Abstract
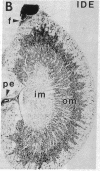
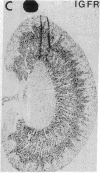
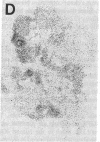
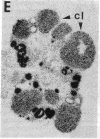
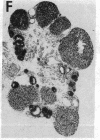
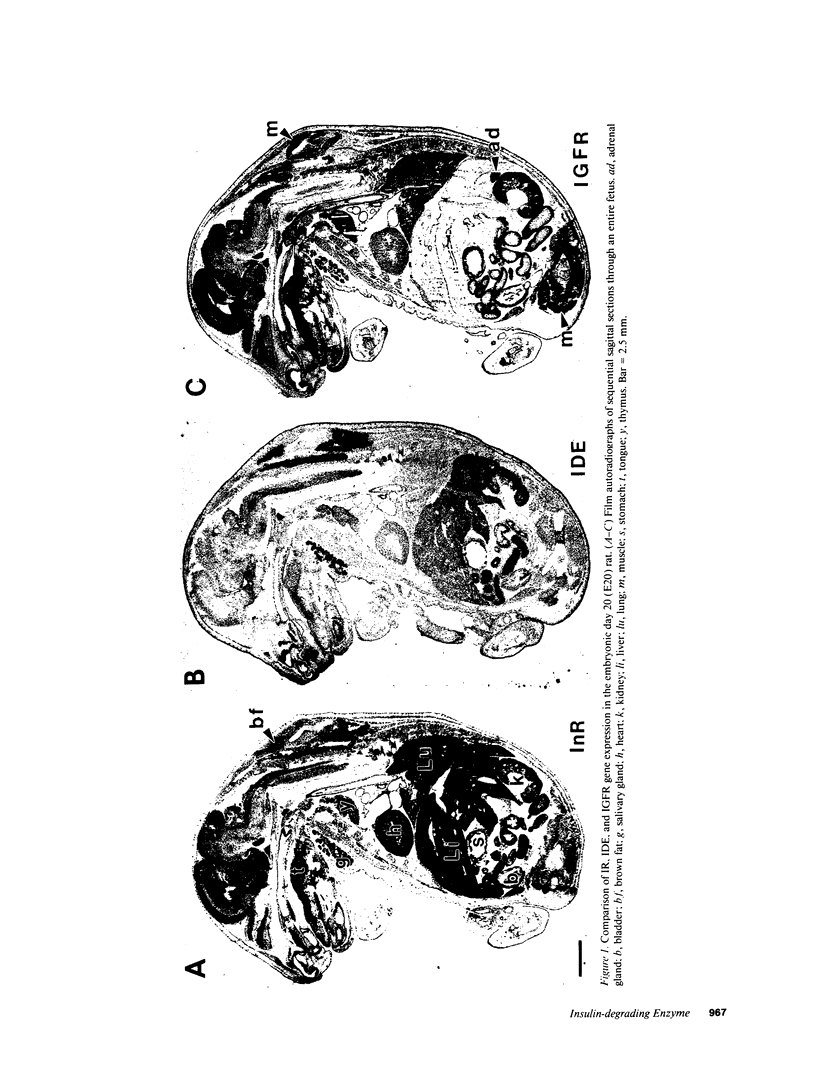
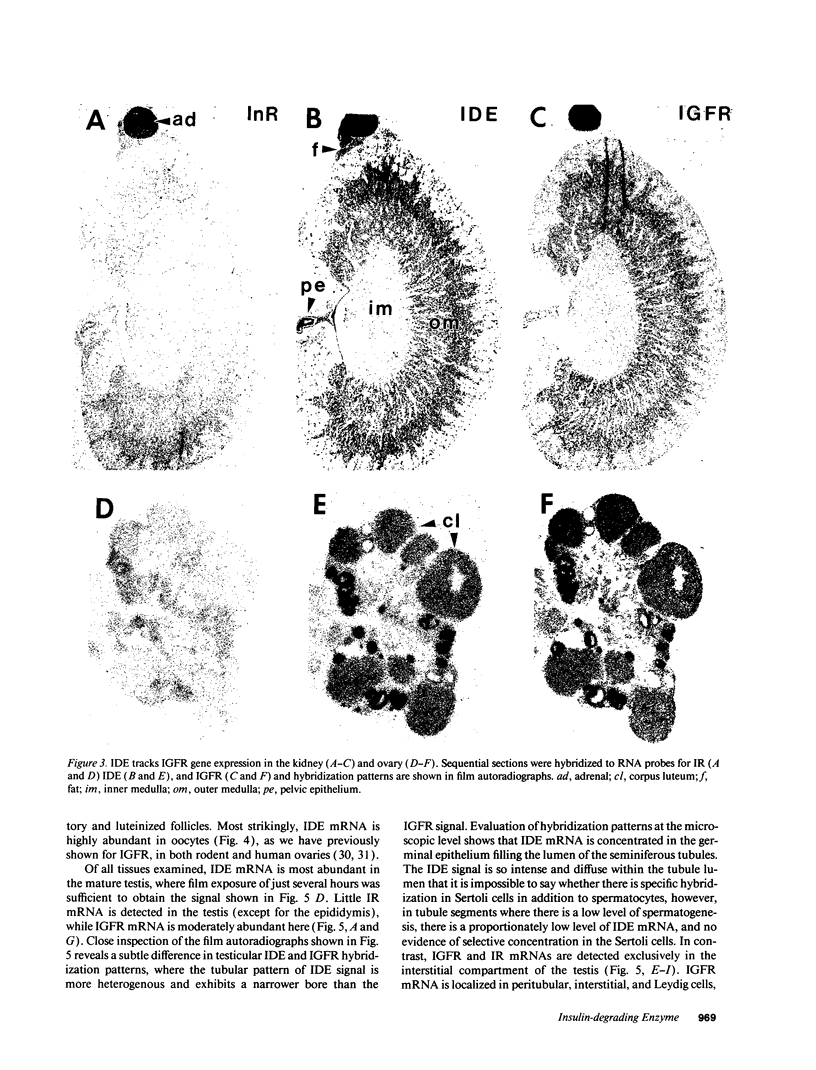
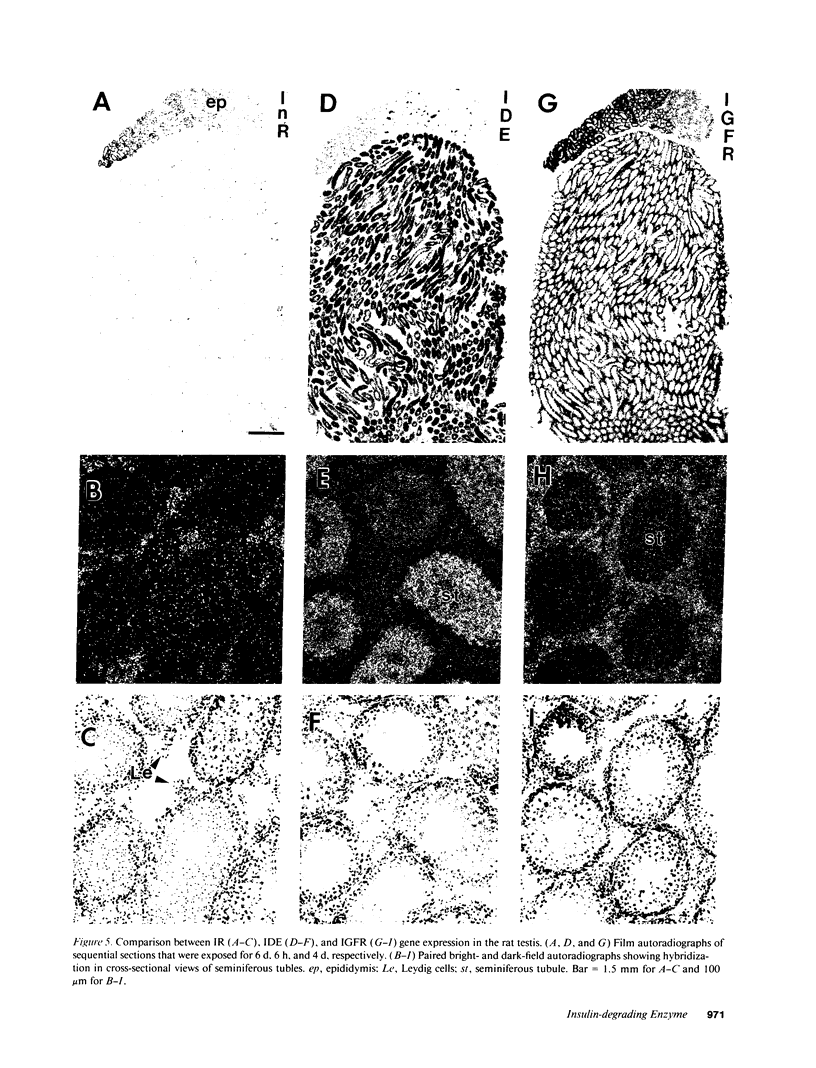
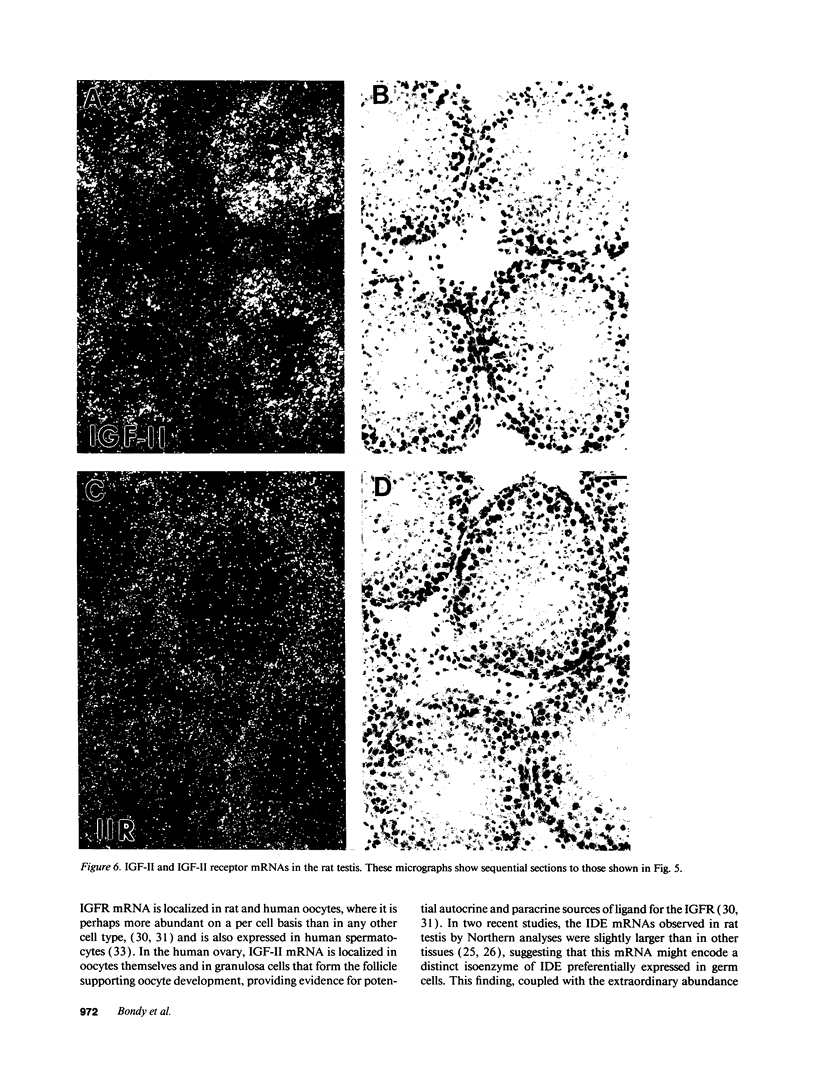
Insulin-degrading enzyme (IDE) hydrolyzes both insulin and IGFs and has been proposed to play a role in signal termination after binding of these peptides to their receptors. In situ hybridization was used to investigate the cellular distribution of IDE mRNA and to compare it with insulin receptor (IR) and IGF-I receptor (IGFR) gene expression in serial thin sections from a variety of tissues in embryonic and adult rats. IDE mRNA is highly abundant in kidney and liver, tissues known to play a role in insulin degradation. IDE and IR mRNAs are highly coexpressed in brown fat and liver. The highest level IDE gene expression, on a per cell basis, is found in germinal epithelium. IDE and IGFR mRNAs are colocalized in oocytes, while IDE is colocalized with the IGF-II receptor in spermatocytes, suggesting that IDE may be involved with degradation of IGF-II in the testis. In summary, IDE expression demonstrates significant anatomical correlation with insulin/IGF receptors. These data are compatible with a role for IDE in degrading insulin and IGFs after they bind to and are internalized with their respective receptors and may also suggest a novel role for IDE in germ cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affholter J. A., Fried V. A., Roth R. A. Human insulin-degrading enzyme shares structural and functional homologies with E. coli protease III. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1415–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.3059494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama H., Yokono K., Shii K., Ogawa W., Taniguchi H., Baba S., Kasuga M. Natural regulatory mechanisms of insulin degradation by insulin degrading enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Aug 16;170(3):1325–1330. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90539-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assoian R. K., Tager H. S. Peptide intermediates in the cellular metabolism of insulin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9078–9085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEYER R. E. A study of insulin metabolism in an insulin tolerant strain of mice. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1955 Aug;19(4):309–332. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0190309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J. Cellular proteolysis. An overview. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1992 Dec 31;674:1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1992.tb27472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister H., Müller D., Rehbein M., Richter D. The rat insulin-degrading enzyme. Molecular cloning and characterization of tissue-specific transcripts. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 15;317(3):250–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81286-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. S., Butler P. E. Intracellular proteases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:333–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckworth W. C. Insulin degradation: mechanisms, products, and significance. Endocr Rev. 1988 Aug;9(3):319–345. doi: 10.1210/edrv-9-3-319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdös E. G., Skidgel R. A. Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) and related regulators of peptide hormones. FASEB J. 1989 Feb;3(2):145–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagan J. M., Waxman L. Purification of a protease in red blood cells that degrades oxidatively damaged haemoglobin. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 1;277(Pt 3):779–786. doi: 10.1042/bj2770779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehm B. D., Rosner M. R. Regulation of insulin, epidermal growth factor, and transforming growth factor-alpha levels by growth factor-degrading enzymes. Endocrinology. 1991 Mar;128(3):1603–1610. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-3-1603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel F. G., Mahoney M. J., Duckworth W. C. Degradation of intraendosomal insulin by insulin-degrading enzyme without acidification. Diabetes. 1991 Apr;40(4):436–443. doi: 10.2337/diab.40.4.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Smith R. M., Smith J. A., Jarett L. Inhibition of insulin-degrading enzyme increases translocation of insulin to the nucleus in H35 rat hepatoma cells: evidence of a cytosolic pathway. Endocrinology. 1993 Jun;132(6):2293–2298. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.6.8504733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hari J., Shii K., Roth R. A. In vivo association of [125I]-insulin with a cytosolic insulin-degrading enzyme: detection by covalent cross-linking and immunoprecipitation with a monoclonal antibody. Endocrinology. 1987 Feb;120(2):829–831. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-2-829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayalar C., Wong W. T. Metalloendoprotease inhibitors which block the differentiation of L6 myoblasts inhibit insulin degradation by the endogenous insulin-degrading enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8928–8934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner R. J., Goldberg A. L. A high molecular weight metalloendoprotease from the cytosol of mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):967–976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo W. L., Gehm B. D., Rosner M. R. Regulation of insulin degradation: expression of an evolutionarily conserved insulin-degrading enzyme increases degradation via an intracellular pathway. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Oct;5(10):1467–1476. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo W. L., Montag A. G., Rosner M. R. Insulin-degrading enzyme is differentially expressed and developmentally regulated in various rat tissues. Endocrinology. 1993 Feb;132(2):604–611. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.2.7678795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lennarz W. J., Strittmatter W. J. Cellular functions of metallo-endoproteinases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jul 22;1071(2):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90022-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misbin R. I., Almira E. C. Degradation of insulin and insulin-like growth factors by enzyme purified from human erythrocytes. Comparison of degradation products observed with A14- and B26-[125I]monoiodoinsulin. Diabetes. 1989 Feb;38(2):152–158. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.2.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misbin R. I., Almira E. C., Duckworth W. C., Mehl T. D. Inhibition of insulin degradation by insulin-like growth factors. Endocrinology. 1983 Oct;113(4):1525–1527. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-4-1525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller D., Baumeister H., Buck F., Richter D. Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is a high-affinity substrate for rat insulin-degrading enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 5;202(2):285–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien D. A., Gabel C. A., Rockett D. L., Eddy E. M. Receptor-mediated endocytosis and differential synthesis of mannose 6-phosphate receptors in isolated spermatogenic and sertoli cells. Endocrinology. 1989 Dec;125(6):2973–2984. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-6-2973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps B. H., Varandani P. T., Shroyer L. A. Insulin B chain-degrading neutral peptidase activity in the rat. Tissue distribution and the effects of starvation and streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jun;195(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90321-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Mesirow M. L., Yokono K., Baba S. Degradation of insulin-like growth factors I and II by a human insulin degrading enzyme. Endocr Res. 1984;10(2):101–112. doi: 10.3109/07435808409035411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth R. A., Steele-Perkins G., Hari J., Stover C., Pierce S., Turner J., Edman J. C., Rutter W. J. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor receptors and responses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):537–543. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shii K., Baba S., Yokono K., Roth R. A. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a cytosolic insulin-degrading enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6503–6506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shii K., Roth R. A. Inhibition of insulin degradation by hepatoma cells after microinjection of monoclonal antibodies to a specific cytosolic protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4147–4151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Smeekens S. P., Ohagi S., Chan S. J. The new enzymology of precursor processing endoproteases. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23435–23438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. G., Johnson D. E., Bauer G. E. [125I]-insulin metabolism by the rat liver in vivo: evidence that a neutral thiol-protease mediates rapid intracellular insulin degradation. Metabolism. 1990 Mar;39(3):231–241. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90041-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Bondy C. Anatomy of the human ovarian insulin-like growth factor system. Biol Reprod. 1993 Mar;48(3):467–482. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod48.3.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Bondy C. Anatomy of the insulin-like growth factor system in the human testis. Fertil Steril. 1993 Nov;60(5):897–904. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)56294-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Bondy C. Insulin-like growth factor-II and its binding proteins in placental development. Endocrinology. 1992 Sep;131(3):1230–1240. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.3.1380437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou J., Chin E., Bondy C. Cellular pattern of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-I receptor gene expression in the developing and mature ovarian follicle. Endocrinology. 1991 Dec;129(6):3281–3288. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-6-3281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]