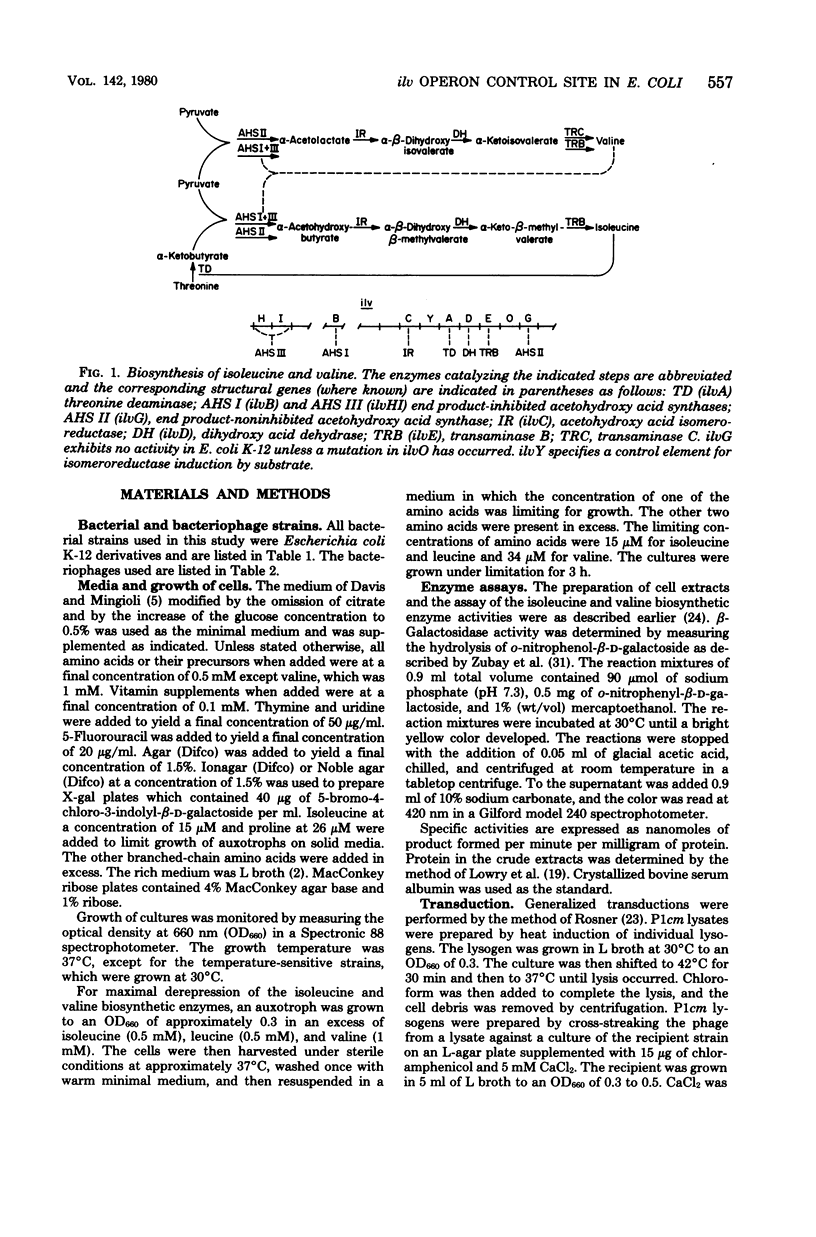
Abstract
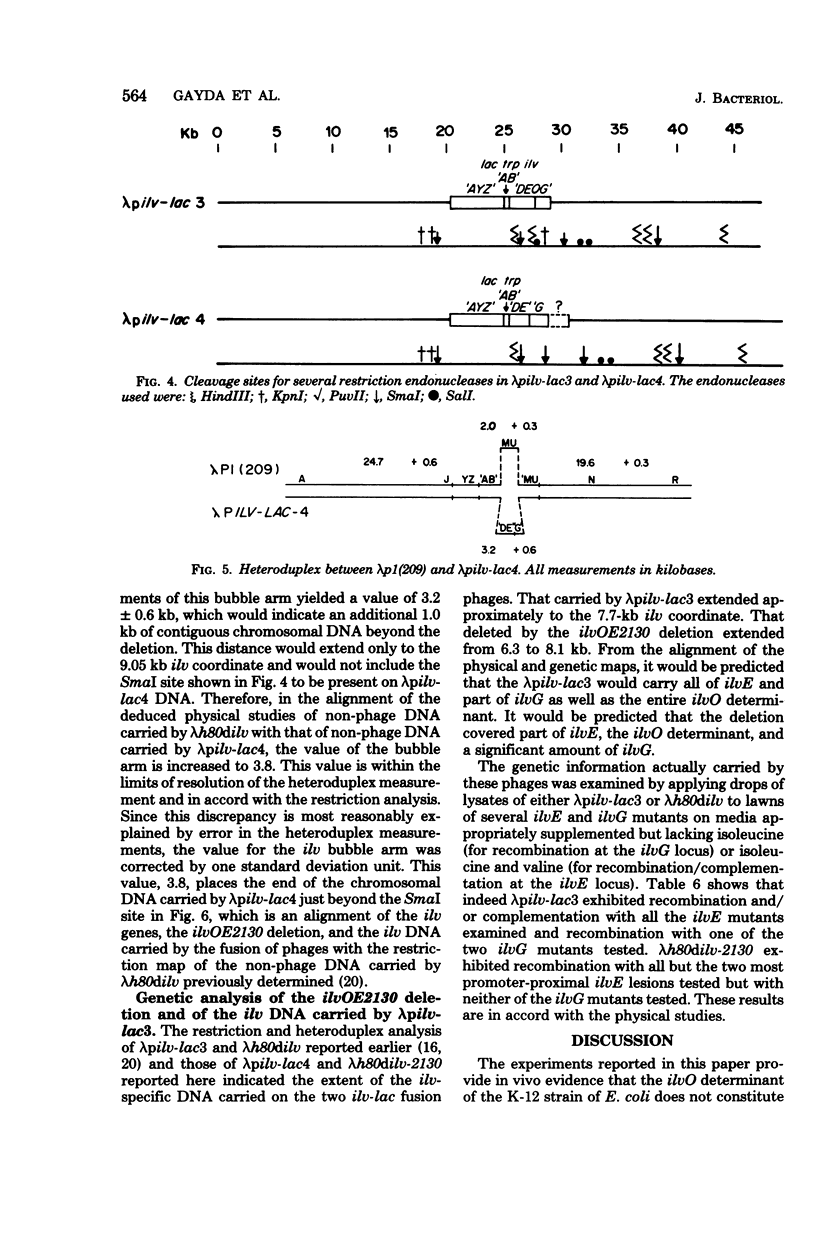
A strain of Escherichia coli K-12 containing a deletion extending from early in the ilvE gene toward the ilvG gene was shown to exhibit a higher expression of the downstream genes, ilvD and ilvA, than did an ilv+ strain. The elevated expression was under apparently normal ilv-specific control, however. The deletion was transferred to the ilv region of lamba h80dilv and shown by restriction endonuclease and heteroduplex analysis to extend through the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) shown, in the preceding paper (C. S. Subrahmanyam, G. M. McCorkle, and H. E. Umbarget, J. Bacteriol 142:547--555, 1980), to contain the ilvO determinant. The deletion was also transferred to an ilv-lac fusion strain and shown to cause an increase in beta-galactosidase formation while allowing retention of ilv-specific control. Transducing phages excised from these fusion strains with and without the ilvO determinant were compared. The phage carrying the ilvO+ determinant contained ilv DNA extending only into but not through the ilvG gene. It did not exhibit an ilv-specific control of beta-galactosidase formation. The phage carrying the deletion of ilvO but containing ilv DNA extending beyond the ilvG gene exhibited ilv-specific control of beta-galactosidase formation. It was concluded that the multivalently controlled ilv-specific promoter affecting ilv operon expression lies upstream from ilvG and that the ilvO region in the wild-type K-12 strain is a region of polarity preventing ilvG expression and reducing ilvEDA expression.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes W. M. DNA sequence from the histidine operon control region: seven histidine codons in a row. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4281–4285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Blasi F., Di Lauro R., Frunzio R., Bruni C. B. Nucleotide sequence of the attenuator region of the histidine operon of Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4276–4280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin N. C. Altered reading of genetic signals fused to the N operon of bacteriophage lambda: genetic evidence for modification of polymerase by the protein product of the N gene. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):33–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90161-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemmill R. M., Wessler S. R., Keller E. B., Calvo J. M. leu operon of Salmonella typhimurium is controlled by an attenuation mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4941–4945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe M. M. Prophage deletion mapping of bacteriophage Mu-1. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):93–101. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson E. N., Yanofsky C. Thr region between the operator and first structural gene of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli may have a regulatory function. J Mol Biol. 1973 May 5;76(1):89–101. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONDO E., MITSUHASHI S. DRUG RESISTANCE OF ENTERIC BACTERIA. IV. ACTIVE TRANSDUCING BACTERIOPHAGE P1 CM PRODUCED BY THE COMBINATION OF R FACTOR WITH BACTERIOPHAGE P1. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88:1266–1276. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1266-1276.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai T. Regulation of the expression of the histidine operon in Salmonella typhimurium. Nature. 1974 Jun 7;249(457):523–527. doi: 10.1038/249523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Kaya K. M., Chamberlin M. J. Escherichia coli RNA polymerase-rifampicin complexes bound at promoter sites block RNA chain elongation by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and T7-specific RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 26;17(26):5798–5804. doi: 10.1021/bi00619a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline E. L., Brown C. S., Coleman W. G., Jr, Umbarger H. E. Regulation of isoleucine-valine biosynthesis in an ilvDAC deletion strain of Escherichia coli K-12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Apr 23;57(4):1144–1151. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90816-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leathers T. D., Noti J., Umbarger H. E. Physical characterization of ilv-lac fusions. J Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;140(1):251–260. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.1.251-260.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Yanofsky C. Transcription termination at the trp operon attenuators of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: RNA secondary structure and regulation of termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4365–4369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCorkle G. M., Leathers T. D., Umbarger H. E. Physical organization of the ilvEDAC genes of Escherichia coli strain K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):89–93. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGilvray D., Umbarger H. E. Regulation of transaminase C synthesis in Escherichia coli: conditional leucine auxotrophy. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):715–723. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.715-723.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Smith F. J., Umbarger H. E. Mutations affecting the formation of acetohydroxy acid synthase II in Escherichia coli K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 1;169(3):299–314. doi: 10.1007/BF00382276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. M., Smolin D. E., Umbarger H. E. Polarity and the regulation of the ilv gene cluster in Escherichia coli strain K-12. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Oct 18;148(2):111–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00268374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subrahmanyam C. S., McCorkle G. M., Umbarger H. E. Physical location of the ilvO determinant in Escherichia coli K-12 deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):547–555. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.547-555.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonder Haar R. A., Umbarger H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli K-12: detection and measurement of ilv-specific messenger ribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):687–696. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.687-696.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. D., Wild J., Umbarger H. E. Positive control of ilvC expression in Escherichia coli K-12; identification and mapping of regulatory gene ilvY. J Bacteriol. 1979 Sep;139(3):1014–1020. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.3.1014-1020.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Brown K., Killingly D., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of the leader region of the phenylalanine operon of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


