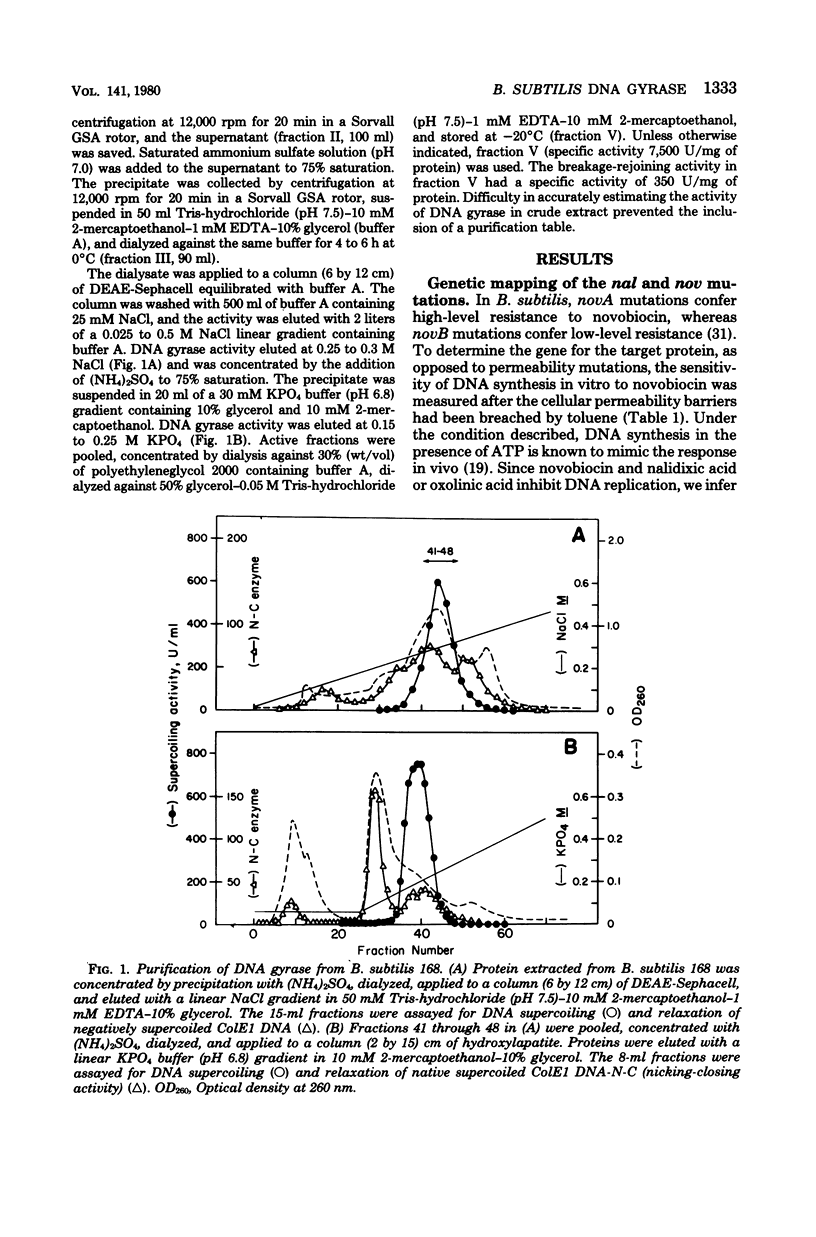
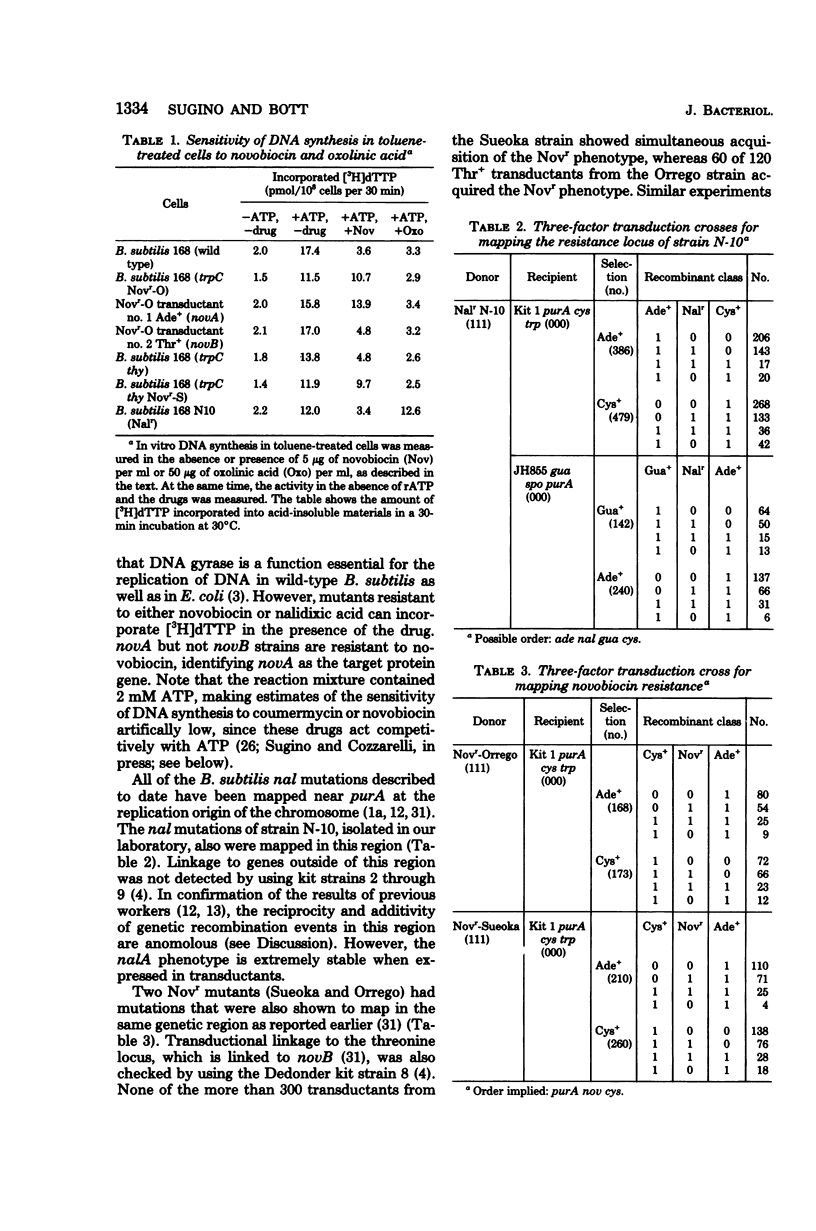
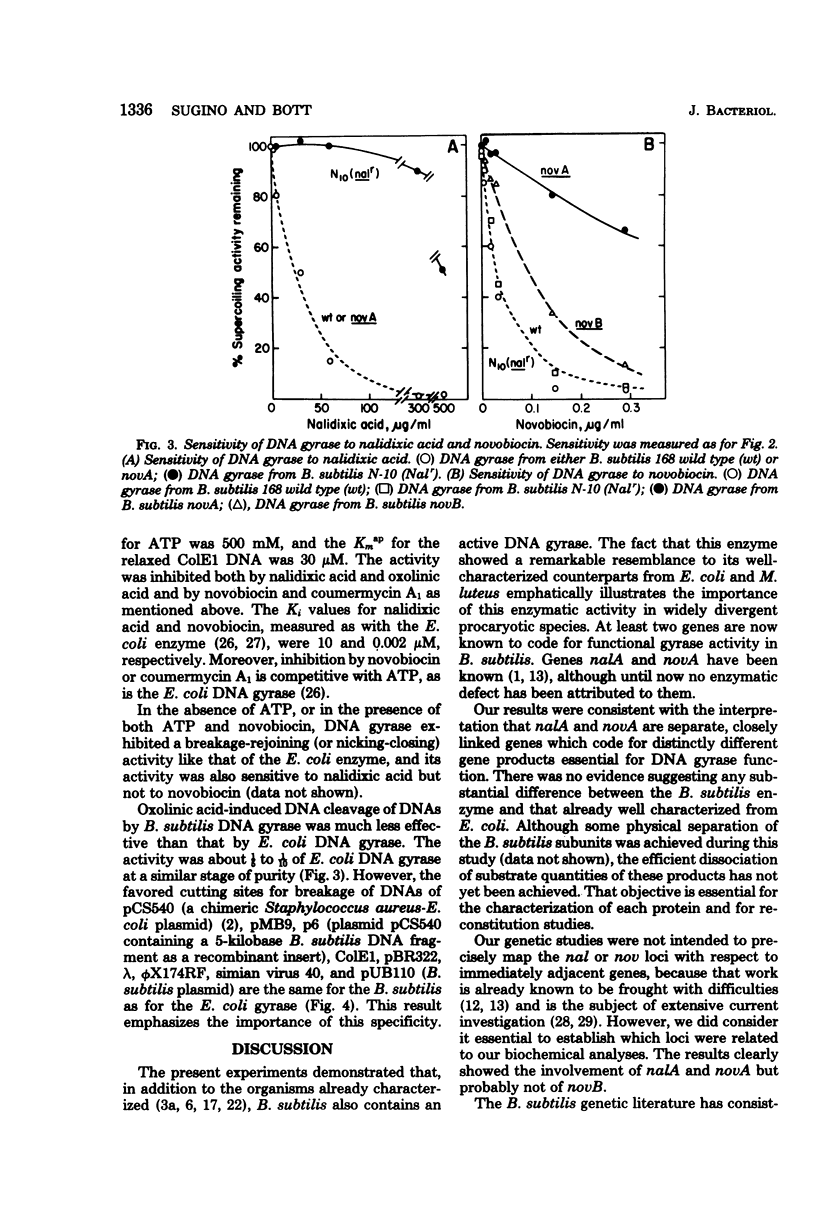
Abstract
Bacillus subtilis 168 was shown to contain a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) gyrase activity which closely resembled those of the enzymes isolated from Escherichia coli and Micrococcus luteus in its enzymatic requirements, substrate specificity, and sensitivity to several antibiotics. The enzyme was purified from the wild type and nalidixic acid-resistant and novobiocin-resistant mutants of B. subtilis and was functionally characterized in vitro. The genetic loci nalA and novA but not novB were shown to code for portions of the functional gyrase. Enzyme from the antibiotic-resistant mutants was resistant to the drug in vitro. The most striking observation was the remarkable similarity between the B. subtilis enzyme and other DNA gyrases, especially with respect to the oxolinic acid-induced DNA cleavage in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. All of the enzymes appeared to possess the same specificity of cutting sites regardless of the source or type of DNA used. This result implies that gyrase binding to DNA is highly specific.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown P. O., Peebles C. L., Cozzarelli N. R. A topoisomerase from Escherichia coli related to DNA gyrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6110–6114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R. DNA gyrase and the supercoiling of DNA. Science. 1980 Feb 29;207(4434):953–960. doi: 10.1126/science.6243420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R. The mechanism of action of inhibitors of DNA synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:641–668. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dedonder R. A., Lepesant J. A., Lepesant-Kejzlarová J., Billault A., Steinmetz M., Kunst F. Construction of a kit of reference strains for rapid genetic mapping in Bacillus subtilis 168. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):989–993. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.989-993.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. I. Nalidixic acid resistance: a second genetic character involved in DNA gyrase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4772–4776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Nash H. A. DNA gyrase: an enzyme that introduces superhelical turns into DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3872–3876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellert M., O'Dea M. H., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Novobiocin and coumermycin inhibit DNA supercoiling catalyzed by DNA gyrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Keynan A. Independence of Bacillus subtilis spore outgrowth from DNA synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):111–116. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.111-116.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottfried M., Orrego C., Keynan A., Halvorson H. O. Specific inhibition of outgrowth of Bacillus subtilis spores by novobiocin. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):314–319. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.314-319.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hane M. W., Wood T. H. Escherichia coli K-12 mutants resistant to nalidixic acid: genetic mapping and dominance studies. J Bacteriol. 1969 Jul;99(1):238–241. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.1.238-241.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins N. P., Peebles C. L., Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. Purification of subunits of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase and reconstitution of enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1773–1777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A., Barat M., Anagnostopoulos C. Transformation and transduction in recombination-defective mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1925-1937.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreuzer K. N., McEntee K., Geballe A. P., Cozzarelli N. R. Lambda transducing phages for the nalA gene of Escherichia coli and conditional lethal nalA mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Nov 29;167(2):129–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00266906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Wang J. C. Micrococcus luteus DNA gyrase: active components and a model for its supercoiling of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2098–2102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushita T., White K. P., Sueoka N. Chromosom replication in toluenized Bacillus subtilis cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Jul 28;232(30):111–114. doi: 10.1038/newbio232111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuuchi K., O'Dea M. H., Gellert M. DNA gyrase: subunit structure and ATPase activity of the purified enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5960–5963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Seiki M., Yoshikawa H. Effect of novobiocin on initiation of DNA replication in Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):702–704. doi: 10.1038/281702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Higgins N. P., Kreuzer K. N., Morrison A., Brown P. O., Sugino A., Cozzarelli N. R. Structure and activities of Escherichia coli DNA gyrase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):41–52. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Kubo M., Imamoto F. Promoter-specific inhibition of transcription by antibiotics which act on DNA gyrase. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):420–423. doi: 10.1038/275420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudenbauer W. L. Replication of small plasmids in extracts of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Jun 15;145(3):273–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00325823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Higgins N. P., Brown P. O., Peebles C. L., Cozzarelli N. R. Energy coupling in DNA gyrase and the mechanism of action of novobiocin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4838–4842. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Peebles C. L., Kreuzer K. N., Cozzarelli N. R. Mechanism of action of nalidixic acid: purification of Escherichia coli nalA gene product and its relationship to DNA gyrase and a novel nicking-closing enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Chen S. M., Hoch J. A. Genetic analysis of a class of polymyxin resistant partial revertants of stage O sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis: map of the chromosome region near the origin of replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 23;173(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00267691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Sheflett M., Hoch J. A. New cluster of ribosomal genes in Bacillus subtilis with regulatory role in sporulation. Nature. 1978 Mar 9;272(5649):179–181. doi: 10.1038/272179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]