Abstract
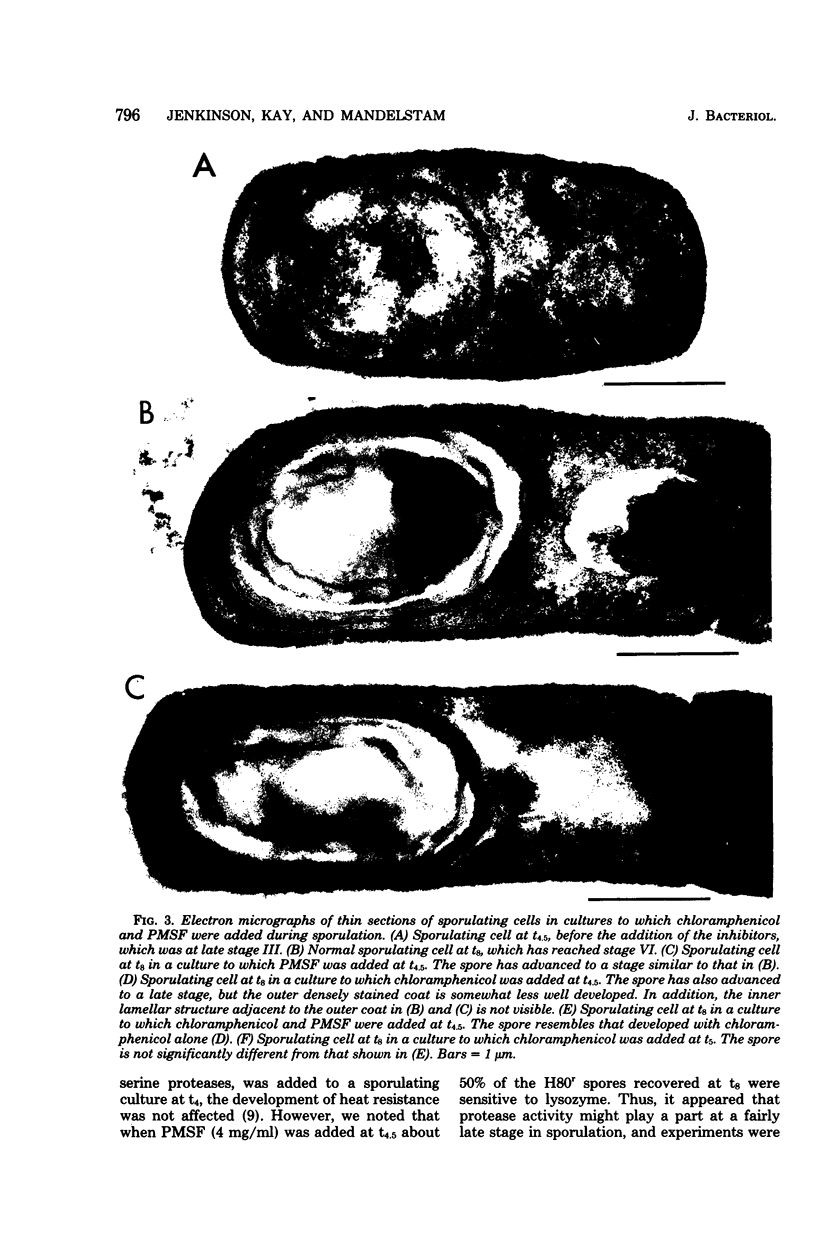
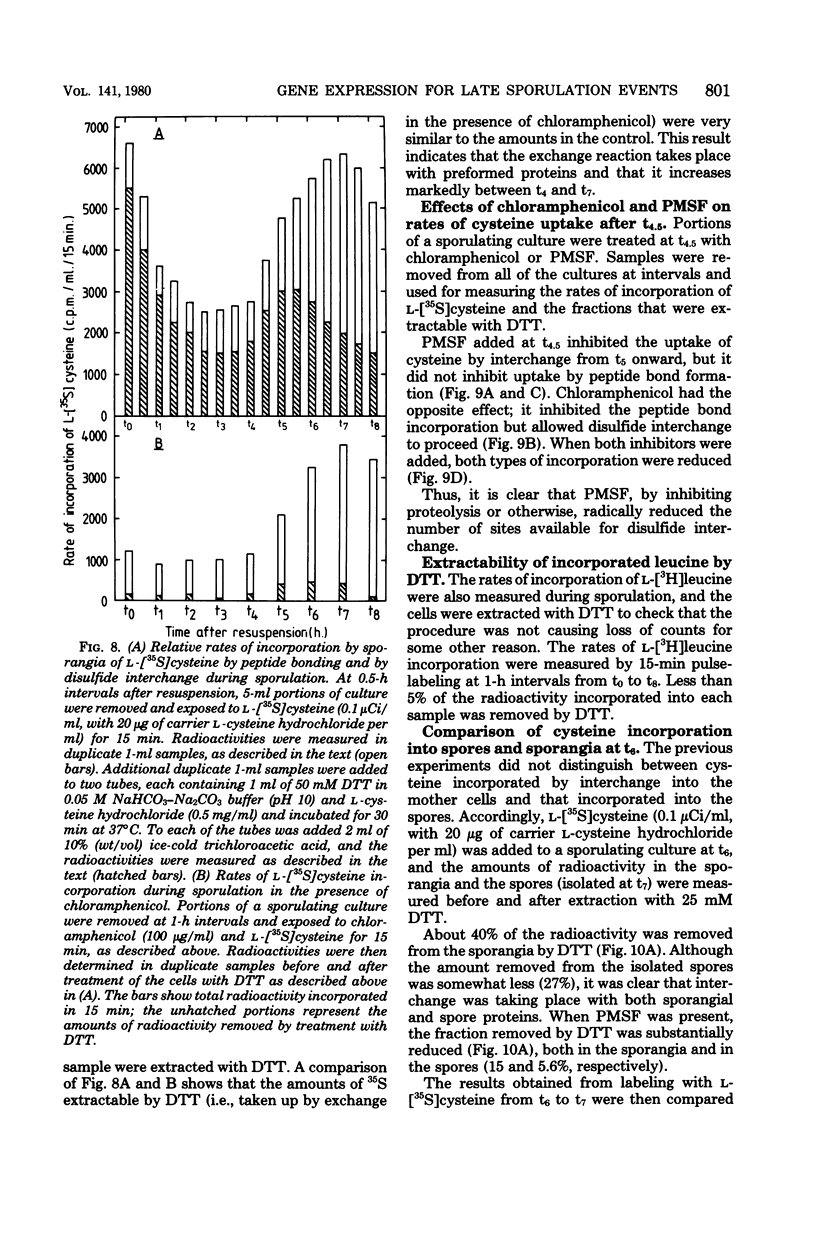
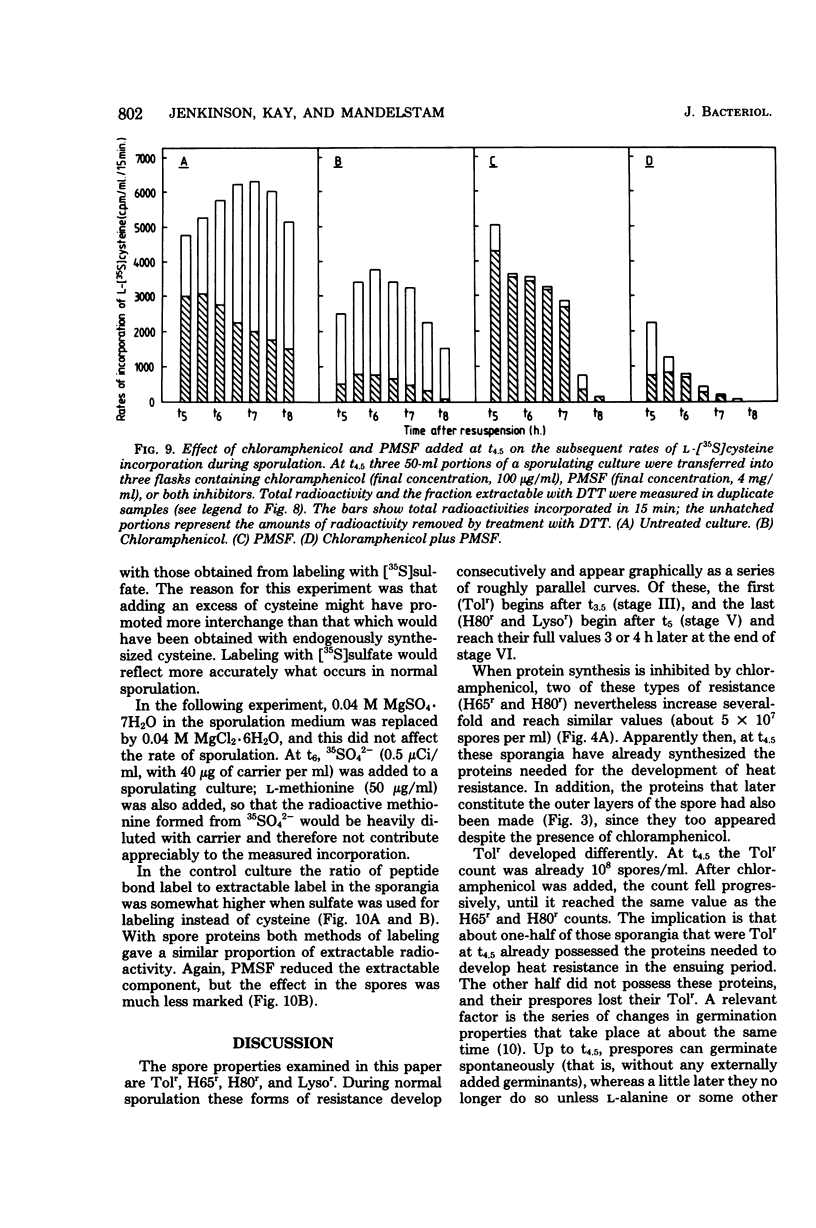
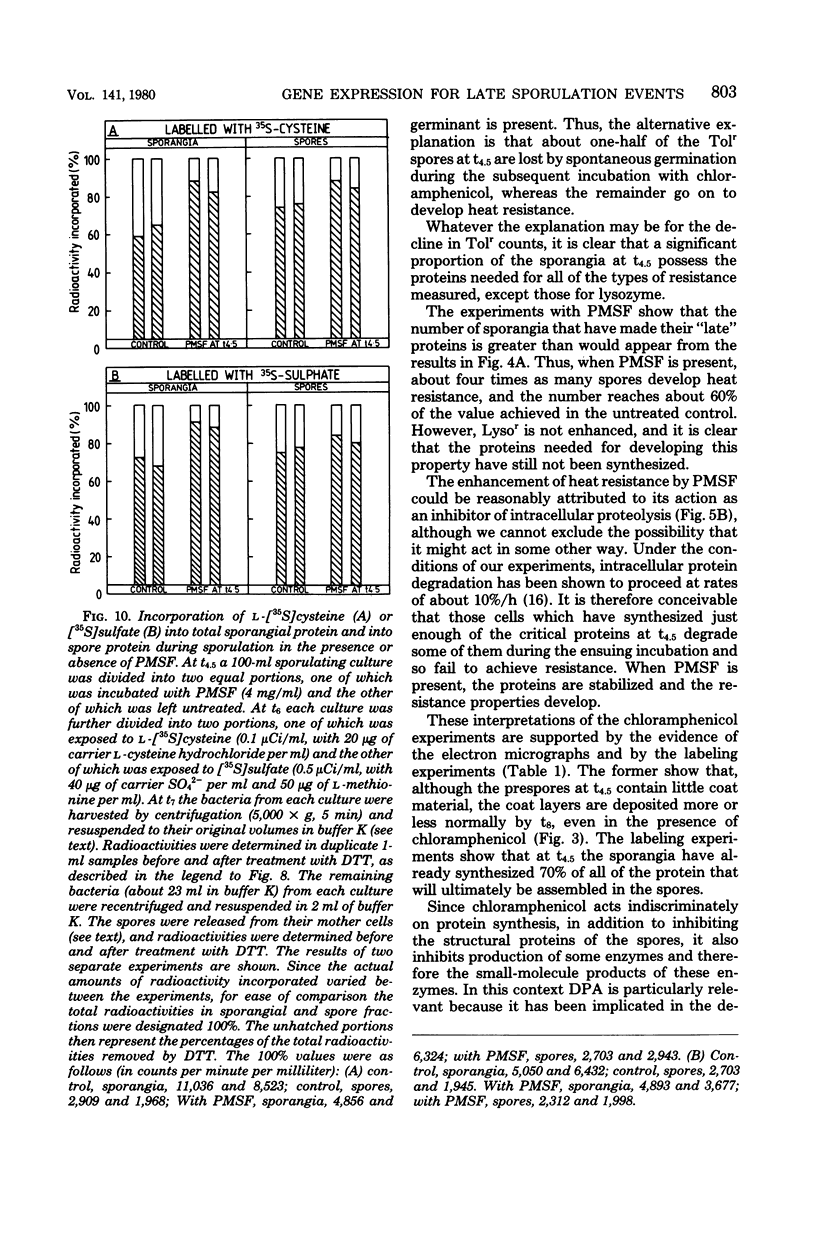
During sporulation in replacement medium, resistance to toluene to heating at 65 degrees C, to lysozyme, and to heating at 80 degrees C appeared in sequence between 4 and 8 h after the induction of sporulation (i.e., between t4 and t8). The addition of sufficient chloramphenicol at t4.5 to prevent protein synthesis nevertheless allowed the emergence of all of these types of resistance except lysozyme resistance. The numbers of spores with these types of resistance (lysozyme resistance again excepted) increased about fourfold when phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (an inhibitor of serine protease activity) was also present. Thus, the observed increases in resistance in the 2 h after the addition of chloramphenicol resulted from the utilization of preformed protein elements. Dipicolinate did not seem to be a determining factor in the development of any of these forms of resistance. Electron micrographs showed that inhibition of protein synthesis did not prevent deposition of the outer layers of the spores. Lysozyme resistance developed differently; synthesis of the relevant proteins began later (t5), and continued synthesis was necessary up to t8. Some processing of proteins made earlier was a prerequisite for lysozyme resistance. Therefore, it appears that from the viewpoint of regulation, the expression of the genes and the production of the proteins for resistance to toluene, heating at 65 degrees C, and heating at 80 degrees C are all stage IV sporulation events, although the resistance properties themselves appear only during stages V and VI. Lysozyme resistance is the only real late event among those examined. The germination characteristics of the spores, which are also late events, are discussed in this context, as they too are dependent on proteins that are synthesized much earlier.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson A. I., Fitz-James P. C. Biosynthesis of bacterial spore coats. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):199–212. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90288-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. I., Fitz-James P. C. Reconstitution of bacterial spore coat layers in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):571–578. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.571-578.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson A. I., Fitz-James P. Structure and morphogenesis of the bacterial spore coat. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Jun;40(2):360–402. doi: 10.1128/br.40.2.360-402.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balassa G., Milhaud P., Raulet E., Silva M. T., Sousa J. C. A Bacillus subtilis mutant requiring dipicolinic acid for the development of heat-resistant spores. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Feb;110(2):365–379. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-2-365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balassa G. Synthèse et fonction des ARN messagers au cours de la sporulation de Bacillus subtilis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1966 Feb;110(2):175–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Aronson A. I. Alterations of spore coat processing and protein turnover in a Bacillus cereus mutant with a defective postexponential intracellular protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1254–1258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. G., Mandelstam J. Use of constructed double mutants for determining the temporal order of expression of sporulation genes in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1254–1263. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1254-1263.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancer B. N., Mandelstam J. Production and possible function of serine protease during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):406–410. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.406-410.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion P., Mandelstam J. Germination properties as marker events characterizing later stages of Bacillus subtilis spore formation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):786–792. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.786-792.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hranueli D., Piggot P. J., Mandelstam J. Statistical estimate of the total number of operons specific for Bacillus subtilis sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):684–690. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.684-690.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JANSSEN F. W., LUND A. J., ANDERSON L. E. Colorimetric assay for dipicolinic acid in bacterial spores. Science. 1958 Jan 3;127(3288):26–27. doi: 10.1126/science.127.3288.26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay D., Warren S. C. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Morphological changes. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):819–824. doi: 10.1042/bj1090819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelstam J. The Leeuwenhoek lecture, 1975: bacterial sporulation: a problem in the biochemistry and genetics of a primitive developmental system. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Apr 13;193(1111):89–106. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelstam J., Waites W. M. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. The role of exoprotease. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(5):793–801. doi: 10.1042/bj1090793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey N. K., Aronson A. I. Properties of the Bacillus subtilis spore coat. J Bacteriol. 1979 Mar;137(3):1208–1218. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.3.1208-1218.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J., Coote J. G. Genetic aspects of bacterial endospore formation. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):908–962. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.908-962.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryter A., Szulmajster J. Action du chloramphénicol sur la sporogenèse de B. subtilis. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1965 May;108(5):640–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterlini J. M., Mandelstam J. Commitment to sporulation in Bacillus subtilis and its relationship to development of actinomycin resistance. Biochem J. 1969 Jun;113(1):29–37. doi: 10.1042/bj1130029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. A. Sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Properties and time of synthesis of alkali-soluble protein of the spore coat. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):505–514. doi: 10.1042/bj1300505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]