; TQSS, Two-Question Screening Survey; pre, before cancer diagnosis; post, after cancer diagnosis.
Footnotes
Declaration of Interest: None.
References
* Indicates the studies included in the meta-analysis.
- *Akechi T, Okamura H, Okuyama T, Furukawa TA, Nishiwaki Y, Uchitomi Y. Psychosocial factors and survival after diagnosis of inoperable non-small cell lung cancer. Psycho-Oncology. 2009;18:23–29. doi: 10.1002/pon.1364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Akechi T, Okuyama T, Sugawara Y, Nakano T, Chima Y, Uchitomi Y. Suicidality in terminally ill Japanese patients with cancer. Cancer. 2004;100:183–191. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Andrykowski MA, Brady M, Hernslee-Downey P. Psychosocial factors predictive of survival after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for leukaemia. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1994;56:432–439. doi: 10.1097/00006842-199409000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anstey KJ, Luszcz MA. Mortality risk varies according to gender and change in depressive status in very old adults. Psychosomatic Medicine. 2002;64:880–888. doi: 10.1097/01.psy.0000028827.64279.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayres A, Hoon PW, Franzoni JB. Influence of mood and adjustment on compliance with chemotherapy among breast cancer patients. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 1994;38:393–402. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(94)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck AT, Steer RA. Manual of the Revised Beck Depression Inventory. Psychological Corporation; San Antonio, TX: 1979. [Google Scholar]
- *Beresford TP, Alfers J, Magnum L, Clapp L, Martin B. Cancer survival probability as a function of ego defense (adaptive) mechanisms versus depressive symptoms. Psychosomatics. 2006;47:247–253. doi: 10.1176/appi.psy.47.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Bergquist H, Ruth M, Hammerlind E. Psychiatric morbidity among patients with cancer of the esophagus or the gastro-esophageal junction: a prospective, longitudinal evaluation. Diseases of the Esophagus. 2007;20:523–529. doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2050.2007.00741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Black SA, Markides KS. Depressive symptoms and mortality in older Mexican Americans. Annales of Epidemiology. 1999;9:45–52. doi: 10.1016/s1047-2797(98)00025-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Broers S, Hengeveld MW, Kaptein AA, Cessie SL, van de Loo, de Vries T. Are pretransplant psychological variables related to survival after bone marrow transplantation? A prospective study of 123 consecutive patients. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 1998;45:341–351. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3999(98)00003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Brown KW, Levy AR, Rosberger Z, Edgar L. Psychological distress and cancer survival: a follow-up 10 years after diagnosis. Pychosomatic Medicine. 2003;65:636–643. doi: 10.1097/01.psy.0000077503.96903.a6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Buccheri G. Depressive reactions to lung cancer are common and often followed by a poor outcome. European Respiratory Journal. 1998;11:173–178. doi: 10.1183/09031936.98.11010173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Chang G, Orav EJ, Tong MY, Antin JH. Predictors of 1-year survival assessed at the time of bone marrow transplantation. Psychosomatics. 2004a;45:378–385. doi: 10.1176/appi.psy.45.5.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Chang G, Orav EJ, McNamara T, Tong MY, Antin JH. Depression, cigarette smoking, and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation outcome. Cancer. 2004b;101:782–789. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chida Y, Hamer M, Wardle J, Steptoe A. Do stress-related psychosocial factors contribute to cancer incidence and survival? Nature Clinical Practice Oncology. 2008;5:468–475. doi: 10.1038/ncponc1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cody M, Nichols S, Brennan C, Armes J, Wilson P, Slevin M. Psychosocial risk factors and lung cancer prognosis. Psycho-Oncology. 1994;3:141. [Google Scholar]
- *Colon EA, Callies AL, Popkin MK, McGlave PB. Depressed mood and other variables related to bone marrow transplant survival in acute leukaemia. Psychosomatics. 1991;32:420–425. doi: 10.1016/S0033-3182(91)72045-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Coryell WH. Diagnosis-specific mortality: primary unipolar depression and Briquet's syndrome. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1981;38:939–942. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1981.01780330097012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyne JC, Stefanek M, Palmer SC. Psychotherapy and survival in cancer: the conflict between hope and evidence. Psychological Bulletin. 2007;133:367–394. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.133.3.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cwinkel JG, Behar LC, Zabora JR. Psychosocial factors that affect the survival of adult cancer patients: a review of research. Journal of Psychosocial Oncology. 1997;15:1–34. [Google Scholar]
- *Dalton SO, Schüz J, Engholm G, Johansen C, Küger S, Steding-Jessen M, Storm HH, Olsen JH. Social inequality in incidence of and survival from cancer in a population-based study in Denmark, 1994–2003: summary of findings. European Journal of Cancer. 2008;44:2074–2085. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2008.06.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Derogatis L, Abeloff M, Melisarastos N. Psychological and coping mechanisms and survival time in metastatic cancer. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1979;242:1504–1508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMatteo MR, Lepper HS, Croghan TW. Depression is a risk factor for noncompliance with medical treatment: meta-analysis of the effects of anxiety and depression on patient adherence. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2000;160:2101–2107. doi: 10.1001/archinte.160.14.2101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Edwards J, DiClemente C, Samuels ML. Psychological characteristics: a pretreatment survival marker of patients with testicular cancer. Journal of Psychosocial Oncology. 1985;3:79–94. [Google Scholar]
- *Ehlers SL. Effects of depression and substance use on head and neck cancer mortality. Unpublished dissertation (Ph D thesis) University of Iowa; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein RM, Street RL. Patient-Centered Communication in Cancer Care: Promoting Healing and Reducing Suffering. National Cancer Institute; Bethesda, MD: 2007. NIH Publication No. 07−6225. [Google Scholar]
- *Faller H, Bulzebruck H, Dings P, Lang H. Coping, distress, and survival among patients with lung cancer. Archives of General Psychiatry. 1999;56:756–762. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.56.8.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Faller H, Schmidt M. Prognostic value of depressive coping and depression in survival of lung cancer patients. Psycho-Oncology. 2004;13:359–363. doi: 10.1002/pon.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Forsén A. Psychosocial stress as a risk for breast cancer. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics. 1991;55:176–185. doi: 10.1159/000288427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Frick E, Motzke C, Fischer N, Busch R, Bumeder I. Is perceived social support a predictor of survival for patients undergoing autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation? Psycho-Oncology. 2005;14:759–770. doi: 10.1002/pon.908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Gathinji M, McGirt MJ, Attenello FJ, Chaichana KL, Than K, Olivi A, Weingart JD, Brem H, Quinones-Hinojosa A. Association of preoperative depression and survival after resection of malignant brain astrocytoma. Surgical Neurology. 2009;71:299–303. doi: 10.1016/j.surneu.2008.07.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese-Davis J, Spiegel D. Emotional suppression and cancer progression. In: Davidson RJ, Scherer K, Hill GG, editors. Handbook of Affective Sciences. Oxford University Press; Oxford; 2003. pp. 1053–1082. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbody S, Sheldon T, Wessely S. Should we screen for depression? British Medical Journal. 2006;332:1027–1030. doi: 10.1136/bmj.332.7548.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Giraldi T, Rodani M, Cartei G, Grassi L. Psychosocial factors and breast cancer: a 6-year Italian follow-up study. Psychotherotherapy and Psychosomatics. 1997;66:229–236. doi: 10.1159/000289140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Goodwin JS, Zhang DD, Ostir G. Effect of depression on diagnosis, treatment, and survival of older women with breast cancer. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2004;52:106–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52018.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassi L, Indelli M, Marzola M, Maestri A, Santini A, Piva E, Boccalon M. Depressive symptoms and quality of life in home-care-assisted cancer patients. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 1996;12:300–307. doi: 10.1016/s0885-3924(96)00181-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Gripp S, Moeller S, Bölke E, Schmitt G, Matuschek C, Asgari S, Asgharzadeh F, Roth S, Budach W, Franz M, Willers R. Survival prediction in terminally ill cancer patients by clinical estimates, laboratory tests, and self-rated anxiety and depression. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2007;25:3313–3320. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.10.5411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Groenvold M, Petersen MA, Idler E, Bjorner JB, Fayers PM, Mouridsen HT. Psychological distress and fatigue predicted recurrence and survival in primary breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 2007;105:209–219. doi: 10.1007/s10549-006-9447-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Grulke N, Larbig W, Kächele H, Bailer H. Pre-transplant depression as risk factor for survival of patients undergoing allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Psycho-Oncology. 2008;17:480–487. doi: 10.1002/pon.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedges LV, Vevea JL. Fixed- and random-effects models in meta-analysis. Psychological Methods. 1998;3:486–504. [Google Scholar]
- *Herrmann C, Brand-Driehorst S, Kaminsky B, Leibing E, Staats H, Rüger U. Diagnostic groups and depressed mood as predictors of 22-month mortality in medical inpatients. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1998;60:570–577. doi: 10.1097/00006842-199809000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Hislop TG, Waxler NE, Coldman AJ, Elwood JM, Kan L. The prognostic significance of psychosocial factors in women with breast cancer. Journal of Chronic Diseases. 1987;40:729–735. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(87)90110-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Hjerl K, Andersen EW, Keiding N, Mouridsen HT, Mortensen PB, Jorgensen T. Depression as a prognostic for breast cancer mortality. Psychosomatics. 2003;44:24–30. doi: 10.1176/appi.psy.44.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Hoodin F, Kalbfleisch KR, Thornton J, Ratanatharathorn V. Psychosocial influences on 305 adults' survival after bone marrow transplantation: depression, smoking, and behavioral self-regulation. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2004;57:145–154. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3999(03)00599-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopko DR, Bell JL, Armento ME, Hunt MK, Lejuez CW. Behavior therapy for depressed cancer patients in primary care. Psychotherapy. 2005;42:236–243. [Google Scholar]
- *Jamieson RN, Burish TG, Wallston KA. Psychogenic factors in predicting survival of breast cancer patients. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 1987;5:768–772. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.5.768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juni P, Witschi A, Bloch R, Egger M. The hazards of scoring the quality of clinical trials for meta-analysis. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1999;282:1054–1060. doi: 10.1001/jama.282.11.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Kaplan GA, Reynolds P. Depression and cancer mortality and morbidity: prospective evidence from the Alameda Country study. Journal of Behavioral Medicine. 1988;11:1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF00846165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Karvonen-Gutierrez CA, Ronis DL, Fowler KE, Terrell JE, Gruber SB, Duffy SA. Quality of life scores predict survival among patients with head and neck cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2008;26:2754–2760. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.12.9510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Kawamura T, Shioiri T, Takahashi K, Ozdemir V, Someya T. Survival rate and causes of mortality in the elderly with depression: a 15-year prospective study of a Japanese community sample, the Matsunoyama-Niigata suicide prevention project. Journal of Investigative Medicine. 2007;55:106–114. doi: 10.2310/6650.2007.06040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King DA, Heisel MJ, Lyness JM. Assessment and psychological treatment of depression in older adults with terminal or life-threatening illnesses. Clinical Psychology. 2005;12:339–353. [Google Scholar]
- *Kissane DW, Grabsch B, Clarke DM, Smith GC, Love AW, Bloch S, Snyder RD, Li Y. Supportive-expressive group therapy for women with metastatic breast cancer: survival and psychosocial outcome from a randomized controlled trial. Psycho-Oncology. 2007;16:277–286. doi: 10.1002/pon.1185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinkman S. Competing demands in psychosocial care: a model for the identification and treatment of depressive disorders in primary care. General Hospital Psychiatry. 1997;19:98–111. doi: 10.1016/s0163-8343(96)00145-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Lam PT, Leung MW, Tse CY. Identifying prognostic factors for survival in advanced cancer patients: a prospective study. Hong Kong Medical Journal. 2007;13:453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Lehto US, Ojanen M, Dyba T, Aromaa A, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P. Baseline psychosocial predictors of survival in localised breast cancer. British Journal of Cancer. 2006;94:1245–1252. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Lehto US, Ojanen M, Dyba T, Aromaa A, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen P. Baseline psychosocial predictors of survival in localized melanoma. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2007;63:151–152. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2007.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Leigh H, Percarpio B, Ossahl C, Ungerer J. Psychological predictors of survival in cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy. Psychotherapy and Psychosomatics. 1987;47:65–73. doi: 10.1159/000288000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy SM, Roberts DC. Psychoneuroimmunology: prediction of cancer outcomes. In: Schneider N, McCabe P, Baum A, editors. Behavioral Medicine: Stress and Disease Processes. Erlbaum; Hillsdale: 1992. pp. 165–174. [Google Scholar]
- Lipsey MW, Wilson DB. Practical Meta-analysis. Sage; Thousand Oaks, CA: 2004. [Google Scholar]
- *Litofsky NS, Farace E, Anderson F, Meyers CA, Huang W, Laws ER. Depression in patients with high-grade glioma: results of the glioma outcome study. Neurosurgery. 2004;54:358–366. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000103450.94724.a2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd-Williams M, Shiels C, Dowrick C. The development of the Brief Edinburgh Depression Scale (BEDS) to screen for depression in patients with advanced cancer. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2007;99:259–264. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2006.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Lloyd-Williams M, Shiels C, Taylor F, Dennis M. Depression – an independent predictor of early death in patients with advanced cancer. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2009;113:127–132. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2008.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Loberiza FR, Rizzo JD, Bredeson CN, Antin JH, Horowitz MM, Weeks JC, Lee SJ. Association of depressive syndrome and early deaths among patients after stem-cell transplantation for malignant diseases. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2002;20:2118–2126. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.08.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovibold PF. Long-term stability of depression, anxiety, and stress syndromes. Journal of Abnormal Psychology. 1998;107:520–526. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.107.3.520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee R, Williams S, Elwood M. Depression and the development of cancer: a meta-analysis. Social Science & Medicine. 1994;38:187–192. doi: 10.1016/0277-9536(94)90314-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Mainio A, Hakko H, Timonen M, Niemelä A, Koivukangas J, Räsänen P. Depression in relation to survival among neurosurgical patients with a primary brain tumour: a 5-year follow-up study. Neurosurgery. 2005;56:1234–1241. doi: 10.1227/01.neu.0000159648.44507.7f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Mainio A, Tuunanen S, Hakko H, Niemelä A, Koivukangas J, Räsänen P. Decreased quality of life and depression as predictors for shorter survival among patients with low-grade gliomas: a follow-up from 1990 to 2003. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience. 2006;256:516–521. doi: 10.1007/s00406-006-0674-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massie JW, Popkin MK. Depressive disorders. In: Holland J, editor. Psycho-Oncology. Oxford University Press; New York: 1998. pp. 518–540. [Google Scholar]
- *Murphy KC, Jenkins PL, Whittaker JA. Psychosocial morbidity and survival in adult bone marrow transplant recipients – a follow-up study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1996;18:199–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mystakidou K, Tsilika E, Parpa E, Smyrniotis V, Galanos A, Vlahos L. Beck Depression Inventory: exploring its psychometric properties in a palliative care population of advanced cancer patients. European Journal of Cancer Care. 2007;6:244–250. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2354.2006.00728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Nakaya N, Saito-Nakaya K, Akizuki N, Yoshikawa E, Kobayakawa M, Fujimori M, Nagai K, Nishiwaki Y, Fukudo S, Tsubono Y, Uchitomi Y. Depression and survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer after curative resection: a preliminary study. Cancer Science. 2006;97:199–205. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Nakaya N, Saito-Nakaya K, Akechi T, Kuriyama S, Inagaki M, Kikuchi N, Nagai K, Tsugane S, Nishiwaki Y, Tsuji I, Uchitomi Y. Negative psychological aspects and survival in lung cancer patients. Psycho-Oncology. 2008;17:466–473. doi: 10.1002/pon.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Naughton MJ, Hendron JE, Miller AA, Kornblith AB, Chao D, Holland J. The health-related quality of life and survival of small-cell lung cancer patients: results of a companion study to CALGB 9033. Quality of Life Research. 2002;11:235–248. doi: 10.1023/a:1015257121369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onitilo AA, Nietert PJ, Egede LE. Effect of depression on all-cause mortality in adults with cancer and differential effects of cancer site. General Hospital Psychiatry. 2006;28:396–402. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2006.05.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Osborne RH, Sali A, Aaronson NK, Elsworth GR, Mdzewski B, Sinclair AJ. Immune function and adjustment style: do they predict survival in breast cancer? Psycho-Oncology. 2004;13:199–210. doi: 10.1002/pon.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Ösby U, Brandt L, Correia N, Ekbom A, Sparen P. Excess mortality in bipolar and unipolar disorder in Sweden. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2001;58:844–850. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.58.9.844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Palmer JL, Fisch MJ. Association between symptom distress and survival in outpatients seen in a palliative care cancer centre. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 2005;29:565–571. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2004.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmar MB, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Statistics in Medicine. 1998;17:2815–2834. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-0258(19981230)17:24<2815::aid-sim110>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Penninx BW, Guralnik JM, Pahor M, Ferrucci L, Cerhan JR, Wallace R, Havlik RJ. Chronically depressed mood and cancer risk in older persons. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. 1998;90:1888–1893. doi: 10.1093/jnci/90.24.1888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Persky VW, Kempthorne-Rawson J, Shekelle RB. Personality and risk of cancer: 20-year follow-up of the Western Electric Study. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1987;49:435–449. doi: 10.1097/00006842-198709000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Phillips KA, Osborne RH, Giles GG, Dite GS, Apicella C, Hopper JL. Psychosocial factors and survival of young women with breast cancer: a population-based prospective cohort study. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2008;26:4666–4671. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.14.8718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Pirl WF, Temel JS, Billings A, Dahlin C, Jackson V, Prigerson HG, Greer J, Lynch TJ. Depression after diagnosis of advanced non-small cell lung cancer and survival: a pilot study. Psychosomatics. 2008;49:218–224. doi: 10.1176/appi.psy.49.3.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Prieto JM, Atala J, Blanch E, Rovina M, Cicera E, Espinal A, Gasto C. Role of depression as a predictor of mortality among cancer patients after stem-cell transplantation. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2005;23:6063–6071. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.05.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff LS. The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Psychological Measurement. 1977;1:385–401. [Google Scholar]
- *Ratcliffe MA, Dawson AA, Walker LG. Eysenck Personality Inventory L-scores in patients with Hodgkin's disease and Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Psycho-Oncology. 1995;4:39–45. [Google Scholar]
- *Richardson JL, Zarnegar Z, Bisno B, Levine A. Psychosocial status at initiation of cancer treatment and survival. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 1990;34:189–201. doi: 10.1016/0022-3999(90)90053-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Ringdal GI, Gotestam KG, Kaasa S, Kvinnsland S, Ringdahl K. Prognostic factors and survival in a heterogeneous sample of cancer patients. British Journal of Cancer. 1996;73:1594–1599. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1996.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth AJ, Modi R. Psychiatric issues in older cancer patients. Critical Reviews of Oncology/Hematology. 2003;48:185–197. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2003.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin JR, Linden W, Philipps MJ. Depression as a predictor of disease progression and mortality in cancer patients. Cancer. 2009;115:5349–5361. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Saito-Nakaya K, Nakaya N, Fujimori M, Akizuki N, Yoshikawa E, Kobyakawa M. Marital status, social support and survival after curative resection in non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Science. 2006;97:206–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2006.00159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Schulz R, Bookwala J, Knapp JE, Scheier M, Williamson GM. Pessimism, age and cancer mortality. Psychology and Aging. 1996;11:304–309. doi: 10.1037//0882-7974.11.2.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellick SM, Crooks DL. Depression and cancer: an appraisal of the literature for prevalence, detection, and practice guideline development for psychological interventions. Psycho-Oncology. 1999;8:315–333. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1611(199907/08)8:4<315::AID-PON391>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Sheibani-Rad S, Velanovich V. Effects of depression on the survival of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 2006;32:58–61. doi: 10.1097/01.mpa.0000191643.17173.d3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Shekele RB, Raynor WJ, Ostfeld AM, Garron DC, Bieliauskas LA, Liu S, Maliza C, Paul O. Psychological depression and 17-year risk of death from cancer. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1981;43:118–119. doi: 10.1097/00006842-198104000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirey J, Bruce ML, Alexopoulos GS. Perceived stigma and patient-rated severity of illness as predictors of antidepressant drug adherence. Psychiatric Services. 2001;52:1615–1620. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.52.12.1615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedslund G, Ringdahl GI. Meta-analysis of the effects of psychosocial interventions on survival time in cancer patients. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2004;57:123–131. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3999(03)00575-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegel D, Giese-Davis J. Depression and cancer: mechanisms and disease progression. Biological Psychiatry. 2003;54:269–282. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(03)00566-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Steel JL, Geller DA, Gamblin TC, Olek MC, Carr BL. Depression, immunity, and survival in patients with hepatobiliary carcinoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2007;25:2397–2405. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.06.4592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Stein S, Linn MW, Stein EM. Psychological correlates of survival in nursing home cancer patients. Gerontologist. 1989;29:224–228. doi: 10.1093/geront/29.2.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Stommel M, Given BA, Given CW. Depression and functional status as predictors of death among cancer patients. Cancer. 2002;94:2719–2727. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Stockler MR, O'Connell R, Nowak AK, Goldstein D, Turner J, Wilcken NR. Effect of sertraline on symptoms and survival in patients with advanced cancer, but without major depression: a placebo-controlled double-blind randomised trial. Lancet Oncology. 2007;8:603–612. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Tian J, Chen ZC, Hang LF. The effects of psychological status of the patients with digestive system cancers on prognosis of the disease. Cancer Nursing. 2009;32:230–235. doi: 10.1097/NCC.0b013e31819b59c0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Tschuschke V, Hertenstein B, Arnold R, Bunjes D, Denzinger R, Kaechele H. Associations between coping and survival time of adult leukemia patients receiving allogeneic bone marrow transplantation: results of a prospective study. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2001;50:277–285. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3999(01)00202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Watson M, Haviland JS, Greer S, Davidson J, Bliss JM. Influence of psychological response on survival in breast cancer: a population-based cohort study. Lancet. 1999;354:1331–1336. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(98)11392-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Watson M, Homewood J, Haviland J, Bliss JM. Influence of psychological response on breast cancer survival: 10-year follow-up of population-based cohort. European Journal of Cancer. 2005;41:1710–1714. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2005.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Whooley MA, Browner WS. Association between depressive symptoms and mortality in older women. Archives of Internal Medicine. 1998;158:2129–2135. doi: 10.1001/archinte.158.19.2129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Wilson KG, Chochinov HM, Skirko MG. Depression and anxiety disorders in palliative cancer care. Journal of Pain and Symptom Management. 2007;33:118–129. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.07.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulsin LR, Vaillant GE, Wells VE. A systematic review of the mortality of depression. Psychosomatic Medicine. 1999;61:6–17. doi: 10.1097/00006842-199901000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond AS, Snaith RP. The Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavia. 1983;67:361–370. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1983.tb09716.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- *Zonderman AB, Costa P, McCrae RR. Depression as a risk for cancer morbidity and mortality in a nationally representative sample. Journal of the American Medical Association. 1989;262:1191–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]