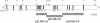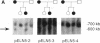Abstract
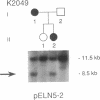
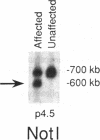
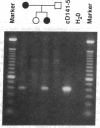
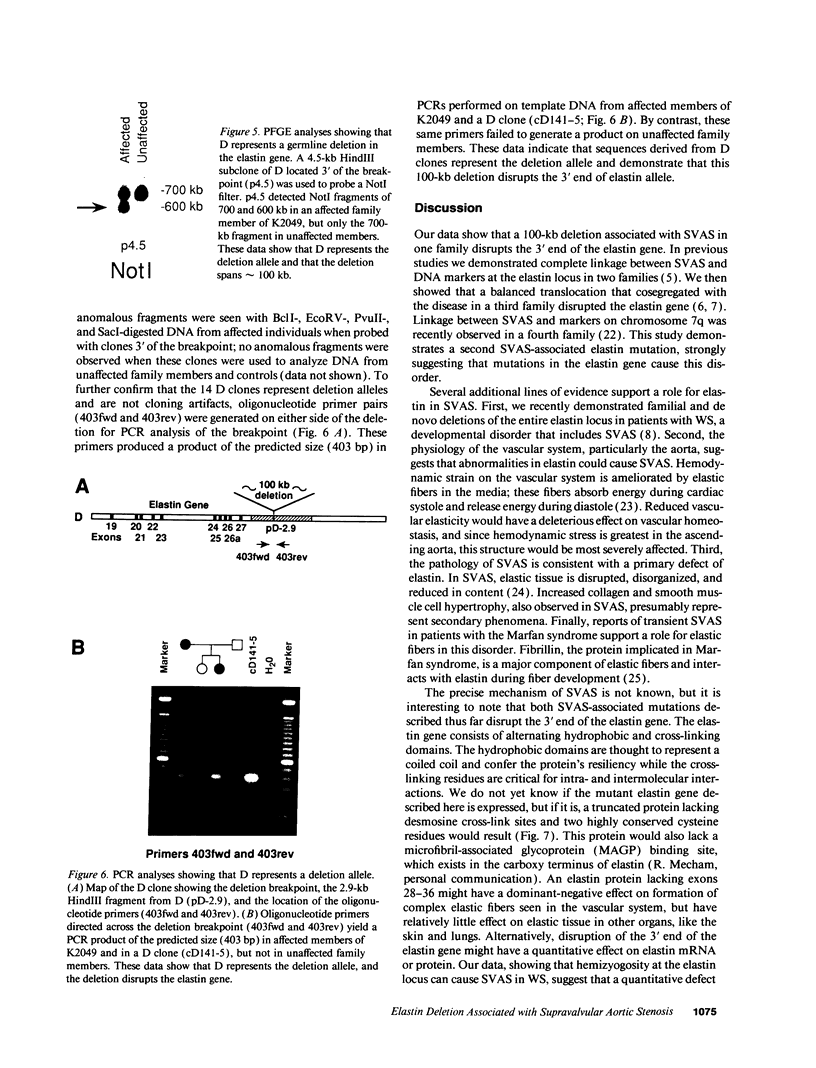
Supravalvular aortic stenosis (SVAS) is an inherited vascular disease that can cause heart failure and death. SVAS can be inherited as an autosomal dominant trait or as part of a developmental disorder, Williams syndrome (WS). In recent studies we presented evidence suggesting that a translocation disrupting the elastin gene caused SVAS in one family while deletions involving the entire elastin locus caused WS. In this study, pulsed-field, PCR, and Southern analyses showed that a 100-kb deletion of the 3' end of the elastin gene cosegregated with the disease in another SVAS family. DNA sequence analysis localized the breakpoint between elastin exons 27 and 28, the same region disrupted by the SVAS-associated translocation. These data indicate that mutations in the elastin gene cause SVAS and suggest that elastin exons 28-36 may encode critical domains for vascular development.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bashir M. M., Indik Z., Yeh H., Ornstein-Goldstein N., Rosenbloom J. C., Abrams W., Fazio M., Uitto J., Rosenbloom J. Characterization of the complete human elastin gene. Delineation of unusual features in the 5'-flanking region. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8887–8891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach G. L., Siems J. E., Faraci F. M., Heistad D. D. Mechanics and composition of arterioles in brain stem and cerebrum. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):H493–H501. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.2.H493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botto M., Fong K. Y., So A. K., Barlow R., Routier R., Morley B. J., Walport M. J. Homozygous hereditary C3 deficiency due to a partial gene deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4957–4961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran M. E., Atkinson D. L., Ewart A. K., Morris C. A., Leppert M. F., Keating M. T. The elastin gene is disrupted by a translocation associated with supravalvular aortic stenosis. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90168-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISENBERG R., YOUNG D., JACOBSON B., BOITO A. FAMILIAL SUPRAVALVULAR AORTIC STENOSIS. Am J Dis Child. 1964 Oct;108:341–347. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1964.02090010343002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ensing G. J., Schmidt M. A., Hagler D. J., Michels V. V., Carter G. A., Feldt R. H. Spectrum of findings in a family with nonsyndromic autosomal dominant supravalvular aortic stenosis: a Doppler echocardiographic study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1989 Feb;13(2):413–419. doi: 10.1016/0735-1097(89)90520-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewart A. K., Morris C. A., Ensing G. J., Loker J., Moore C., Leppert M., Keating M. A human vascular disorder, supravalvular aortic stenosis, maps to chromosome 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3226–3230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm T., Wesselhoeft H. Zur Genetik des Williams-Beuren-Syndroms und der isolierten Form der supravalvulären Aortenstenose. Untersuchungen von 128 Familien. Z Kardiol. 1980 Mar;69(3):168–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Indik Z., Yeh H., Ornstein-Goldstein N., Sheppard P., Anderson N., Rosenbloom J. C., Peltonen L., Rosenbloom J. Alternative splicing of human elastin mRNA indicated by sequence analysis of cloned genomic and complementary DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5680–5684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel L. M., Smith K. D., Boyer S. H., Borgaonkar D. S., Wachtel S. S., Miller O. J., Breg W. R., Jones H. W., Jr, Rary J. M. Analysis of human Y-chromosome-specific reiterated DNA in chromosome variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1245–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacerra G., Fioretti G., De Angioletti M., Pagano L., Guarino E., de Bonis C., Viola A., Maglione G., Scarallo A., De Rosa L. (Alpha)alpha 5.3: a novel alpha(+)-thalassemia deletion with the breakpoints in the alpha 2-globin gene and in close proximity to an Alu family repeat between the psi alpha 2- and psi alpha 1-globin genes. Blood. 1991 Nov 15;78(10):2740–2746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. A., Demsey S. A., Leonard C. O., Dilts C., Blackburn B. L. Natural history of Williams syndrome: physical characteristics. J Pediatr. 1988 Aug;113(2):318–326. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris C. A., Loker J., Ensing G., Stock A. D. Supravalvular aortic stenosis cosegregates with a familial 6; 7 translocation which disrupts the elastin gene. Am J Med Genet. 1993 Jul 1;46(6):737–744. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320460634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris T., Thacker J. Formation of large deletions by illegitimate recombination in the HPRT gene of primary human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1392–1396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor W. N., Davis J. B., Jr, Geissler R., Cottrill C. M., Noonan J. A., Todd E. P. Supravalvular aortic stenosis. Clinical and pathologic observations in six patients. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Feb;109(2):179–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson T. M., Michels V. V., Lindor N. M., Pastores G. M., Weber J. L., Schaid D. J., Driscoll D. J., Feldt R. H., Thibodeau S. N. Autosomal dominant supravalvular aortic stenosis: localization to chromosome 7. Hum Mol Genet. 1993 Jul;2(7):869–873. doi: 10.1093/hmg/2.7.869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai L. Y., Keene D. R., Engvall E. Fibrillin, a new 350-kD glycoprotein, is a component of extracellular microfibrils. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2499–2509. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto J., Christiano A. M., Kähäri V. M., Bashir M. M., Rosenbloom J. Molecular biology and pathology of human elastin. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Nov;19(4):824–829. doi: 10.1042/bst0190824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Lewis K. A., Ruiz J. C., Rothenberg B., Zhao J., Evans G. A. Cosmid vectors for rapid genomic walking, restriction mapping, and gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2160–2164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]