Abstract
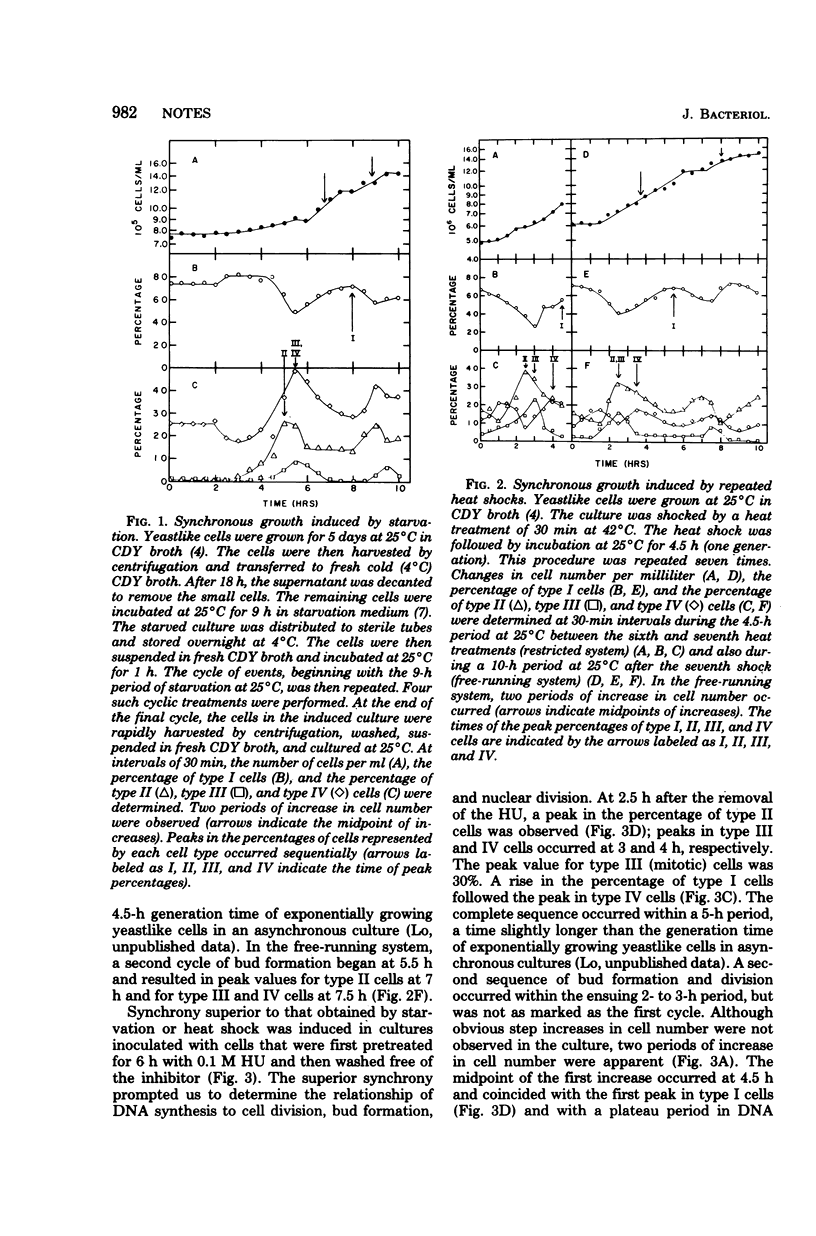
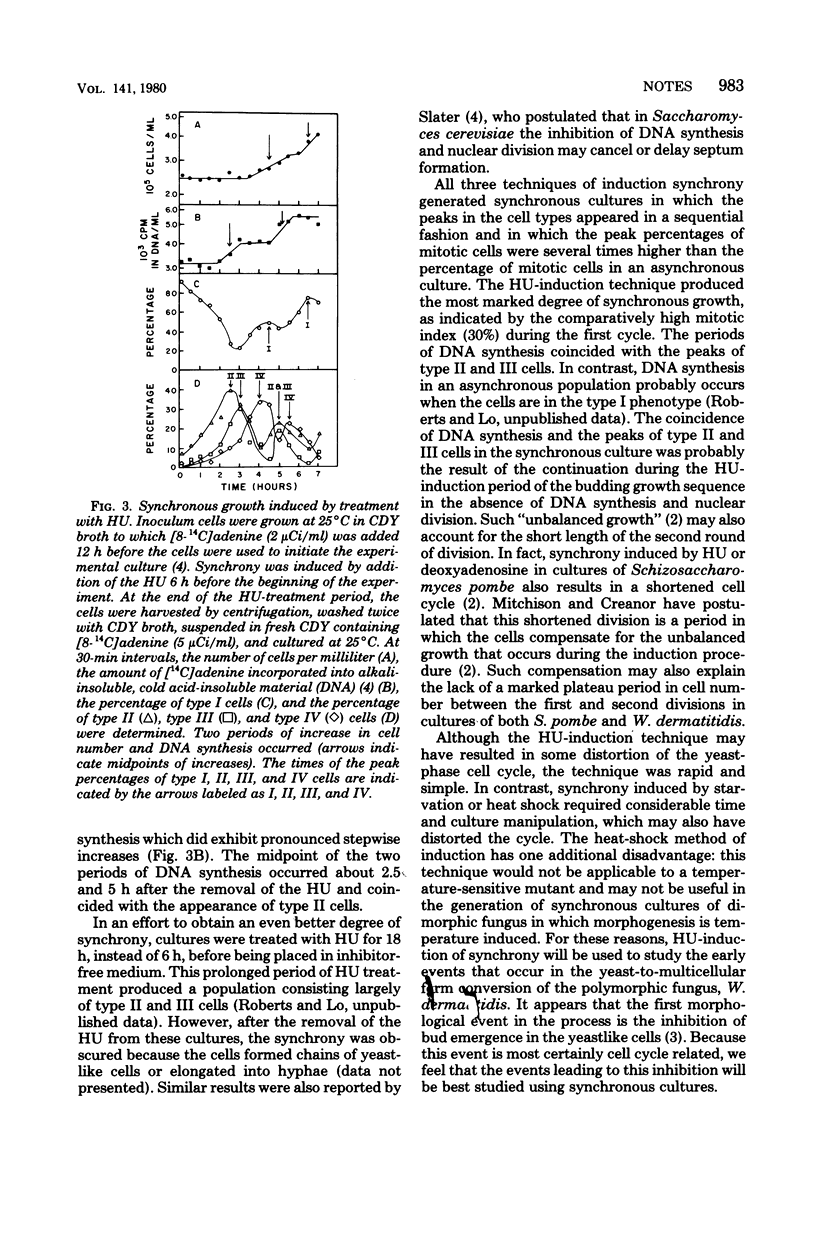
Synchronous yeast-phase cultures of Wangiella dermatitidis were induced by starvation, heat shock, and inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis by hydroxyurea. Hydroxyurea-induced synchrony resulted in some distortion of the yeast-phase cell cycle. However, induction of synchrony by hydroxyurea is a rapid and simple technique which generates a marked degree of synchronous growth.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Mitchison J. M., Creanor J. Induction synchrony in the fission yeast. Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Aug;67(2):368–374. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90421-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. L., Szaniszlo P. J. Temperature-sensitive multicellular mutants of Wangiella dermatitidis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):622–632. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.622-632.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M. L. Effect of reversible inhibition of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis on the yeast cell cycle. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):263–270. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.263-270.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater M. L. Rapid nuclear staining method for Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1339–1341. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1339-1341.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



