Abstract
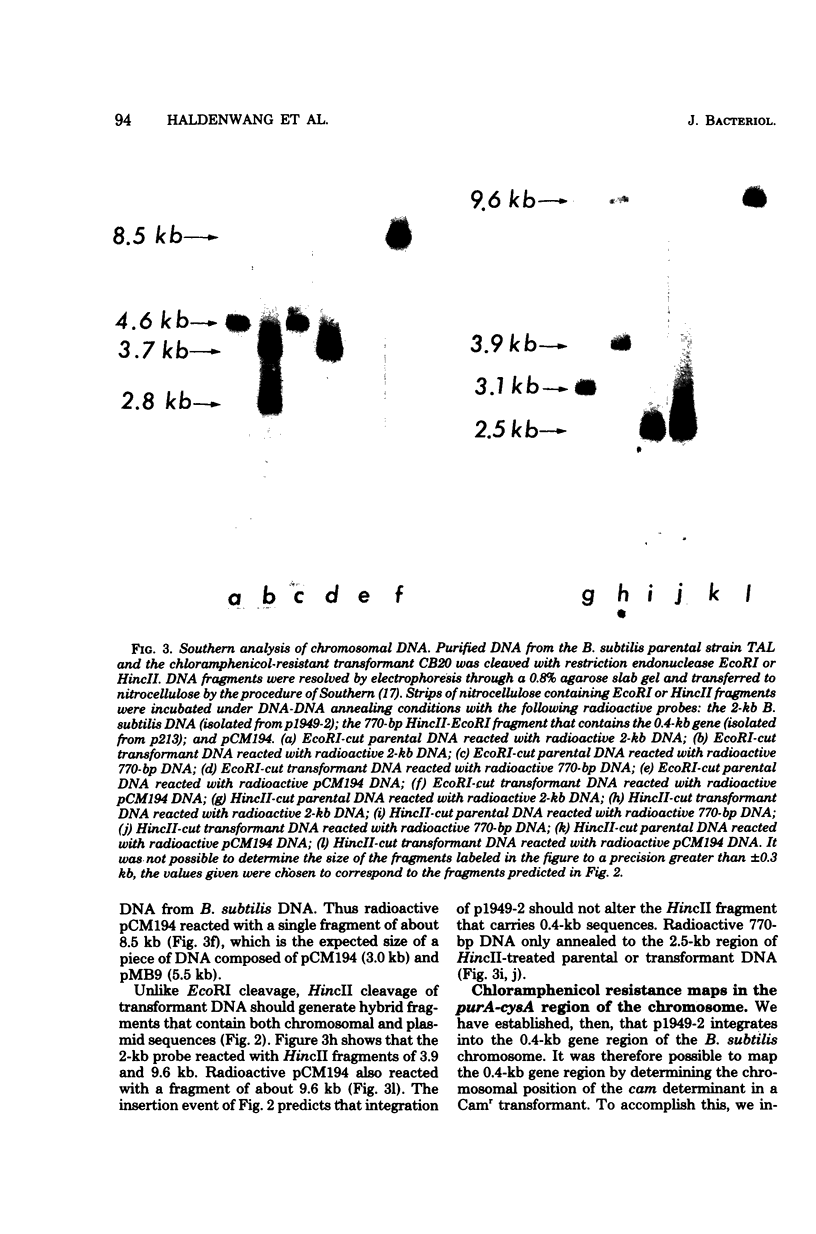
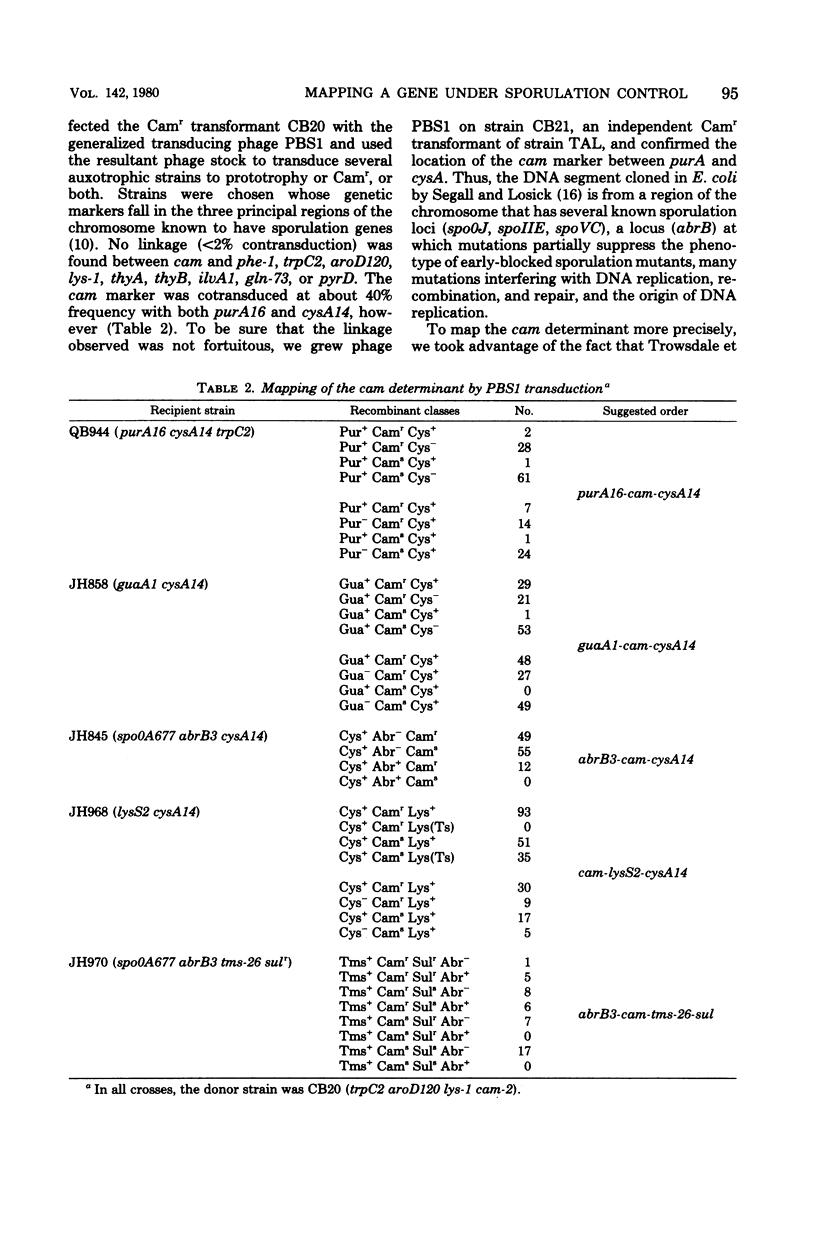
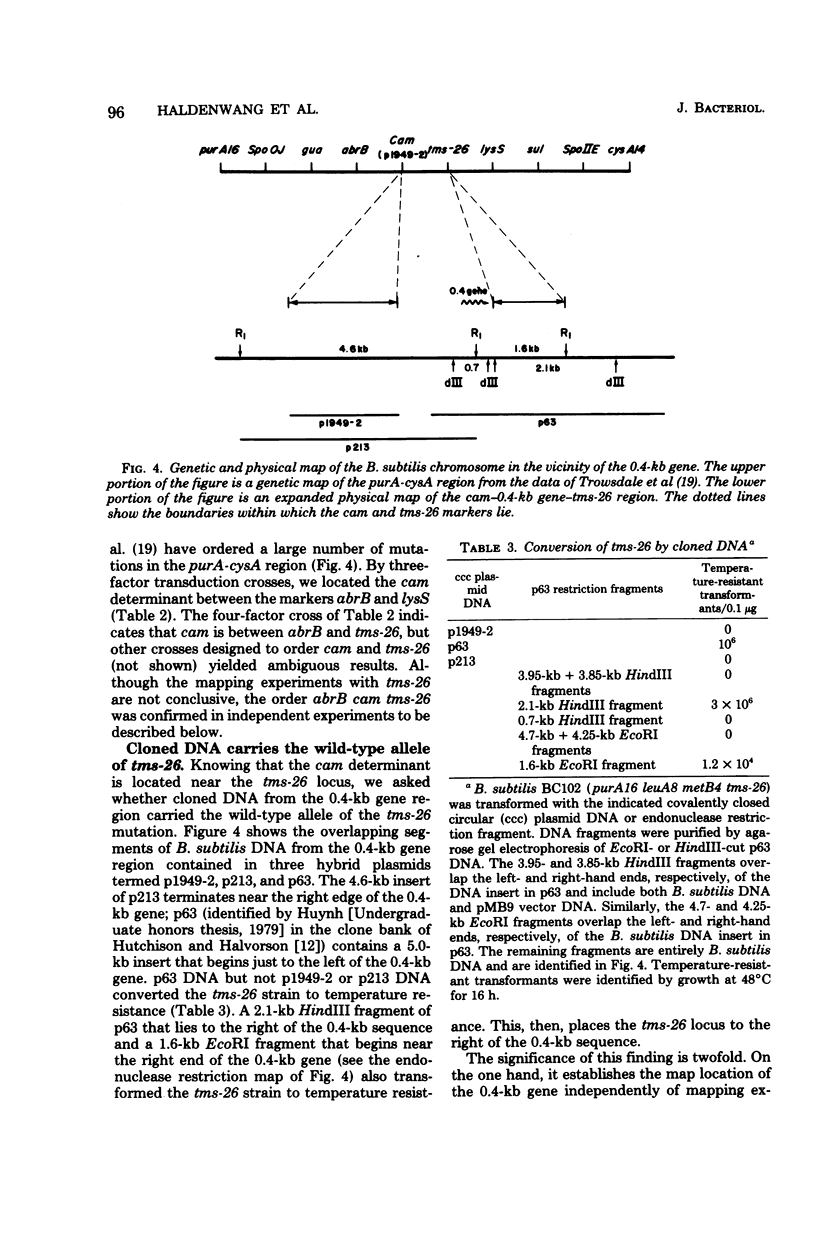
A segment of Bacillus subtilis deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) previously cloned in Escherichia coli contains a gene (the 0.4-kilobase [kb] gene) whose transcription is activated at an early stage of spore development. To map the genetic location of the 0.4-kb gene, we constructed a hybrid plasmid that inserts a chloramphenicol resistance determinant into the B. subtilis chromosome by recombination at a site of homology between cloned B. subtilis DNA and the chromosome. This hybrid plasmid (p1949-2) was constructed from the E. coli plasmid pMB9, the B. sultilis chloramphenicol resistance plasmid pCM194 (whose replication function was inactivated), and B. subtilis DNA from the vicinity of the 0.4-kb gene. Transformation of B. subtilis cells to drug resistance by p1949-2 was dependent upon the B. subtilis RecE+ phenotype and resulted in specific and predictable changes in the pattern of endonuclease restriction sites in the 0.4-kb gene region of the chromosome. Chloramphenicol resistance in cells transformed by p1949-2 was mapped to the purA-cysA region of the B. subtilis chromosome, a region. In addition, DNA adjacent to the 0.4-kb gene was shown to contain the wild-type allele of genetic marker (tms-26) from that region.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland J. C., Marmur J. Identification of conserved genetic functions in Bacillus by use of temperature-sensitive mutants. Bacteriol Rev. 1968 Dec;32(4 Pt 1):302–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Cirigliano C. Genetic characterization of recombination-deficient mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):488–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.488-493.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. H., Wilson G. A., Young F. E. Mechanism of integrating foreign DNA during transformation of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Contente S., Dubnau D. Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus plasmids introduced by transformation into Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):318–329. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.318-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryczan T. J., Dubnau D. Construction and properties of chimeric plasmids in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1428–1432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldenwang W. G., Losick R. A modified RNA polymerase transcribes a cloned gene under sporulation control in Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):256–260. doi: 10.1038/282256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A., Barat M., Anagnostopoulos C. Transformation and transduction in recombination-defective mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1925-1937.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A. Genetics of bacterial sporulation. Adv Genet. 1976;18:69–98. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60437-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison K. W., Halvorson H. O. Cloning of randomly sheared DNA fragments from a phi 105 lysogen of Bacillus subtilis identification of prophage-containing clones. Gene. 1980 Feb;8(3):267–278. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polisky B., Greene P., Garfin D. E., McCarthy B. J., Goodman H. M., Boyer H. W. Specificity of substrate recognition by the EcoRI restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3310–3314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Losick R. Cloned Bacillus subtilis DNA containing a gene that is activated early during sporulation. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):751–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90289-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugino A., Goodman H. M., Heyneker H. L., Shine J., Boyer H. W., Cozzarelli N. R. Interaction of bacteriophage T4 RNA and DNA ligases in joining of duplex DNA at base-paired ends. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jun 10;252(11):3987–3994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Chen S. M., Hoch J. A. Genetic analysis of a class of polymyxin resistant partial revertants of stage O sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis: map of the chromosome region near the origin of replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 23;173(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00267691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. Use of temperature-sensitive mutants to study gene expression during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):928–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.928-936.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





