Abstract
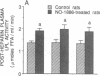
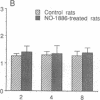
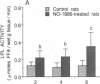
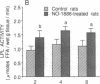
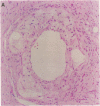
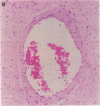
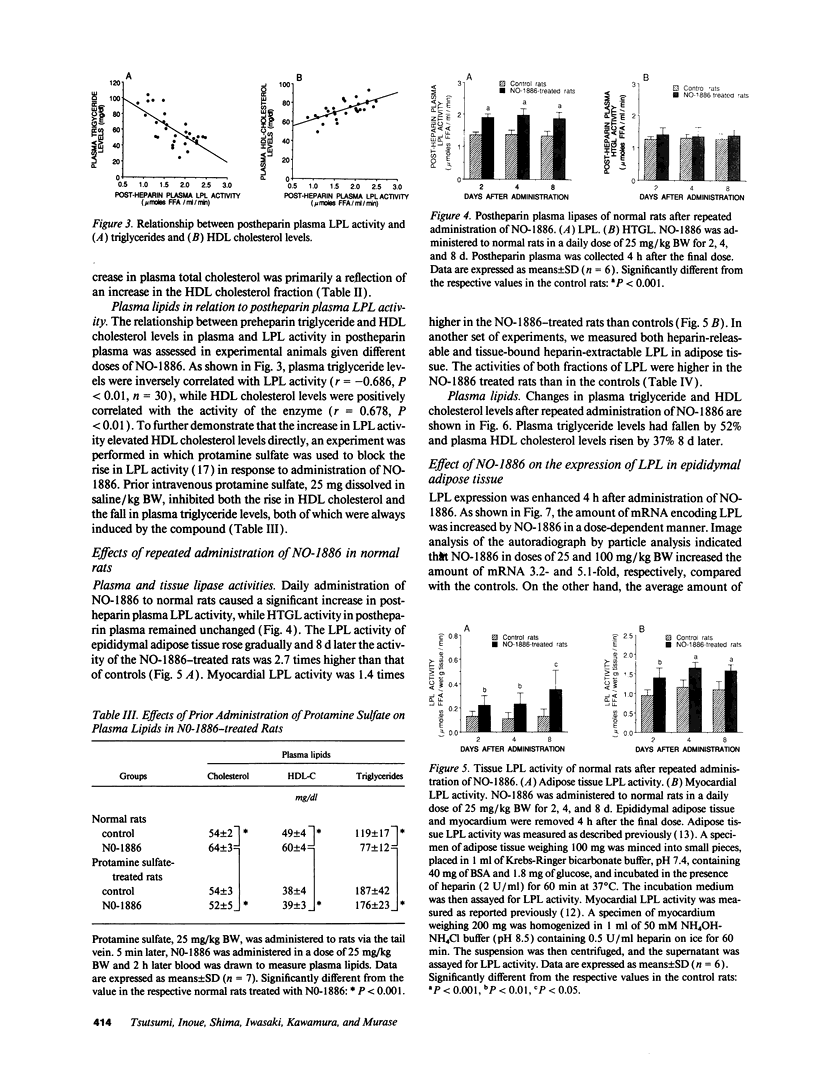
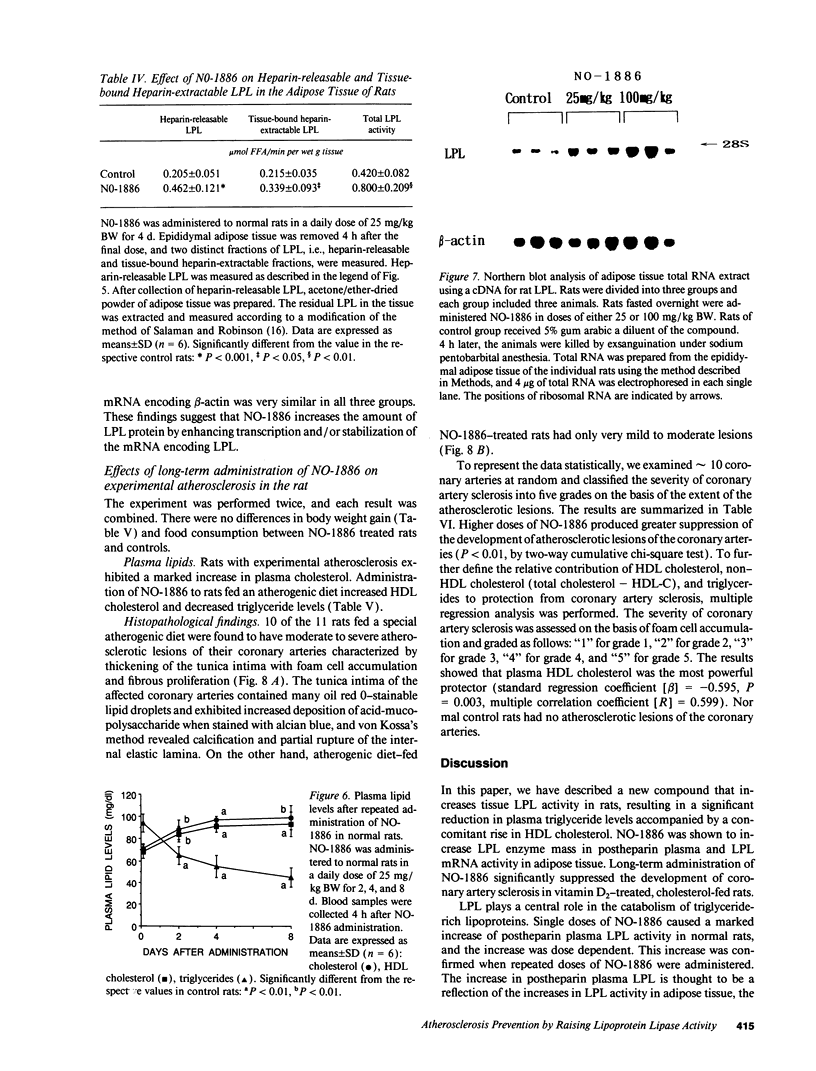
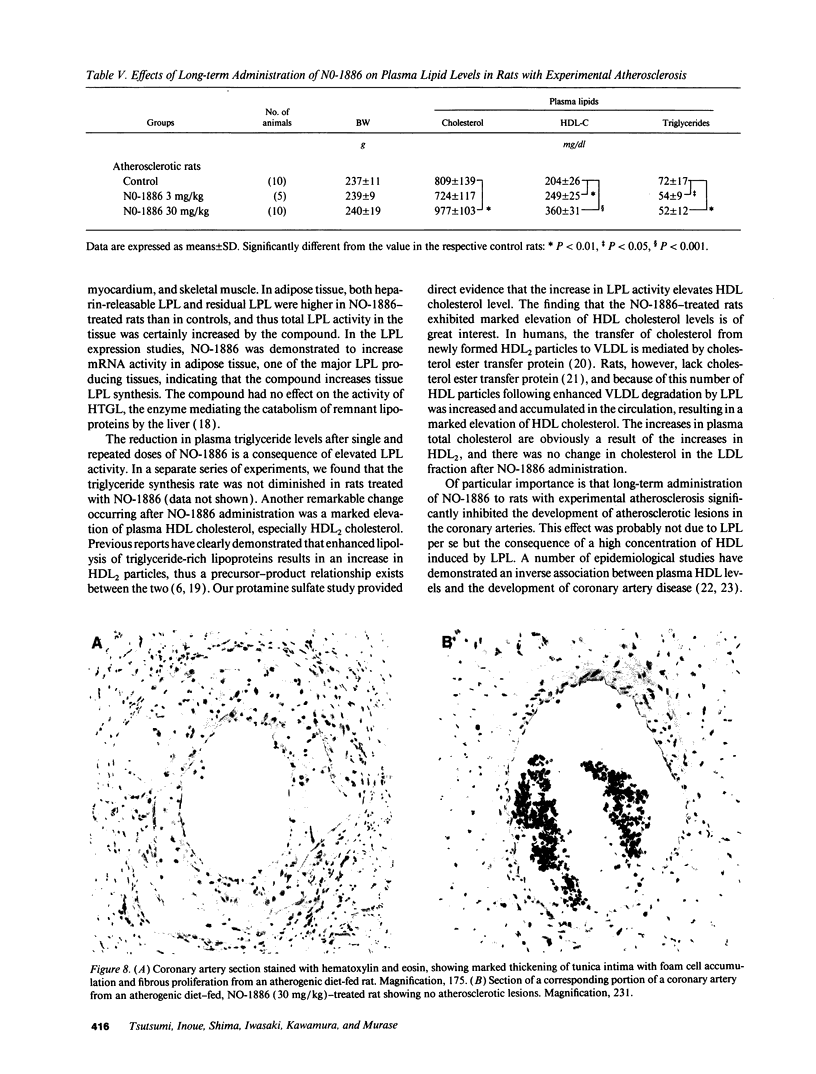
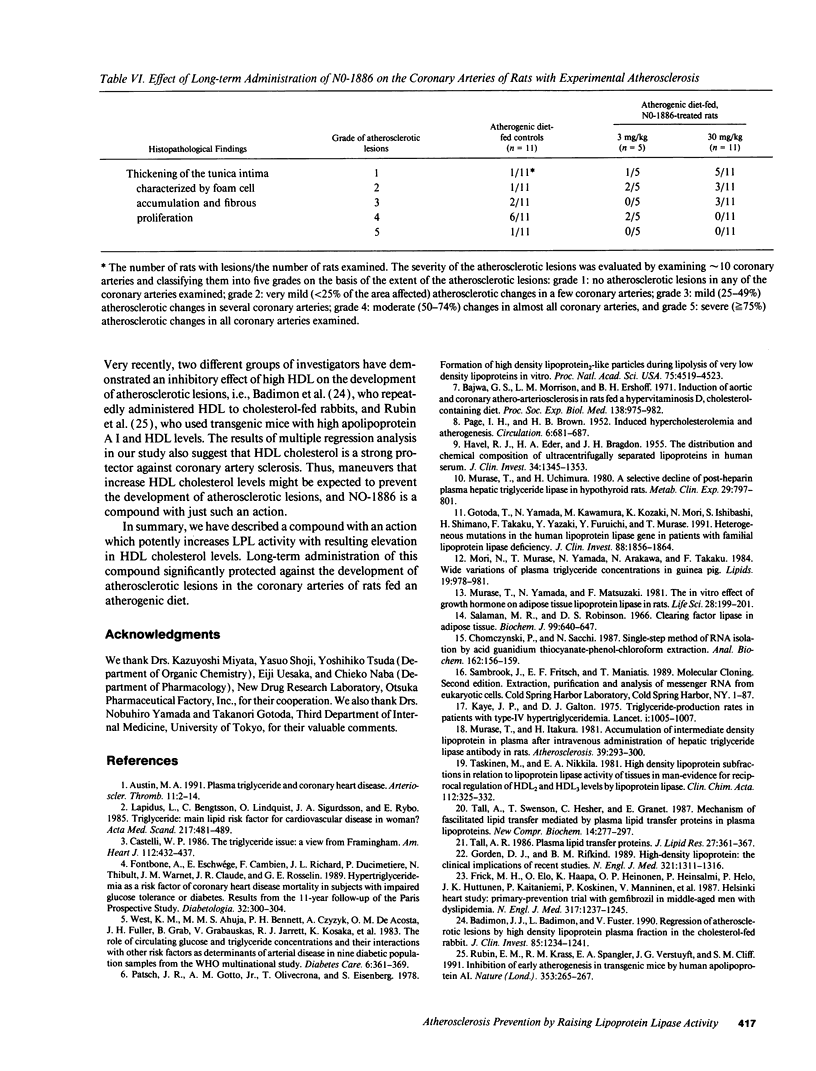
We have discovered a novel compound, NO-1886, which possesses a powerful lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activity-increasing action. Administration of NO-1886 increased LPL activity in the postheparin plasma, adipose tissue, and myocardium of rats, and produced a reduction in plasma triglyceride levels with concomitant elevation of HDL cholesterol levels. Administration of NO-1886 increased LPL enzyme mass in postheparin plasma and mRNA activity in epididymal adipose tissue, and it was concluded that the mode of action of this compound is stimulation of tissue LPL synthesis. We also conducted long-term studies to assess the impact of increases in LPL activity and HDL levels on the development of atherosclerotic lesions in rats. Administration of NO-1886 for as long as 90 d significantly decreased the degree of atherosclerotic changes in the coronary arteries of vitamin D2-treated, cholesterol-fed rats. Statistical analysis indicated that increased concentration of HDL is the factor contributing mostly to the prevention of coronary artery sclerosis. In summary, the results of our study indicate that compound NO-1886 increases LPL activity, causing an elevation in HDL levels, and that long-term administration of NO-1886 to rats with experimental atherosclerosis provides significant protection against the development of coronary artery lesions.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin M. A. Plasma triglyceride and coronary heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Jan-Feb;11(1):2–14. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badimon J. J., Badimon L., Fuster V. Regression of atherosclerotic lesions by high density lipoprotein plasma fraction in the cholesterol-fed rabbit. J Clin Invest. 1990 Apr;85(4):1234–1241. doi: 10.1172/JCI114558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bajwa G. S., Morrison L. M., Ershoff B. H. Induction of aortic and coronary athero-arteriosclerosis in rats fed a hypervitaminosis D, cholesterol-containing diet. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Dec;138(3):975–982. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-36030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castelli W. P. The triglyceride issue: a view from Framingham. Am Heart J. 1986 Aug;112(2):432–437. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(86)90296-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontbonne A., Eschwège E., Cambien F., Richard J. L., Ducimetière P., Thibult N., Warnet J. M., Claude J. R., Rosselin G. E. Hypertriglyceridaemia as a risk factor of coronary heart disease mortality in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes. Results from the 11-year follow-up of the Paris Prospective Study. Diabetologia. 1989 May;32(5):300–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00265546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frick M. H., Elo O., Haapa K., Heinonen O. P., Heinsalmi P., Helo P., Huttunen J. K., Kaitaniemi P., Koskinen P., Manninen V. Helsinki Heart Study: primary-prevention trial with gemfibrozil in middle-aged men with dyslipidemia. Safety of treatment, changes in risk factors, and incidence of coronary heart disease. N Engl J Med. 1987 Nov 12;317(20):1237–1245. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198711123172001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. J., Rifkind B. M. High-density lipoprotein--the clinical implications of recent studies. N Engl J Med. 1989 Nov 9;321(19):1311–1316. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198911093211907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoda T., Yamada N., Kawamura M., Kozaki K., Mori N., Ishibashi S., Shimano H., Takaku F., Yazaki Y., Furuichi Y. Heterogeneous mutations in the human lipoprotein lipase gene in patients with familial lipoprotein lipase deficiency. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1856–1864. doi: 10.1172/JCI115507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J. P., Galton D. J. Triglyceride-production rates in patients with type-4 hypertriglyceridaemia. Lancet. 1975 May 3;1(7914):1005–1007. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)91948-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapidus L., Bengtsson C., Lindquist O., Sigurdsson J. A., Rybo E. Triglycerides--main lipid risk factor for cardiovascular disease in women? Acta Med Scand. 1985;217(5):481–489. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1985.tb03251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori N., Murase T., Yamada N., Arakawa N., Takaku F. Wide variations of plasma triglyceride concentrations in guinea pigs. Lipids. 1984 Dec;19(12):978–981. doi: 10.1007/BF02534738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase T., Itakura H. Accumulation of intermediate density lipoprotein in plasma after intravenous administration of hepatic triglyceride lipase antibody in rats. Atherosclerosis. 1981 Jun;39(3):293–300. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(81)90015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase T., Uchimura H. A selective decline of postheparin plasma hepatic triglyceride lipase in hypothyroid rats. Metabolism. 1980 Aug;29(8):797–801. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(80)90207-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase T., Yamada N., Matsuzaki F. The in vitro effect of growth hormone on adipose tissue lipoprotein lipase in rats. Life Sci. 1981 Jan 12;28(2):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90553-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAGE I. H., BROWN H. B. Induced hypercholesterolemia and atherogenesis. Circulation. 1952 Nov;6(5):681–687. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.6.5.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patsch J. R., Gotto A. M., Jr, Olivercrona T., Eisenberg S. Formation of high density lipoprotein2-like particles during lipolysis of very low density lipoproteins in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4519–4523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin E. M., Krauss R. M., Spangler E. A., Verstuyft J. G., Clift S. M. Inhibition of early atherogenesis in transgenic mice by human apolipoprotein AI. Nature. 1991 Sep 19;353(6341):265–267. doi: 10.1038/353265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaman M. R., Robinson D. S. Clearing-factor lipase in adipose tissue. A medium in which the enzyme activity of tissue from starved rats increases in vitro. Biochem J. 1966 Jun;99(3):640–647. doi: 10.1042/bj0990640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R. Plasma lipid transfer proteins. J Lipid Res. 1986 Apr;27(4):361–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taskinen M. R., Nikkilä E. A. High density lipoprotein subfractions in relation to lipoprotein lipase activity of tissues in man--evidence for reciprocal regulation of HDL2 and HDL3 levels by lipoprotein lipase. Clin Chim Acta. 1981 May;112(3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(81)90455-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West K. M., Ahuja M. M., Bennett P. H., Czyzyk A., De Acosta O. M., Fuller J. H., Grab B., Grabauskas V., Jarrett R. J., Kosaka K. The role of circulating glucose and triglyceride concentrations and their interactions with other "risk factors" as determinants of arterial disease in nine diabetic population samples from the WHO multinational study. Diabetes Care. 1983 Jul-Aug;6(4):361–369. doi: 10.2337/diacare.6.4.361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]