Abstract
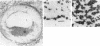
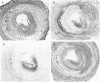
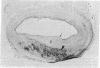
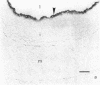
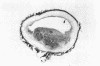
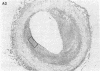
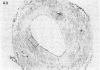
A ruptured atherosclerotic plaque leads to exposure of deeper layers of the plaque to flowing blood and subsequently to thrombus formation. In contrast to the wealth of data on the occurrence of thrombi, little is known about the reasons why an atherosclerotic plaque is thrombogenic. One of the reasons is the relative inaccessibility of the atherosclerotic plaque. We have circumvented this problem by using 6-microns cryostat cross sections of human coronary arteries. These sections were mounted on coverslips that were exposed to flowing blood in a rectangular perfusion chamber. In normal-appearing arteries, platelet deposition was seen on the luminal side of the intima and on the adventitia. In atherosclerotic arteries, strongly increased platelet deposition was seen on the connective tissue of specific parts of the atherosclerotic plaque. The central lipid core of an advanced plaque was not reactive towards platelets. The results indicate that the atherosclerotic plaque by itself is more thrombogenic than the normal vessel wall. To study the cause of the increased thrombus formation on the atherosclerotic plaque, perfusion studies were combined with immunohistochemical studies. Immunohistochemical studies of adhesive proteins showed enrichment of collagen types I, III, V, and VI, vitronectin, fibronectin, fibrinogen/fibrin, and thrombospondin in the atherosclerotic plaque. Laminin and collagen type IV were not enriched. von Willebrand Factor (vWF) was not present in the plaque. The pattern of increased platelet deposition in serial cross sections corresponded best with areas in which collagen types I and III were enriched, but there were also areas in the plaque where both collagens were enriched but no increased reactivity was seen. Inhibition of platelet adhesion with a large range of antibodies or specific inhibitors showed that vWF from plasma and collagen types I and/or III in the plaque were involved. Fibronectin from plasma and fibronectin, fibrinogen, laminin, and thrombospondin in the vessel wall had no effect on platelet adhesion. We conclude that the increased thrombogenicity of atherosclerotic lesions is due to changes in quantity and nature of collagen types I and/or III.
Full text
PDF

















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. C. Heavy metal intensification of DAB-based HRP reaction product. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Jun;29(6):775–775. doi: 10.1177/29.6.7252134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agbanyo F. R., Sixma J. J., de Groot P. G., Languino L. R., Plow E. F. Thrombospondin-platelet interactions. Role of divalent cations, wall shear rate, and platelet membrane glycoproteins. J Clin Invest. 1993 Jul;92(1):288–296. doi: 10.1172/JCI116563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYERS S. O., FRIEDMAN M. CONTRIBUTION OF ATHEROMATOUS GRUEL TO THROMBUS FORMATION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Feb;115:436–438. doi: 10.3181/00379727-115-28934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badimon L., Badimon J. J. Mechanisms of arterial thrombosis in nonparallel streamlines: platelet thrombi grow on the apex of stenotic severely injured vessel wall. Experimental study in the pig model. J Clin Invest. 1989 Oct;84(4):1134–1144. doi: 10.1172/JCI114277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastida E., Escolar G., Ordinas A., Sixma J. J. Fibronectin is required for platelet adhesion and for thrombus formation on subendothelium and collagen surfaces. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1437–1442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumgartner H. R., Sakariassen K. S. Factors controlling thrombus formation on arterial lesions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;454:162–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb11855.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berndt M. C., Du X. P., Booth W. J. Ristocetin-dependent reconstitution of binding of von Willebrand factor to purified human platelet membrane glycoprotein Ib-IX complex. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):633–640. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bini A., Fenoglio J. J., Jr, Mesa-Tejada R., Kudryk B., Kaplan K. L. Identification and distribution of fibrinogen, fibrin, and fibrin(ogen) degradation products in atherosclerosis. Use of monoclonal antibodies. Arteriosclerosis. 1989 Jan-Feb;9(1):109–121. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.9.1.109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T. M., Jacobs J. W., Condra C. An inhibitor of collagen-stimulated platelet activation from the salivary glands of the Haementeria officinalis leech. I. Identification, isolation, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6893–6898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. J., Thomas A. Thrombosis and acute coronary-artery lesions in sudden cardiac ischemic death. N Engl J Med. 1984 May 3;310(18):1137–1140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198405033101801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. J., Thomas T. The pathological basis and microanatomy of occlusive thrombus formation in human coronary arteries. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1981 Aug 18;294(1072):225–229. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1981.0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWood M. A., Spores J., Notske R., Mouser L. T., Burroughs R., Golden M. S., Lang H. T. Prevalence of total coronary occlusion during the early hours of transmural myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 16;303(16):897–902. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010163031601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk E. Plaque rupture with severe pre-existing stenosis precipitating coronary thrombosis. Characteristics of coronary atherosclerotic plaques underlying fatal occlusive thrombi. Br Heart J. 1983 Aug;50(2):127–134. doi: 10.1136/hrt.50.2.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gown A. M., Tsukada T., Ross R. Human atherosclerosis. II. Immunocytochemical analysis of the cellular composition of human atherosclerotic lesions. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):191–207. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves H. M., Kinlough-Rathbone R. L., Richardson M., Jørgensen L., Moore S., Mustard J. F. Thrombin generation and fibrin formation following injury to rabbit neointima. Studies of vessel wall reactivity and platelet survival. Lab Invest. 1982 Jun;46(6):605–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guettier C., Hinglais N., Bruneval P., Kazatchkine M., Bariety J., Camilleri J. P. Immunohistochemical localization of S protein/vitronectin in human atherosclerotic versus arteriosclerotic arteries. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1989;414(4):309–313. doi: 10.1007/BF00734084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantgan R. R., Endenburg S. C., Cavero I., Marguerie G., Uzan A., Sixma J. J., de Groot P. G. Inhibition of platelet adhesion to fibrin(ogen) in flowing whole blood by Arg-Gly-Asp and fibrinogen gamma-chain carboxy terminal peptides. Thromb Haemost. 1992 Dec 7;68(6):694–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantgan R. R., Hindriks G., Taylor R. G., Sixma J. J., de Groot P. G. Glycoprotein Ib, von Willebrand factor, and glycoprotein IIb:IIIa are all involved in platelet adhesion to fibrin in flowing whole blood. Blood. 1990 Jul 15;76(2):345–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M. D., Ohgren Y., Ruoslahti E. Serum spreading factor (vitronectin) is present at the cell surface and in tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4003–4007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heras M., Chesebro J. H., Penny W. J., Bailey K. R., Badimon L., Fuster V. Effects of thrombin inhibition on the development of acute platelet-thrombus deposition during angioplasty in pigs. Heparin versus recombinant hirudin, a specific thrombin inhibitor. Circulation. 1989 Mar;79(3):657–665. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.3.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindriks G., Ijsseldijk M. J., Sonnenberg A., Sixma J. J., de Groot P. G. Platelet adhesion to laminin: role of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions, shear rate, and platelet membrane glycoproteins. Blood. 1992 Feb 15;79(4):928–935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdijk W. P., Sakariassen K. S., Nievelstein P. F., Sixma J. J. Role of factor VIII-von Willebrand factor and fibronectin in the interaction of platelets in flowing blood with monomeric and fibrillar human collagen types I and III. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):531–540. doi: 10.1172/JCI111729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdijk W. P., Sixma J. J. Fibronectin in artery subendothelium is important for platelet adhesion. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):598–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houdijk W. P., de Groot P. G., Nievelstein P. F., Sakariassen K. S., Sixma J. J. Subendothelial proteins and platelet adhesion. von Willebrand factor and fibronectin, not thrombospondin, are involved in platelet adhesion to extracellular matrix of human vascular endothelial cells. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Jan-Feb;6(1):24–33. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.1.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeynes B. J., Warren B. A. Thrombogenicity of components of atheromatous material. An animal and in vitro model of cerebral atheroembolism. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1981 Jul;105(7):353–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIRK J. E. Thromboplastin activities of human arterial and venous tissues. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Apr;109:890–892. doi: 10.3181/00379727-109-27369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuda S., Okada Y., Minamoto T., Oda Y., Matsui Y., Nakanishi I. Collagens in human atherosclerosis. Immunohistochemical analysis using collagen type-specific antibodies. Arterioscler Thromb. 1992 Apr;12(4):494–502. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.12.4.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. M., Schultz L. D., Condra C., Karczewski J., Connolly T. M. An inhibitor of collagen-stimulated platelet activation from the salivary glands of the Haementeria officinalis leech. II. Cloning of the cDNA and expression. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6899–6904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocher O., Gabbiani G. Cytoskeletal features of normal and atheromatous human arterial smooth muscle cells. Hum Pathol. 1986 Sep;17(9):875–880. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80637-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kragel A. H., Reddy S. G., Wittes J. T., Roberts W. C. Morphometric analysis of the composition of atherosclerotic plaques in the four major epicardial coronary arteries in acute myocardial infarction and in sudden coronary death. Circulation. 1989 Dec;80(6):1747–1756. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.80.6.1747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawler J., Simons E. R. Cooperative binding of calcium to thrombospondin. The effect of calcium on the circular dichroism and limited tryptic digestion of thrombospondin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12098–12101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. B., Prevosti L. G., Kramer W. S., Lu D. Y., Leon M. B. Platelet adherence and thrombus formation with flowing human blood on atherosclerotic plaque: reduced thrombogenicity of Watanabe-heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit aortic subendothelium. Thromb Res. 1989 Apr 15;54(2):99–114. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(89)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyford C. L., Connor W. E., Hoak J. C., Warner E. D. The coagulant and thrombogenic properties of human atheroma. Circulation. 1967 Aug;36(2):284–293. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.36.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCullagh K. G., Duance V. C., Bishop K. A. The distribution of collagen types I, III and V (AB) in normal and atherosclerotic human aorta. J Pathol. 1980 Jan;130(1):45–55. doi: 10.1002/path.1711300107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Raugi G. J., Bornstein P. Interactions of thrombospondin with extracellular matrix proteins: selective binding to type V collagen. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):646–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols T. C., Bellinger D. A., Tate D. A., Reddick R. L., Read M. S., Koch G. G., Brinkhous K. M., Griggs T. R. von Willebrand factor and occlusive arterial thrombosis. A study in normal and von Willebrand's disease pigs with diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 May-Jun;10(3):449–461. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwenhuis H. K., Akkerman J. W., Houdijk W. P., Sixma J. J. Human blood platelets showing no response to collagen fail to express surface glycoprotein Ia. Nature. 1985 Dec 5;318(6045):470–472. doi: 10.1038/318470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nievelstein P. F., D'Alessio P. A., Sixma J. J. Fibronectin in platelet adhesion to human collagen types I and III. Use of nonfibrillar and fibrillar collagen in flowing blood studies. Arteriosclerosis. 1988 Mar-Apr;8(2):200–206. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.8.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons T. J., Haycraft D. L., Hoak J. C., Sage H. Interaction of platelets and purified collagens in a laminar flow model. Thromb Res. 1986 Aug 15;43(4):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. D., Davies M. J., Born G. V. Influence of plaque configuration and stress distribution on fissuring of coronary atherosclerotic plaques. Lancet. 1989 Oct 21;2(8669):941–944. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90953-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakariassen K. S., Aarts P. A., de Groot P. G., Houdijk W. P., Sixma J. J. A perfusion chamber developed to investigate platelet interaction in flowing blood with human vessel wall cells, their extracellular matrix, and purified components. J Lab Clin Med. 1983 Oct;102(4):522–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakariassen K. S., Bolhuis P. A., Sixma J. J. Platelet adherence to subendothelium of human arteries in pulsatile and steady flow. 1980 Aug 15-Sep 1Thromb Res. 19(4-5):547–559. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(80)90027-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro S. A. Identification of a 160,000 dalton platelet membrane protein that mediates the initial divalent cation-dependent adhesion of platelets to collagen. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixma J. J., Nievelstein P. F., Zwaginga J. J., de Groot P. G. Adhesion of blood platelets to the extracellular matrix of cultured human endothelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;516:39–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb33028.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. B., Ashall C. Fibronectin distribution in human aortic intima and atherosclerotic lesions: concentration of soluble and collagenase-releasable fractions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 15;880(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90113-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg A., Modderman P. W., Hogervorst F. Laminin receptor on platelets is the integrin VLA-6. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):487–489. doi: 10.1038/336487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stel H. V., Sakariassen K. S., Scholte B. J., Veerman E. C., van der Kwast T. H., de Groot P. G., Sixma J. J., van Mourik J. A. Characterization of 25 monoclonal antibodies to factor VIII-von Willebrand factor: relationship between ristocetin-induced platelet aggregation and platelet adherence to subendothelium. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1408–1415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman I. I., Rand J. H. Subendothelial deposition of von Willebrand's factor requires the presence of endothelial cells. J Lab Clin Med. 1982 Oct;100(4):526–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping P. G., Malliaros J., Holdsworth S. R. Procoagulant activity expression by macrophages from atheromatous vascular plaques. Atherosclerosis. 1989 Oct;79(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(89)90129-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven A. J., Mommersteeg M. E., Akkerman J. W. Metabolic energy is required in human platelets at any stage during optical aggregation and secretion. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Aug 21;800(3):242–250. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90402-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Turitto V. T., Baumgartner H. R. Effect of shear rate on platelet interaction with subendothelium in citrated and native blood. I. Shear rate--dependent decrease of adhesion in von Willebrand's disease and the Bernard-Soulier syndrome. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Nov;92(5):750–764. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wight T. N., Raugi G. J., Mumby S. M., Bornstein P. Light microscopic immunolocation of thrombospondin in human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Apr;33(4):295–302. doi: 10.1177/33.4.3884704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox J. N., Smith K. M., Schwartz S. M., Gordon D. Localization of tissue factor in the normal vessel wall and in the atherosclerotic plaque. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Q. Y., Drouet L., Carrier J. L., Rothschild C., Berard M., Rouault C., Caen J. P., Meyer D. Differential distribution of von Willebrand factor in endothelial cells. Comparison between normal pigs and pigs with von Willebrand disease. Arteriosclerosis. 1987 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–54. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.7.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwaginga J. J., Sixma J. J., de Groot P. G. Activation of endothelial cells induces platelet thrombus formation on their matrix. Studies of new in vitro thrombosis model with low molecular weight heparin as anticoagulant. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Jan-Feb;10(1):49–61. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Rest M., Garrone R. Collagens as multidomain proteins. Biochimie. 1990 Jun-Jul;72(6-7):473–484. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(90)90071-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]