Abstract
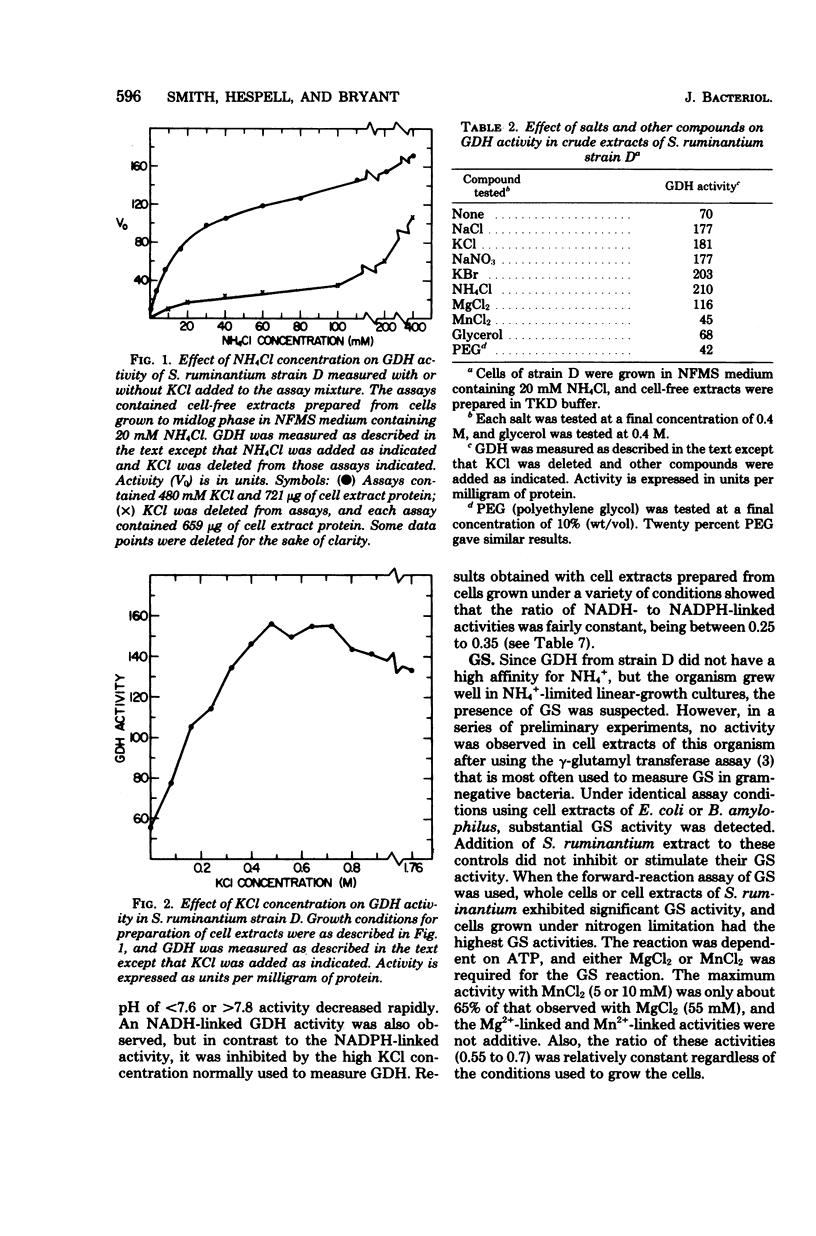
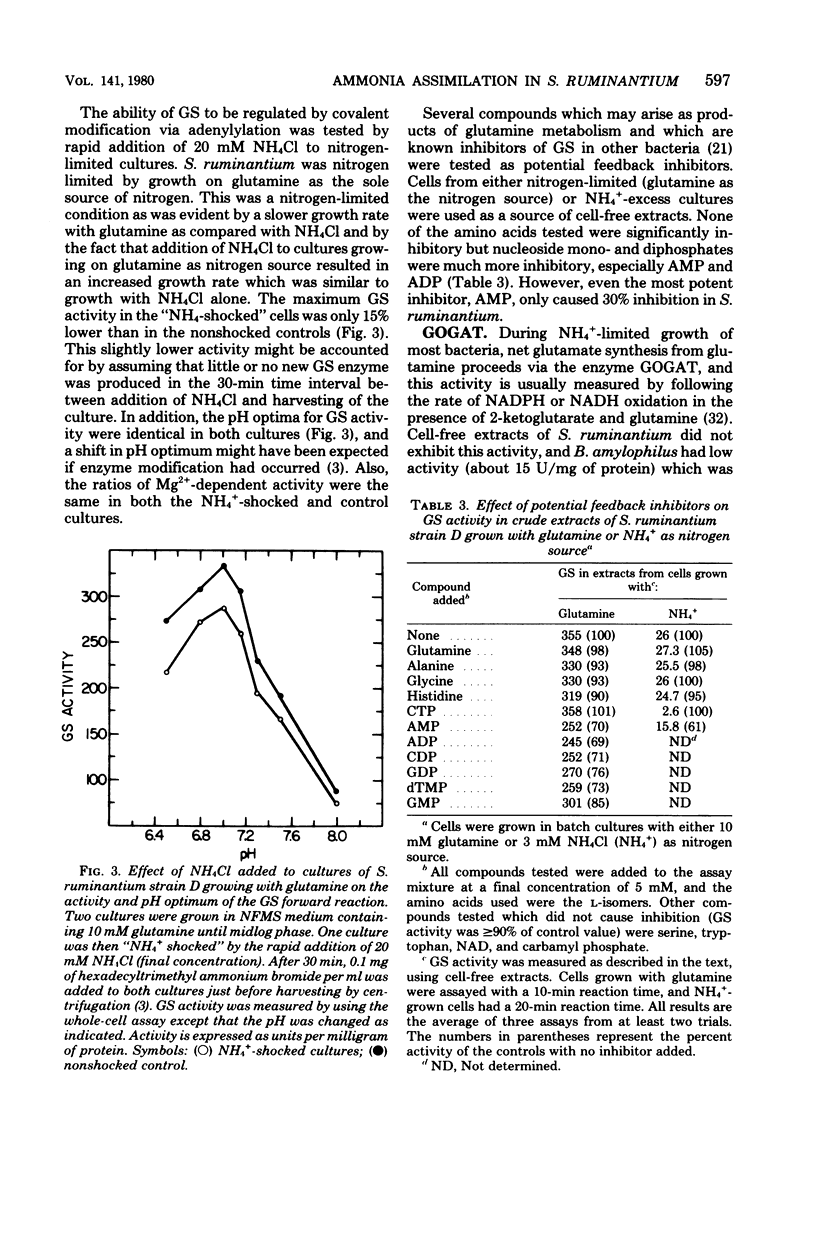
Selenomonas ruminantium was found to possess two pathways for NH4+ assimilation that resulted in net glutamate synthesis. One pathway fixed NH4+ through the action of an NADPH-linked glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH). Maximal GDH activity required KCl (about 0.48 M), but a variety of monovalent salts could replace KCl. Complete substrate saturation of the enzyme by NH4+ did not occur, and apparent Km values of 6.7 and 23 mM were estimated. Also, an NADH-linked GDH activity was observed but was not stimulated by KCl. Cells grown in media containing non-growth-rate-limiting concentrations of NH4+ had the highest levels of GDH activity. The second pathway fixed NH4+ into the amide of glutamine by an ATP-dependent glutamine synthetase (GS). The GS did not display gamma-glutamyl transferase activity, and no evidence for an adenylylation/deadenylylation control mechanism was detected. GS activity was highest in cells grown under nitrogen limitation. Net glutamate synthesis from glutamine was effected by glutamate synthase activity (GOGAT). The GOGAT activity was reductant dependent, and maximal activity occurred with dithionite-reduced methyl viologen as the source of electrons, although NADPH or NADH could partially replace this artificial donor system. Flavin adenine dinucleotide, flavin mononucleotide, or ferredoxin could not replace methyl viologen. GOGAT activity was maximal in cells grown with NH4+ as sole nitrogen source and decreased in media containing Casamino Acids.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison M. J. Biosynthesis of amono acids by ruminal microorganisms. J Anim Sci. 1969 Nov;29(5):797–807. doi: 10.2527/jas1969.295797x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison M. J., Robinson I. M. Biosynthesis of alpha-ketoglutarate by the reductive carboxylation of succinate in Bacteroides ruminicola. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):50–56. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.50-56.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BITENSKY M. W., YIELDING K. L., TOMKINS G. M. THE EFFECT OF ALLOSTERIC MODIFIERS ON THE RATE OF DENATURATION OF GLUTAMATE DEHYDROGENASE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1077–1082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKBURN T. H., HOBSON P. N. Isolation of proteolytic bacteria from the sheep rumen. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Feb;22:282–289. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-1-282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender R. A., Janssen K. A., Resnick A. D., Blumenberg M., Foor F., Magasanik B. Biochemical parameters of glutamine synthetase from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1001-1009.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenchley J. E. Effect of methionine sulfoximine and methionine sulfone on glutamate synthesis in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1973 May;114(2):666–673. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.2.666-673.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenchley J. E., Prival M. J., Magasanik B. Regulation of the synthesis of enzymes responsible for glutamate formation in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6122–6128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Commentary on the Hungate technique for culture of anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1324–1328. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Nutritional features and ecology of predominant anaerobic bacteria of the intestinal tract. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1313–1319. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell D. R., Bryant M. P. Medium without rumen fluid for nonselective enumeration and isolation of rumen bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Sep;14(5):794–801. doi: 10.1128/am.14.5.794-801.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalupa W., Clark J., Opliger P., Lavker R. Ammonia metabolism in rumen bacteria and mucosa from sheep fed soy protein or urea. J Nutr. 1970 Feb;100(2):161–169. doi: 10.1093/jn/100.2.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ely B., Amarasinghe A. B., Bender R. A. Ammonia assimilation and glutamate formation in Caulobacter crescentus. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):225–230. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.225-230.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erfle J. D., Sauer F. S., Mahadevan S. Effect of ammonia concentration on activity of enzymes of ammonia assimilation and on synthesis of amino acids by mixed rumen bacteria in continuous culture. J Dairy Sci. 1977 Jul;60(7):1064–1072. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(77)83989-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass T. L., Bryant M. P., Wolin M. J. Partial purification of ferredoxin from Ruminococcus albus and its role in pyruvate metabolism and reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide by H2. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):463–472. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.463-472.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith C. J., Carlsson J. Mechanism of ammonia assimilation in streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Jun;82(2):253–260. doi: 10.1099/00221287-82-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. S., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. II. Patterns of feedback inhibition in microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1045–1055. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1045-1055.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. S., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. VI. Interactions of inhibitors for Bacillus licheniformis glutamine synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1016–1024. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1016-1024.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. C., Gest H. Inorganic nitrogen assimilation by the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):683–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.683-688.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John A., Isaacson H. R., Bryant M. P. Isolation and characteristics of a ureolytic strain of Selenomonas ruminatium. J Dairy Sci. 1974 Sep;57(9):1003–1014. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(74)85001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyner A. E., Jr, Baldwin R. L. Enzymatic studies of pure cultures of rumen microorganisms. J Bacteriol. 1966 Nov;92(5):1321–1330. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.5.1321-1330.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lea P. J., Miflin B. J. The occurrence of glutamate synthase in algae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 2;64(3):856–862. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leicht W., Werber M. M., Eisenberg H. Purification and characterization of glutamate dehydrogenase from Halobacterium of the Dead Sea. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 19;17(19):4004–4010. doi: 10.1021/bi00612a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magasanik B., Prival M. J., Brenchley J. E., Tyler B. M., DeLeo A. B., Streicher S. L., Bender R. A., Paris C. G. Glutamine synthetase as a regulator of enzyme synthesis. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1974;8(0):119–138. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152808-9.50010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meers J. L., Tempest D. W., Brown C. M. 'Glutamine(amide):2-oxoglutarate amino transferase oxido-reductase (NADP); an enzyme involved in the synthesis of glutamate by some bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):187–194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miflin B. J., Lea P. J. Glutamine and asparagine as nitrogen donors for reductant-dependent glutamate synthesis in pea roots. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;149(2):403–409. doi: 10.1042/bj1490403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahel G., Zelenetz A. D., Tyler B. M. gltB gene and regulation of nitrogen metabolism by glutamine synthetase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):139–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.139-148.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilgrim A. F., Weller R. A., Gray F. V., Belling C. B. Synthesis of microbial protein from ammonia in the sheep's rumen and the proportion of dietary nitrogen converted into microbial nitrogen. Br J Nutr. 1970 Jun;24(2):589–598. doi: 10.1079/bjn19700057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S., Milner L. A rapid radioactive assay for glutamine synthetase, glutaminase, asparagine synthetase, and asparaginase. Anal Biochem. 1970 Oct;37(2):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90069-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REGOLI D., CLARK V. PREVENTION BY ADENOSINE OF THE EFFECT OF ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE ON THE CONCENTRATION OF CIRCULATING PLATELETS. Nature. 1963 Nov 9;200:546–548. doi: 10.1038/200546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tronick S. R., Ciardi J. E., Stadtman E. R. Comparative biochemical and immunological studies of bacterial glutamine synthetases. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):858–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.858-868.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varel V. H., Bryant M. P., Holdeman L. V., Moore W. E. Isolation of ureolytic Peptostreptococcus productus from feces using defined medium; failure of common urease tests. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):594–599. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.594-599.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE D. C., BRYANT M. P., CALDWELL D. R. Cytochromelinked fermentation in Bacteroides ruminicola. J Bacteriol. 1962 Oct;84:822–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.84.4.822-828.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


