Abstract
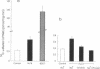
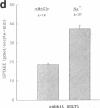
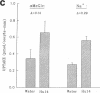
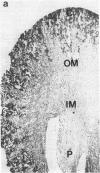
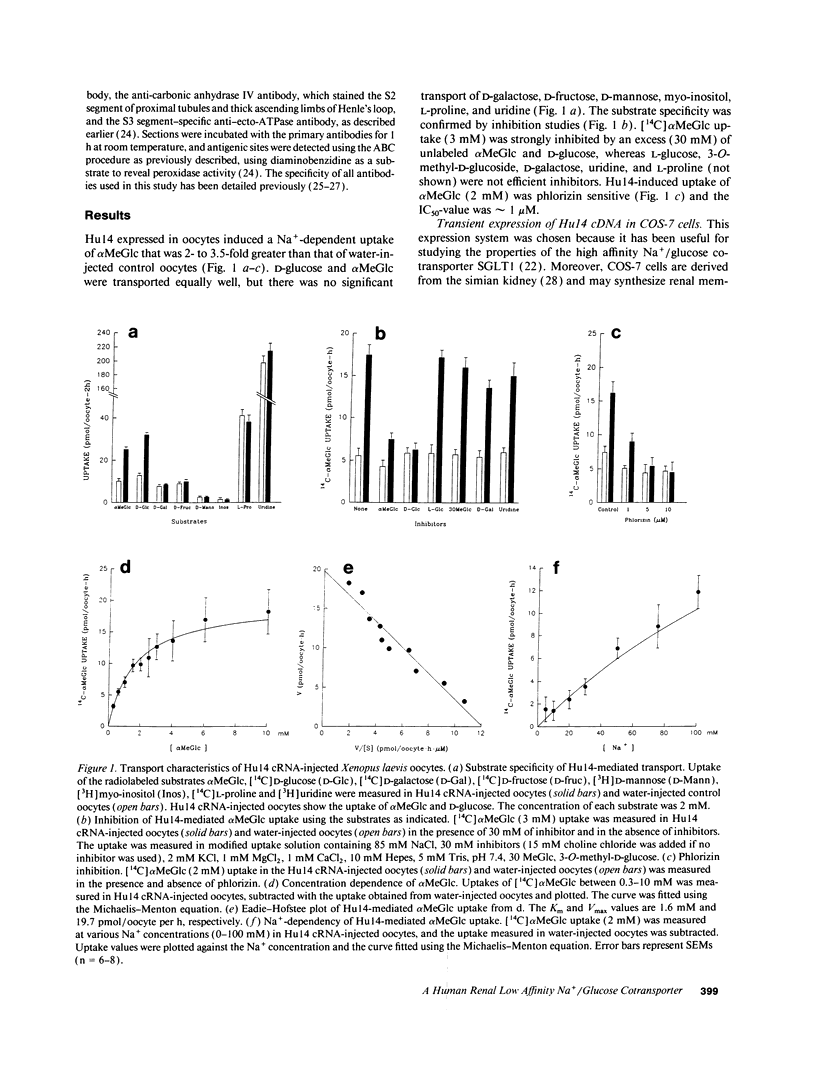
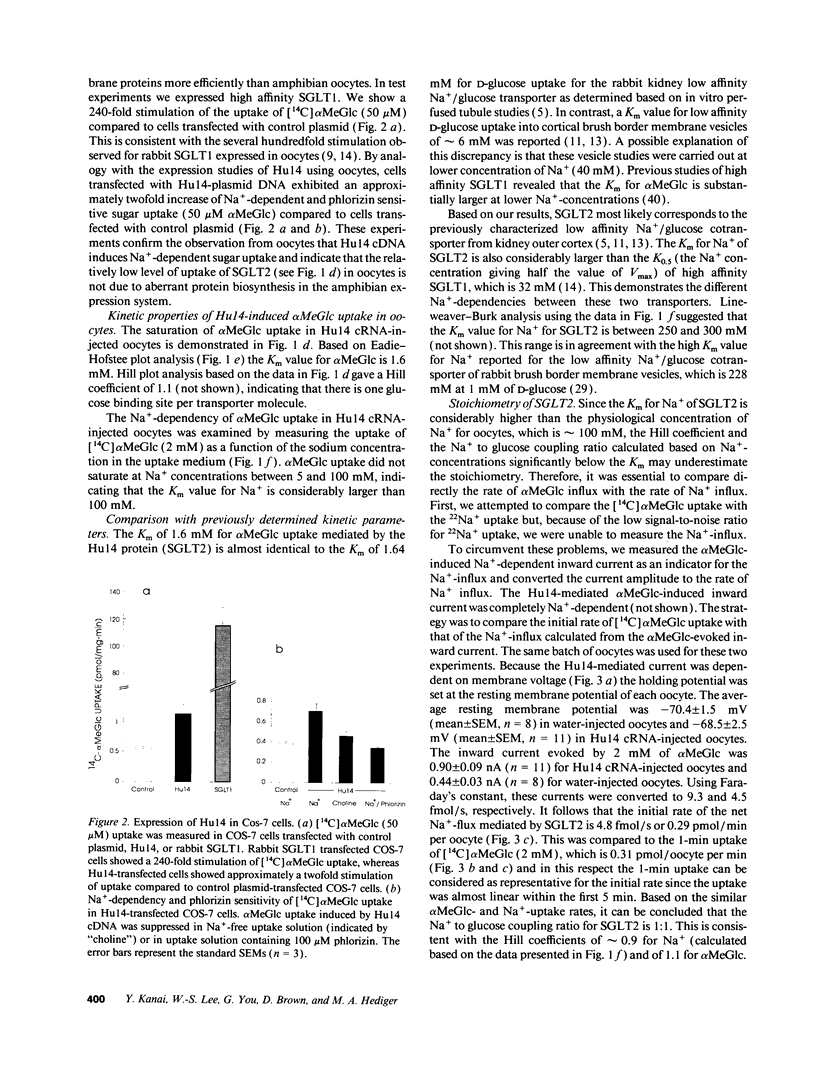
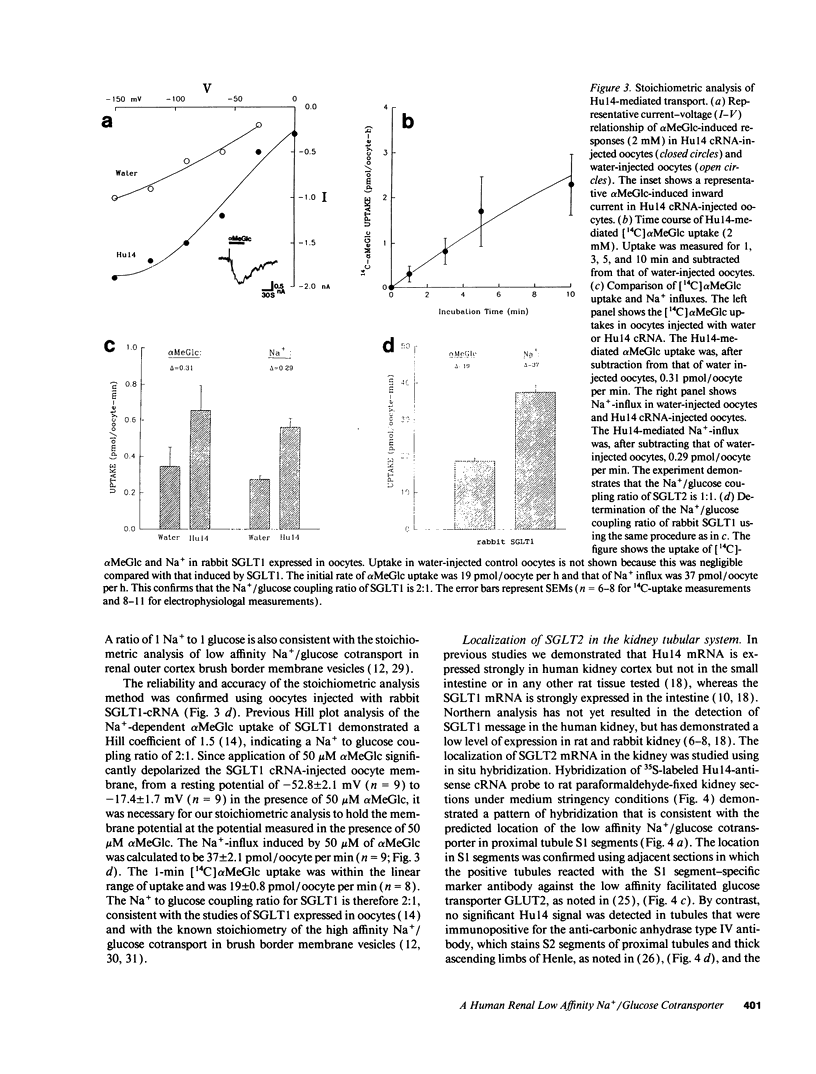
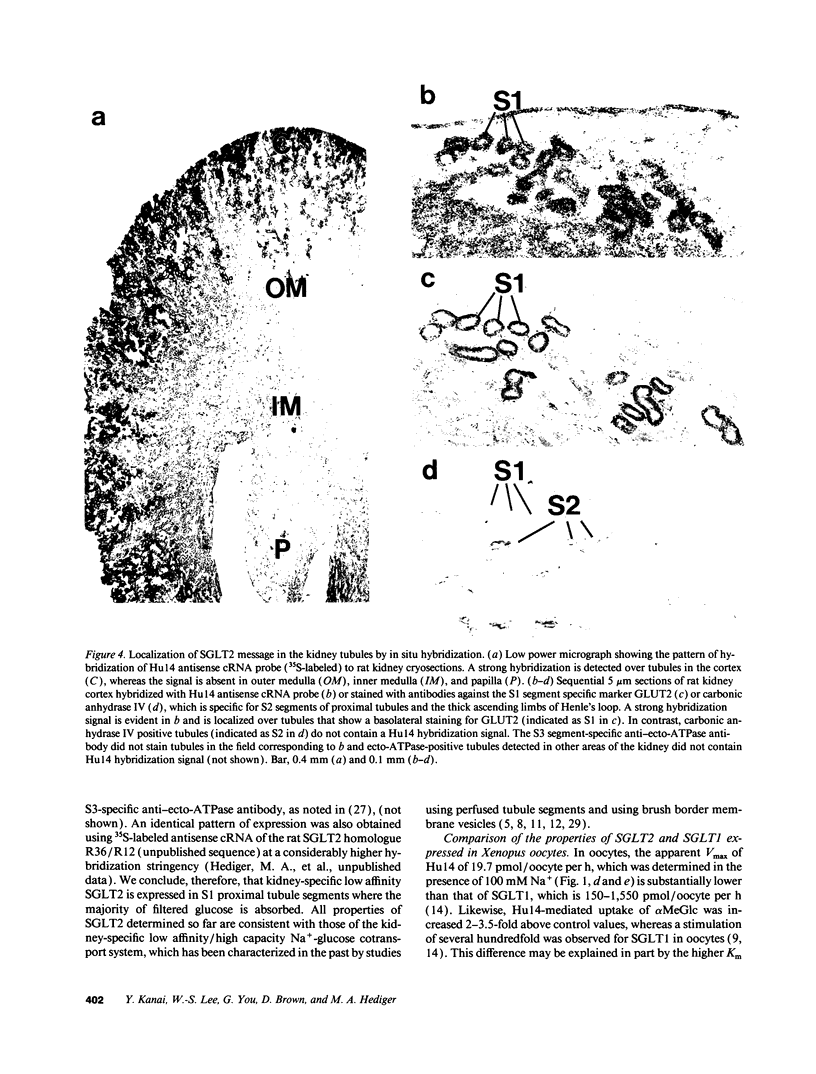
The major reabsorptive mechanism for D-glucose in the kidney is known to involve a low affinity high capacity Na+/glucose cotransporter, which is located in the early proximal convoluted tubule segment S1, and which has a Na+ to glucose coupling ratio of 1:1. Here we provide the first molecular evidence for this renal D-glucose reabsorptive mechanism. We report the characterization of a previously cloned human kidney cDNA that codes for a protein with 59% identity to the high affinity Na+/glucose cotransporter (SGLT1). Using expression studies with Xenopus laevis oocytes we demonstrate that this protein (termed SGLT2) mediates saturable Na(+)-dependent and phlorizin-sensitive transport of D-glucose and alpha-methyl-D-glucopyranoside (alpha MeGlc) with Km values of 1.6 mM for alpha MeGlc and approximately 250 to 300 mM for Na+, consistent with low affinity Na+/glucose cotransport. In contrast to SGLT1, SGLT2 does not transport D-galactose. By comparing the initial rate of [14C]-alpha MeGlc uptake with the Na(+)-influx calculated from alpha MeGlc-evoked inward currents, we show that the Na+ to glucose coupling ratio of SGLT2 is 1:1. Using combined in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry with tubule segment specific marker antibodies, we demonstrate an extremely high level of SGLT2 message in proximal tubule S1 segments. This level of expression was also evident on Northern blots and likely confers the high capacity of this glucose transport system. We conclude that SGLT2 has properties characteristic of the renal low affinity high capacity Na+/glucose cotransporter as previously reported for perfused tubule preparations and brush border membrane vesicles. Knowledge of the structural and functional properties of this major renal Na+/glucose reabsorptive mechanism will advance our understanding of the pathophysiology of renal diseases such as familial renal glycosuria and diabetic renal disorders.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barfuss D. W., Schafer J. A. Differences in active and passive glucose transport along the proximal nephron. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):F322–F332. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1981.241.3.F322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnir B., Lee H. S., Hediger M. A., Wright E. M. Expression and characterization of the intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter in COS-7 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jan 30;1048(1):100–104. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90028-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Zhu X. L., Sly W. S. Localization of membrane-associated carbonic anhydrase type IV in kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7457–7461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee M., Cerami A., Vlassara H. Advanced glycosylation end products in tissue and the biochemical basis of diabetic complications. N Engl J Med. 1988 May 19;318(20):1315–1321. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198805193182007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carney S. L., Wong N. L., Dirks J. H. Acute effects of streptozotocin diabetes on rat renal function. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Jun;93(6):950–961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coady M. J., Pajor A. M., Wright E. M. Sequence homologies among intestinal and renal Na+/glucose cotransporters. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 1):C605–C610. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.4.C605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., Hillman R. E., Patterson J. H., Rosenberg L. E. Renal and intestinal hexose transport in familial glucose-galactose malabsorption. J Clin Invest. 1970 Mar;49(3):576–585. doi: 10.1172/JCI106268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsas L. J., Rosenberg L. E. Familial renal glycosuria: a genetic reappraisal of hexose transport by kidney and intestine. J Clin Invest. 1969 Oct;48(10):1845–1854. doi: 10.1172/JCI106150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannedouche T. P., Delgado A. G., Gnionsahe D. A., Boitard C., Lacour B., Grünfeld J. P. Renal hemodynamics and segmental tubular reabsorption in early type 1 diabetes. Kidney Int. 1990 Apr;37(4):1126–1133. doi: 10.1038/ki.1990.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Budarf M. L., Emanuel B. S., Mohandas T. K., Wright E. M. Assignment of the human intestinal Na+/glucose cotransporter gene (SGLT1) to the q11.2----qter region of chromosome 22. Genomics. 1989 Apr;4(3):297–300. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90333-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Coady M. J., Ikeda T. S., Wright E. M. Expression cloning and cDNA sequencing of the Na+/glucose co-transporter. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):379–381. doi: 10.1038/330379a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Ikeda T., Coady M., Gundersen C. B., Wright E. M. Expression of size-selected mRNA encoding the intestinal Na/glucose cotransporter in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2634–2637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Turk E., Pajor A. M., Wright E. M. Molecular genetics of the human Na+/glucose cotransporter. Klin Wochenschr. 1989 Sep 1;67(17):843–846. doi: 10.1007/BF01717337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hediger M. A., Turk E., Wright E. M. Homology of the human intestinal Na+/glucose and Escherichia coli Na+/proline cotransporters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5748–5752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda T. S., Hwang E. S., Coady M. J., Hirayama B. A., Hediger M. A., Wright E. M. Characterization of a Na+/glucose cotransporter cloned from rabbit small intestine. J Membr Biol. 1989 Aug;110(1):87–95. doi: 10.1007/BF01870995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Hediger M. A. Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature. 1992 Dec 3;360(6403):467–471. doi: 10.1038/360467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai Y., Stelzner M. G., Lee W. S., Wells R. G., Brown D., Hediger M. A. Expression of mRNA (D2) encoding a protein involved in amino acid transport in S3 proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1992 Dec;263(6 Pt 2):F1087–F1092. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.6.F1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich G. A., Randles J. Sodium-sugar coupling stoichiometry in chick intestinal cells. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jul;247(1 Pt 1):C74–C82. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.247.1.C74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A. M., Gupta R. K., Spitzer A. Intracellular sodium in proximal tubules of diabetic rats. Role of glucose. Kidney Int. 1988 Apr;33(4):792–797. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo D. D., Hazama A., Supplisson S., Turk E., Wright E. M. Relaxation kinetics of the Na+/glucose cotransporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5767–5771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mager S., Naeve J., Quick M., Labarca C., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Steady states, charge movements, and rates for a cloned GABA transporter expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90309-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. I., Panayotova-Heiermann M., Feigl G., Schölermann B., Kinne R. K. Sequence comparison of the sodium-D-glucose cotransport systems in rabbit renal and intestinal epithelia. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 2;1089(1):121–123. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pajor A. M., Hirayama B. A., Wright E. M. Molecular evidence for two renal Na+/glucose cotransporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Apr 29;1106(1):216–220. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90241-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parent L., Supplisson S., Loo D. D., Wright E. M. Electrogenic properties of the cloned Na+/glucose cotransporter: I. Voltage-clamp studies. J Membr Biol. 1992 Jan;125(1):49–62. doi: 10.1007/BF00235797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo D., Kimmich G. A. Kinetic analysis of mechanism of intestinal Na+-dependent sugar transport. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):C498–C509. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.5.C498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabolić I., Culić O., Lin S. H., Brown D. Localization of ecto-ATPase in rat kidney and isolated renal cortical membrane vesicles. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 2):F217–F228. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.2.F217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer J. A., Williams J. C., Jr Transport of metabolic substrates by the proximal nephron. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:103–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Lodish H. F., Brown D. Differential localization of two glucose transporter isoforms in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):C286–C294. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk E., Zabel B., Mundlos S., Dyer J., Wright E. M. Glucose/galactose malabsorption caused by a defect in the Na+/glucose cotransporter. Nature. 1991 Mar 28;350(6316):354–356. doi: 10.1038/350354a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Moran A. Further studies of proximal tubular brush border membrane D-glucose transport heterogeneity. J Membr Biol. 1982;70(1):37–45. doi: 10.1007/BF01871587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Moran A. Heterogeneity of sodium-dependent D-glucose transport sites along the proximal tubule: evidence from vesicle studies. Am J Physiol. 1982 Apr;242(4):F406–F414. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1982.242.4.F406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Moran A. Stoichiometric studies of the renal outer cortical brush border membrane D-glucose transporter. J Membr Biol. 1982;67(1):73–80. doi: 10.1007/BF01868649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J., Silverman M. Sugar uptake into brush border vesicles from normal human kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2825–2829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. J. Stoichiometry of cotransport systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;456:10–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb14839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. G., Mohandas T. K., Hediger M. A. Localization of the Na+/glucose cotransporter gene SGLT2 to human chromosome 16 close to the centromere. Genomics. 1993 Sep;17(3):787–789. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. G., Pajor A. M., Kanai Y., Turk E., Wright E. M., Hediger M. A. Cloning of a human kidney cDNA with similarity to the sodium-glucose cotransporter. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 2):F459–F465. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.3.F459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]