Abstract
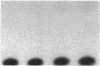
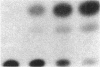
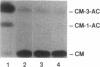
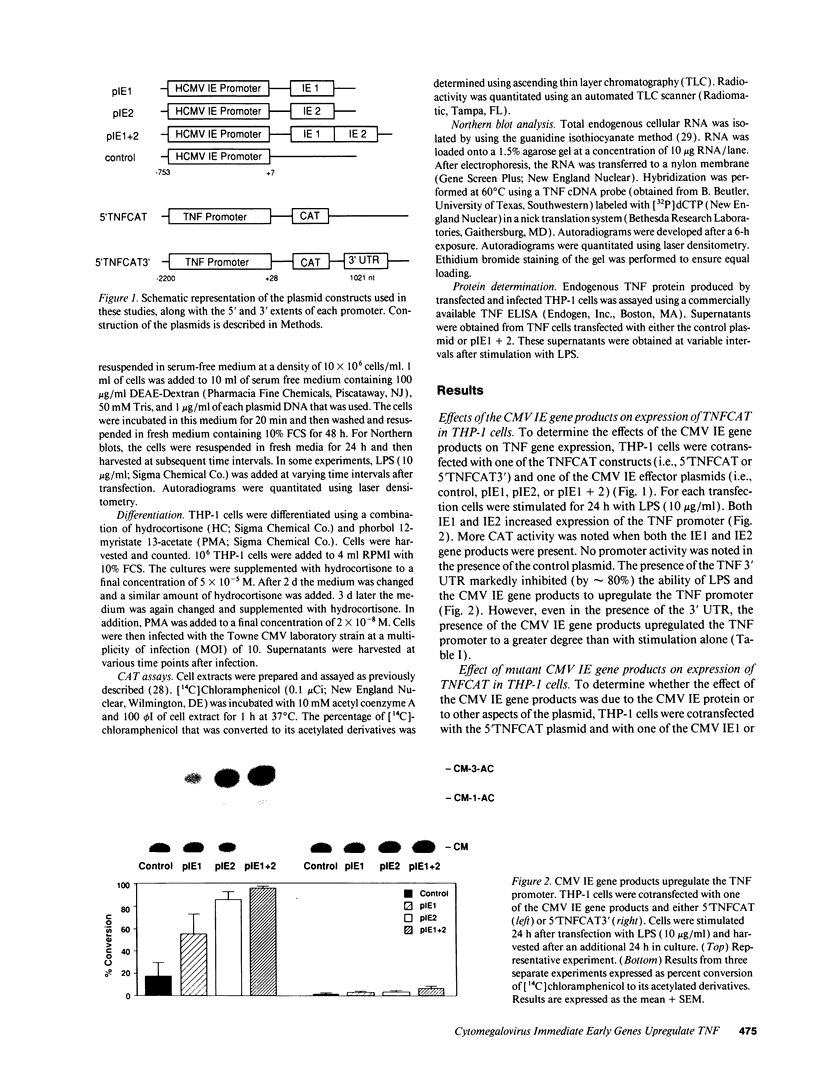
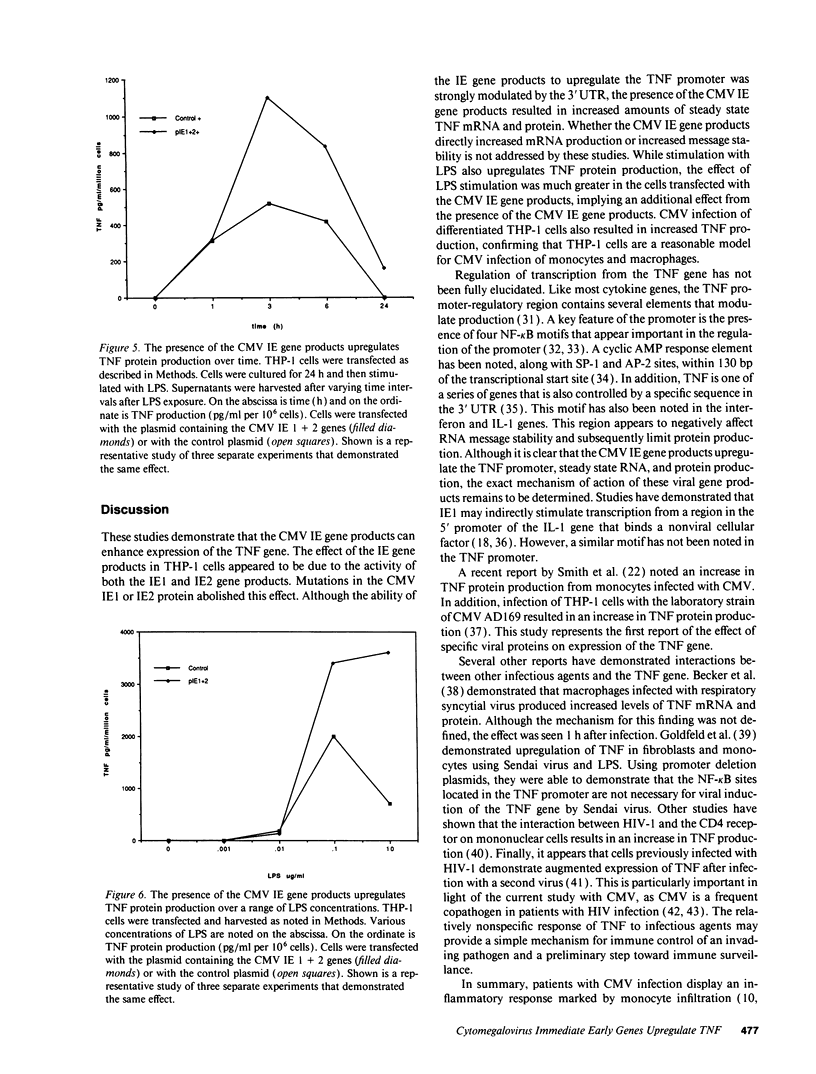
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is an important cause of disease in the immunocompromised patient and CMV infection is associated with predominantly mononuclear inflammatory response. Since products of the CMV immediate early (IE) gene region are potent trans-activators, we used the monocyte cell line THP-1 and a transient transfection assay to determine if these viral proteins upregulate expression of the TNF gene. The IE genes of CMV upregulated TNF gene activity as judged by increases in promoter activity, steady state mRNA, and protein production. The presence or absence of the 3' untranslated region of the TNF gene did not affect gene expression induced by the IE gene products. These studies suggest that activation of TNF gene expression by the CMV IE gene products may, in part, account for the inflammatory response associated with CMV infections.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker S., Quay J., Soukup J. Cytokine (tumor necrosis factor, IL-6, and IL-8) production by respiratory syncytial virus-infected human alveolar macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4307–4312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Brown T. A CAT reporter construct allows ultrasensitive estimation of TNF synthesis, and suggests that the TNF gene has been silenced in non-macrophage cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1991 Apr;87(4):1336–1344. doi: 10.1172/JCI115137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Cachectin and tumour necrosis factor as two sides of the same biological coin. Nature. 1986 Apr 17;320(6063):584–588. doi: 10.1038/320584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Cerami A. Tumor necrosis, cachexia, shock, and inflammation: a common mediator. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:505–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Greenwald D., Hulmes J. D., Chang M., Pan Y. C., Mathison J., Ulevitch R., Cerami A. Identity of tumour necrosis factor and the macrophage-secreted factor cachectin. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):552–554. doi: 10.1038/316552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee S. N., Fiala M., Weiner J., Stewart J. A., Stacey B., Warmer N. Primary cytomegalovirus and opportunistic infections. Incidence in renal transplant recipients. JAMA. 1978 Nov 24;240(22):2446–2449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Corey G. R. Cytomegalovirus infection in the normal host. Medicine (Baltimore) 1985 Mar;64(2):100–114. doi: 10.1097/00005792-198503000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collart M. A., Baeuerle P., Vassalli P. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha transcription in macrophages: involvement of four kappa B-like motifs and of constitutive and inducible forms of NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crump J. W., Geist L. J., Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Stinski M. F., Hunninghake G. W. The immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus require only proximal promoter elements to upregulate expression of interleukin-1 beta. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Jun;6(6):674–677. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/6.6.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Addario M., Roulston A., Wainberg M. A., Hiscott J. Coordinate enhancement of cytokine gene expression in human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected promonocytic cells. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6080–6089. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6080-6089.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. G., Kenney S. C., Kamine J., Pagano J. S., Huang E. S. Immediate-early gene region of human cytomegalovirus trans-activates the promoter of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8642–8646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew W. L. Cytomegalovirus infection in patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1988 Aug;158(2):449–456. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.2.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drouet C., Shakhov A. N., Jongeneel C. V. Enhancers and transcription factors controlling the inducibility of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha promoter in primary macrophages. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1694–1700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economou J. S., Rhoades K., Essner R., McBride W. H., Gasson J. C., Morton D. L. Genetic analysis of the human tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin promoter region in a macrophage cell line. J Exp Med. 1989 Jul 1;170(1):321–326. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geist L. J., Monick M. M., Stinski M. F., Hunninghake G. W. The immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus upregulate expression of the interleukin-2 and interleukin-2 receptor genes. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1991 Sep;5(3):292–296. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/5.3.292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfeld A. E., Doyle C., Maniatis T. Human tumor necrosis factor alpha gene regulation by virus and lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9769–9773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths P. D., Grundy J. E. Molecular biology and immunology of cytomegalovirus. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 15;241(2):313–324. doi: 10.1042/bj2410313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeier C., Walker S. M., Sissons P. J., Sinclair J. H. The 72K IE1 and 80K IE2 proteins of human cytomegalovirus independently trans-activate the c-fos, c-myc and hsp70 promoters via basal promoter elements. J Gen Virol. 1992 Sep;73(Pt 9):2385–2393. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-9-2385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermiston T. W., Malone C. L., Witte P. R., Stinski M. F. Identification and characterization of the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early region 2 gene that stimulates gene expression from an inducible promoter. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3214–3221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3214-3221.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Monks B. G., Geist L. J., Monick M. M., Monroy M. A., Stinski M. F., Webb A. C., Dayer J. M., Auron P. E., Fenton M. J. The functional importance of a cap site-proximal region of the human prointerleukin 1 beta gene is defined by viral protein trans-activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3439–3448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto G. K., Monick M. M., Clark B. D., Auron P. E., Stinski M. F., Hunninghake G. W. Modulation of interleukin 1 beta gene expression by the immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1853–1857. doi: 10.1172/JCI114645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. A., Mills J. Serious cytomegalovirus disease in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Clinical findings, diagnosis, and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):585–594. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malone C. L., Vesole D. H., Stinski M. F. Transactivation of a human cytomegalovirus early promoter by gene products from the immediate-early gene IE2 and augmentation by IE1: mutational analysis of the viral proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1498–1506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1498-1506.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill J. E., Koyanagi Y., Chen I. S. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha can be induced from mononuclear phagocytes by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 binding to the CD4 receptor. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4404–4408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4404-4408.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. D., Flournoy N., Thomas E. D. Risk factors for cytomegalovirus infection after human marrow transplantation. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):478–488. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monick M. M., Geist L. J., Stinski M. F., Hunninghake G. W. The immediate early genes of human cytomegalovirus upregulate expression of the cellular genes myc and fos. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Sep;7(3):251–256. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb/7.3.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., McGlave P., Ramsay N. K., Rhame F., Cohen E., Perry G. S., 3rd, Goldman A. I., Kersey J. A prospective study of infectious diseases following bone marrow transplantation: emergence of Aspergillus and Cytomegalovirus as the major causes of mortality. Infect Control. 1983 Mar-Apr;4(2):81–89. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700057805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., O'Hare P., Sha L., LaFemina R. L., Hayward G. S. trans-activation and autoregulation of gene expression by the immediate-early region 2 gene products of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1167–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1167-1179.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., Strieter R. M., Eskandari M. K., Nguyen D. T., Genord M. A., Raiford C. L., Kunkel S. L. Role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in lipopolysaccharide-induced pathologic alterations. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jan;136(1):49–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Saini S. S., Raffeld M., Manischewitz J. F., Wahl S. M. Cytomegalovirus induction of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by human monocytes and mucosal macrophages. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1642–1648. doi: 10.1172/JCI116035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Stinski M. F. Autoregulation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):676–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.676-682.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F., Roehr T. J. Activation of the major immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus by cis-acting elements in the promoter-regulatory sequence and by virus-specific trans-acting components. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):431–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.431-441.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tevethia M. J., Spector D. J., Leisure K. M., Stinski M. F. Participation of two human cytomegalovirus immediate early gene regions in transcriptional activation of adenovirus promoters. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):276–285. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90119-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Wei H., Manogue K. R., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Nguyen H. T., Kuo G. C., Beutler B., Cotran R. S., Cerami A. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia, and inflammation. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1211–1227. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turtinen L. W., Assimacopoulos A., Haase A. T. Increased monokines in cytomegalovirus infected myelomonocytic cell cultures. Microb Pathog. 1989 Aug;7(2):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]