Abstract
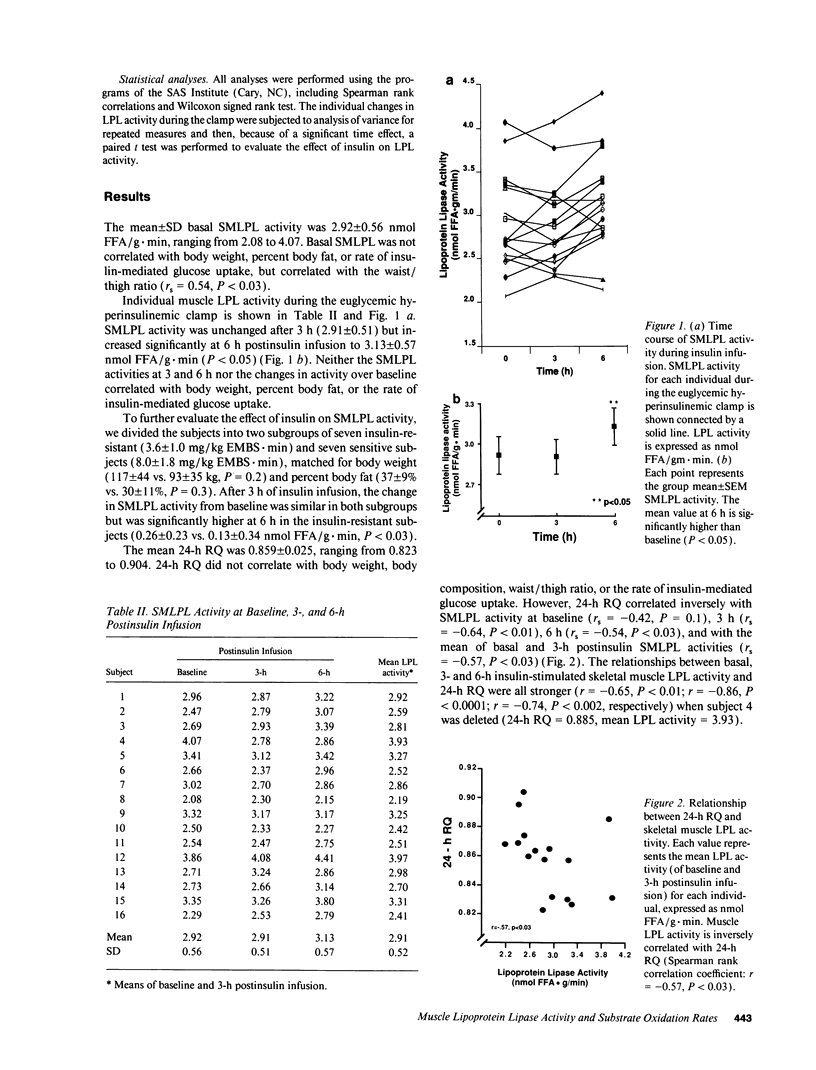
A low ratio of whole-body 24-h fat/carbohydrate (CHO) oxidation has been shown to be a predictor of subsequent body weight gain. We tested the hypothesis that the variability of this ratio may be related to differences in skeletal muscle metabolism. Since lipoprotein lipase (LPL) plays a pivotal role in partitioning lipoprotein-borne triglycerides to adipose (storage) and skeletal muscle (mostly oxidation), we postulated that a low ratio of fat/CHO oxidation was associated with a low skeletal muscle LPL (SMLPL) activity. As an index of substrate oxidation, 24-h RQ was measured under sedentary and eucaloric conditions in 16 healthy nondiabetic Pima males. During a 6-h euglycemic, hyperinsulinemic clamp, muscle biopsies were obtained at baseline, 3, and 6 h. Heparin-elutable SMLPL activity was 2.92 +/- 0.56 nmol free fatty acids/g.min (mean +/- SD) at baseline, was unchanged (2.91 +/- 0.51) at the third hour, and increased significantly (P < 0.05) to 3.13 +/- 0.57 at the sixth hour of the clamp. The mean (of baseline and 3-h) SMLPL activity correlated inversely with 24-h RQ (r = 0.57, P < 0.03) but not with body size, body composition, or insulin-mediated glucose uptake. Since SMLPL activity is related to the ratio of whole body fat/CHO oxidation rate, a decreased muscle LPL activity may, therefore, predispose to obesity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRES R., CADER G., ZIERLER K. L. The quantitatively minor role of carbohydrate in oxidative metabolism by skeletal muscle in intact man in the basal state; measurements of oxygen and glucose uptake and carbon dioxide and lactate production in the forearm. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jun;35(6):671–682. doi: 10.1172/JCI103324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTZAN M. A., ANDRES R., CADER G., ZIERLER K. L. Heterogeneity of forearm metabolism with special reference to free fatty acids. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jan;41:116–125. doi: 10.1172/JCI104453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette-Mackie E. J., Masuno H., Dwyer N. K., Olivecrona T., Scow R. O. Lipoprotein lipase in myocytes and capillary endothelium of heart: immunocytochemical study. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):E818–E828. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.256.6.E818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borensztajn J., Rone M. S., Babirak S. P., McGarr J. A., Oscai L. B. Effect of exercise on lipoprotein lipase activity in rat heart and skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol. 1975 Aug;229(2):394–397. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1975.229.2.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagenais G. R., Tancredi R. G., Zierler K. L. Free fatty acid oxidation by forearm muscle at rest, and evidence for an intramuscular lipid pool in the human forearm. J Clin Invest. 1976 Aug;58(2):421–431. doi: 10.1172/JCI108486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H. Insulin resistance: an adaptation for weight maintenance. Lancet. 1992 Dec 12;340(8833):1452–1453. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92633-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckel R. H. Lipoprotein lipase. A multifunctional enzyme relevant to common metabolic diseases. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 20;320(16):1060–1068. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904203201607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Jr, Yost T. J., Eckel R. H. Tissue-specific regulation of lipoprotein lipase activity by insulin/glucose in normal-weight humans. Metabolism. 1991 Feb;40(2):214–216. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(91)90178-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finegood D. T., Bergman R. N., Vranic M. Estimation of endogenous glucose production during hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic glucose clamps. Comparison of unlabeled and labeled exogenous glucose infusates. Diabetes. 1987 Aug;36(8):914–924. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.8.914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman I., Mandarino L., Gerich J. Estimation and kinetic analysis of insulin-independent glucose uptake in human subjects. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jun;244(6):E632–E635. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.6.E632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISSEKUTZ B., Jr, MILLER H. I., PAUL P., RODAHL K. SOURCE OF FAT OXIDATION IN EXERCISING DOGS. Am J Physiol. 1964 Sep;207:583–589. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.3.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz B., Jr, Paul P. Intramuscular energy sources in exercising normal and pancreatectomized dogs. Am J Physiol. 1968 Jul;215(1):197–204. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1968.215.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs I., Lithell H., Karlsson J. Dietary effects on glycogen and lipoprotein lipase activity in skeletal muscle in man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 May;115(1):85–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07048.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jéquier E., Acheson K., Schutz Y. Assessment of energy expenditure and fuel utilization in man. Annu Rev Nutr. 1987;7:187–208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.07.070187.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiens B., Lithell H., Mikines K. J., Richter E. A. Effects of insulin and exercise on muscle lipoprotein lipase activity in man and its relation to insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1124–1129. doi: 10.1172/JCI114275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillioja S., Bogardus C. Obesity and insulin resistance: lessons learned from the Pima Indians. Diabetes Metab Rev. 1988 Aug;4(5):517–540. doi: 10.1002/dmr.5610040508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder C., Chernick S. S., Fleck T. R., Scow R. O. Lipoprotein lipase and uptake of chylomicron triglyceride by skeletal muscle of rats. Am J Physiol. 1976 Sep;231(3):860–864. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.231.3.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie B. G., Dudley G. A., Kaciuba-Uscilko H., Terjung R. L. Uptake of chylomicron triglycerides by contracting skeletal muscle in rats. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1980 Nov;49(5):851–855. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1980.49.5.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagulesparan M., Savage P. J., Knowler W. C., Johnson G. C., Bennett P. H. Increased in vivo insulin resistance in nondiabetic Pima Indians compared with Caucasians. Diabetes. 1982 Nov;31(11):952–956. doi: 10.2337/diacare.31.11.952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollare T., Vessby B., Lithell H. Lipoprotein lipase activity in skeletal muscle is related to insulin sensitivity. Arterioscler Thromb. 1991 Sep-Oct;11(5):1192–1203. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.11.5.1192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravussin E., Lillioja S., Anderson T. E., Christin L., Bogardus C. Determinants of 24-hour energy expenditure in man. Methods and results using a respiratory chamber. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1568–1578. doi: 10.1172/JCI112749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman J. S., Kosmakos F. C., Howard B. V., Taskinen M. R., Kuusi T., Nikkila E. A. Characterization of lipase activities in obese Pima indians. Decreases with weight reduction. J Clin Invest. 1982 Oct;70(4):791–797. doi: 10.1172/JCI110675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidell J. C., Muller D. C., Sorkin J. D., Andres R. Fasting respiratory exchange ratio and resting metabolic rate as predictors of weight gain: the Baltimore Longitudinal Study on Aging. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1992 Sep;16(9):667–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinburn B. A., Nyomba B. L., Saad M. F., Zurlo F., Raz I., Knowler W. C., Lillioja S., Bogardus C., Ravussin E. Insulin resistance associated with lower rates of weight gain in Pima Indians. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):168–173. doi: 10.1172/JCI115274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan M. H., Sata T., Havel R. J. The significance of lipoprotein lipase in rat skeletal muscles. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):363–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taskinen M. R., Nikkilä E. A. Lipoprotein lipase of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle in human obesity: response to glucose and to semistarvation. Metabolism. 1981 Aug;30(8):810–817. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade A. J., Marbut M. M., Round J. M. Muscle fibre type and aetiology of obesity. Lancet. 1990 Apr 7;335(8693):805–808. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90933-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurlo F., Larson K., Bogardus C., Ravussin E. Skeletal muscle metabolism is a major determinant of resting energy expenditure. J Clin Invest. 1990 Nov;86(5):1423–1427. doi: 10.1172/JCI114857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurlo F., Lillioja S., Esposito-Del Puente A., Nyomba B. L., Raz I., Saad M. F., Swinburn B. A., Knowler W. C., Bogardus C., Ravussin E. Low ratio of fat to carbohydrate oxidation as predictor of weight gain: study of 24-h RQ. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 1):E650–E657. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1990.259.5.E650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


