Abstract
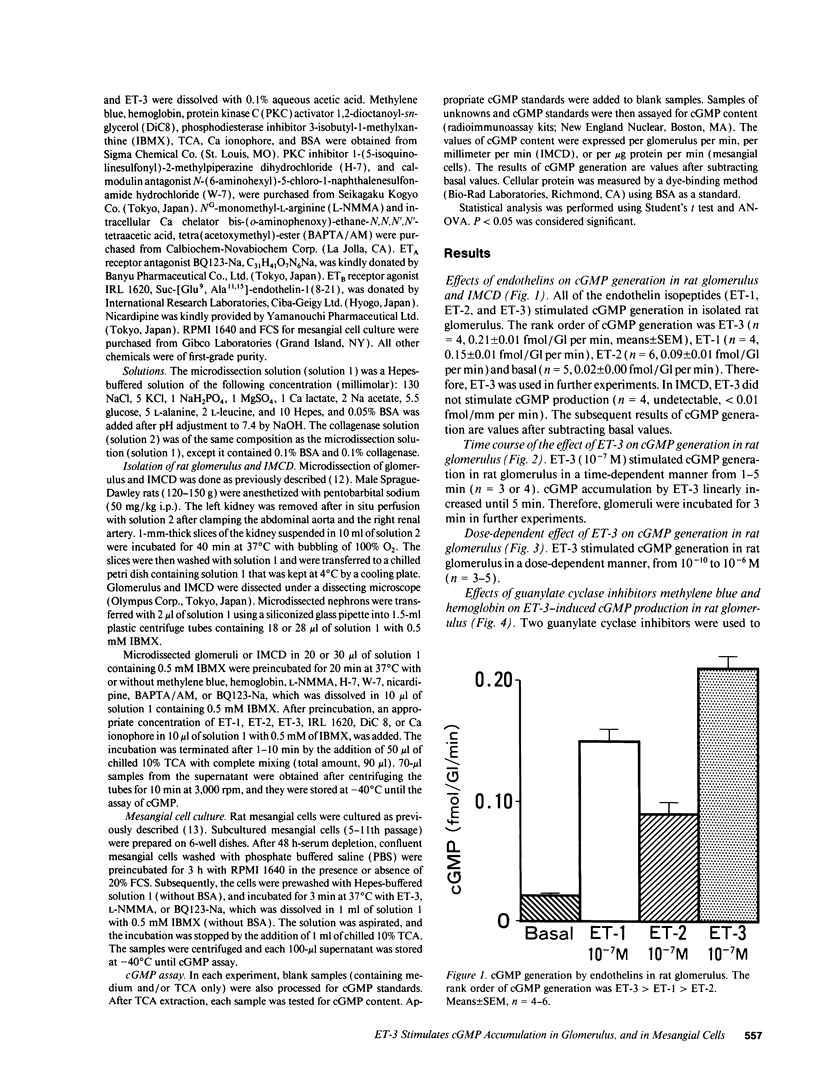
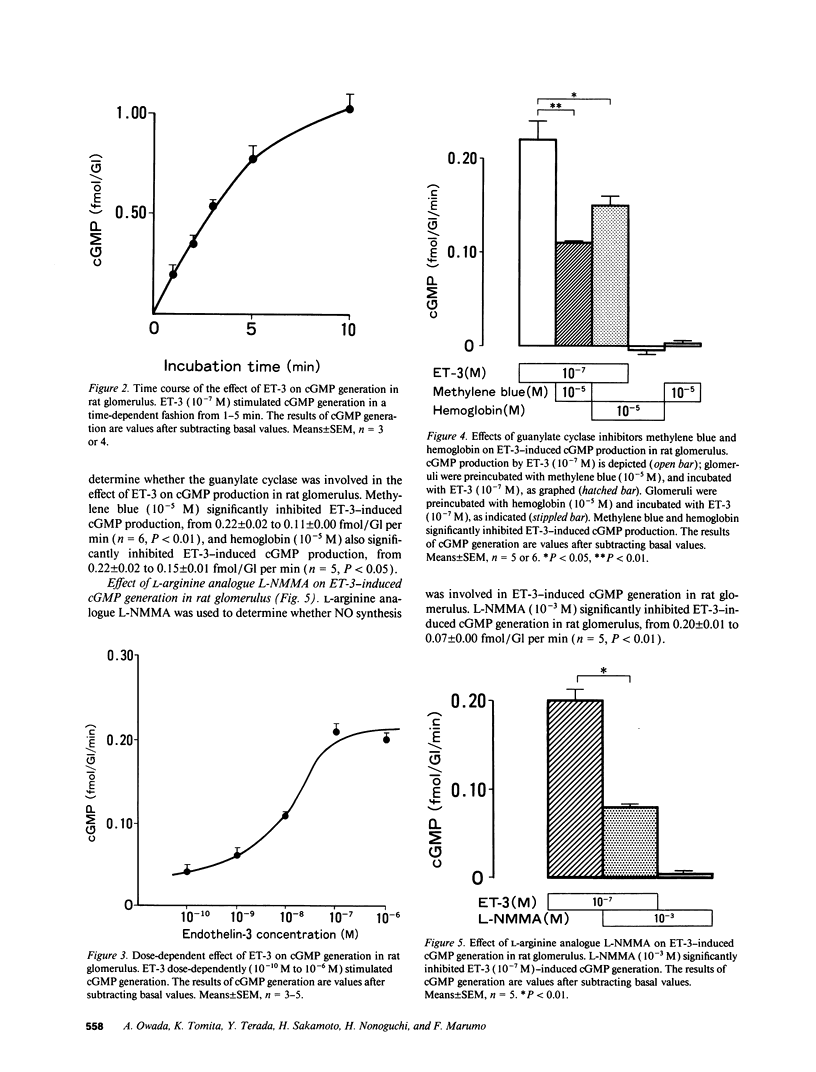
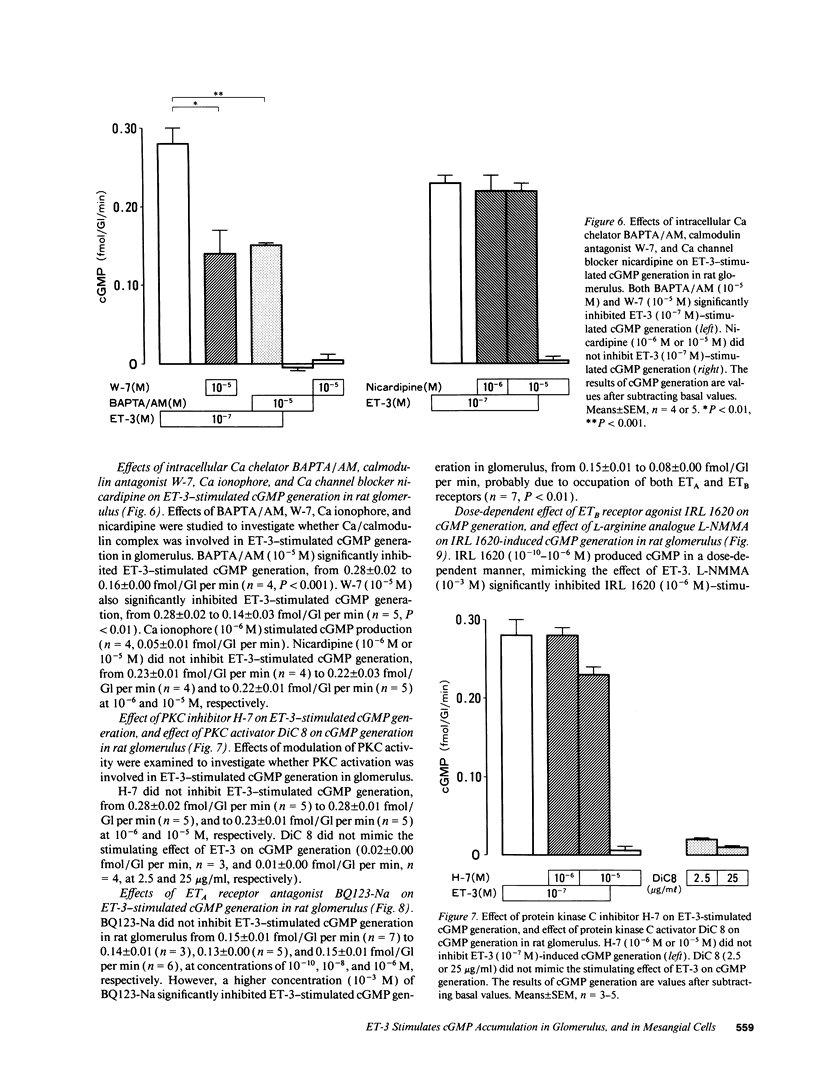
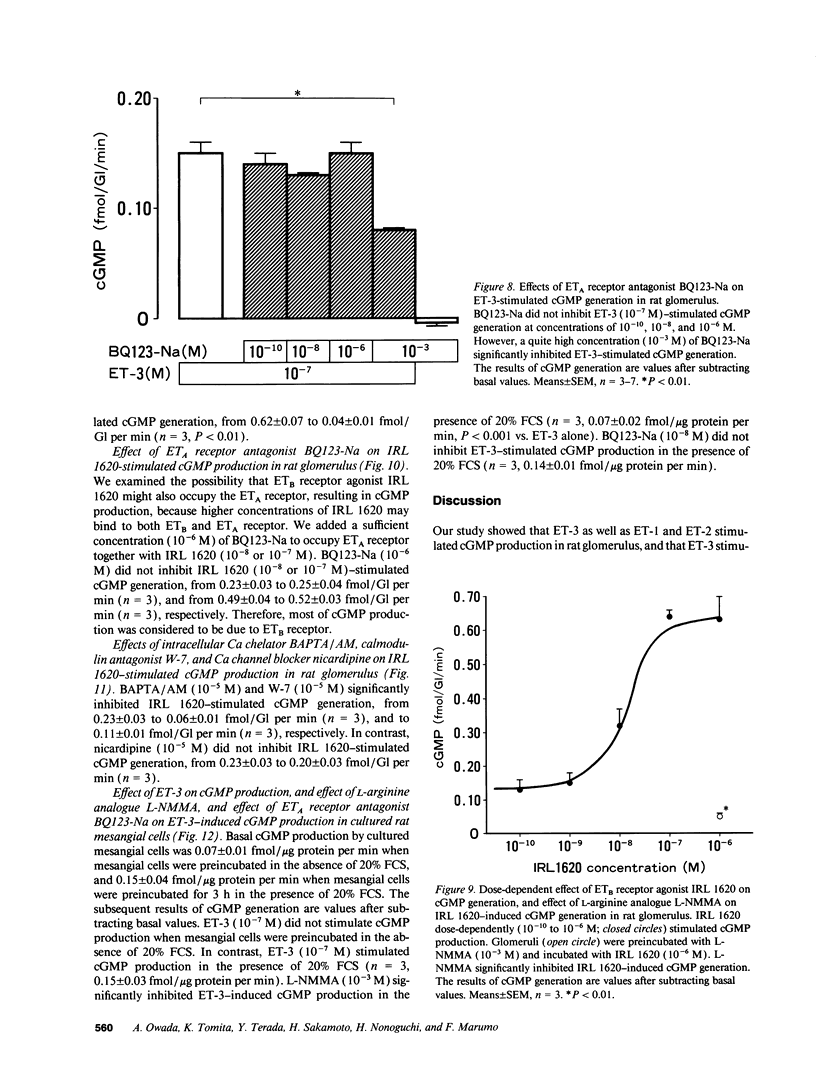
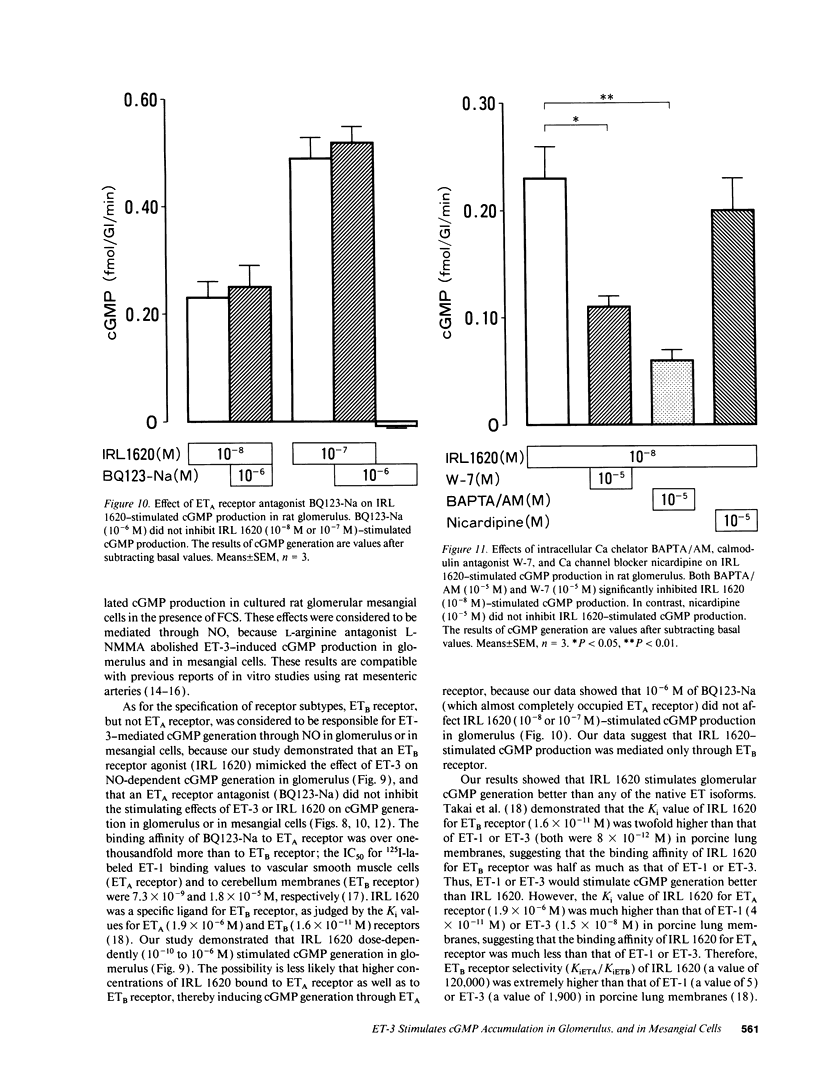
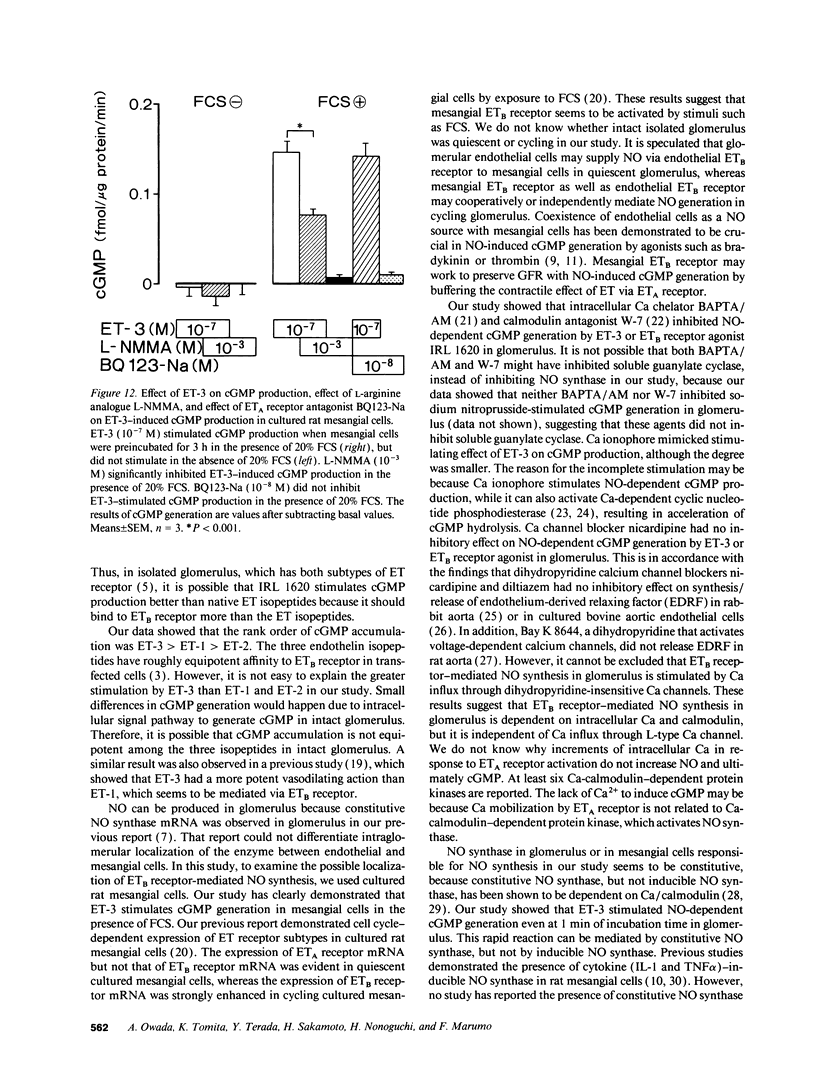
We investigated the effects of endothelins on receptor-mediated cyclic nucleotide metabolism in rat glomerulus, inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD), and also in cultured rat glomerular mesangial cells. Endothelin (ET)-3 dose-dependently stimulated cGMP accumulation in glomerulus, which was higher than that of ET-1 or ET-2. ETB receptor agonist IRL 1620 produced cGMP in a dose-dependent manner, mimicking the effect of ET-3. ETA receptor antagonist BQ123-Na did not inhibit ET-3- or IRL 1620-stimulated cGMP generation. NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA) significantly inhibited ET-3- or IRL 1620-induced cGMP production, suggesting that ET-3- or IRL 1620-stimulated cGMP generation was mediated through nitric oxide (NO). Intracellular Ca chelator BAPTA/AM and calmodulin antagonist W-7, but not Ca channel blocker nicardipine, significantly inhibited ET-3- or IRL 1620-induced cGMP generation. In cultured rat mesangial cells, ET-3 stimulated cGMP generation through NO in the presence of fetal calf serum, which was not inhibited by addition of BQ123-Na. In IMCD, ET-3 had no stimulative effect on cGMP generation. We conclude that ET-3 stimulates NO-induced cGMP generation through ETB receptor in glomerulus. This effect seems to be mediated through intracellular Ca/calmodulin, but not through Ca influx via L-type Ca channel. Mesangial cells can be a source of NO coupled to ETB receptor activation in glomerulus. From these results, mesangial ETB receptor may work to counteract the vasoconstrictive effect of endothelin caused via ETA receptor in glomerulus.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai H., Hori S., Aramori I., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA encoding an endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):730–732. doi: 10.1038/348730a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botting R. M., Vane J. R. Endothelins: potent releasers of prostacyclin and EDRF. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm. 1990 May-Jun;42(3):203–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda N., Izumi Y., Soma M., Watanabe Y., Watanabe M., Hatano M., Sakuma I., Yasuda H. L-NG-monomethyl arginine inhibits the vasodilating effects of low dose of endothelin-3 on rat mesenteric arteries. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 16;167(2):739–745. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92087-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haneda M., Kikkawa R., Maeda S., Togawa M., Koya D., Horide N., Kajiwara N., Shigeta Y. Dual mechanism of angiotensin II inhibits ANP-induced mesangial cGMP accumulation. Kidney Int. 1991 Aug;40(2):188–194. doi: 10.1038/ki.1991.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Sasaki Y., Tanaka T., Endo T., Ohno S., Fujii Y., Nagata T. N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide, a calmodulin antagonist, inhibits cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4354–4357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara M., Noguchi K., Saeki T., Fukuroda T., Tsuchida S., Kimura S., Fukami T., Ishikawa K., Nishikibe M., Yano M. Biological profiles of highly potent novel endothelin antagonists selective for the ETA receptor. Life Sci. 1992;50(4):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90331-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Yanagisawa M., Kimura S., Kasuya Y., Miyauchi T., Goto K., Masaki T. The human endothelin family: three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2863–2867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayakody R. L., Kappagoda C. T., Senaratne M. P., Sreeharan N. Absence of effect of calcium antagonists on endothelium-dependent relaxation in rabbit aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 May;91(1):155–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08994.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. A., Ballermann B. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates soluble guanylate cyclase in bovine glomerular mesangial cells via an L-arginine-dependent mechanism. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1843–1852. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. A., Brock T. A., Ballermann B. J. Glomerular endothelial cells respond to calcium-mobilizing agonists with release of EDRF. Am J Physiol. 1990 May;258(5 Pt 2):F1295–F1303. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.5.F1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mügge A., Peterson T., Harrison D. G. Release of nitrogen oxides from cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells is not impaired by calcium channel antagonists. Circulation. 1991 Apr;83(4):1404–1409. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.83.4.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namiki A., Hirata Y., Ishikawa M., Moroi M., Aikawa J., Machii K. Endothelin-1- and endothelin-3-induced vasorelaxation via common generation of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Life Sci. 1992;50(10):677–682. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90470-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor K. J., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the induction of nitric oxide synthase and the related cell damage in adenocarcinoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Oct 21;1097(3):227–231. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(91)90040-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeilschifter J., Rob P., Mülsch A., Fandrey J., Vosbeck K., Busse R. Interleukin 1 beta and tumour necrosis factor alpha induce a macrophage-type of nitric oxide synthase in rat renal mesangial cells. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jan 15;203(1-2):251–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb19854.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto H., Sasaki S., Hirata Y., Imai T., Ando K., Ida T., Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Marumo F. Production of endothelin-1 by rat cultured mesangial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):462–468. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90354-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai T., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Miyazaki H., Kimura S., Goto K., Masaki T. Cloning of a cDNA encoding a non-isopeptide-selective subtype of the endothelin receptor. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):732–735. doi: 10.1038/348732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shultz P. J., Schorer A. E., Raij L. Effects of endothelium-derived relaxing factor and nitric oxide on rat mesangial cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jan;258(1 Pt 2):F162–F167. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.1.F162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Lincoln T. M. Angiotensin decreases cyclic GMP accumulation produced by atrial natriuretic factor. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):C147–C150. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.1.C147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spedding M., Schini V., Schoeffter P., Miller R. C. Calcium channel activation does not increase release of endothelial-derived relaxant factors (EDRF) in rat aorta although tonic release of EDRF may modulate calcium channel activity in smooth muscle. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1130–1137. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198611000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoos B. A., Carretero O. A., Farhy R. D., Scicli G., Garvin J. L. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor inhibits transport and increases cGMP content in cultured mouse cortical collecting duct cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Mar;89(3):761–765. doi: 10.1172/JCI115653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai M., Umemura I., Yamasaki K., Watakabe T., Fujitani Y., Oda K., Urade Y., Inui T., Yamamura T., Okada T. A potent and specific agonist, Suc-[Glu9,Ala11,15]-endothelin-1(8-21), IRL 1620, for the ETB receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Apr 30;184(2):953–959. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90683-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada Y., Tomita K., Nonoguchi H., Marumo F. Different localization of two types of endothelin receptor mRNA in microdissected rat nephron segments using reverse transcription and polymerase chain reaction assay. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jul;90(1):107–112. doi: 10.1172/JCI115822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada Y., Tomita K., Nonoguchi H., Marumo F. Polymerase chain reaction localization of constitutive nitric oxide synthase and soluble guanylate cyclase messenger RNAs in microdissected rat nephron segments. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):659–665. doi: 10.1172/JCI115908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita K., Nonoguchi H., Marumo F. Effects of endothelin on peptide-dependent cyclic adenosine monophosphate accumulation along the nephron segments of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):2014–2018. doi: 10.1172/JCI114667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torre V., Matthews H. R., Lamb T. D. Role of calcium in regulating the cyclic GMP cascade of phototransduction in retinal rods. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7109–7113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner T. D., Mitchell J. A., de Nucci G., Vane J. R. Endothelin-1 and endothelin-3 release EDRF from isolated perfused arterial vessels of the rat and rabbit. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1989;13 (Suppl 5):S85–S102. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198900135-00021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zatz R., de Nucci G. Effects of acute nitric oxide inhibition on rat glomerular microcirculation. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 2):F360–F363. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1991.261.2.F360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


