Abstract
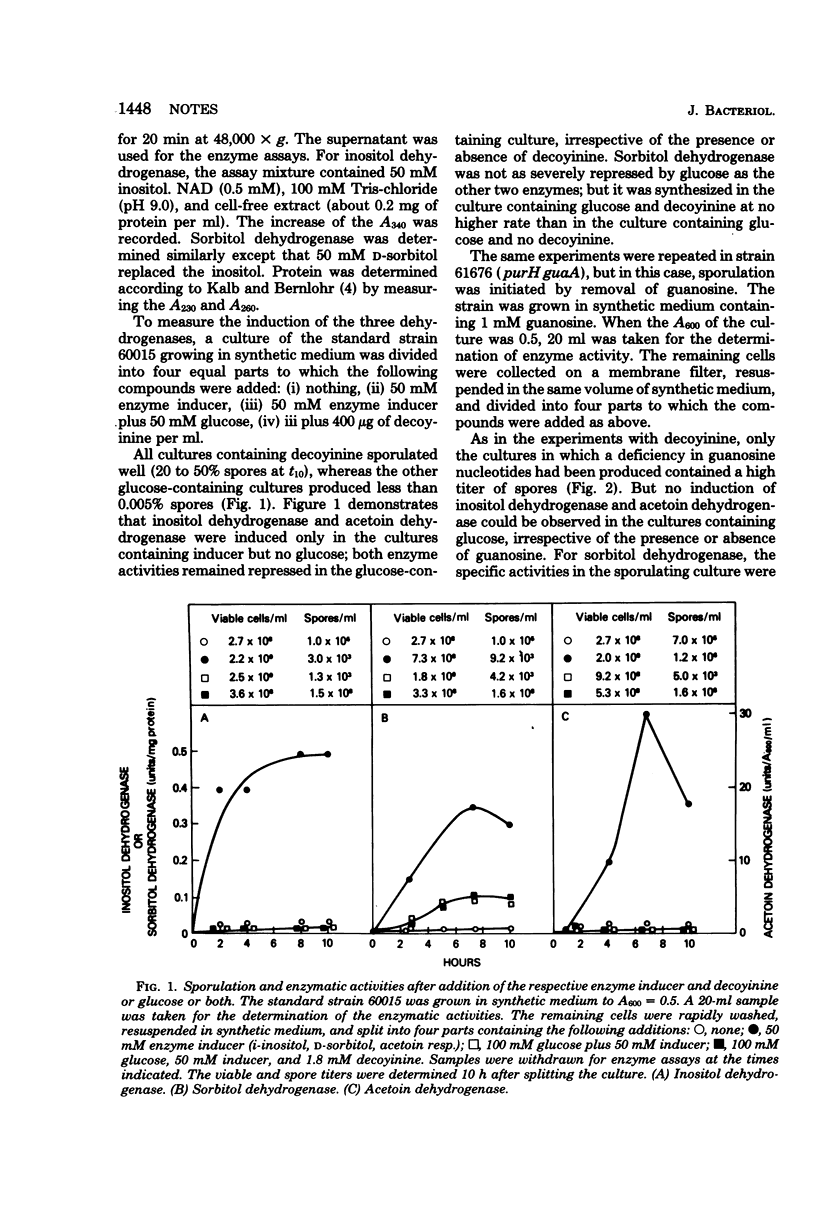
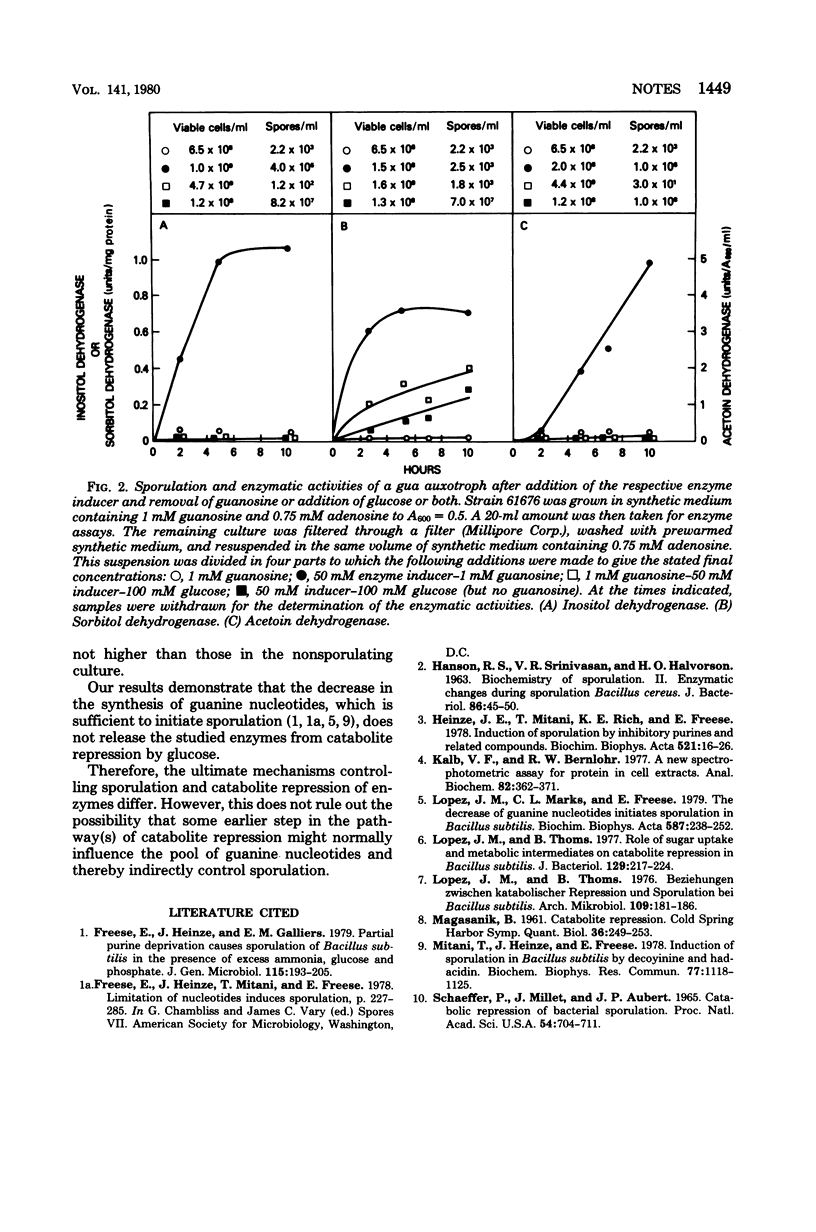
In the presence of excess glucose, a decrease of guanine nucleotides in Bacillus subtilis initiated sporulation but did not prevent catabolite repression of three enzymes. Therefore, the ultimate mechanism(s) repressing enzyme synthesis differs from that suppressing sporulation.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Freese E., Heinze J. E., Galliers E. M. Partial purine deprivation causes sporulation of Bacillus subtilis in the presence of excess ammonia, glucose and phosphate. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Nov;115(1):193–205. doi: 10.1099/00221287-115-1-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON R. S., SRINIVASAN V. R., HALVORSON H. O. BIOCHEMISTRY OF SPORULATION. II. ENZYMATIC CHANGES DURING SPORULATION OF BACILLUS CEREUS. J Bacteriol. 1963 Jul;86:45–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.1.45-50.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinze J. E., Mitani T., Rich K. E., Freese E. Induction of sporulation by inhibitory purines and related compounds. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 21;521(1):16–26. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(78)90245-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb V. F., Jr, Bernlohr R. W. A new spectrophotometric assay for protein in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(2):362–371. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. M., Marks C. L., Freese E. The decrease of guanine nucleotides initiates sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 4;587(2):238–252. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez J. M., Thoms B. Role of sugar uptake and metabolic intermediates on catabolite repression in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jan;129(1):217–224. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.1.217-224.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López J. M., Thoms B. Beziehungen zwischen katabolischer Repression und Sporulation bei Bacillus subtilis. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Aug;109(1-2):181–186. doi: 10.1007/BF00425133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGASANIK B. Catabolite repression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1961;26:249–256. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1961.026.01.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitani T., Heinze J. E., Freese E. Induction of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis by decoyinine or hadacidin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):1118–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80094-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


