Abstract
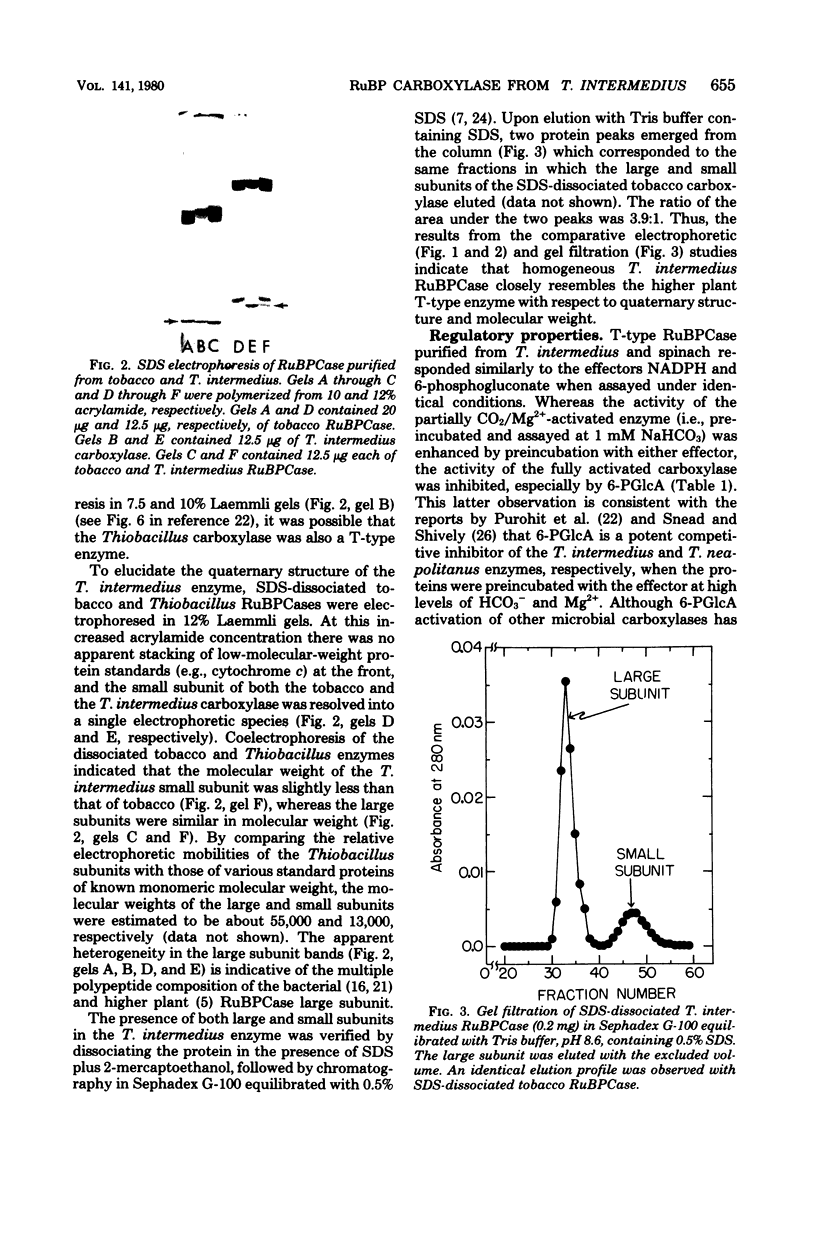
Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (EC 4.1.1.39) has been purified to homogeneity from glutamate-CO2-thiosulfate-grown Thiobacillus intermedius by pelleting the protein from the 93,000 X g supernatant fluid followed by ammonium sulfate fractionation and sedimentation into a discontinuous sucrose density gradient. The molecular weight of the native protein approximated that of the higher plant enzyme (550,000) based on its relative electrophoretic mobility in polyacrylamide disc gels compared with that of standards of known molecular weight, including crystalline tobacco ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase. Sodium dodecyl sulfate electrophoresis in 12% polyacrylamide disc gels and Sephadex G-100 chromatography in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate indicated that the purified Thiobacillus protein, like the tobacco enzyme, consisted of two types of nonidentical subunits. The molecular weights of the large and small subunits were estimated to be about 55,000 and 13,000, respectively, by means of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The carboxylase activity of the protein purified from spinach leaves and T. intermedius responded similarly to the effectors reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate and 6-phosphogluconate. Contrary to a previous report (K. Purohit, B. A. McFadden, and A. L. Cohen, J. Bacteriol. 127:505-515, 1976), these results indicate that ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase purified from Thiobacillus intermedius closely resembles the higher plant enzyme with respect to quaternary structure, molecular weight, and regulatory properties.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles A. M., White B. Physical properties and metabolite regulation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from Thiobacillus A2. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Jun;108(2):203–209. doi: 10.1007/BF00428952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chollet R., Anderson L. L. Cyanate modification of essential lysyl residues in the catalytic subunit of tobacco ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 7;525(2):455–467. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90242-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chollet R., Anderson L. L. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase activities by temperature pretreatment and chloroplast metabolites. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Sep;176(1):344–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christeller J. T., Laing W. A. A kinetic study of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):467–473. doi: 10.1042/bj1730467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Activation of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate and other chloroplast metabolites. Plant Physiol. 1974 Oct;54(4):556–559. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.4.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Takabe T., Nishimura M., Akazawa T. Role of the large and small subunits of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in the activation by CO2 and Mg2+. J Biochem. 1979 Apr;85(4):923–930. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a132424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlis V. B., Gordon G. L., McFadden B. A. Regulation of activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from Pseudomonas oxalaticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 16;84(3):699–705. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90761-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlis V. B., Jr, Gordon G. L., McFadden B. A. Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase from Pseudomonas oxalacticus. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):287–298. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.287-298.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. T., Charles A. M. Properties and regulation of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase from Thiobacillus novellus. Arch Microbiol. 1975 Sep 30;105(1):51–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00447113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden B. A., Purohit K. Chemosynthetic, photosynthetic, and cyanobacterial ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase. Basic Life Sci. 1978;11:179–207. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-8106-8_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A., Cohen A. L. Purification, quaternary structure, composition, and properties of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Thiobacillus intermedius. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):505–515. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.505-515.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A. Quaternary structure and oxygenase activity of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Hydrogenomonas eutropha. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):415–421. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.415-421.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A., Shaykh M. M. D-Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and polyhedral inclusion bodies in Thiobacillus intermedius. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):516–522. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.516-522.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutner A. C., Lane M. D. Nonidentical subunits of ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Aug 23;28(4):531–537. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(67)90346-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schloss J. V., Phares E. F., Long M. V., Norton I. L., Stringer C. D., Hartman F. C. Isolation, characterization, and crystallization of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase from autotrophically grown Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):490–501. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.490-501.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. II. Quaternary structure, composition, catalytic, and immunological properties. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3459–3464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. One-step isolation of microbial ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(3):231–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00696237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]