Abstract
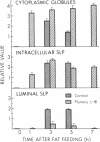
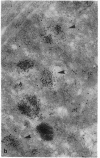
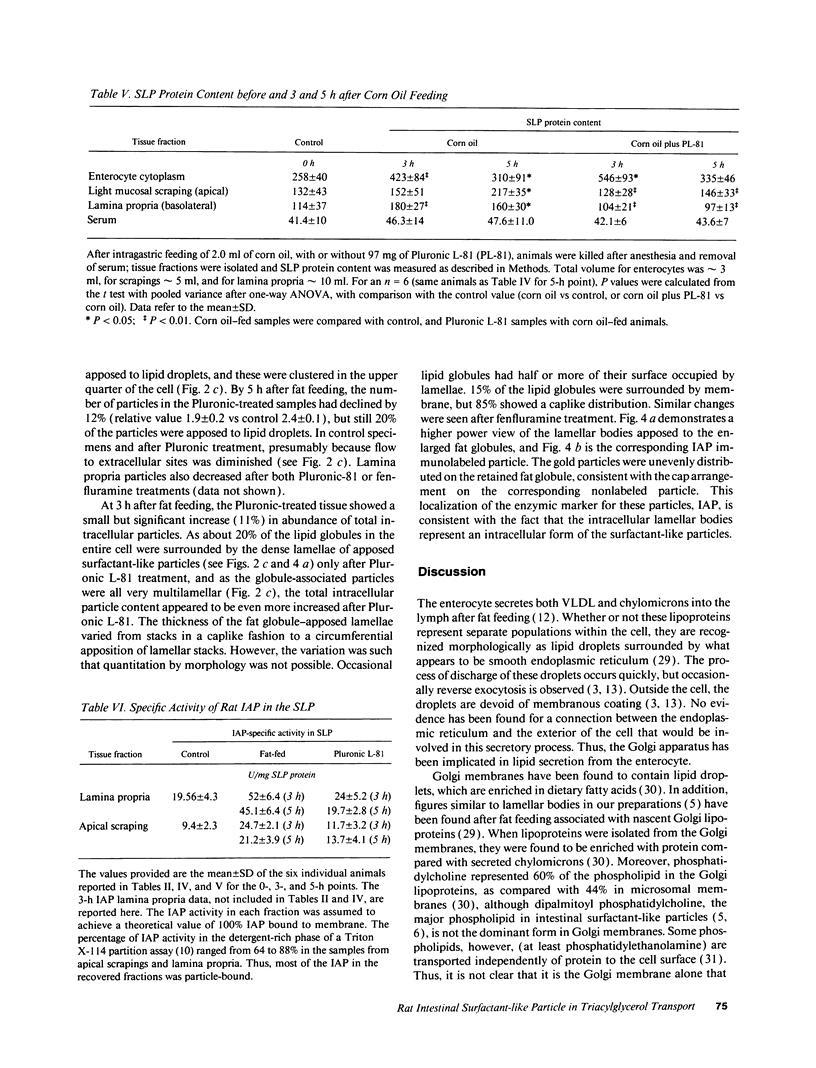
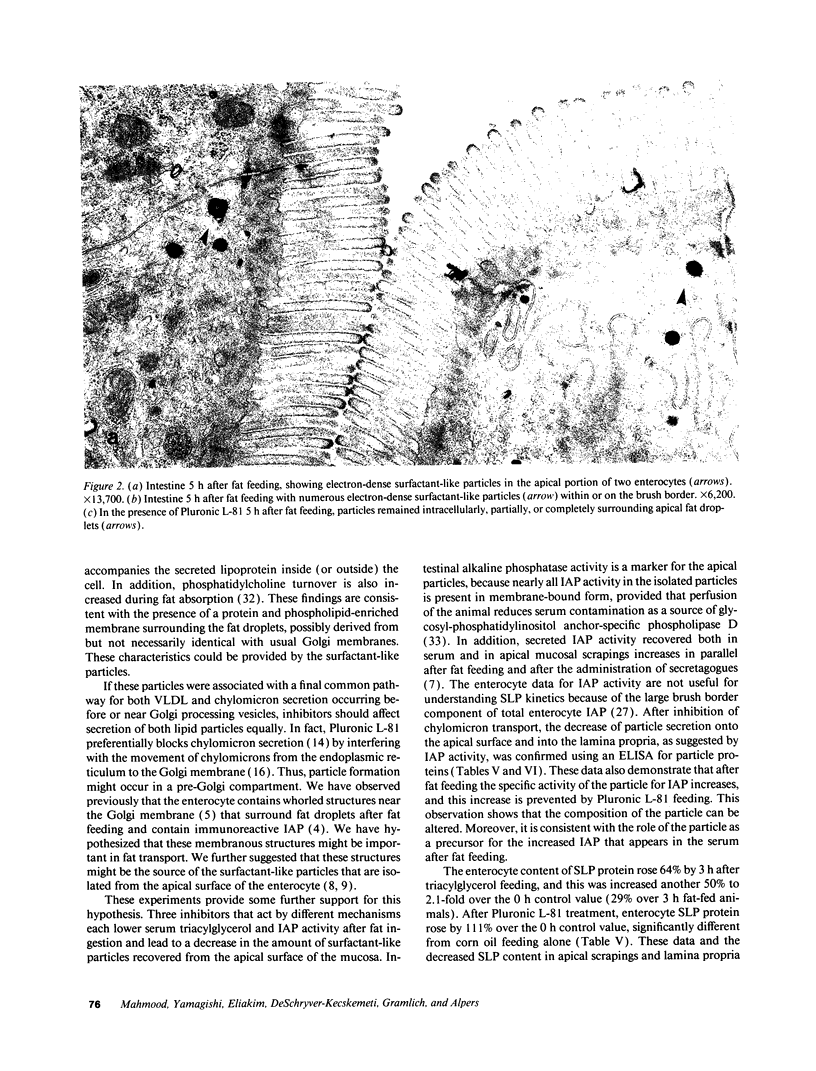
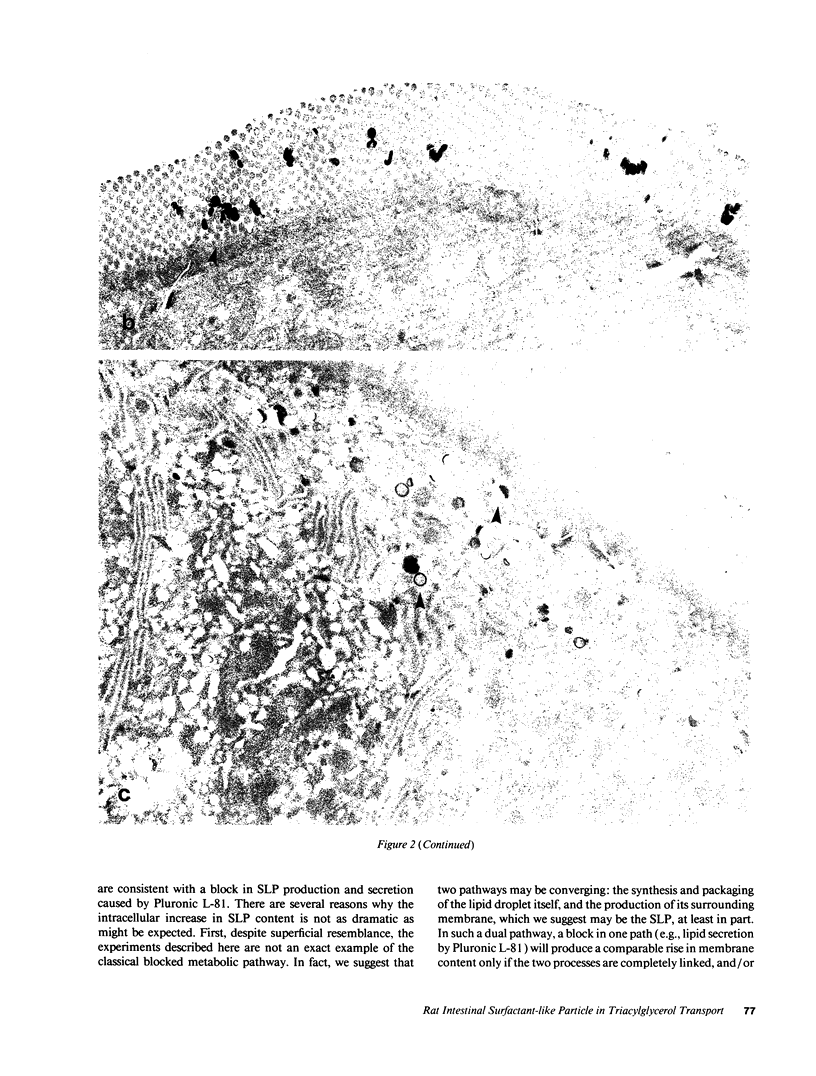
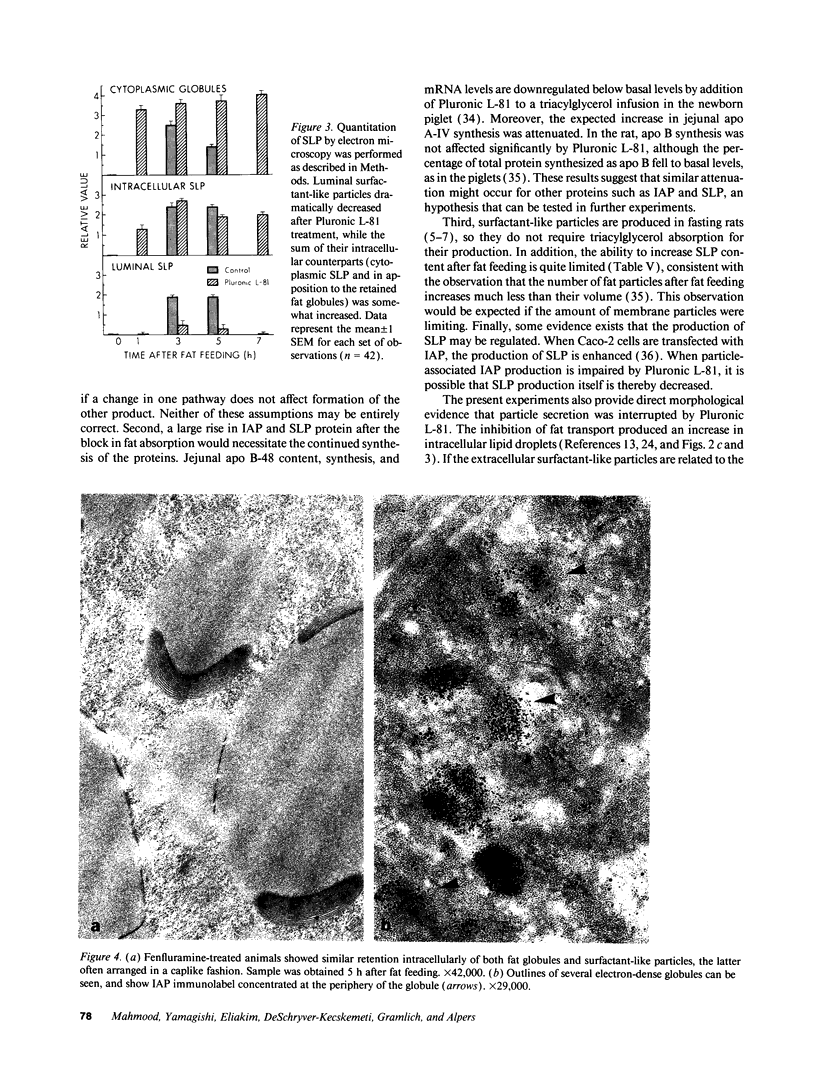
To further examine whether surfactant-like particles (DeSchryver-Kecskemeti, K., R. Eliakim, S. Carroll, W. F. Stenson, M. A. Moxley, and D. H. Alpers. 1989. J. Clin. Invest. 84:1355-1361) were involved in the transepithelial transport of lipid, alkaline phosphatase activity and surfactant-like particle content were measured in apical mucosal scrapings, enterocytes, lamina propria, and serum after inhibition of chylomicron transport. Serum triacylglycerol levels were decreased 60-76% by Pluronic L-81, fenfluramine, and choline deficiency compared with fat-fed controls. 5 h after triacylglycerol feed, alkaline phosphatase activity in all three experimental groups was decreased compared with controls by 52-69% in mucosal scrapings and by 33-72% in serum. A parallel decline (60%) in alkaline phosphatase activity occurred in the lamina propria of Pluronic-treated animals. Total particle content (measured by an ELISA using antiserum against purified particle) after Pluronic treatment was decreased in mucosal scrapings, lamina propria, and serum by 16, 22, and 29% at 3 h and by 33, 40, and 8%, respectively, at 5 h after fat feeding. In contrast, particle content was increased in enterocytes by 29% 3 h and by 8% 5 h after fat feeding. By electron microscopy, enterocytes from Pluronic- and fenfluramine-treated animals exhibited a two- to threefold increase in large intracellular cytoplasmic lipid globules and the appearance of lamellae in apposition, with a marked decrease in the number of surfactant-like particles overlying the brush border. These changes, produced by inhibition of chylomicron transport, in the distribution of surfactant-like particles and particle-bound alkaline phosphatase are consistent with a role for these particles in transepithelial triacylglycerol transport across and out of the enterocyte.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpers D. H., Eliakim R., DeSchryver-Kecskemeti K. Secretion of hepatic and intestinal alkaline phosphatases: similarities and differences. Clin Chim Acta. 1990 Jan 15;186(2):211–223. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(90)90039-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alpers D. H., Lock D. R., Lancaster N., Poksay K., Schonfeld G. Distribution of apolipoproteins A-I and B among intestinal lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1985 Jan;26(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berryman M. A., Rodewald R. D. An enhanced method for post-embedding immunocytochemical staining which preserves cell membranes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 Feb;38(2):159–170. doi: 10.1177/38.2.1688894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizzi A., Veneroni E., Garattini S. Effect of fenfluramine on the intestinal absorption of triglycerides. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 Aug;23(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. D. Effect of intestinal chylomicron secretory blockade on apolipoprotein synthesis in the newborn piglet. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 1;283(Pt 1):81–85. doi: 10.1042/bj2830081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunelle C. W., Bochenek W. J., Abraham R., Kim D. N., Rodgers J. B. Effect of hydrophobic detergent on lipid absorption in the rat and on lipid and sterol balance in the swine. Dig Dis Sci. 1979 Sep;24(9):718–725. doi: 10.1007/BF01314470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSchryver-Kecskemeti K., Eliakim R., Carroll S., Stenson W. F., Moxley M. A., Alpers D. H. Intestinal surfactant-like material. A novel secretory product of the rat enterocyte. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1355–1361. doi: 10.1172/JCI114306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSchryver-Kecskemeti K., Eliakim R., Green K., Alpers D. H. A novel intracellular pathway for rat intestinal digestive enzymes (alkaline phosphatase and sucrase) via a lamellar particle. Lab Invest. 1991 Sep;65(3):365–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliakim R., Becich M. J., Green K., Alpers D. H. Both tissue and serum phospholipases release rat intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):G618–G625. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.4.G618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliakim R., Becich M. J., Green K., Alpers D. H. Developmental expression of intestinal surfactant-like particles in rats. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 1):G269–G279. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1991.261.2.G269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliakim R., DeSchryver-Kecskemeti K., Nogee L., Stenson W. F., Alpers D. H. Isolation and characterization of a small intestinal surfactant-like particle containing alkaline phosphatase and other digestive enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20614–20619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliakim R., Mahmood A., Alpers D. H. Rat intestinal alkaline phosphatase secretion into lumen and serum is coordinately regulated. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 10;1091(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90213-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. I., Nylund B. Intestinal fat digestion, absorption, and transport. A review. Am J Clin Nutr. 1980 May;33(5):1108–1139. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/33.5.1108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern J., Tso P., Mansbach C. M., 2nd Mechanism of lipid mobilization by the small intestine after transport blockade. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):74–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI113604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Fujimoto K., Cardelli J. A., Nutting D. F., Bergstedt S., Tso P. Fat feeding increases size, but not number, of chylomicrons produced by small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1990 Nov;259(5 Pt 1):G709–G719. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1990.259.5.G709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins A. P., Thompson R. P. Trophic effect of Efamol on the rat small-intestinal mucosa. Clin Sci (Lond) 1989 Nov;77(5):555–559. doi: 10.1042/cs0770555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama I., Arai K., Sakagishi Y., Ikezawa H., Komoda T. Blood appearance of rat alkaline phosphatase originating from the duodenum in vitro. J Chromatogr. 1987 Sep 25;420(2):275–286. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(87)80184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Prasad A. R. A phospholipase D specific for the phosphatidylinositol anchor of cell-surface proteins is abundant in plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):980–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Bennett B. D., Morré D. J., Gray M. E., Thistlethwaite W., LeQuire V. S. Lipoproteins associated with the Golgi apparatus isolated from epithelial cells of rat small intestine. Lab Invest. 1971 Nov;25(5):435–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansbach C. M., 2nd, Parthasarathy S. A re-examination of the fate of glyceride-glycerol in neutral lipid absorption and transport. J Lipid Res. 1982 Sep;23(7):1009–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura S., Asakura H., Miyairi M., Morishita T., Ishii H., Tsuchiya M. [Study on the fat absorption and transportation into intestinal lymph of rats--differences in the absorption of saturated and unsaturated long chain fatty acids and the role of intestinal alkaline phosphate (author's transl)]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 1979 Apr;76(4):871–880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nutting D., Hall J., Barrowman J. A., Tso P. Further studies on the mechanism of inhibition of intestinal chylomicron transport by Pluronic L-81. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 22;1004(3):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ockner R. K., Hughes F. B., Isselbacher K. J. Very low density lipoproteins in intestinal lymph: role in triglyceride and cholesterol transport during fat absorption. J Clin Invest. 1969 Dec;48(12):2367–2373. doi: 10.1172/JCI106203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALAY S. L., KARLIN L. J. An electron microscopic study of the intestinal villus. II. The pathway of fat absorption. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 May 25;5(3):373–384. doi: 10.1083/jcb.5.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parlier R. D., Frase S., Mansbach C. M., 2nd Intraenterocyte distribution of absorbed lipid and effects of phosphatidylcholine. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 1):G349–G355. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1989.256.2.G349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. S., Taeusch H. W., Jr, Benson B., Hawgood S. An electrophoretic and immunochemical characterization of human surfactant-associated proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Dec 7;791(2):226–238. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(84)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabesin S. M., Holt P. R. Intestinal lipid absorption: evidence for an intrinsic defect of chylomicron secretion by normal rat distal intestine. Lipids. 1975 Dec;10(12):840–846. doi: 10.1007/BF02532330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. W. Electron microscopic study of intestinal fat absorption in vitro from mixed micelles containing linolenic acid, monoolein, and bile salt. J Lipid Res. 1966 Mar;7(2):307–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift L. L., Soulé P. D., Gray M. E., LeQuire V. S. Intestinal lipoprotein synthesis. Comparison of nascent Golgi lipoproteins from chow-fed and hypercholesterolemic rats. J Lipid Res. 1984 Jan;25(1):1–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi Y., Mizunuma T. Cytochemistry of fat absorption. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;89:115–136. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61301-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tietze C. C., Becich M. J., Engle M., Stenson W. F., Mahmood A., Eliakim R., Alpers D. H. Caco-2 cell transfection by rat intestinal alkaline phosphatase cDNA increases surfactant-like particles. Am J Physiol. 1992 Nov;263(5 Pt 1):G756–G766. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.5.G756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso P., Balint J. A. Formation and transport of chylomicrons by enterocytes to the lymphatics. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jun;250(6 Pt 1):G715–G726. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.250.6.G715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso P., Drake D. S., Black D. D., Sabesin S. M. Evidence for separate pathways of chylomicron and very low-density lipoprotein assembly and transport by rat small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1984 Dec;247(6 Pt 1):G599–G610. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.6.G599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vance J. E., Aasman E. J., Szarka R. Brefeldin A does not inhibit the movement of phosphatidylethanolamine from its sites for synthesis to the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8241–8247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young G. P., Friedman S., Yedlin S. T., Allers D. H. Effect of fat feeding on intestinal alkaline phosphatase activity in tissue and serum. Am J Physiol. 1981 Dec;241(6):G461–G468. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.241.6.G461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young G. P., Yedlin S. T., Alpers D. H. Distribution of soluble and membranous forms of alkaline phosphatase in the small intestine of the rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 17;676(2):257–265. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90194-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young G. P., Yedlin S. T., Alpers D. H. Independent biosynthesis of soluble and membrane-bound alkaline phosphatases in the suckling rat ileum. Biochem J. 1981 Dec 15;200(3):645–654. doi: 10.1042/bj2000645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeisel S. H. Choline deficiency. J Nutr Biochem. 1990 Jul;1(7):332–349. doi: 10.1016/0955-2863(90)90001-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]