Abstract
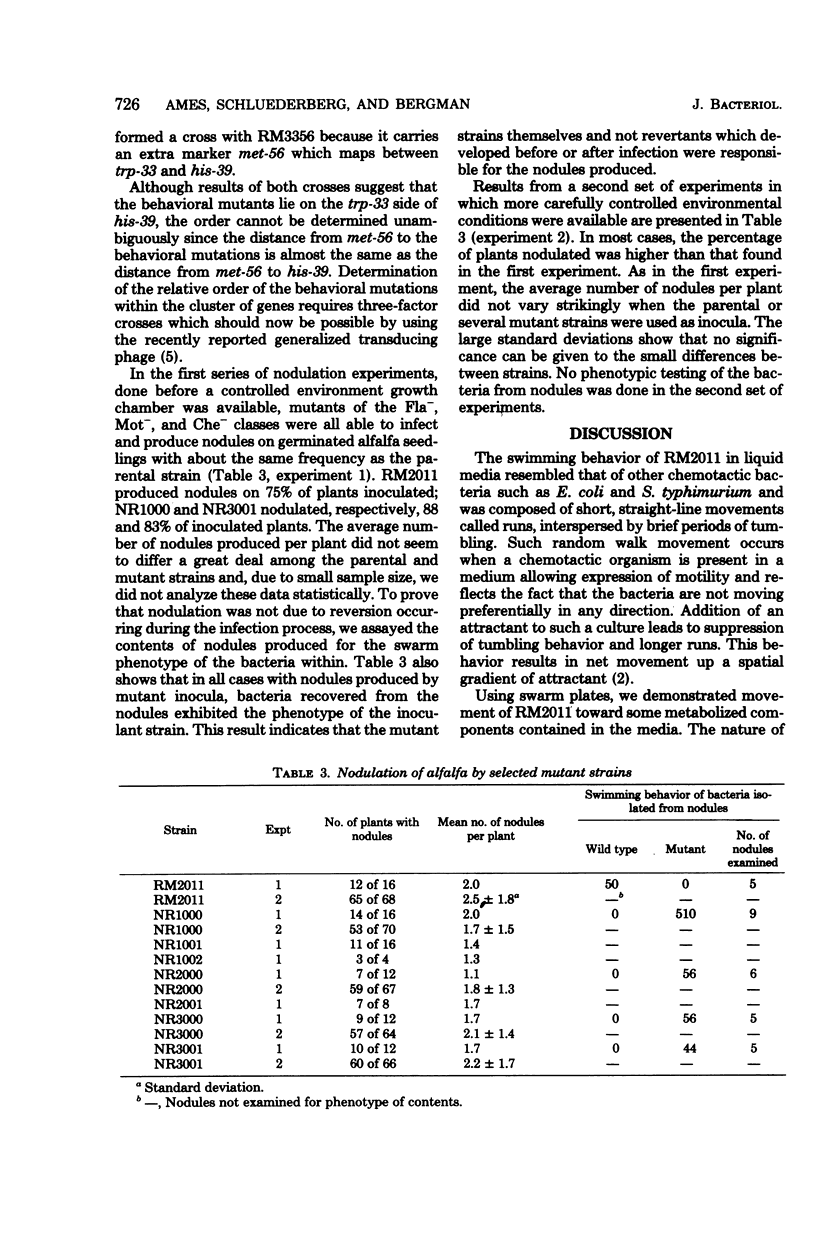
Rhizobium meliloti exhibited behavior resembling that of other chemotactic bacteria. Nonflagellated, nonmotile but flagellated, and nonchemotactic mutants were isolated, and genetic mapping placed all three types of lesions within a small region of the R. Meliloti chromosome. Results from nodulation experiments performed with these mutants indicate that members of the three classes (Fla-, Mot-, and Che-) infect and produce as many nodules on alfalfa plants as does the wild-type strain.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J. A method for measuring chemotaxis and use of the method to determine optimum conditions for chemotaxis by Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Jan;74(1):77–91. doi: 10.1099/00221287-74-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adler J. Chemotaxis in bacteria. J Supramol Struct. 1976;4(3):305–317. doi: 10.1002/jss.400040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B., Adler J., Dahl M. M. Nonchemotactic mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):390–398. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.390-398.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C. Chemotaxis in bacteria. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1975;4(00):119–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.04.060175.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadesús J., Olivares J. General transduction in Rhizobium meliloti by a thermosensitive mutant of bacteriophage DF2. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):316–317. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.316-317.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Currier W. W., Strobel G. A. Chemotaxis of Rhizobium spp. to a Glycoprotein Produced by Birdsfoot Trefoil Roots. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):434–436. doi: 10.1126/science.196.4288.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dazzo F. B., Yanke W. E., Brill W. J. Trifolin: a Rhizobium recognition protein from white clover. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Mar 20;539(3):276–286. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(78)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Signer E. R. Genetic mapping of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2076–2078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napoli C., Albersheim P. Infection and nodulation of clover by nonmotile Rhizobium trifolii. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):979–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.979-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. cheA, cheB, and cheC genes of Escherichia coli and their role in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):758–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.758-770.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West M., Burdash N. M., Freimuth F. Simplified silver-plating stain for flagella. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Oct;6(4):414–419. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.4.414-419.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



