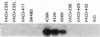Abstract
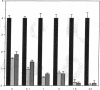
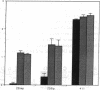
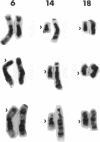
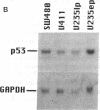
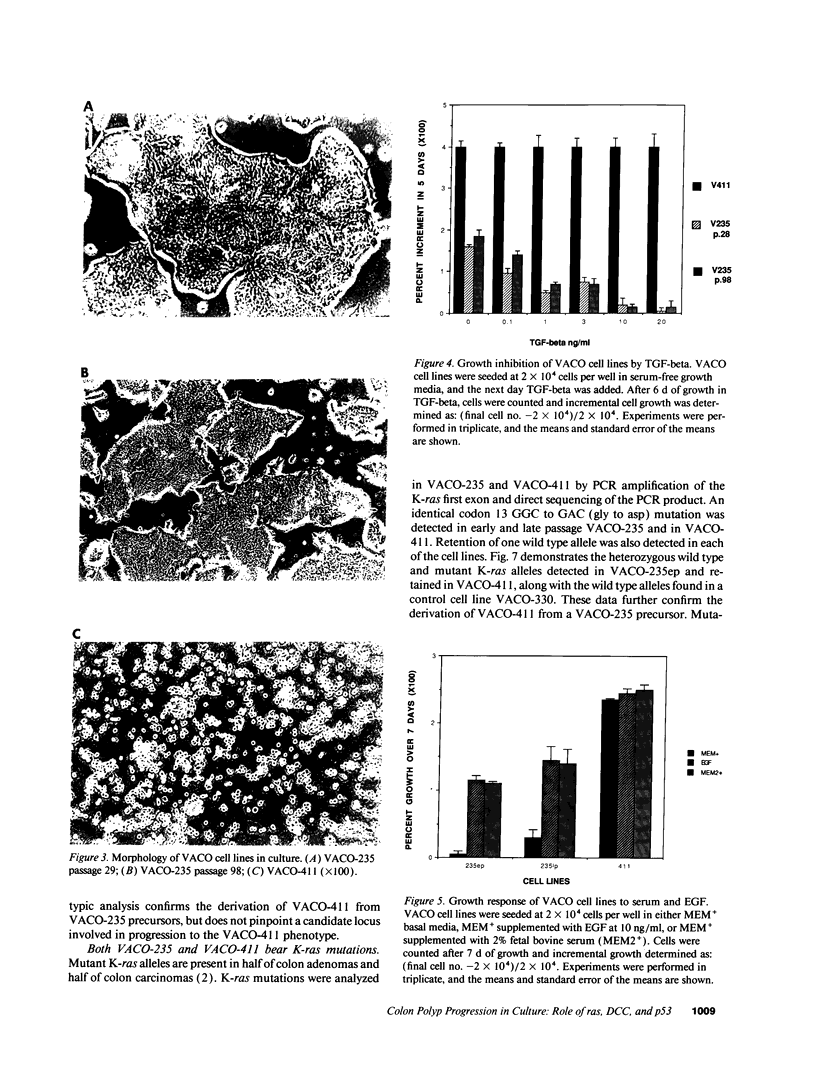
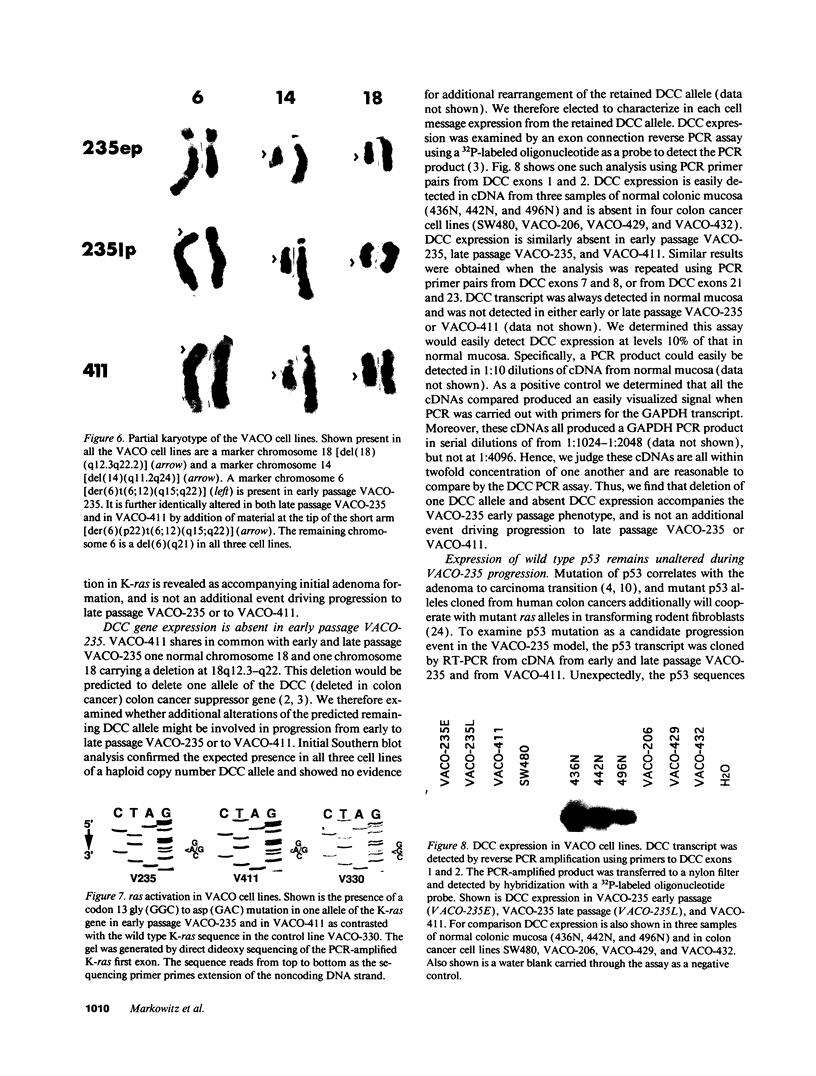
We describe the spontaneous progression of a colon adenoma cell line to tumorigenicity and growth factor independence. This system allows direct comparison of biologic stages of malignant progression with alterations of colon cancer suppressor genes and oncogenes. VACO-235, a human colon adenoma cell line, is at early passages nontumorigenic in the nude mouse, unable to grow in soft agar, growth stimulated by serum and EGF, and growth inhibited by TGF-beta. VACO-235 daughter passages 93 and higher have in culture spontaneously progressed to being weakly tumorigenic, but retain all other growth characteristics of VACO-235 early passages. A mouse xenograft from late passage VACO-235 was reestablished in culture as the granddaughter cell line, VACO-411. VACO-411 is highly tumorigenic, clones in soft agar, and is unresponsive to serum, EGF, and TGF-beta. Early passage VACO-235 bears a mutant K-ras allele, bears only mutant APC alleles, expresses no DCC transcripts, and expresses only wild type p53 transcripts. VACO-411 retains the identical genotype, still expressing only wild type p53. Colonic cells after ras mutation, APC mutation, and DCC inactivation remain nontumorigenic and growth factor dependent. Malignant progression involves at least two additional steps, and in VACO-411 can proceed by a novel pathway not requiring p53 inactivation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Paraskeva C., Markowitz S., Willson J. K., Hamilton S., Vogelstein B. p53 gene mutations occur in combination with 17p allelic deletions as late events in colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1990 Dec 1;50(23):7717–7722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Haron J. A., Stone E. M., Dennison O. E., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. Cloning and sequencing of a deoxyribonucleic acid copy of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid isolated from chicken muscle. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1605–1613. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Cho K. R., Nigro J. M., Kern S. E., Simons J. W., Ruppert J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Thomas G., Kinzler K. W. Identification of a chromosome 18q gene that is altered in colorectal cancers. Science. 1990 Jan 5;247(4938):49–56. doi: 10.1126/science.2294591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filmus J., Kerbel R. S. Development of resistance mechanisms to the growth-inhibitory effects of transforming growth factor-beta during tumor progression. Curr Opin Oncol. 1993 Jan;5(1):123–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyette M. C., Cho K., Fasching C. L., Levy D. B., Kinzler K. W., Paraskeva C., Vogelstein B., Stanbridge E. J. Progression of colorectal cancer is associated with multiple tumor suppressor gene defects but inhibition of tumorigenicity is accomplished by correction of any single defect via chromosome transfer. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1387–1395. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddow S., Fowlis D. J., Parkinson K., Akhurst R. J., Balmain A. Loss of growth control by TGF-beta occurs at a late stage of mouse skin carcinogenesis and is independent of ras gene activation. Oncogene. 1991 Aug;6(8):1465–1470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Finlay C. A., Quartin R. S., Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B., Levine A. J. Mutant p53 DNA clones from human colon carcinomas cooperate with ras in transforming primary rat cells: a comparison of the "hot spot" mutant phenotypes. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Dec;1(12):571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo R., Gatter K., Bartek J., Lane D., Harris A. L. Increased expression of mutant forms of p53 oncogene in primary lung cancer. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):675–679. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90801-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ionov Y., Peinado M. A., Malkhosyan S., Shibata D., Perucho M. Ubiquitous somatic mutations in simple repeated sequences reveal a new mechanism for colonic carcinogenesis. Nature. 1993 Jun 10;363(6429):558–561. doi: 10.1038/363558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning A. M., Williams A. C., Game S. M., Paraskeva C. Differential sensitivity of human colonic adenoma and carcinoma cells to transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta): conversion of an adenoma cell line to a tumorigenic phenotype is accompanied by a reduced response to the inhibitory effects of TGF-beta. Oncogene. 1991 Aug;6(8):1471–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S. D., Molkentin K., Gerbic C., Jackson J., Stellato T., Willson J. K. Growth stimulation by coexpression of transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor-receptor in normal and adenomatous human colon epithelium. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jul;86(1):356–362. doi: 10.1172/JCI114709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz S., Krystal G., Lebacq-Verheyden A. M., Way J., Sausville E. A., Battey J. Transcriptional activation and DNase I hypersensitive sites are associated with selective expression of the gastrin-releasing peptide gene. J Clin Invest. 1988 Sep;82(3):808–815. doi: 10.1172/JCI113683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massey A. C., Coppola M. A., Thomas C. Y. Origin of pathogenic determinants of recombinant murine leukemia viruses: analysis of Bxv-1-related xenotropic viruses from CWD mice. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5491–5499. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5491-5499.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBain J. A., Weese J. L., Meisner L. F., Wolberg W. H., Willson J. K. Establishment and characterization of human colorectal cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1984 Dec;44(12 Pt 1):5813–5821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll U. M., Riou G., Levine A. J. Two distinct mechanisms alter p53 in breast cancer: mutation and nuclear exclusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7262–7266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan R., Lawlor K. G., Schaapveld R. Q., Cho K. R., Vogelstein B., Bui-Vinh Tran P., Osborne M. P., Telang N. T. Antisense RNA to the putative tumor-suppressor gene DCC transforms Rat-1 fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1992 Mar;7(3):553–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishisho I., Nakamura Y., Miyoshi Y., Miki Y., Ando H., Horii A., Koyama K., Utsunomiya J., Baba S., Hedge P. Mutations of chromosome 5q21 genes in FAP and colorectal cancer patients. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):665–669. doi: 10.1126/science.1651563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliner J. D., Kinzler K. W., Meltzer P. S., George D. L., Vogelstein B. Amplification of a gene encoding a p53-associated protein in human sarcomas. Nature. 1992 Jul 2;358(6381):80–83. doi: 10.1038/358080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paraskeva C., Buckle B. G., Sheer D., Wigley C. B. The isolation and characterization of colorectal epithelial cell lines at different stages in malignant transformation from familial polyposis coli patients. Int J Cancer. 1984 Jul 15;34(1):49–56. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910340109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paraskeva C., Hague A., Rooney N., Williams A. C., Harper S. J., Hanlon K. A., Atkinson R. J., Corfield A. P. A single human colonic adenoma cell line can be converted in vitro to both a colorectal adenocarcinoma and a mucinous carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1992 Jun 19;51(4):661–664. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910510426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell S. M., Zilz N., Beazer-Barclay Y., Bryan T. M., Hamilton S. R., Thibodeau S. N., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K. W. APC mutations occur early during colorectal tumorigenesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 17;359(6392):235–237. doi: 10.1038/359235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. J., Johnson K. A., Bryan T. M., Hill D. E., Markowitz S., Willson J. K., Paraskeva C., Petersen G. M., Hamilton S. R., Vogelstein B. The APC gene product in normal and tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2846–2850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M. The four classes of endogenous murine leukemia virus: structural relationships and potential for recombination. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2659–2669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2659-2669.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki Y., Orita M., Shiraishi M., Hayashi K., Sekiya T. Detection of ras gene mutations in human lung cancers by single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis of polymerase chain reaction products. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):1037–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Oshimura M., Kikuchi R., Seki M., Hayashi T., Miyaki M. Suppression of tumorigenicity in human colon carcinoma cells by introduction of normal chromosome 5 or 18. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):340–342. doi: 10.1038/349340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor A. D., Moore DH I. I., Edgerton S. M., Kawasaki E. S., Reihsaus E., Lynch H. T., Marcus J. N., Schwartz L., Chen L. C., Mayall B. H. Accumulation of p53 tumor suppressor gene protein: an independent marker of prognosis in breast cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1992 Jun 3;84(11):845–855. doi: 10.1093/jnci/84.11.845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Kern S. E., Preisinger A. C., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Smits A. M., Bos J. L. Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. N Engl J Med. 1988 Sep 1;319(9):525–532. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198809013190901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman B. E., Saxon P. J., Pasquale S. R., Jones G. R., Geiser A. G., Stanbridge E. J. Introduction of a normal human chromosome 11 into a Wilms' tumor cell line controls its tumorigenic expression. Science. 1987 Apr 10;236(4798):175–180. doi: 10.1126/science.3031816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. C., Harper S. J., Paraskeva C. Neoplastic transformation of a human colonic epithelial cell line: in vitro evidence for the adenoma to carcinoma sequence. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 1;50(15):4724–4730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willson J. K., Bittner G. N., Oberley T. D., Meisner L. F., Weese J. L. Cell culture of human colon adenomas and carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1987 May 15;47(10):2704–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu S. P., Theodorescu D., Kerbel R. S., Willson J. K., Mulder K. M., Humphrey L. E., Brattain M. G. TGF-beta 1 is an autocrine-negative growth regulator of human colon carcinoma FET cells in vivo as revealed by transfection of an antisense expression vector. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):187–196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]