Abstract
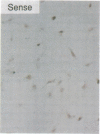
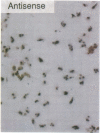
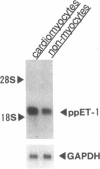
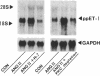
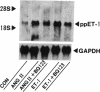
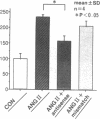
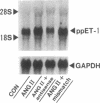
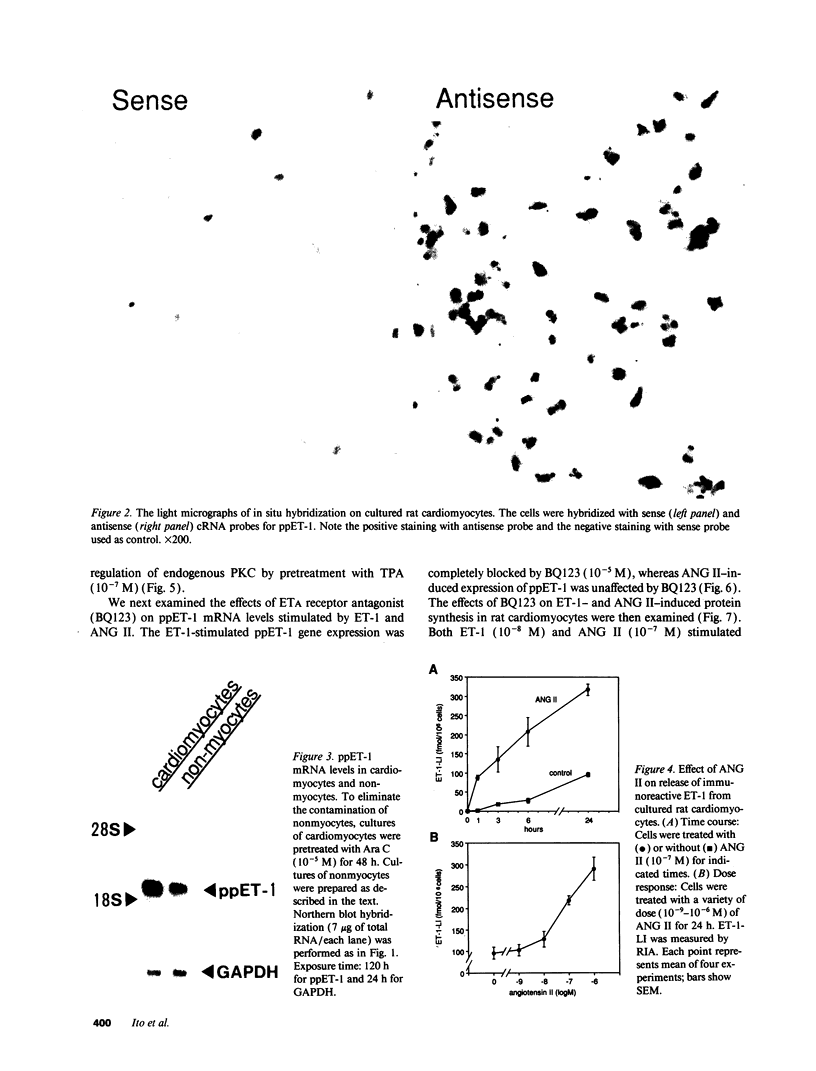
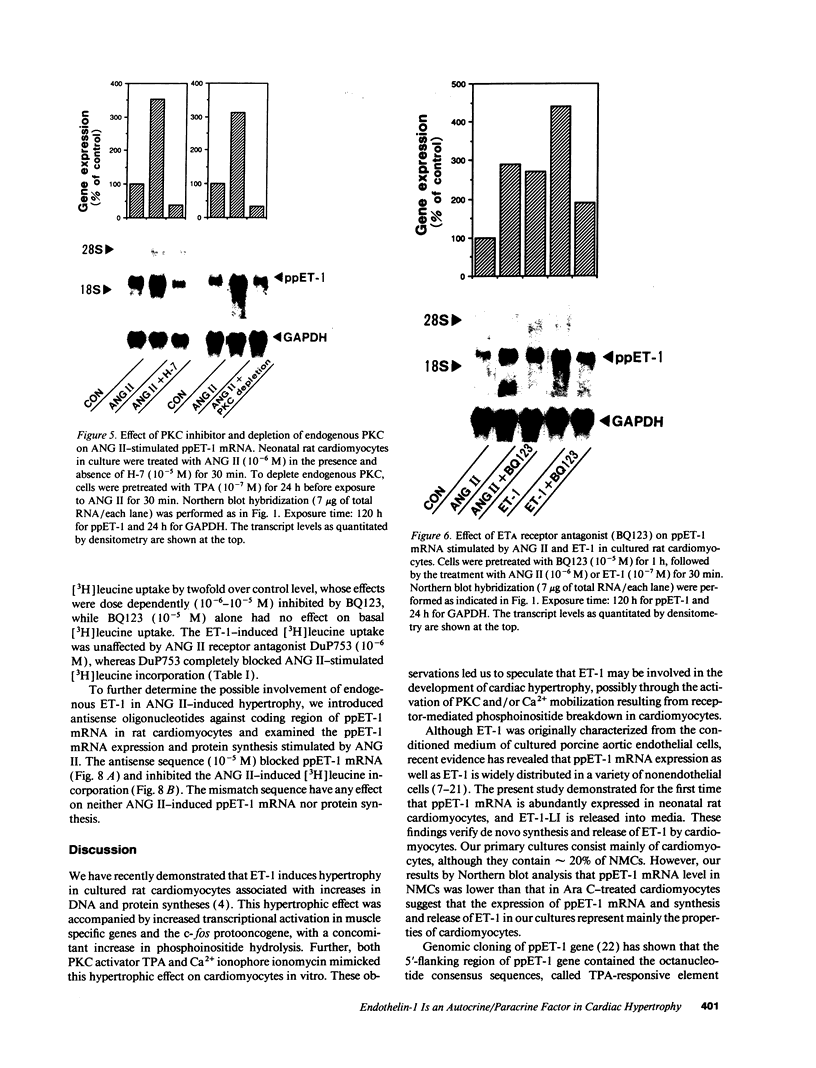
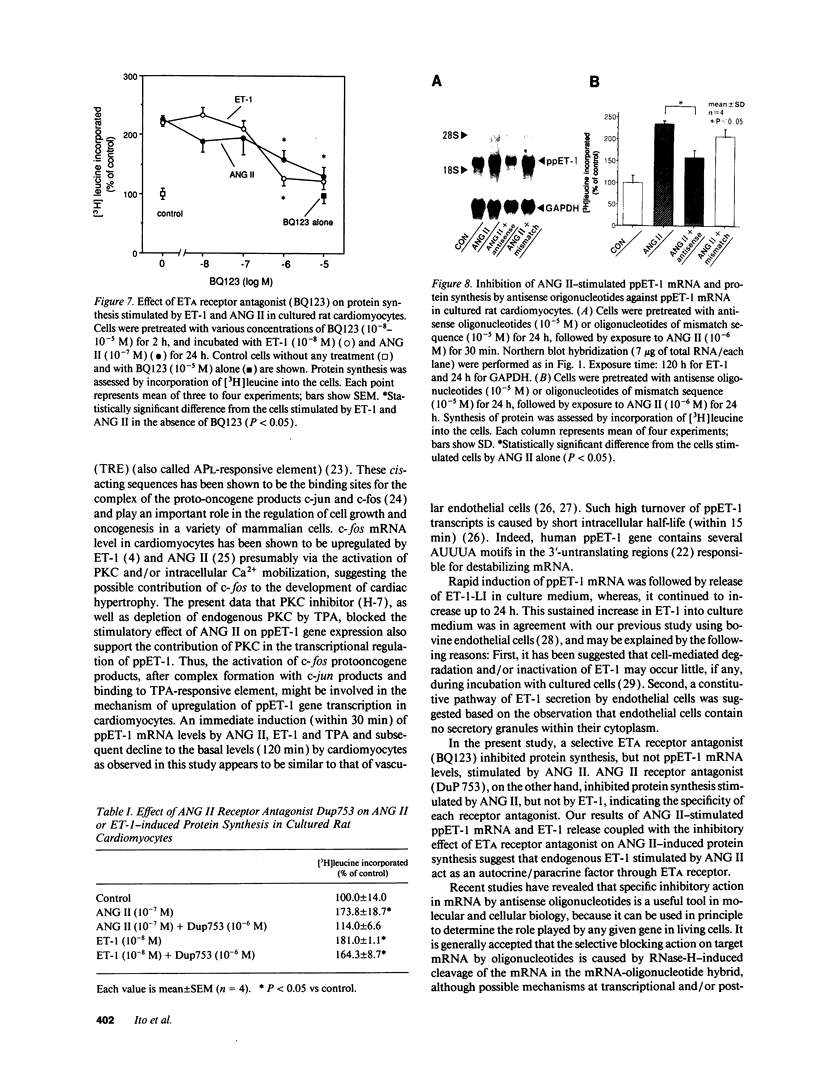
To elucidate the cellular mechanism by which angiotensin II (ANG II) induces cardiac hypertrophy, we investigated the possible autocrine/paracrine role of endogenous endothelin-1 (ET-1) in ANG II-induced hypertrophy of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes by use of synthetic ET-1 receptor antagonist and antisense oligonucleotides to preproET-1 (ppET-1) mRNA. Northern blot analysis and in situ hybridization revealed that ppET-1 mRNA was expressed in cardiomyocytes, but, to a lesser extent, in nonmyocytes as well. ANG II upregulated ppET-1 mRNA level by threefold over control level as early as 30 min, and it stimulated release of immunoreactive ET-1 from cardiomyocytes in a dose- and time-dependent manner. ET-1 stimulated ppET-1 mRNA levels after 30 min in a similar fashion as ANG II. Tetradecanoylphorbol-acetate (10(-7) M) mimicked the effects of ANG II and ET-1 on induction of ppET-1 mRNA. ANG II-induced ppET-1 gene expression was completely blocked by protein kinase C inhibitor H-7 or by down-regulation of endogenous protein kinase C by pretreatment with phorbol ester. ET-1 and ANG II stimulated twofold increase [3H]leucine incorporation into cardiomyocytes, whose effects were similarly and dose dependently inhibited by endothelin A receptor antagonist (BQ123). Introduction of antisense sequence against coding region of ppET-1 mRNA into cardiomyocytes resulted in complete blockade with ppET-1 mRNA levels and [3H]leucine incorporation stimulated by ANG II. These results suggest that endogenous ET-1 locally generated and secreted by cardiomyocytes may contribute to ANG II-induced cardiac hypertrophy via an autocrine/paracrine fashion.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker K. M., Aceto J. F. Angiotensin II stimulation of protein synthesis and cell growth in chick heart cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 2):H610–H618. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.2.H610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori T., Hirata Y., Ohta K., Shichiri M., Shimokado K., Marumo F. Concomitant secretion of big endothelin and its C-terminal fragment from human and bovine endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91984-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii Y., Moreira J. E., Orlando C., Maggi M., Aurbach G. D., Brandi M. L., Sakaguchi K. Endothelin as an autocrine factor in the regulation of parathyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4235–4239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn A. W., Resink T. J., Scott-Burden T., Powell J., Dohi Y., Bühler F. R. Stimulation of endothelin mRNA and secretion in rat vascular smooth muscle cells: a novel autocrine function. Cell Regul. 1990 Aug;1(9):649–659. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.9.649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Takagi Y., Fukuda Y., Marumo F. Endothelin is a potent mitogen for rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis. 1989 Aug;78(2-3):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90227-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata Y., Yoshimi H., Takaichi S., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Binding and receptor down-regulation of a novel vasoconstrictor endothelin in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1988 Oct 24;239(1):13–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Toulmé J. J. Specific regulation of gene expression by antisense, sense and antigene nucleic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 21;1049(2):99–125. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90031-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara M., Noguchi K., Saeki T., Fukuroda T., Tsuchida S., Kimura S., Fukami T., Ishikawa K., Nishikibe M., Yano M. Biological profiles of highly potent novel endothelin antagonists selective for the ETA receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(4):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90331-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai T., Hirata Y., Emori T., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Marumo F. Induction of endothelin-1 gene by angiotensin and vasopressin in endothelial cells. Hypertension. 1992 Jun;19(6 Pt 2):753–757. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.19.6.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Mitsui Y., Kobayashi M., Masaki T. The human preproendothelin-1 gene. Complete nucleotide sequence and regulation of expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14954–14959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Hirata Y., Hiroe M., Tsujino M., Adachi S., Takamoto T., Nitta M., Taniguchi K., Marumo F. Endothelin-1 induces hypertrophy with enhanced expression of muscle-specific genes in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Circ Res. 1991 Jul;69(1):209–215. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.1.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Miller S. C., Billingham M. E., Akimoto H., Torti S. V., Wade R., Gahlmann R., Lyons G., Kedes L., Torti F. M. Doxorubicin selectively inhibits muscle gene expression in cardiac muscle cells in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4275–4279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyses L., Nouskas J., Vetter H. Inhibition of endothelin-1 induced myocardial protein synthesis by an antisense oligonucleotide against the early growth response gene-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Nov 27;181(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta K., Hirata Y., Imai T., Kanno K., Emori T., Shichiri M., Marumo F. Cytokine-induced release of endothelin-1 from porcine renal epithelial cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):578–584. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90370-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta K., Hirata Y., Shichiri M., Kanno K., Emori T., Tomita K., Marumo F. Urinary excretion of endothelin-1 in normal subjects and patients with renal disease. Kidney Int. 1991 Feb;39(2):307–311. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Cohen D. R., Curran T., Bos T. J., Vogt P. K., Bohmann D., Tjian R., Franza B. R., Jr Fos-associated protein p39 is the product of the jun proto-oncogene. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1010–1016. doi: 10.1126/science.3130660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto H., Sasaki S., Hirata Y., Imai T., Ando K., Ida T., Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Marumo F. Production of endothelin-1 by rat cultured mesangial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90354-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Inoue A., Ryan U. S., Kimura S., Mitsui Y., Goto K., Masaki T. cDNA cloning, sequence analysis and tissue distribution of rat preproendothelin-1 mRNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Feb 28;175(1):44–47. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shichiri M., Hirata Y., Nakajima T., Ando K., Imai T., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Marumo F. Endothelin-1 is an autocrine/paracrine growth factor for human cancer cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1991 May;87(5):1867–1871. doi: 10.1172/JCI115210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shubeita H. E., McDonough P. M., Harris A. N., Knowlton K. U., Glembotski C. C., Brown J. H., Chien K. R. Endothelin induction of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis, sarcomere assembly, and cardiac gene expression in ventricular myocytes. A paracrine mechanism for myocardial cell hypertrophy. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20555–20562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P., Savion S. Differentiation of rat myocytes in single cell cultures with and without proliferating nonmyocardial cells. Cross-striations, ultrastructure, and chronotropic response to isoproterenol. Circ Res. 1982 Jan;50(1):101–116. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Hoshi H., Mitsui Y. Endothelin stimulates hypertrophy and contractility of neonatal rat cardiac myocytes in a serum-free medium. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):149–151. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80995-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takuwa N., Takuwa Y., Yanagisawa M., Yamashita K., Masaki T. A novel vasoactive peptide endothelin stimulates mitogenesis through inositol lipid turnover in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7856–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]