Abstract
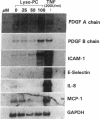
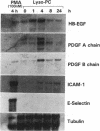
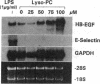
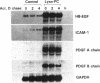
Lysophosphatidylcholine (lyso-PC) is a major phospholipid component of atherogenic lipoproteins (e.g., oxidized LDL and beta-VLDL) and also can be generated through the action of leukocyte-secreted phospholipase A2 at sites of inflammation. We have previously reported that lyso-PC can activate cultured endothelia, resulting in the selective upregulation of adhesion molecules, such as vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1. In this study, we have found that lyso-PC increased steady state mRNA levels for two smooth muscle/fibroblast-directed growth factors, the A and B chains of PDGF and heparin-binding EGF-like protein (HB-EGF), in cultured human endothelial cells. Lyso-PC did not upregulate the expression of certain other inducible endothelial genes, including E-selectin, IL-8, or monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in the same cells, in contrast to the coordinate pattern of activation typically observed with other stimuli, such as TNF alpha, bacterial endotoxin, or PMA. Nuclear runoff assays documented an increased transcriptional rate for the HB-EGF gene in lyso-PC-treated cells. Northern blot analyses, after actinomycin D treatment, further indicated that the increased amounts of mRNA for HB-EGF, PDGF A and B chains, and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 were not dependent upon message stabilization. We conclude that lyso-PC can induce growth factor gene expression in cultured endothelial cells and thus may contribute to the migration and proliferation of smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts in various response-to-injury settings in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevilacqua M. P., Stengelin S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Seed B. Endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1: an inducible receptor for neutrophils related to complement regulatory proteins and lectins. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1160–1165. doi: 10.1126/science.2466335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisolm G. M. Oxidized lipoproteins and leukocyte-endothelial interactions: growing evidence for multiple mechanisms. Lab Invest. 1993 Apr;68(4):369–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Bonthron D. T., Orkin S. H. Alternative RNA splicing affects function of encoded platelet-derived growth factor A chain. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):621–624. doi: 10.1038/328621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T. Endothelial nuclear factor-kappa B and the initiation of the atherosclerotic lesion. Lab Invest. 1993 May;68(5):499–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Ginsburg D., Boss J. M., Orkin S. H., Pober J. S. Cultured human endothelial cells express platelet-derived growth factor B chain: cDNA cloning and structural analysis. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):748–750. doi: 10.1038/316748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Obin M. S., Brock A. F., Luis E. A., Hass P. E., Hébert C. A., Yip Y. K., Leung D. W., Lowe D. G., Kohr W. J. Endothelial interleukin-8: a novel inhibitor of leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1601–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.2688092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar K. A., Hajjar D. P., Silverstein R. L., Nachman R. L. Tumor necrosis factor-mediated release of platelet-derived growth factor from cultured endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):235–245. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashiyama S., Abraham J. A., Miller J., Fiddes J. C., Klagsbrun M. A heparin-binding growth factor secreted by macrophage-like cells that is related to EGF. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):936–939. doi: 10.1126/science.1840698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume N., Cybulsky M. I., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Lysophosphatidylcholine, a component of atherogenic lipoproteins, induces mononuclear leukocyte adhesion molecules in cultured human and rabbit arterial endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1138–1144. doi: 10.1172/JCI115932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libby P., Hansson G. K. Involvement of the immune system in human atherogenesis: current knowledge and unanswered questions. Lab Invest. 1991 Jan;64(1):5–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marikovsky M., Breuing K., Liu P. Y., Eriksson E., Higashiyama S., Farber P., Abraham J., Klagsbrun M. Appearance of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor in wound fluid as a response to injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):3889–3893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.3889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montgomery K. F., Osborn L., Hession C., Tizard R., Goff D., Vassallo C., Tarr P. I., Bomsztyk K., Lobb R., Harlan J. M. Activation of endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6523–6527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro J. M., Cotran R. S. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: atherogenesis and inflammation. Lab Invest. 1988 Mar;58(3):249–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neish A. S., Williams A. J., Palmer H. J., Whitley M. Z., Collins T. Functional analysis of the human vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 promoter. J Exp Med. 1992 Dec 1;176(6):1583–1593. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.6.1583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn M. T., Parthasarathy S., Steinberg D. Lysophosphatidylcholine: a chemotactic factor for human monocytes and its potential role in atherogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2805–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick N., Collins T., Atkinson W., Bonthron D. T., Dewey C. F., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr Platelet-derived growth factor B chain promoter contains a cis-acting fluid shear-stress-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4591–4595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins B. J., Stier P., Ernst T., Wong G. G. The human homolog of the JE gene encodes a monocyte secretory protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4687–4695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins B. J., Yoshimura T., Leonard E. J., Pober J. S. Cytokine-activated human endothelial cells synthesize and secrete a monocyte chemoattractant, MCP-1/JE. Am J Pathol. 1990 Jun;136(6):1229–1233. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The pathogenesis of atherosclerosis: a perspective for the 1990s. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):801–809. doi: 10.1038/362801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Makgoba M. W., Seed B. ICAM, an adhesion ligand of LFA-1, is homologous to the neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM. Nature. 1988 Feb 18;331(6157):624–627. doi: 10.1038/331624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starksen N. F., Harsh G. R., 4th, Gibbs V. C., Williams L. T. Regulated expression of the platelet-derived growth factor A chain gene in microvascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14381–14384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Pruzanski W. Role of secretory phospholipases A2 in the pathobiology of disease. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):391–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voraberger G., Schäfer R., Stratowa C. Cloning of the human gene for intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and analysis of its 5'-regulatory region. Induction by cytokines and phorbol ester. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 15;147(8):2777–2786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witztum J. L., Steinberg D. Role of oxidized low density lipoprotein in atherogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1172/JCI115499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
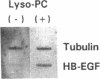
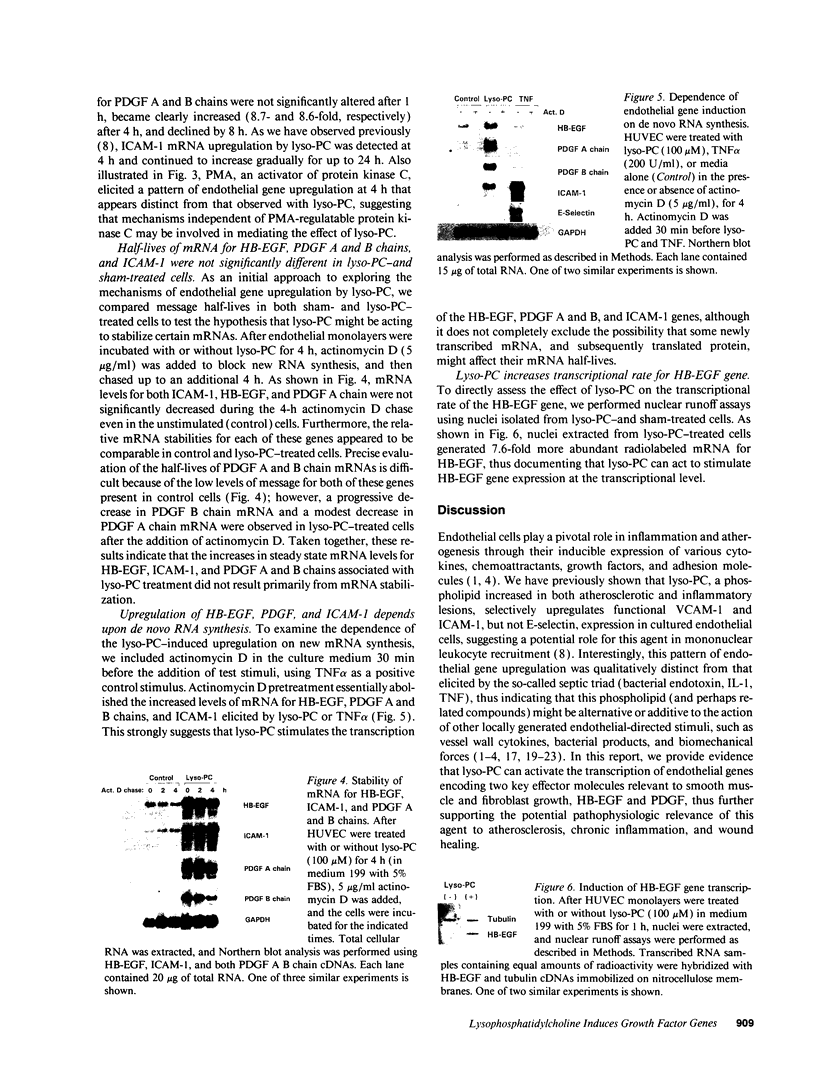
- Yoshizumi M., Kourembanas S., Temizer D. H., Cambria R. P., Quertermous T., Lee M. E. Tumor necrosis factor increases transcription of the heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor gene in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9467–9469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]