Abstract
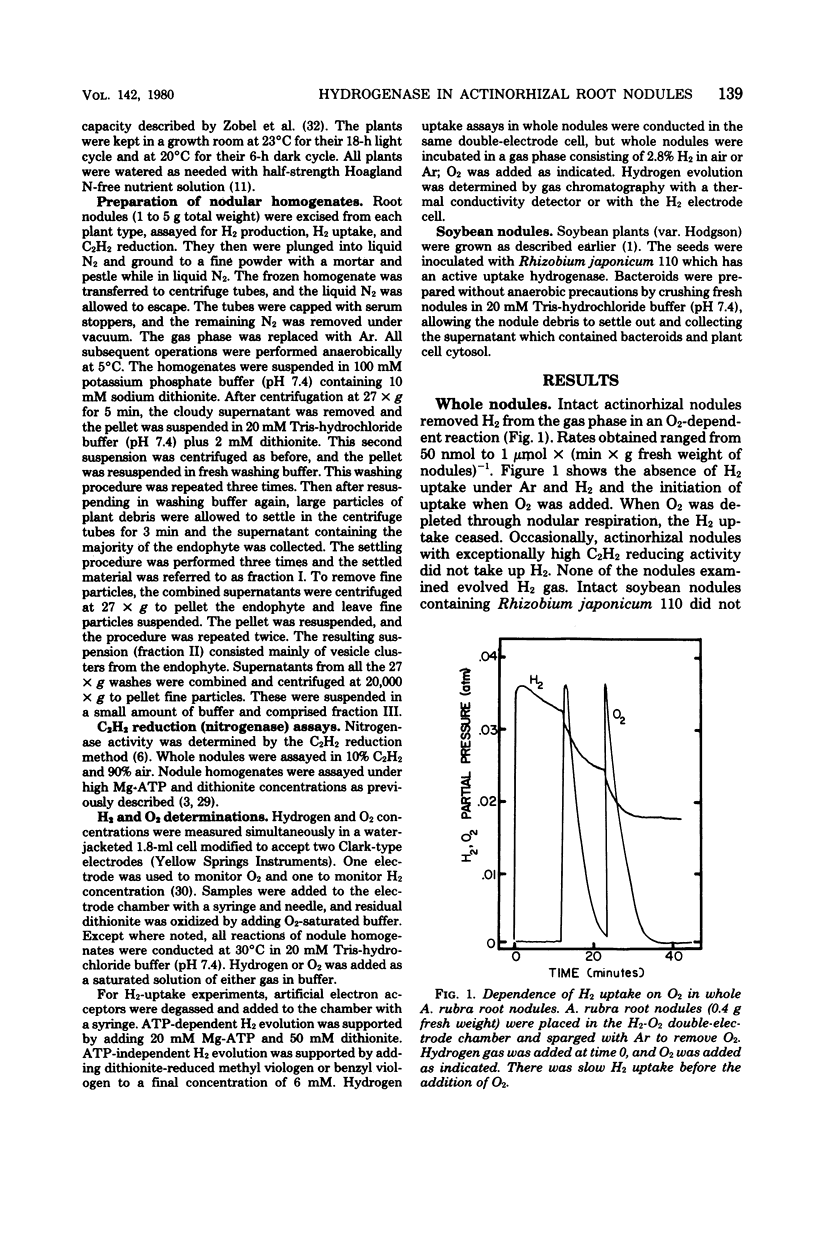
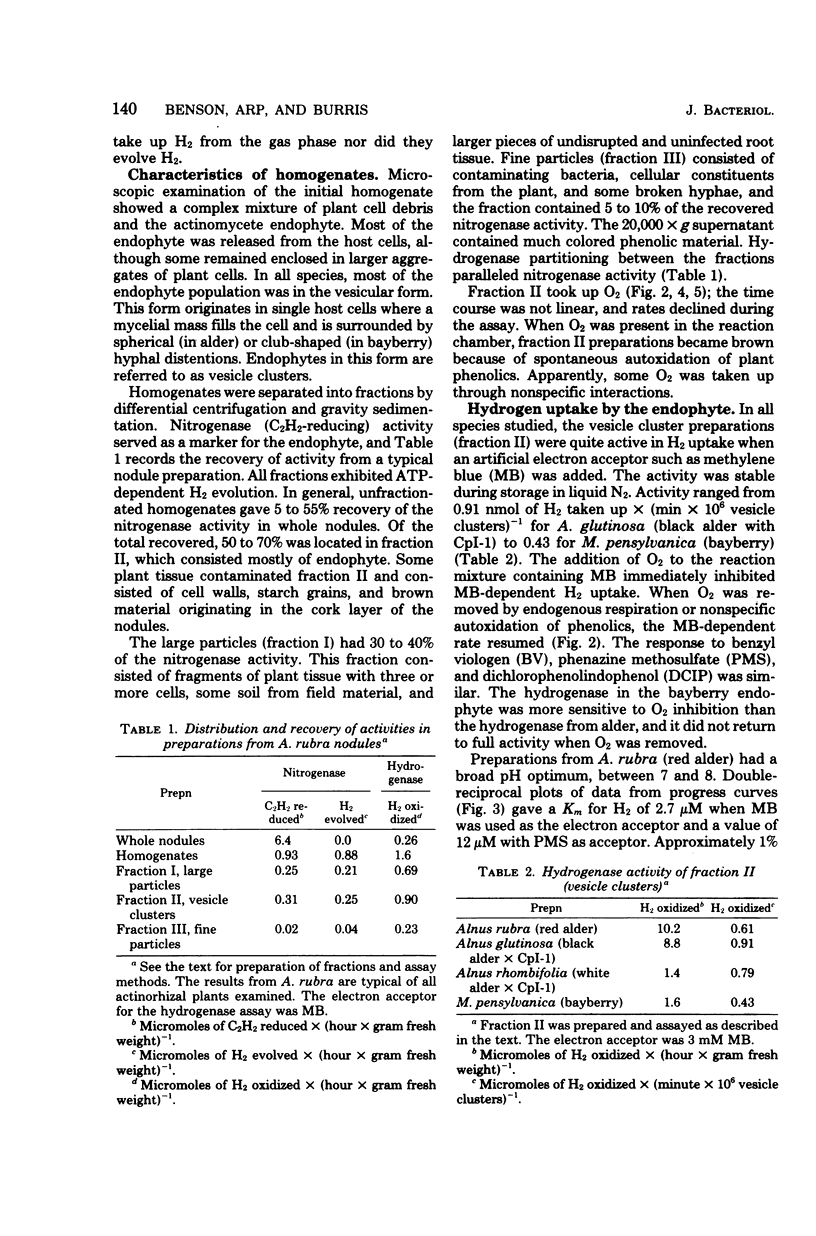
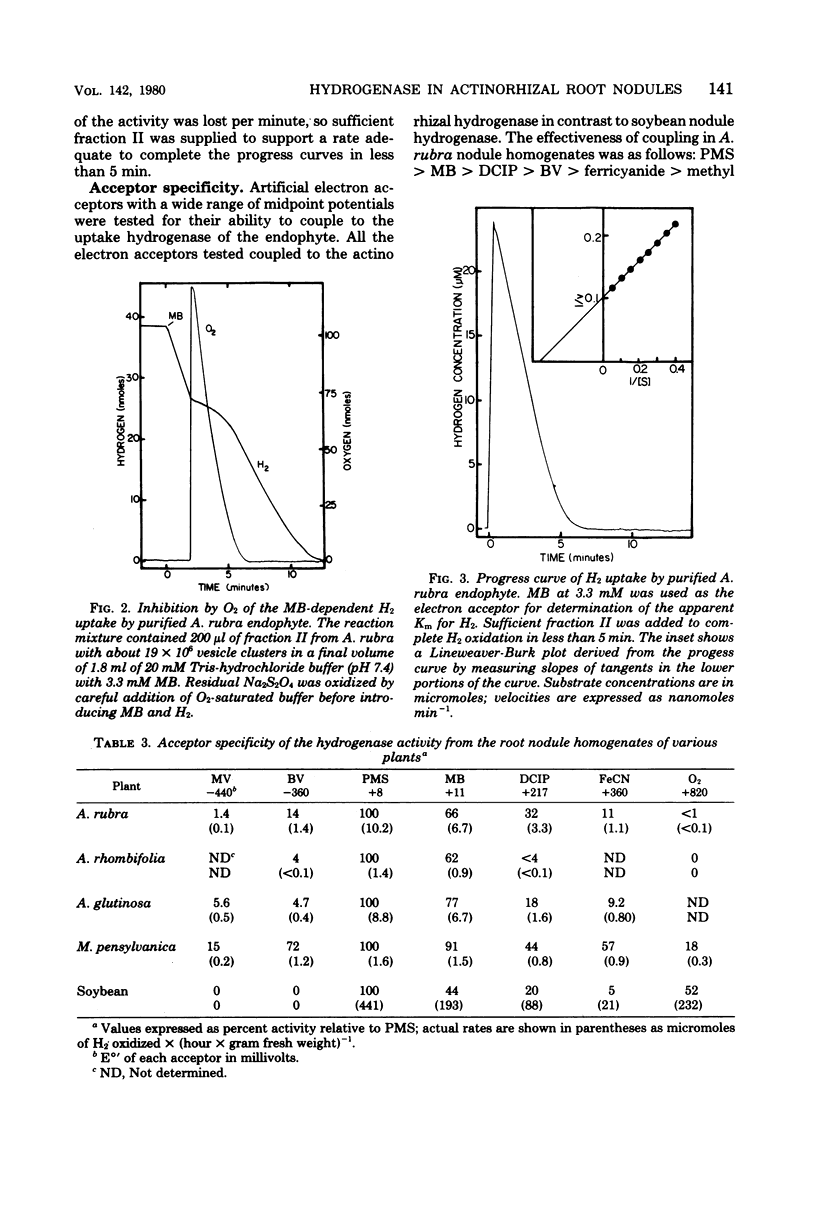
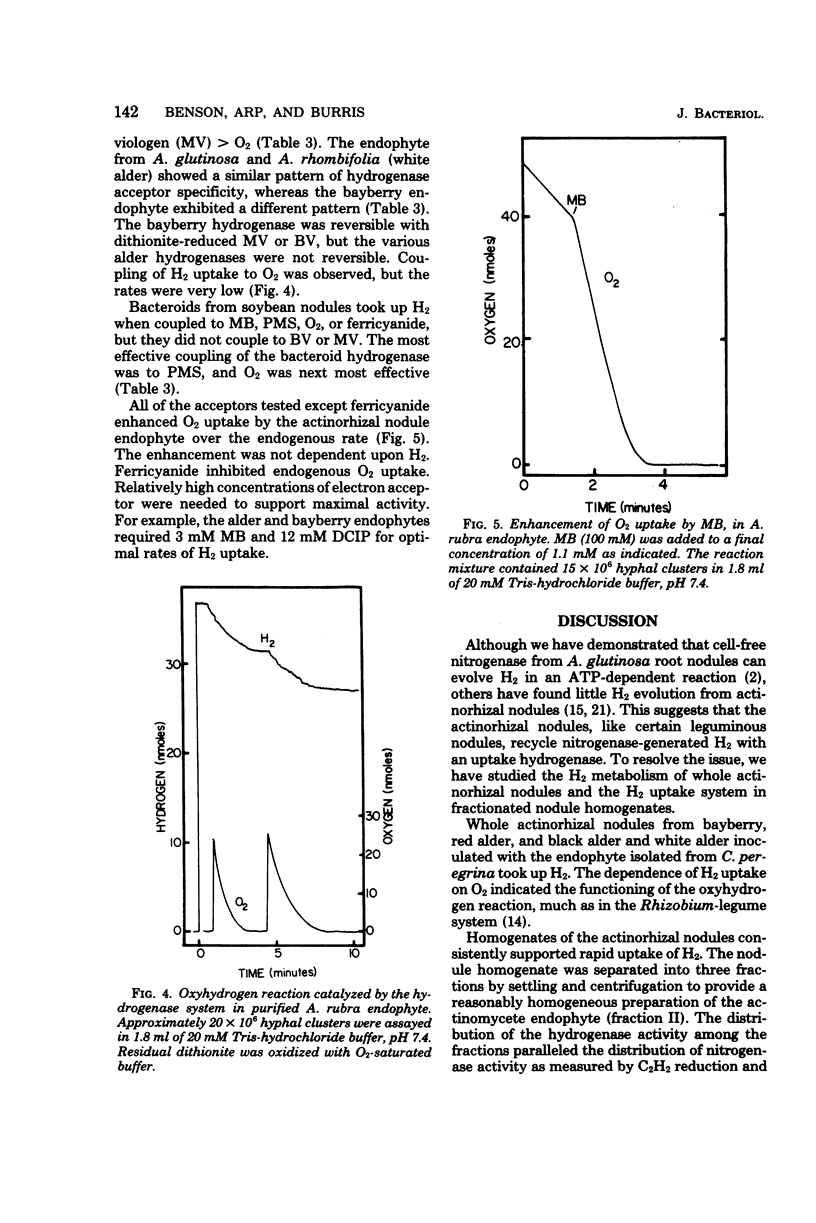
Hydrogenases were measured in intact actinorhizal root nodules and from disrupted nodules of Alnus glutinosa, Alnus rhombifolia, Alnus rubra, and Myrica pensylvanica. Whole nodules took up H2 in an O2-dependent reaction. Endophyte preparations oxidized H2 through the oxyhydrogen reaction, but rates were enhanced when hydrogen uptake was coupled to artificial electron acceptors. Oxygen inhibited artifical acceptor-dependent H2 uptake. The hydrogenase system from M. pensylvanica had a different pattern of coupling to various electron acceptors than the hydrogenase systems from the alders; only the bayberry system evolved H2 from reduced viologen dyes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arp D. J., Burris R. H. Purification and properties of the particulate hydrogenase from the bacteroids of soybean root nodules. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 11;570(2):221–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson D. R., Arp D. J., Burris R. H. Cell-free nitrogenase and hydrogenase from actinorhizal root nodules. Science. 1979 Aug 17;205(4407):688–689. doi: 10.1126/science.205.4407.688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callaham D., Deltredici P., Torrey J. G. Isolation and Cultivation in vitro of the Actinomycete Causing Root Nodulation in Comptonia. Science. 1978 Feb 24;199(4331):899–902. doi: 10.1126/science.199.4331.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. O. Hydrogenase in legume root nodule bacteroids: occurrence and properties. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;85(3):193–201. doi: 10.1007/BF00408844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerich D. W., Ruiz-Argüeso T., Ching T. M., Evans H. J. Hydrogen-dependent nitrogenase activity and ATP formation in Rhizobium japonicum bacteroids. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):153–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.153-160.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J. C., Chen C. H., Burris R. H. Inhibition of nitrogenase-catalyzed reductions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jan 18;292(1):256–270. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae R. E., Hanus J., Evans H. J. Properties of the hydrogenase system in Rhizobium japonicum bacteroids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Jan 30;80(2):384–390. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90688-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schink B., Schlegel H. G. The membrane-bound hydrogenase of Alcaligenes eutrophus. I. Solubilization, purification, and biochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 12;567(2):315–324. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90117-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert K. R., Evans H. J. Hydrogen evolution: A major factor affecting the efficiency of nitrogen fixation in nodulated symbionts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1207–1211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R., Healey F. P., Myers J. Amperometric measurement of hydrogen evolution in chlamydomonas. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jul;48(1):108–110. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter H. C., Burris R. H. Nitrogenase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:409–426. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.002205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zobel R. W., Del Tredici P., Torrey J. G. Method for growing plants aeroponically. Plant Physiol. 1976 Mar;57(3):344–346. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.3.344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


