Abstract
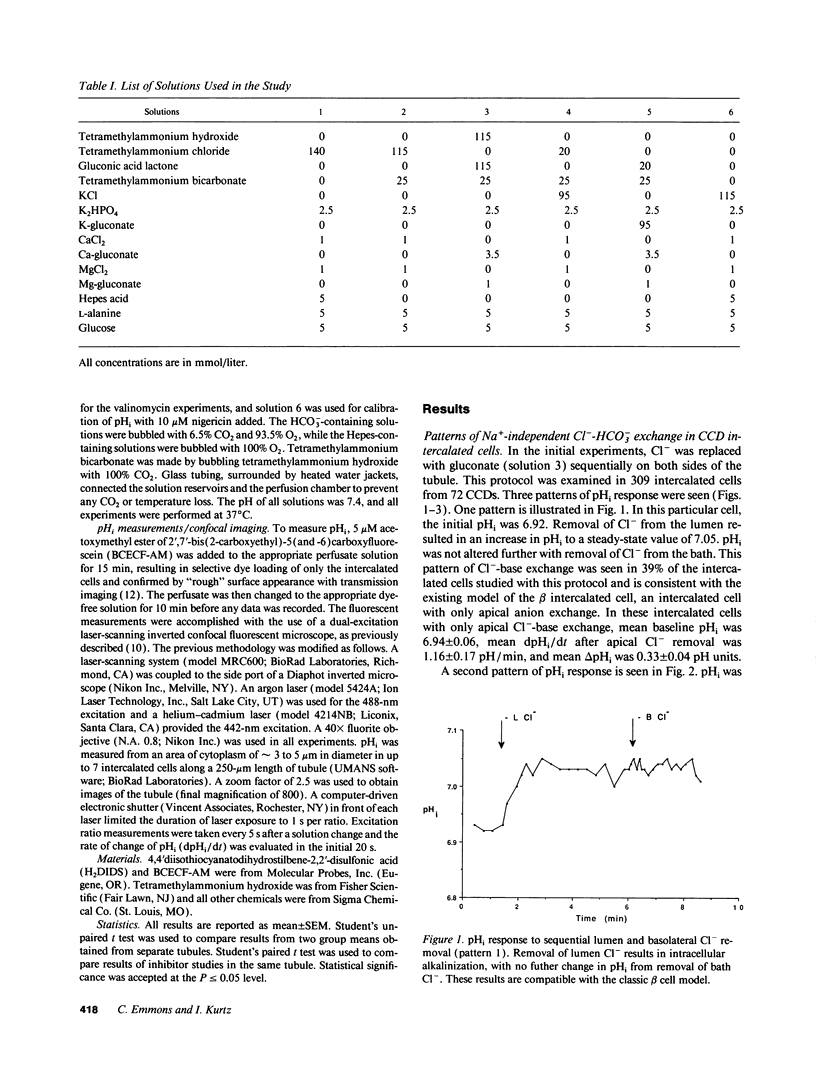
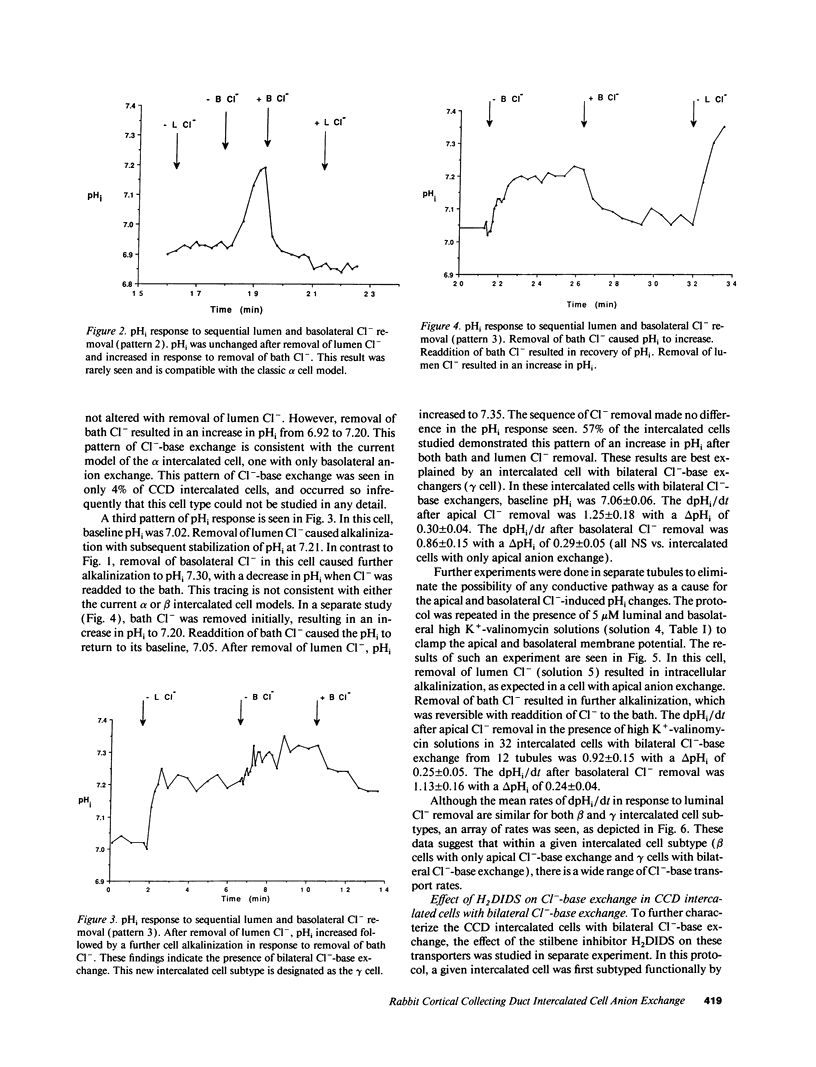
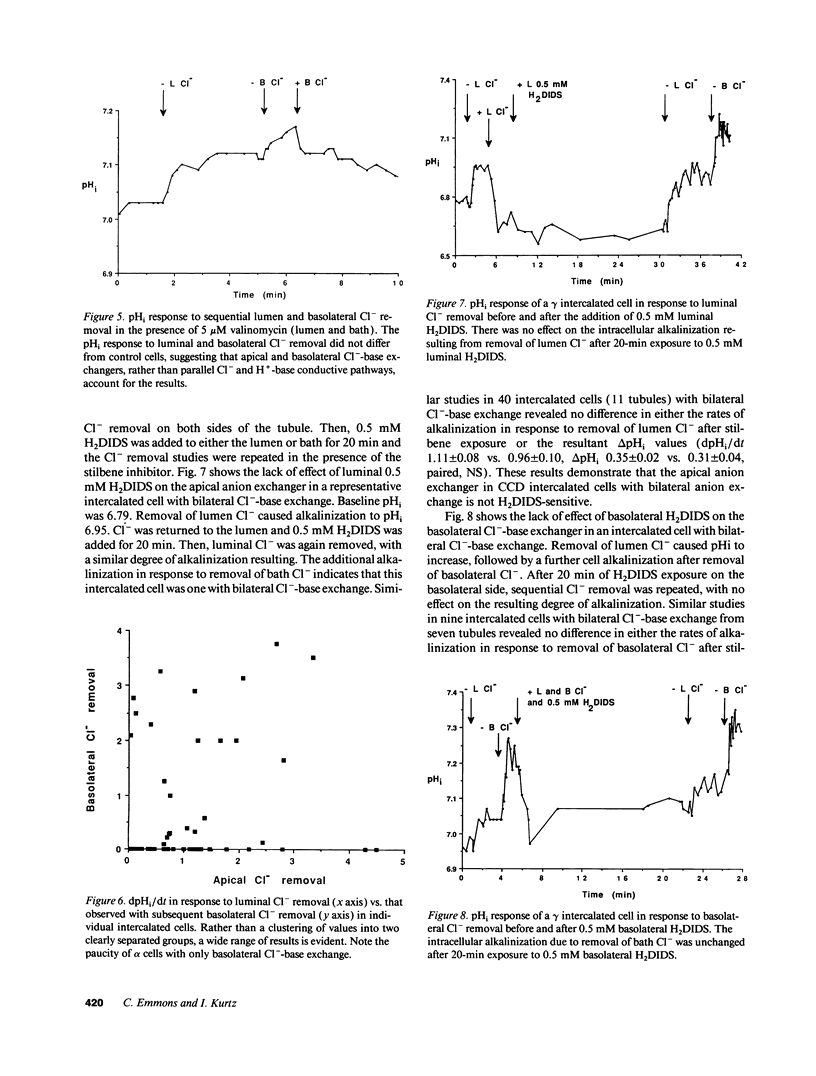
The distribution of Na(+)-independent Cl(-)-HCO3- exchange was studied in individual intercalated cells from in vitro perfused rabbit outer CCDs using dual excitation laser scanning confocal microscopy by measuring the pHi response to sequential removal of Cl- from both sides of the tubule. Three patterns of intracellular pH (pHi) response were observed. 39% of intercalated cells had only apical Cl(-)-HCO3- exchange (beta cell), 4% had only basolateral Cl(-)-HCO3- exchange (alpha cell), and 57% had both apical and basolateral Cl(-)-HCO3- exchange (gamma cell). Valinomycin-high K+ voltage clamping had no effect on the pHi response of intercalated cells with bilateral Cl(-)-HCO3- exchange. Although the mean rates of dpHi/dt following apical Cl- removal were similar in beta cells compared to gamma cells, a wide range of apical rates was seen among individual beta and gamma intercalated cells. Neither the apical nor the basolateral Cl(-)-HCO3- exchanger in gamma cells was inhibited by 0.5 mM H2DIDS. Binding of apical peanut lectin was seen both in beta cells and in gamma cells. In 41% of CCDs with four to seven intercalated cells studied, all intercalated cells were of the same subtype. We conclude that the majority of intercalated cells from the rabbit outer CCD have both apical and basolateral Na(+)-independent Cl(-)-HCO3- exchangers (gamma cells), which are stilbene-insensitive. Intercalated cells with only basolateral Cl(-)-HCO3- exchange are very uncommon in the rabbit outer CCD. There is a tendency for all intercalated cells in a given rabbit outer CCD to be of the same subtype (either all beta cells or all gamma cells), suggesting the presence of CCD intertubule heterogeneity at the same cortical level. This finding may account for intertubule differences in transepithelial H(+)-base transport.
Full text
PDF
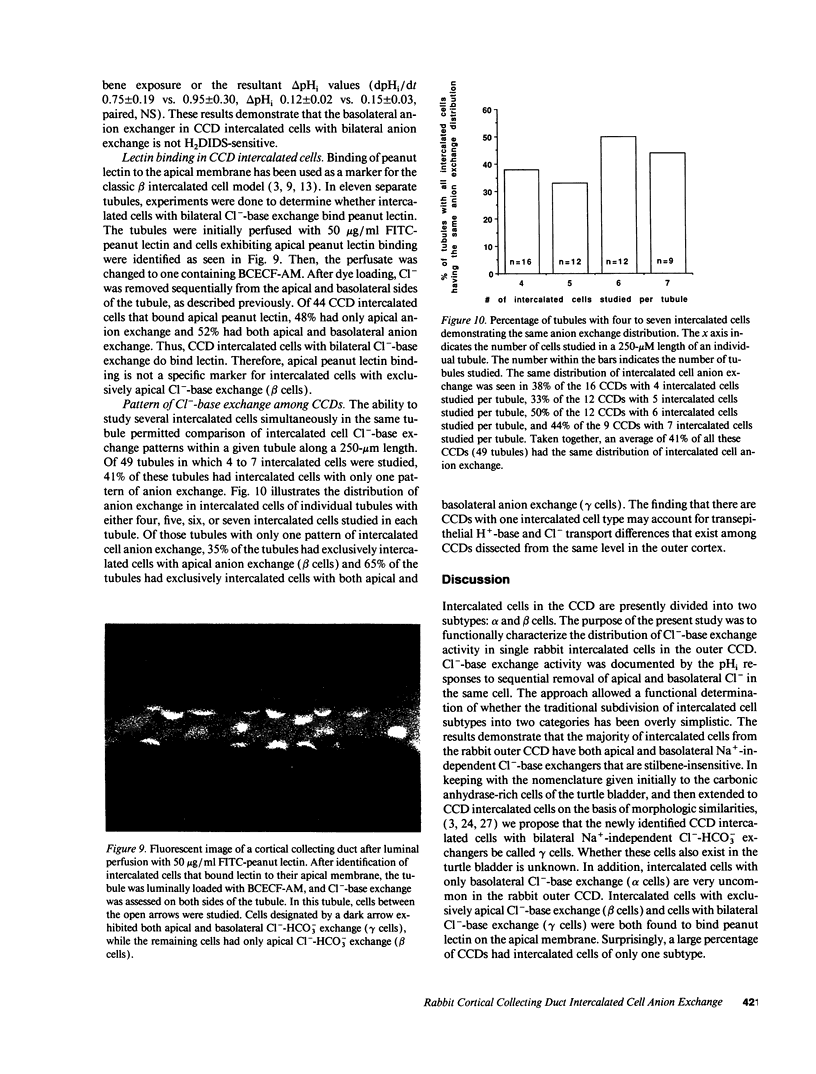


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper S. L., Natale J., Gluck S., Lodish H. F., Brown D. Subtypes of intercalated cells in rat kidney collecting duct defined by antibodies against erythroid band 3 and renal vacuolar H+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5429–5433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton L. J., Maddox D. A., Gennari F. J., Deen W. M. Analysis of PCO2 variations in the renal cortex. I. Single nephron. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 2):F349–F360. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.2.F349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atherton L. J., Maddox D. A., Gennari F. J., Deen W. M. Analysis of PCO2 variations in the renal cortex. II. Countercurrent exchange. Am J Physiol. 1988 Aug;255(2 Pt 2):F361–F371. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.2.F361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastani B., Purcell H., Hemken P., Trigg D., Gluck S. Expression and distribution of renal vacuolar proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatase in response to chronic acid and alkali loads in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jul;88(1):126–136. doi: 10.1172/JCI115268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C. A., Rector F. C., Jr Mechanism of proximal NaCl reabsorption in the proximal tubule of the mammalian kidney. Semin Nephrol. 1991 Mar;11(2):86–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D., Hirsch S., Gluck S. An H+-ATPase in opposite plasma membrane domains in kidney epithelial cell subpopulations. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):622–624. doi: 10.1038/331622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmons C. L., Matsuzaki K., Stokes J. B., Schuster V. L. Axial heterogeneity of rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 2):F498–F505. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.4.F498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuya H., Breyer M. D., Jacobson H. R. Functional characterization of alpha- and beta-intercalated cell types in rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1991 Sep;261(3 Pt 2):F377–F385. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.3.F377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Tisher C. C., Linser P. J., Madsen K. M. Ultrastructural localization of carbonic anhydrase II in subpopulations of intercalated cells of the rat kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1990 Sep;1(3):245–256. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V13245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koeppen B. M., Biagi B. A., Giebisch G. H. Intracellular microelectrode characterization of the rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jan;244(1):F35–F47. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1983.244.1.F35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinney T. D., Burg M. B. Bicarbonate transport by rabbit cortical collecting tubules. Effect of acid and alkali loads in vivo on transport in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1977 Sep;60(3):766–768. doi: 10.1172/JCI108830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muto S., Yasoshima K., Yoshitomi K., Imai M., Asano Y. Electrophysiological identification of alpha- and beta-intercalated cells and their distribution along the rabbit distal nephron segments. J Clin Invest. 1990 Dec;86(6):1829–1839. doi: 10.1172/JCI114913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridderstrale Y., Kashgarian M., Koeppen B., Giebisch G., Stetson D., Ardito T., Stanton B. Morphological heterogeneity of the rabbit collecting duct. Kidney Int. 1988 Nov;34(5):655–670. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom S. C., Weinman E. J., O'Neil R. G. Microelectrode assessment of chloride-conductive properties of cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1984 Aug;247(2 Pt 2):F291–F302. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1984.247.2.F291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satlin L. M., Schwartz G. J. Cellular remodeling of HCO3(-)-secreting cells in rabbit renal collecting duct in response to an acidic environment. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1279–1288. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Bonsib S. M., Jennings M. L. Two types of collecting duct mitochondria-rich (intercalated) cells: lectin and band 3 cytochemistry. Am J Physiol. 1986 Sep;251(3 Pt 1):C347–C355. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.251.3.C347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate-stimulated bicarbonate secretion in rabbit cortical collecting tubules. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jun;75(6):2056–2064. doi: 10.1172/JCI111925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Fejes-Tóth G., Naray-Fejes-Tóth A., Gluck S. Colocalization of H(+)-ATPase and band 3 anion exchanger in rabbit collecting duct intercalated cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Apr;260(4 Pt 2):F506–F517. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.260.4.F506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster V. L., Stokes J. B. Chloride transport by the cortical and outer medullary collecting duct. Am J Physiol. 1987 Aug;253(2 Pt 2):F203–F212. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.253.2.F203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Barasch J., Al-Awqati Q. Plasticity of functional epithelial polarity. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):368–371. doi: 10.1038/318368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz G. J., Satlin L. M., Bergmann J. E. Fluorescent characterization of collecting duct cells: a second H+-secreting type. Am J Physiol. 1988 Nov;255(5 Pt 2):F1003–F1014. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.5.F1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Star R. A., Burg M. B., Knepper M. A. Bicarbonate secretion and chloride absorption by rabbit cortical collecting ducts. Role of chloride/bicarbonate exchange. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1123–1130. doi: 10.1172/JCI112067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetson D. L., Steinmetz P. R. Alpha and beta types of carbonic anhydrase-rich cells in turtle bladder. Am J Physiol. 1985 Oct;249(4 Pt 2):F553–F565. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.4.F553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Kurtz I. H+/base transport in principal cells characterized by confocal fluorescence imaging. Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 1):C365–C373. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner I. D., Hamm L. L. Regulation of intracellular pH in the rabbit cortical collecting tubule. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jan;85(1):274–281. doi: 10.1172/JCI114423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner I. D., Hamm L. L. Use of fluorescent dye BCECF to measure intracellular pH in cortical collecting tubule. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):F957–F964. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1989.256.5.F957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasoshima K., Satlin L. M., Schwartz G. J. Adaptation of rabbit cortical collecting duct to in vitro acid incubation. Am J Physiol. 1992 Oct;263(4 Pt 2):F749–F756. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.263.4.F749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]