Abstract
Osteoclast inhibitory peptide-1 (OIP) is an autocrine/paracrine inhibitor of osteoclast differentiation, and mice that overexpress OIP-1 in osteoclast lineage cells develop an osteopetrosis bone phenotype. In this study, we show that OIP-1 binding to the Fcγ receptor IIB (FcγRIIB) inhibits osteoclast differentiation. Confocal microscopy revealed colocalization of OIP-1 with FcγRIIB in osteoclasts, and we observed that OIP-1 carboxy-terminal GPI-linked peptide forms a 1:1 complex with recombinant FcγRIIB protein with an affinity binding of a dissociation constant of approximately 4 μm. Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-bearing adapter proteins (FcRγ and DNAX-activating protein of molecular mass 12 kDa) are critical for osteoclast development, and OIP-1 transgenic mouse-derived preosteoclast cells demonstrated suppression (6-fold) of ITAM phosphorylation of FcRγ but not DNAX-activating protein of molecular mass 12 kDa. Interestingly, these preosteoclast cells demonstrated increased levels (4-fold) of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif phosphorylation of FcγRIIB and Src homology 2-domain-containing proteins tyrosine phosphatase 1 activation. Further, OIP-1 mouse-derived preosteoclasts cells demonstrated inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase activation (4.5-fold), compared with wild-type mice. These results suggest that cross-regulation of immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif and ITAM bearing Fc receptors may play a role in OIP-1 suppression of spleen tyrosine kinase activation and inhibition of osteoclast differentiation. Thus, OIP-1 is an important physiologic regulator of osteoclast development and may have therapeutic utility for bone diseases with high bone turnover.
OIP-1 signals through the membrane FcγRIIB in the osteoclast precursor cells to inhibit osteoclast differentiation and may have therapeutic utility for treatment of bone diseases with high bone turnover, such as osteoporosis and Paget’s disease
We have previously identified and characterized the osteoclast inhibitory peptide-1 (OIP-1/hSca) as an autocrine/paracrine inhibitor of osteoclast differentiation (1,2). More recently, we have shown that targeted overexpression of OIP-1 in osteoclast lineage cells produces an osteopetrosis bone phenotype in mice (3). OIP-1/hSca, also termed retinoic acid-induced gene expression or human thymic sheared antigen (TSA-1/Sca-2), is a Ly-6 gene-related differentiation antigen expressed on immature thymocytes and thymic epithelial cells (4). OIP-1/hSca is a glycophosphatidylinositol (GPI)-linked membrane protein (16 kDa) containing a 79-amino acid extracellular peptide and a 32-amino acid carboxy-terminal GPI-linked peptide (c-peptide). We have shown that the OIP-1 c-peptide region is critical for its osteoclast inhibitory activity (1); however, a functional cognate receptor/membrane protein that interacts with OIP-1 in osteoclast progenitor cells is unknown.
We have previously shown that interferon-γ stimulates OIP-1 expression in osteoclast precursor cells (2). Sca-2, a murine homolog of OIP-1, is a marker gene expressed during early T-cell development/activation and may play a regulatory role in thymocyte differentiation (5). Previously, Sca-2 has been described to function as a modulator of the T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling pathway (6). An anti-Sca-2 monoclonal antibody inhibited tyrosine phosphorylation of cluster of differentiation 3 (CD3)ζ chains and IL-2 production induced by anti-CD3 stimulation in T-cell hybridomas, suggesting that a signal via Sca-2 regulates early and late events in TCR signaling (7). GPI-anchored proteins are membrane bound and can be shed from the cell surface in membrane-bound vesicles or released by the action of phospholipase C. In addition, GPI-linked proteins transmit signals to the cell interior by interacting with nonreceptor type tyrosine kinases p56lck and 59fyn (8). However, TSA1/Sca-2 GPI-anchored membrane protein lacks transmembrane and cytoplasmic regions, and how Sca-2 transmits signals into the cell cytoplasm is unclear. Recently, it has been reported that Sca-2 is physically and functionally associated with CD3ζ chains of the TCR complex (9).
Evidence suggests a physical association between TSA-1 and Fcγ receptor IIB (FcγRIIB) on the surface of activated B cells (10). FcγRIIB contains an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM). ITIM-containing receptors were originally identified by their ability to inhibit signaling by immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)-bearing receptors (11). Most recent studies indicate that Ly49Q, an ITIM-bearing natural killer receptor, functions as a positive regulator of osteoclast differentiation (12). Src homology 2 (SH2)-domain-containing proteins tyrosine phosphatase 1 (SHP1) and SHP2 and SH2-domain-containing inositol-5-phosphatase-1 (SHIP1) having affinity for ITIM has been shown to negatively regulate osteoclastogenesis (13,14). ITAM-bearing common γ-subunit of FcRs (FcγRI and FcγRIII) and DNAX-activating protein of molecular mass 12 kDa (DAP12) are crucial for osteoclast development. Spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) functions as an adaptor molecule for ITAM signaling of FcRγ and DAP12 (15). Also, ITAM-based activation of Syk plays a central role in multiple biological functions beyond the adaptive immune response, including bone resorption (16). In this study, we demonstrate that OIP-1 binding to the FcγRIIB expressed on osteoclast progenitor cells results in inhibition of osteoclast differentiation and implicate OIP-1 as an important physiologic regulator of bone remodeling.
Materials and Methods
Reagents
OIP-1/hSca c-peptide (NFSAADGGLRASVTLLGAGLLLSLLPALLRFGP) was synthesized by Genemed Synthesis, Inc. (San Francisco, CA). OIP-1 expression plasmid OIP-1 CDS 5-3 was constructed as described earlier (2). OIP-1 c-peptide was labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) following the manufacturer’s protocol (Pierce, Rockford, IL). Recombinant mouse receptor activator for nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) ligand (RANKL) (catalog no. 462-TR-010), mouse macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) (catalog no. 416-ML-010) and extracellular domain of the mouse FcγRI protein (catalog no. 2074), human FcγRIIA protein (catalog no. 1330), mouse FcγRIIB protein (catalog no. 1460), mouse FcγRIII protein (catalog no. 1960), and monoclonal mouse anti-FcγRIIB antibody (catalog no. MAB-14601) were obtained from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN). Small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) were custom designed for FcγRIIB (NM_001077189) (QIAGEN, Inc., Valencia, CA). Antigoat polyclonal DAP12 antibody (sc-7853) and SHIP1/2 antibody (sc-14503) were obtained from Santa Cruz Biotechnologies (Santa Cruz, CA). Anti-FcεRI, γ-chain specific rabbit polyclonal IgG (catalog no. 06-727), antiphosphotyrosine (p-Y) (clone 4G10) mouse monoclonal IgG (catalog no. 12-302), and anti-SHP1/2 (clone NL213) rabbit monoclonal IgG (catalog no. 05-742) were purchased from Upstate Cell Signaling Solutions (Lake Placid, NY), and antirabbit Syk, anti-pSyk, and anti-pSHP2 antibodies were obtained from Cell Signaling (La Jolla, CA). Antiphospho-SHIP1/2 antibody (Stemcell Technologies, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada) and antirabbit pSHP1 (PY536) antibody were obtained from Abcam (Cambridge, MA).
Animals
We have recently developed OIP-1 transgenic mice that overexpress OIP-1 in osteoclast lineage cells using the mouse tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) gene promoter (3). FcγRII−/− (stock no. 002848) deficient mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). All procedures involving animal use were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Medical University of South Carolina.
Cell culture and transfection
RAW 264.7 cells obtained from American Type Culture Collection (Rockville, MD) were cultured (at 37 C, 5% CO2) in DMEM supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum and antibiotics. RAW 264.7 cells were transiently transfected with plasmid OIP-1 CDS 5-3 expression vector and 10 μm siRNA against FcγRIIB by lipofectamine. After 48 h, total-cell lysates obtained from these cells were subjected to Western blot analysis for OIP-1 and FcγRIIB expression using rabbit anti-OIP-1 and anti-FcγRIIB antibody, respectively.
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis
The OIP-1 c-peptide binding with FcγRIIB membrane receptor in RAW 264.7 cells was determined by FACS analysis. The RAW 264.7 cells transfected with nonspecific control and FcγRIIB siRNA were harvested using enzyme-free dissociation buffer, washed once, resuspended in 100 μl FACS buffer, and incubated with 10 μm FITC-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide or nonspecific peptide at 4 C for 2 h. Cells were washed twice and resuspended in 500 μl FACS buffer and subjected to FACS analysis. Live cells were gated using propidium iodide (Roche, Indianapolis, IN) staining, and 10,000 events were acquired using a BD FACS Calibur flow cytometer and analyzed using BD Cell Quest software (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA).
Coimmunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay
The cell lysates from RAW 264.7 cells transfected with or without OIP-1 cDNA expression vector and wild-type (WT), OIP-1, FcγRII−/− mouse bone marrow-derived preosteoclast cells were subjected to Co-IP. Briefly, 250 μg of protein were incubated with agarose A for 2 h to preclear nonspecific binding. Cell lysates were centrifuged, and the supernatant obtained was incubated either with anti-OIP-1 antibody, anti-FcγRIIB antibody, FcRγ chain specific antibody, anti-DAP12 antibody, or control IgG overnight at 4 C on an orbital shaker. The immune complexes were captured by adding 100 μl protein A agarose (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) beads and incubated for 2 h at 4 C followed by centrifugation. The pellets were boiled for 5 min in reducing sample buffer and subjected to SDS-PAGE. The gels were either stained with Coomassie brilliant blue or analyzed by Western blotting as described (15).
Mass spectrometric analysis
The OIP-1 IP obtained as described was resolved in SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue, and gel plugs were processed for trypsin digestion and mass spectrometric analysis as previously described (17). Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI) time-of-flight (TOF) mass spectrometry (MS) and TOF/TOF tandem MS were performed on a Voyager 4700 (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) using data-dependent tandem MS acquisition on the 10 most abundant ions present in each MALDI-TOF peptide mass map. MALDI-TOF peptide mass maps and accompanying tandem mass spectra were then collectively searched against the SWISS-PROT and NCBInr databases using GPS Explorer software (Applied Biosystems) running the MASCOT database search engine (Matrix-Science, Boston, MA). The FcγRIIB (CD32) protein identified in the immune complex with OIP-1 was further confirmed by Western blot analysis.
Microtiter binding assay
The affinity constant for OIP-1 binding with different types of recombinant extracellular domains of FcγR proteins (FcγRI, FcγRIIA, FcγRIIB, and FcγRIII) was determined with a microtiter binding assay as previously described (18). Briefly, recombinant FcγR proteins (20 μg) in 0.1 m sodium carbonate buffer (pH 9.5) were coated overnight at 4 C in microtiter plates and blocked with 2% fetal serum albumin in PBS for 1 h at 37 C. OIP-1 c-peptide (0–10 μm) or a nonspecific control peptide was loaded in triplicate and incubated for 3 h at 37 C, followed by the addition of 100 μl anti-OIP-1 antibody (1 μg/ml) or 100 μl anti-FcγRIIB specific antibody (1 μg/ml) for a competition assay at room temperature for 2 h. Horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat antirabbit IgG (1:20,000) in blocking buffer was added (1 h, room temperature), and the reaction was visualized by the addition of 50 μl chromogenic substrate for 30 min. The reaction was stopped with 100 μl 2N H2SO4, and absorbance at 492 nm was measured with a reduction at 630 nm using an ELISA plate reader. Dissociation constant (Kd) were determined by nonlinear curve fit of the Hill function using Kaleidagraph 4.03.
Equilibrium dialysis assay
The binding affinity of FITC-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide was measured by equilibrium dialysis assay as described (19). Custom microdialysis chambers (75 μl volume) were separated by a dialysis membrane with a 10,000-Da cutoff. The dialysis chamber containing 10 μm of recombinant FcγRIIB protein with FITC-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide incubated at 4 C overnight. The free and bound OIP-1 fluorescence intensity was measured using a spectrofluorimeter.
Osteoclast culture and bone resorption activity assay
WT, OIP-1 transgenic, and FcγRII-deficient (FcγRII−/−) (20) mouse bone marrow cells were cultured to form osteoclasts as described (2). Briefly, mouse bone marrow-derived nonadherent cells (1.3 × 106/ml) were cultured in 96-well plates in the presence of RANKL (100 ng/ml) and M-CSF (10 ng/ml) with or without OIP-1 c-peptide (0–100 ng/ml) for 5 d. At the end of the culture period, the cells were fixed either with 2% glutaraldehyde in PBS for 20 min and stained for TRAP activity or fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for confocal imaging. TRAP positive multinucleated osteoclasts containing three or more nuclei were scored microscopically.
To determine the bone resorption activity, WT and FcγRII−/− mouse bone marrow cells treated with 10 ng/ml M-CSF for 12 h, and nonadherent bone marrow mononuclear cells (1 × 106 cells/well) collected were cultured to form osteoclasts on sterile dentine slices for 10 d with or without OIP-1 c-peptide (100 ng/ml) as described (2). At the end of the culture period, cells were removed using 1 m NaOH and stained with 0.1% toluidine blue. The areas of resorption lacunae on the digital images were quantified using a computerized image analysis (Adobe Photoshop and Scion MicroImaging version β 4.2). The percentage of the resorbed area was calculated relative to total dentine disc area.
Quantitative real-time RT-PCR
Total RNA (2 μg) isolated from the WT, OIP-1 transgenic mice and FcγRII−/−-deficient mouse bone marrow-derived osteoclast cells was reverse transcribed using random hexamers and Maloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase (Applied Biosystems). The resulting cDNAs were subjected to quantitative real-time RT-PCR using gene specific primers for NFATc1: 5′-TTCCTTCAGCCAATCATCCCCCCAGTTAC-3′ (sense) and 5′-CGATGTCTGTCTCCCCTTTCCTCAGCTC-3′ (antisense); c-Fos: 5′-CAA CGC CGA CTA CGA GGC GTC AT-3′ (sense) and 5′-CAA GTG TGC ACG CGC TCA GAC AA-3′ (antisense); and TRAP: 5′-GGCCGGCCACTACCCCATCT-3′ (sense) and 5′-CACCGTAGCGACAAGCAGGACTCT-3′ (antisense). Relative levels of gene expressions were normalized in all the samples analyzed with respect to the levels of ß-actin: 5′-TTCTTTGCAGCTCCTTCGTTGCCG-3′ (sense) and 5′-TGGATGGCTACGTACATGGCTGGG-3′ (antisense) amplification.
Western blot analysis
The nonadherent bone marrow cells derived from WT and OIP-1 transgenic mice were cultured with RANKL and M-CSF (10 ng/ml) for 2 d as described (3). Total-cell lysates obtained from these preosteoclast cells were subjected to IP analysis of ITIM phosphorylation of FcγRIIB, ITAM phosphorylation of FcRγ and DAP12 proteins, and phosphorylation was determined using p-Y antibody. The expressions of FcγRIIB, OIP-1, DAP12, Syk, p-Syk, SHP 1/2, pSHP1, pSHP2, SHIP1/2, pSHIP1/2, and β-actin were analyzed by Western blotting.
Confocal image analysis
Confocal microscopy was used to view the passage of fluorescently labeled OIP-1 c-peptide and binding with FcγRIIB on RAW 264.7 cells. Mouse bone marrow-derived osteoclasts and RAW 264.7 cell cultures were washed three times with PBS and fixed with 2% (vol/vol) paraformaldehyde in PBS for 30 min. The cell membranes were permeabilized with 0.1% (vol/vol) Triton X-100 in PBS for 5 min. Subsequently, the cells were washed and incubated with FITC-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide or with anti-FcγRIIB and anti-OIP-1 antibody for 2 h at room temperature. The cells were washed three times and incubated with Alexa 568-conjugated antigoat or Alexa 488 antirabbit antibody (Molecular Probes, Carlsbad, CA) for 1 h. The nuclei were stained with DRAQ5 (Axxora Platform, San Diego, CA) for 10 min, and confocal image analysis of the cells was performed with Leica TCS SP2 AOBS laser-scanning microscopy (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany).
Statistical analysis
Results are presented as mean ± sd for five independent experiments and were compared by Student’s t test. Results were considered significantly different for values of P < 0.05.
Results
OIP-1 binding to membrane FcγRIIB in osteolast progenitor cells
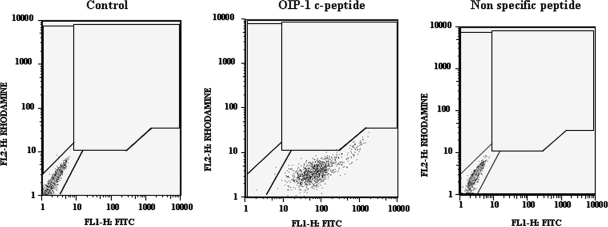
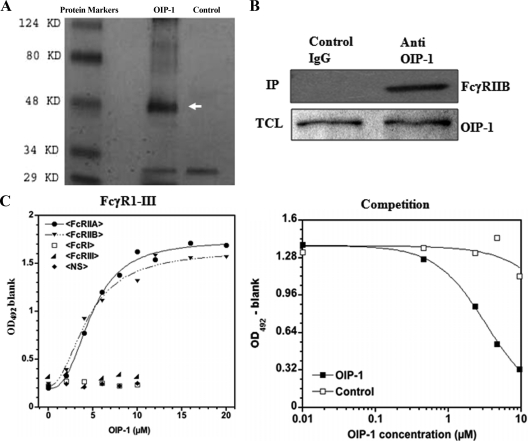
We sought to identify a membrane receptor in homogeneous population of RAW 264.7 osteoclast progenitor cells (21) that binds to the OIP-1 c-peptide and mediates its osteoclast inhibitory activity. As shown in Fig. 1, FITC-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide (10 μm) bound to RAW 264.7 cells as measured by increased mean fluorescence relative to control cells. In addition, RAW cells incubated with a scrambled sequence control peptide showed no significant binding. These results indicate the presence of an OIP-1-specific surface receptor/membrane protein partner in the osteoclast progenitor cells. To further identify the OIP-1 binding protein in the osteoclast progenitor cells, we transiently transfected RAW 264.7 cells with an OIP-1 expression vector due to low abundance of OIP-1 expression in these cells. OIP-1 Co-IP and SDS-PAGE analysis demonstrated a 42-kDa protein (Fig. 2A). MS analysis of the peptide maps with a total ion score 189 were searched against the SWISS-PROT database. We thus identified the FcγRIIB (CD32) associated with OIP-1 in osteoclast progenitor cells. To confirm that FcγRIIB was present in the OIP-1 IPs from osteoclast progenitor cells, immunoblotting was performed with FcγRIIB specific antibody. As shown in Fig. 2B, Western blot analysis further confirmed the presence of FcγRIIB in the OIP-1 IPs. In contrast, no band was detected in immune complexes obtained with a nonspecific antibody.
Figure 1.
FACS analysis of OIP-1 c-peptide binding to RAW 264.7 cells. RAW cells were incubated with 10 μm fluorescein-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide or nonspecific peptide for 2 h and subjected to FACS analysis as described in Materials and Methods. FL, Fluorochrome.
Figure 2.
OIP-1 binding to FcγRIIB in RAW 264.7 cells. A, Cells were transfected with OIP-1 expression vector, and the cell lysates were Co-IP with anti-OIP-1 or control nonspecific IgG antibody. Immune complexes were separated on 12% polyacrylamide gels and stained with coomassie brilliant blue and (B) blot transferred onto nitrocellulose for Western blot analysis using FcγRIIB specific antibody (upper panel). Lower panel shows the Western blot analysis of OIP-1 expression in total-cell lysates (TCL) used for IP. Protein content of the samples was normalized with respect to the levels of OIP-1 expression. C, Affinity binding of OIP-1 c-peptide to the recombinant FcγR proteins. OIP-1 c-peptide or nonspecific control peptide were incubated in increasing amounts (0–10 μm) with the different types of FcγR proteins (FcγRI, FcRγIIA, FcγRIIB, and FcγRIII) immobilized in a microtiter plate, and OIP-1 affinity binding was measured as described in Materials and Methods. In a competition assay, OIP-1 c-peptide or nonspecific peptide was incubated with FcγRIIB protein immobilized in a microtiter plate, and the binding rate of anti-FcγRIIB antibody was measured.
We then performed a microtiter binding assay to confirm the specificity of OIP-1 affinity binding to recombinant extracellular domain of FcγR proteins (FcγRI, FcRγIIA, FcγRIIB, and FcγRIII). As shown in Fig. 2C, OIP-1 c-peptide bound to FcγRIIA and FcγRIIB with an affinity of Kd = 4.4 and 4.8 ± 1.8 μm, respectively, as calculated from a fit of the Hill function to the data (22). The χ2 values for the nonlinear regressions ranged from 0.0007 to 0.005 when using 1:1 stoichiometry and no cooperativity; reasonable fits were not found with other stoichiometries, and allowing for cooperativity did not approve the fits as assessed from normal analyses of the residuals. OIP-1 binding to FcγRIIB was further confirmed with a competition assay measuring OIP-1 c-peptide inhibition of anti-FcγRIIB antibody binding to immobilized FcγRIIB in a dose-dependent manner in comparison with a scrambled-sequence control peptide. The results indicated a Kd of 3.2 ± 0.2 μm. In contrast, OIP-1 c-peptide showed no affinity binding to FcγRI and FcγRIII. We also measured OIP-1 binding to FcγRIIB in an equilibrium dialysis assay as described in Materials and Methods. FITC-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide incubated with FcγRIIB had a binding affinity of Kd = 3.3 ± 0.4 μm. These results indicate that OIP-1 binds specifically to the FcγRIIB expressed in murine osteoclast progenitor cells.
FcγRIIB siRNA inhibits OIP-1 binding to osteoclast progenitor cells
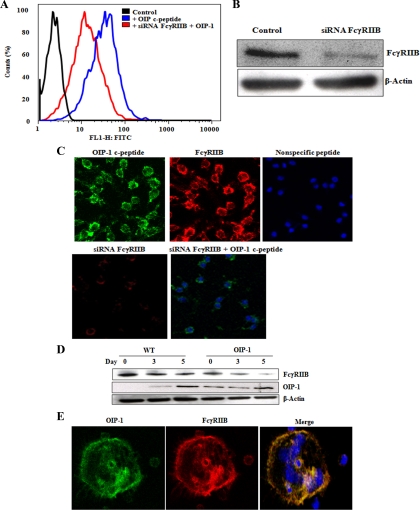
We further tested whether siRNA suppression of FcγRIIB inhibits OIP-1 binding to osteoclast progenitor cells. As shown in Fig. 3A, FACS analysis demonstrated that binding of FITC-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide to RAW 264.7 cells and siRNA suppression of FcγRIIB significantly inhibited c-peptide binding. Western blot analysis confirmed siRNA suppression of FcγRIIB expression in these cells (Fig. 3B). We further confirmed the inhibition of OIP-1 c-peptide binding to RAW 264.7 cells transfected with FcγRIIB siRNA by confocal microscopic analysis. As shown in Fig. 3C, FITC-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide bound to the RAW cell membrane compared with nonspecific control peptide-treated cells. siRNA suppression of FcγRIIB expression significantly decreased c-peptide binding to these cells, thereby confirming OIP-1-specific binding with FcγRIIB in osteoclast progenitor cells.
Figure 3.
siRNA suppression of FcγRIIB inhibits OIP-1 c-peptide binding to RAW 264.7 cells. A, Fluorescein-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide (10 μm) was incubated with control or FcγRIIB siRNA transfected RAW 264.7 cells. FACS analysis showed a high affinity binding of FITC-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide to control cells. siRNA suppression of FcγRIIB expression inhibited OIP-1 c-peptide binding. B, Western blot analysis of siRNA suppression of FcγRIIB expression in total-cell lysates. C, Confocal image analysis of OIP-1 c-peptide binding to RAW 264.7 cells. FITC-conjugated OIP-1 c-peptide or nonspecific peptide was incubated with control or FcγRIIB siRNA transfected cells as described in Materials and Methods. The upper panel depicts the binding of OIP-1 c-peptide to the cell membrane in contrast to a control nonspecific peptide-treated cells and the expression of FcγRIIB in RAW 264.7 cells. The lower panel shows siRNA suppression of FcγRIIB expression and a significant decrease in c-peptide binding to cells transfected with FcγRIIB siRNA. D, OIP-1 and FcγRIIB expression during osteoclast differentiation. WT and OIP-1 transgenic mouse bone marrow cells were cultured in the presence of 10 ng/ml M-CSF for 24 h. The nonadherent cells were treated with M-CSF (10 ng/ml) and stimulated with or without RANKL (100 ng/ml) for indicated time period. Total-cell lysates prepared were subjected to Western blot analysis for FcγRIIB and OIP-1 expression. β-Actin expression levels were also analyzed to normalize the protein loading onto the gels in all the samples. E, Colocalization of OIP-1 with FcγRIIB on the osteoclast membrane. The OIP-1 transgenic mouse bone marrow-derived nonadherent cells were cultured with M-CSF and RANKL for 7 d to form osteoclasts. The cultures were fixed and processed for confocal image analysis using anti-OIP-1 antibody and FcγRIIB antibody. The merged image demonstrated colocalization of OIP-1 with FcγRIIB on the osteoclast membrane. Magnification, ×60.
We recently developed mice that overexpress OIP-1 in osteoclast lineage cells and characterized inhibition of osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption activity in vivo (3). We further examined the FcγRIIB expression during osteoclast differentiation in WT and OIP-1 mouse bone marrow cultures. Western blot analysis demonstrated that the expression levels of FcγRIIB was significantly decreased during osteoclastogenesis in the WT and OIP-1 mouse bone marrow cultures stimulated with M-CSF and RANKL. We also detected low levels of OIP-1 expression in preosteoclast cells from WT mice. However, high level expression in OIP-1 mouse derived preosteoclast cells (Fig. 3D). We further examined colocalization of OIP-1 with FcγRIIB in osteoclast cells. Confocal microscopy analysis showed colocalization of OIP-1 expression with the FcγRIIB in osteoclasts formed in OIP-1 transgenic mouse bone marrow cultures (Fig. 3E, merged image). These results further suggest a functional role for FcγRIIB in OIP-1 inhibition of osteoclast differentiation.
FcγRIIB participation in OIP-1 inhibition of osteoclast differentiation
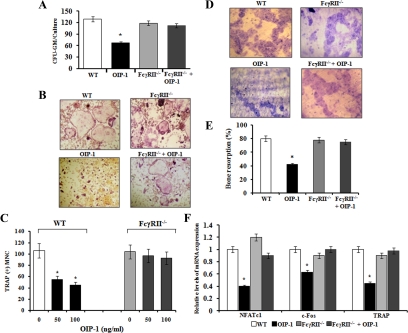
FcRγ transmembrane adapter proteins play an important role in osteoclastogenesis (23). Colony-forming unit granulocyte-macrophage (CFU-GM) is the early osteoclast precursor, and increased in numbers of CFU-GM in pathological conditions resulted in increased osteoclast formation (3). We therefore examined the effect of OIP-1 on FcγRII−/−-deficient mouse bone marrow cells for osteoclast precursor growth in methyl-cellulose cultures as described (3). Consistent with our previous findings that OIP-1 treatment inhibits CFU-GM colony formation in the WT mouse bone marrow cultures. In contrast, OIP-1 c-peptide treatment to FcγRII−/−-deficient mouse bone marrow-derived nonadherent cells showed no significant change in CFU-GM colony formation (Fig. 4A). We then examined whether FcγRIIB mediates OIP-1 inhibition of osteoclast differentiation in vitro. As shown in Fig. 4, B and C, OIP-1 c-peptide treatment inhibit osteoclast formation in WT mouse bone marrow cultures in a dose-dependent manner consistent with our previous results (1). In contrast, OIP-1 c-peptide did not inhibit osteoclast formation in FcγRII−/− mouse bone marrow cultures (Fig. 4, B and C). We also tested the effect of OIP-1 c-peptide on bone resorption capacity of osteoclasts formed in WT and FcγRII−/− mouse bone marrow cultures. As shown in Fig. 4, D and E, osteoclasts formed in WT mouse bone marrow cultures in the presence of OIP-1 c-peptide (100 ng/ml) demonstrated a significant decrease (42.7%) in resorption area on dentine slices compared with control untreated cultures. However, OIP-1 c-peptide did not affect bone resorption activity of osteoclasts formed in FcγRII−/− mouse bone marrow cultures. The osteoclast formation and bone resorption activity in FcRγ−/− mouse bone marrow cultures was not significantly different compared with WT mice as reported (23). Real-time PCR analysis confirmed that OIP-1 treatment to the FcγRII−/− mouse bone marrow cultures did not demonstrate a significant change in the levels of TRAP, c-Fos, and nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 (NFATc1) mRNA expression during osteoclast differentiation compared with WT mice (Fig. 4F).
Figure 4.
OIP-1 inhibition of osteoclast formation. A, CFU-GM formation in WT and FcγRII−/− mouse bone marrow cultures. WT and FcγRII−/− mouse-derived nonadherent cells were cultured with hGM-CSF (10 ng/ml) in 1.2% methyl cellulose to form CFU-GM colonies. At the end of a 7-d culture period, CFU-GM colonies (aggregates, >50 cells) formed in these cultures were scored using a light microscope. B, WT and FcγRII−/− mouse bone marrow-derived nonadherent cells were stimulated with RANKL (100 ng/ml) and M-CSF (10 ng/ml) for 5 d with or without OIP-1 c-peptide (0–100 ng/ml) for osteoclast differentiation. Magnification, ×20. C, The TRAP (+) multinucleated osteoclasts formed in these cultures were scored. D, WT and FcγRII−/− mouse bone marrow-derived nonadherent cells (1 × 106) were cultured to form osteoclasts on dentine slices for 10 d and (E) the percentage of resorbed area on dentine was quantified as described in Materials and Methods. The results represent quadruplicate cultures of five independent experiments (P < 0.05). F, Real-time PCR analysis of osteoclast differentiation marker genes, TRAP, c-Fos, and NFATc1 expression levels in WT and FcγRII−/− mouse bone marrow cultures treated with or without OIP-1.
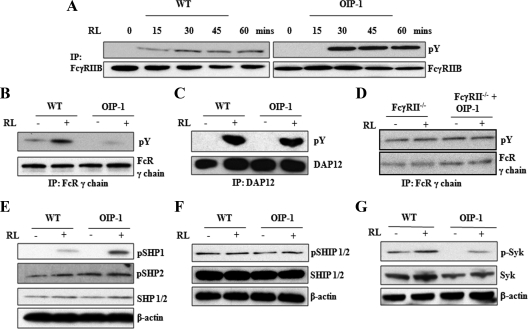
OIP-1 inhibits the ITAM phosphorylation of FcRγ and stimulates the ITIM phosphorylation of FcγRIIB in preosteoclasts cells
FcRγ and DAP12 transmembrane adapter proteins containing ITAM domain signaling play an important role in osteoclast differentiation (15), and the recruitment of Syk to phosphorylated ITAM domains of these adapter proteins is critical for functional osteoclast development (23). Further, ITIM-bearing FcγRIIB adapter proteins are known to inhibit ITAM signaling (24). Therefore, we further examined the OIP-1 inhibition of FcR signaling during osteoclast differentiation by Western blot analysis. Interestingly, total-cell lysates obtained from OIP-1 mice-derived preosteoclast cells stimulated with RANKL (0–60 min) demonstrated increased levels (4-fold) of ITIM phosphorylation of FcγRIIB compared with WT mice (Fig. 5A). In contrast, OIP-1 mouse-derived preosteoclasts cells stimulated with RANKL (60 min) demonstrated inhibition of ITAM phosphorylation of FcRγ-subunit. However, ITAM phosphorylation of DAP12 protein was not affected in OIP-1 mice-derived preosteoclast cells compared with WT mice (Fig. 5, B and C). Also, OIP-1 c-peptide treatment to nonadherent bone marrow cells obtained from FcγRII−/−-deficient mice showed no significant change in the phosphorylation of ITAM (Fig. 5D). The tyrosyl-phosphorylated ITIM has affinity with cytoplasmic SH2 domain-containing phosphatases like SHP1, SHP2, and SHIP proteins (25). Evidence indicates that these inhibitory proteins dephosphorylate tyrosines in ITAMs bearing FcRs (11). Therefore, we further determined the levels of SHP1,2 and SHIP in the OIP-1 transgenic mice-derived preosteoclast cells. Total-cell lysates obtained from OIP-1 mice-derived preosteoclast cells stimulated with RANKL demonstrated a significant increase (3-fold) in phosphorylation of SHP1 but not SHP2. Also, there is no significant change in the levels of phospho-SHIP (pSHIP), pSHIP1 and pSHIP2. Interestingly, preosteoclast cells from OIP-1 mice stimulated with RANKL had a 4.5-fold decrease in the levels of phospho-Syk compared with WT mice (Fig. 5, E–G), suggesting that FcγRIIB-containing ITIM recruits pSHP1 in OIP-1-derived preosteoclasts cells and down-regulates the ITAM signaling of FcRγ. β-Actin expression levels were normalized in all samples analyzed as loading controls in these experiments. Thus, our results indicate that OIP-1 signals through the membrane FcγRIIB in osteoclast progenitor cells to inhibit osteoclast differentiation.
Figure 5.
OIP-1 inhibits the ITAM phosphorylation of FcRγ chain and stimulates the ITIM phosphorylation of FcγRIIB. A, WT and OIP-1 mouse bone marrow cells were cultured in the presence of M-CSF (10 ng/ml) for 24 h. The nonadherent cells were treated with M-CSF (10 ng/ml) and stimulated with RANKL (100 ng/ml) for the indicated period (0–60 min). Total-cell lysates obtained were IP with FcγRIIB and Western blot analyzed using p-Y antibody. B, WT and OIP-1 mouse bone marrow-derived nonadherent cells were treated with M-CSF and stimulated with or without RANKL (RL) for 60 min. The total-cell lysates were subjected to IP with FcR γ-chain specific antibody followed by Western blot analysis using p-Y antibody. C, Total-cell lysates were IP with DAP12 antibody and Western blot analyzed using p-Y antibody. D, The nonadherent bone marrow cells obtained from FcγRII−/− mice treated with M-CSF and with or without OIP-1 were stimulated with RANKL for 60 min. Total-cell lysates were IP with FcR γ-chain specific antibody and Western blot analyzed using p-Y antibody. E–G, WT and OIP-1 mouse bone marrow-derived nonadherent cells were treated with M-CSF and stimulated with or without RANKL for 2 d. The total-cell lysates obtained from the preosteoclasts was subjected to Western blot analysis for SHP1/2, pSHP1, pSHP2, SHIP1/2, pSHIP1/2, Syk, p-Syk, and β-actin expression.
Discussion
OIP-1 is a member of the Ly-6 gene family that is highly expressed in activated T cells and a low level expression in osteoclasts (1). OIP-1 overexpression in osteoclast lineage cells produced an osteopetrotic bone phenotype in mice due to inhibition of osteoclast formation/bone resorption activity in vivo (3). Ly-6A (Sca-1) knockout mice had decreased bone mineral density and bone mineral content (26), implicating an essential role for the LY-6 gene family in normal bone remodeling. Our findings with FACS and MS analysis suggested that OIP-1 binds to the membrane FcγRIIB adapter protein expressed in osteoclast progenitor cells. Microtiter binding experiments demonstrated that the OIP-1 c-peptide binds to recombinant FcγRIIB protein with an affinity of Kd approximately 4 μm. However, it is notable that the affinities of FcγRII for its traditional IgG ligands are also on the order of 1 μm (27). Most important is the fact that OIP-1 inhibition of osteoclast differentiation observed at 3 μm in our previous studies correlates with the measured affinity binding of OIP-1 with FcγRIIB. Lack of binding to FcγRI and FcγRIII confers the specificity of OIP-1 binding to FcγRIIB. Because the α-subunits are highly conserved in their ligand binding extracellular domain, it is not surprising to see high affinity binding with both FcγRIIA and IIB proteins. However, FcγRIIA expression is known to be restricted to human cells (28). Also, microscopic evidence of colocalization of OIP-1 expression with FcγRIIB on the osteoclasts membrane further suggests a functional role for OIP-1 affinity binding with FcγRIIB in osteoclasts. Our results, indicating a significant decrease in FcγRIIB expression upon osteoclast maturation, imply OIP-1 inhibition of FcγRIIB signaling during osteoclast differentiation.
FcRγ signaling through ITAM domain is critical for osteoclast differentiation under physiological conditions. Osteoclast precursors derived from the OIP-1 mice demonstrated suppression of ITAM phosphorylation of FcR γ-chain but not DAP12 protein compared with WT mice. The FcR common γ-chain is an essential component of the FcRs (FcεRI, FcγRI, and FcγRIII), which play a key role in the signaling functions (29,30). However, our findings that OIP-1 interaction with FcγRIIB and stimulation of ITIM phosphorylation suggests that OIP-1 ligation to FcγRIIB suppressed ITAM activation of FcRγ. These results are consistent with previous studies that cross-regulation of ITIM and ITAM signaling may occur in an autocrine/paracrine manner, as it has been reported earlier (31). Previously, it has been reported that mice lacking the immunomodulatory adapter proteins DAP12 and FcRγ exhibit severe osteopetrosis. However, they develop teeth, distinguishing their phenotype from Src−/− and RANKL-deficient mice (23). Similarly, OIP-1-overexpressing mice despite the osteopetrotic bone phenotype had normal tooth eruption. Therefore, it is possible that OIP-1 binding and FcγRIIB signaling may have implications in spatial skeletal modeling. It has been shown that in osteoclast precursor cells, FcRγ and DAP12 associate with multiple immunoreceptors. Therefore, OIP-1 may influence the ITAM-dependent costimulatory signaling-activated multiple immunoreceptors that are essential for the maintenance of bone homeostasis (15). In this study, activation of SHP1 in OIP-1 mouse-derived preosteoclasts indicates SHP1 modulation of ITIM-ITAM costimulatory signaling to inhibit osteoclast formation. Preosteoclast cells from OIP-1 mice in the presence or absence of RANKL had significantly less phospho-Syk compared with WT mice. However, it has been shown recently that Syk deficiency diminishes osteoclast function but does not impair differentiation in concert with c-Src, αvβ3 integrin, and ITAM immunoreceptors (32). Therefore, it is unlikely that OIP-1 may affect ITAM-dependent calcium signaling through phospholipase C-γ during osteoclast differentiation. Besides, it is also reported that ITAM phosphorylation and Syk activation are through the γ-chain of FcγRI and FcγRIII proteins (23,33). Thus, it is possible that costimulatory signals among ITIM and ITAM motifs may involve in OIP-1 suppression of Syk activation (28). Although FcRγ is also involved in signal transduction of osteoclast-associated receptor (34), which is critical for osteoclast differentiation, the effect of OIP-1 on downstream signaling molecules is yet to be elucidated. We have previously shown that the OIP-1 signaling mechanism is independent of NF-κB activation and involves suppression of p-c-Jun kinase to inhibit osteoclast formation (2). Also, OIP-1 mouse-derived preosteoclast cells had significantly less TRAF-2 and NFATc1 expression, but TRAF-6 and RANK expression were unchanged in these cells (3). Recent studies also demonstrated that Bruton’s tyrosine kinase and Tec tyrosine kinases in cooperation with RANK signaling modulate the osteoclast function (33). However, we find no change in Tec and Bruton’s tyrosine kinase levels in OIP-1 mouse preosteoclasts cells compared with WT mice (data not shown). Therefore, our findings of OIP-1 interaction with FcγRIIB should provide further insights into complex regulatory mechanisms operative during osteoclast differentiation. Thus, our results suggest that cross-regulation of ITIM and ITAM bearing FcRs may play a role in OIP-1 suppression of Syk activation and inhibition of osteoclast differentiation.
OIP-1 overexpression in osteoclast lineage in vivo or synthetic OIP-1 c-peptide treatment to bone marrow cultures relatively at high concentrations affect ITAM signaling essential for osteoclast development. However, we show that OIP-1 is expressed at low levels in preosteoclast cells from WT mice. Further, OIP-1 also termed TSA-1 has been shown to be critical for normal embryonic development due to lethality in gene knockout mice (35). Earlier, we have demonstrated that inflammatory cytokines, such as interferon-γ and IL-12, induce OIP-1 expression in preosteoclast cells (2,36). Thus, OIP-1 may have a regulatory role in osteoclast development in bone microenvironment at physiological/pathologic conditions. In summary, OIP-1 signals through the membrane FcγRIIB in the osteoclast precursor cells to inhibit osteoclast differentiation and may have therapeutic utility for treatment of bone diseases with high bone turnover, such as osteoporosis and Paget’s disease of the bone.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Daniel R. Knapp at the Medical University of South Carolina for providing the proteomics core facility assistance.
Footnotes
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health Grant DE 12603, the Department of Defense Medical Research Award PR080480, and the Extramural Research Facilities Program of the National Center for Research Resources Grant C06 RR015455.
Disclosure Summary: The authors have nothing to disclose.
First Published Online July 7, 2010
Abbreviations: CD3, Cluster of differentiation 3; CFU-GM, colony-forming unit granulocyte-macrophage; Co-IP, coimmunoprecipitation; c-peptide, carboxy-terminal GPI-linked peptide; DAP12, DNAX-activating protein of molecular mass 12 kDa; FACS, fluorescence-activated cell sorting; FcγRIIB, Fcγ receptor IIB; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; GPI, glycophosphatidylinositol; ITAM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif; ITIM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif; Kd, dissociation constant; MALDI, matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization; M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MS, mass spectrometry; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; NFATc1, nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1; OIP-1/hSca, osteoclast inhibitory peptide-1; RANKL, receptor activator for nuclear factor κB ligand; pSHIP, phospho-SHIP; p-Y, antiphosphotyrosine; SH2, Src homology 2; SHIP, SH2-domain-containing inositol-5-phosphatase; SHP, SH2-domain-containing proteins tyrosine phosphatase; siRNA, small interfering RNA; Syk, spleen tyrosine kinase; TCR, T-cell receptor; TOF, time-of-flight; TRAP, tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase; TSA-1/Sca-2, human thymic sheared antigen; WT, wild type.
References
- Koide M, Kurihara N, Maeda H, Reddy SV 2002 Identification of the functional domain of osteoclast inhibitory peptide-1/hSca. J Bone Miner Res 17:111–118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide M, Maeda H, Roccisana JL, Kawanabe N, Reddy SV 2003 CytokineRegulation and the signaling mechanism of osteoclast inhibitory peptide-1 (OIP-1/hSca) to inhibit osteoclast formation. J Bone Miner Res 18:458–465 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugarajan S, Irie K, Musselwhite C, Key Jr LL, Ries WL, Reddy SV 2007 Transgenic mice with OIP-1/hSca overexpression targeted to the osteoclast lineage develop an osteopetrosis bone phenotype. J Pathol 213:420–428 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao M, Yu M, Tong JH, Ye J, Zhu J, Huang QH, Fu G, Yu L, Zhao SY, Waxman S, Lanotte M, Wang ZY, Tan JZ, Chan SJ, Chen Z 1996 RIG-E, a human homolog of the murine Ly-6 family, is induced by retinoic acid during the differentiation of acute promyelocytic leukemia cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5910–5914 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNeil I, Kennedy J, Godfrey DI, Jenkins NA, Masciantonio M, Mineo C, Gilbert DJ, Copeland NG, Boyd RL, Zlotnik A 1993 Isolation of a cDNA encoding thymic shared antigen-1. A new member of the Ly6 family with a possible role in T cell development. J Immunol 151:6913–6923 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosugi A, Saitoh S, Narumiya S, Miyake K, Hamaoka T 1994 Activation-induced expression of thymic shared antigen-1 on T lymphocytes and its inhibitory role for TCR-mediated IL-2 production. Int Immunol 6:1967–1976 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh S, Kosugi A, Noda S, Yamamoto N, Ogata M, Minami Y, Miyake K, Hamaoka T 1995 Modulation of TCR-mediated signaling pathway by thymic shared antigen-1 (TSA-1)/stem cell antigen-2 (Sca-2). J Immunol 155:5574–5581 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanová I, Horejsí V, Ansotegui IJ, Knapp W, Stockinger H 1991 GPI-anchored cell-surface molecules complexed to protein tyrosine kinases. Science 254:1016–1019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosugi A, Saitoh S, Noda S, Miyake K, Yamashita Y, Kimoto M, Ogata M, Hamaoka T 1998 Physical and functional association between thymic shared antigen-1/stem cell antigen-2 and the T cell receptor complex. J Biol Chem 273:12301–12306 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding L, Shevach EM 2001 Inhibition of the function of the FcγRIIB by a monoclonal antibody to thymic shared antigen-1, a Ly-6 family antigen. Immunology 104:28–36 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daëron M, Latour S, Malbec O, Espinosa E, Pina P, Pasmans S, Fridman WH 1995 The same tyrosine-based inhibition motif, in the intracytoplasmic domain of Fc γ RIIB, regulates negatively BCR-, TCR-, and FcR-dependent cell activation. Immunity 3:635–646 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M, Nakashima T, Kodama T, Makrigiannis AP, Toyama-Sorimachi N, Takayanagi H 2010 Ly49Q, an ITIM-bearing NK receptor, positively regulates osteoclast differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 393:432–438 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki K, Didomenico E, Sims NA, Mukhopadhyay K, Neff L, Houghton A, Amling M, Levy JB, Horne WC, Baron R 1999 The tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1 is a negative regulator of osteoclastogenesis and osteoclast resorbing activity: increased resorption and osteopenia in me (v)/me (v) mutant mice. Bone 25:261–267 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita S, Namba N, Zhao JJ, Jiang Y, Genant HK, Silva MJ, Brodt MD, Helgason CD, Kalesnikoff J, Rauh MJ, Humphries RK, Krystal G, Teitelbaum SL, Ross FP 2002 SHIP-deficient mice are severely osteoporotic due to increased numbers of hyper-resorptive osteoclasts. Nat Med 8:943–949 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T, Inui M, Inoue K, Kim S, Suematsu A, Kobayashi E, Iwata T, Ohnishi H, Matozaki T, Kodama T, Taniguchi T, Takayanagi H, Takai T 2004 Costimulatory signals mediated by the ITAM motif cooperate with RANKL for bone homeostasis. Nature 428:758–763 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor S, Jakus Z, Mócsai A 2006 ITAM-based signaling beyond the adaptive immune response. Immunol Lett 104:29–37 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouvry-Patat SA, Schey KL 2007 Characterization of antimicrobial histone sequences and posttranslational modifications by mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 42:664–674 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg R, Juncadella IJ, Ramamoorthi N, Ashish, Ananthanarayanan SK, Thomas V, Rincón M, Krueger JK, Fikrig E, Yengo CM, Anguita J 2006 Cutting edge: CD4 is the receptor for the tick saliva immunosuppressor, Salp15. J Immunol 177:6579–6583 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peitzsch RM, McLaughlin S 1993 Binding of acylated peptides and fatty acids to phospholipid vesicles: pertinence to myristoylated proteins. Biochemistry 32:10436–10443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai T, Ono M, Hikida M, Ohmori H, Ravetch JV 1996 Augmented humoral and anaphylactic responses in Fc γ RII-deficient mice. Nature 379:346–349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Solovyev I, Colombero A, Timms E, Tan HL, Elliott G, Kelley MJ, Sarosi I, Wang L, Xia XZ, Elliott R, Chiu L, Black T, Scully S, Capparelli C, Morony S, Shimamoto G, Bass MB, Boyle WJ 1999 Tumor necrosis factor receptor family member RANK mediates osteoclast differentiation and activation induced by osteoprotegerin ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:3540–3545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill AV 1910 The heat produced in contracture and muscular tone. J Physiol 40:389–403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mócsai A, Humphrey MB, Van Ziffle JA, Hu Y, Burghardt A, Spusta SC, Majumdar S, Lanier LL, Lowell CA, Nakamura MC 2004 The immunomodulatory adapter proteins DAP12 and Fc receptor γ-chain (FcRγ) regulate development of functional osteoclasts through the Syk tyrosine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6158–6163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimmerjahn F, Ravetch JV 2006 Fcγ receptors: old friends and new family members. Immunity 24:19–28 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesourne R, Bruhns P, Fridman WH, Daëron M 2001 Insufficient phosphorylation prevents fc γ RIIB from recruiting the SH2 domain-containing protein-tyrosine phosphatase SHP-1. J Biol Chem 276:6327–6336 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonyadi M, Waldman SD, Liu D, Aubin JE, Grynpas MD, Stanford WL 2003 Mesenchymal progenitor self-renewal deficiency leads to age-dependent osteoporosis in Sca-1/Ly-6A null mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5840–5845 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P, Jiang N, Nagarajan S, Wohlhueter R, Selvaraj P, Zhu C 2007 Affinity and kinetic analysis of Fcγ receptor IIIa (CD16a) binding to IgG ligands. J Biol Chem 282:6210–6221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boross P, Verbeek JS 2006 The complex role of Fcγ receptors in the pathology of arthritis. Springer Semin Immunopathol 28:339–350 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura K, Takeda K, Koya T, Miyahara N, Kodama T, Dakhama A, Takai T, Hirano A, Tanimoto M, Harada M, Gelfand EW 2007 Critical role of the Fc receptor γ-chain on APCs in the development of allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and inflammation. J Immunol 178:480–488 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ra C, Jouvin MH, Blank U, Kinet JP 1989 A macrophage Fc γ receptor and the mast cell receptor for IgE share an identical subunit. Nature 341:752–754 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pricop L, Salmon JE 2002 Redox regulation of Fcγ receptor-mediated phagocytosis: implications for host defense and tissue injury. Antioxid Redox Signal 4:85–95 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou W, Kitaura H, Reeve J, Long F, Tybulewicz VL, Shattil SJ, Ginsberg MH, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL 2007 Syk, c-Src, the αvβ3 integrin, and ITAM immunoreceptors, in concert, regulate osteoclastic bone resorption. J Cell Biol 176:877–888 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara M, Koga T, Okamoto K, Sakaguchi S, Arai K, Yasuda H, Takai T, Kodama T, Morio T, Geha RS, Kitamura D, Kurosaki T, Ellmeier W, Takayanagi H 2008 Tyrosine kinases Btk and Tec regulate osteoclast differentiation by linking RANK and ITAM signals. Cell 132:794–806 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa S, Arase N, Suenaga T, Saita Y, Noda M, Kuriyama T, Arase H, Saito T 2004 Involvement of FcRγ in signal transduction of osteoclast-associated receptor (OSCAR). Int Immunol 16:1019–1025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zammit DJ, Berzins SP, Gill JW, Randle-Barrett ES, Barnett L, Koentgen F, Lambert GW, Harvey RP, Boyd RL, Classon BJ 2002 Essential role for the lymphostromal plasma membrane Ly-6 superfamily molecule thymic shared antigen 1 in development of the embryonic adrenal gland. Mol Cell Biol 22:946–952 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugarajan S, Kawanabe N, Koide M, Tsuruga E, Arroyo JE, Key Jr LL, Reddy SV 2009 IL-12 stimulates the osteoclast inhibitory peptide-1 (OIP-1/hSca) gene expression in CD4+ T cells. J Cell Biochem 107:104–111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]